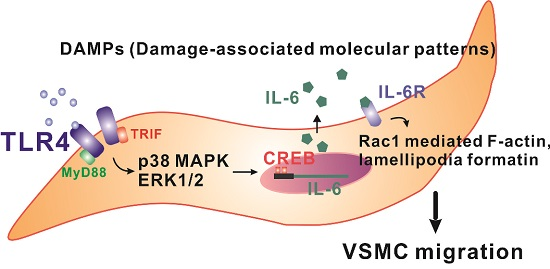
TLR4-Activated MAPK-IL-6 Axis Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. LPS/TLR4 Induced Production of IL-6, But Not IL-10, IL-12, and TNF-α, in VSMCs
2.2. Role of TLR4 in LPS-Induced VSMC Migration
2.3. IL-6 Is Essential for TLR4-Induced VSMC Migration
2.4. TLR4-Induced IL-6 Production and VSMC Migration Are Mediated by p38 MAPK and ERK1/2
2.5. CREB-Mediated IL-6 Production is Crucial for LPS-Induced VSMC Migration
2.6. Rac1-Mediated Actin Stress Fiber Formation Participates in LPS-Induced VSMC Migration
2.7. IL-6 Level Is Positively Correlated with P-CREB Level in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Primary VSMC Isolation and Treatment
4.3. Cytokine Measurement
4.4. Western Blot Analysis
4.5. Migration Assays
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. siRNA Transfection
4.8. F-Actin Staining
4.9. Patient Enrollment and Aortic Tissue Collection
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hansson, G.K.; Hermansson, A. The immune system in atherosclerosis. Nat. Immunol. 2011, 12, 204–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kondo, T.; Kawai, T.; Akira, S. Dissecting negative regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling. Trends Immunol. 2012, 33, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, L.A.; Bryant, C.E.; Doyle, S.L. Therapeutic targeting of Toll-like receptors for infectious and inflammatory diseases and cancer. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 177–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Curtiss, L.K.; Tobias, P.S. Emerging role of Toll-like receptors in atherosclerosis. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, S340–S345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoneveld, A.H.; Hoefer, I.; Sluijter, J.P.; Laman, J.D.; de Kleijn, D.P.; Pasterkamp, G. Atherosclerotic lesion development and Toll like receptor 2 and 4 responsiveness. Atherosclerosis 2008, 197, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.F.; Hsu, Y.J.; Wu, H.F.; Lee, G.L.; Yang, Y.S.; Wu, J.Y.; Yet, S.F.; Wu, K.K.; Kuo, C.C. Endothelium-derived 5-methoxytryptophan is a circulating anti-inflammatory molecule that blocks systemic inflammation. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Sama, A.E.; Wang, H. Role of HMGB1 in cardiovascular diseases. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006, 6, 130–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiechl, S.; Lorenz, E.; Reindl, M.; Wiedermann, C.J.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Bonora, E.; Willeit, J.; Schwartz, D.A. Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms and atherogenesis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P. Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 2002, 420, 868–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libby, P.; Ridker, P.M.; Maseri, A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation 2002, 105, 1135–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis. Nature 2000, 407, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doran, A.C.; Meller, N.; McNamara, C.A. Role of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 812–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owens, G.K.; Kumar, M.S.; Wamhoff, B.R. Molecular regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell differentiation in development and disease. Physiol. Rev. 2004, 84, 767–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orr, A.W.; Hastings, N.E.; Blackman, B.R.; Wamhoff, B.R. Complex regulation and function of the inflammatory smooth muscle cell phenotype in atherosclerosi. J. Vasc. Res. 2010, 47, 168–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaywitz, A.J.; Greenberg, M.E. CREB: A stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 821–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dronadula, N.; Rizvi, F.; Blaskova, E.; Li, Q.; Rao, G.N. Involvement of cAMP-response element binding protein-1 in arachidonic acid-induced vascular smooth muscle cell motility. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 767–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, A.Y.; Sakamoto, K.M.; Miller, L.S. The role of the transcription factor CREB in immune function. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6413–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, H.; Ichiki, T.; Fukuyama, K.; Iino, N.; Masuda, S.; Egashira, K.; Takeshita, A. cAMP-response element-binding protein mediates tumor necrosis factor-α-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2004, 24, 1634–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chava, K.R.; Karpurapu, M.; Wang, D.; Bhanoori, M.; Kundumani-Sridharan, V.; Zhang, Q.; Ichiki, T.; Glasgow, W.C.; Rao, G.N. CREB-mediated IL-6 expression is required for 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.L.; Chang, Y.W.; Wu, J.Y.; Wu, M.L.; Wu, K.K.; Yet, S.F.; Kuo, C.C. TLR 2 induces vascular smooth muscle cell migration through cAMP response element-binding protein-mediated interleukin-6 production. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 2751–2760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warren, J.R. Polymyxin B suppresses the endotoxin inhibition of concanavalin a-mediated erythrocyte agglutination. Infect. Immun. 1982, 35, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kawamoto, T.; Ii, M.; Kitazaki, T.; Iizawa, Y.; Kimura, H. TAK-242 selectively suppresses Toll-like receptor 4-signaling mediated by the intracellular domain. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 584, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Jiang, S.; Tapping, R.I. Toll-like receptor signaling in cell proliferation and survival. Cytokine 2010, 49, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, T.; Akira, S. The role of pattern-recognition receptors in innate immunity: Update on Toll-like receptors. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Newman, W.H. Smooth muscle cell migration stimulated by interleukin 6 is associated with cytoskeletal reorganization. J. Surg. Res. 2003, 111, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassl, C.; Luckow, B.; Schlondorff, D.; Dendorfer, U. Transcriptional regulation of the interleukin-6 gene in mesangial cells. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1999, 10, 1466–1477. [Google Scholar]
- Klemm, D.J.; Watson, P.A.; Frid, M.G.; Dempsey, E.C.; Schaack, J.; Colton, L.A.; Nesterova, A.; Stenmark, K.R.; Reusch, J.E. cAMP response element-binding protein content is a molecular determinant of smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 46132–46141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Small, J.V.; Rottner, K.; Kaverina, I. Functional design in the actin cytoskeleton. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 1999, 11, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellakis, P.; Agrotis, A.; Kyaw, T.S.; Koulis, C.; Ahrens, I.; Mori, S.; Takahashi, H.K.; Liu, K.; Peter, K.; Nishibori, M.; et al. High-mobility group box protein 1 neutralization reduces development of diet-induced atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 313–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Huang, Y. TLR4 antagonist attenuates atherogenesis in LDL receptor-deficient mice with diet-induced type 2 diabetes. Immunobiology 2015, 220, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santulli, G.; Wronska, A.; Uryu, K.; Diacovo, T.G.; Gao, M.; Marx, S.O.; Kitajewski, J.; Chilton, J.M.; Akat, K.M.; Tuschl, T.; et al. A selective microRNA-based strategy inhibits restenosis while preserving endothelial function. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4102–4114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santulli, G. microRNAs distinctively regulate vascular smooth muscle and endothelial cells: Functional implications in angiogenesis, atherosclerosis, and in-stent restenosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 887, 53–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sasu, S.; LaVerda, D.; Qureshi, N.; Golenbock, D.T.; Beasley, D. Chlamydia pneumoniae and chlamydial heat shock protein 60 stimulate proliferation of human vascular smooth muscle cells via toll-like receptor 4 and p44/p42 mitogen-activated protein kinase activation. Circ. Res. 2001, 89, 244–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Chen, L.; Ding, J.; Rong, H.; Dong, W.; Li, X. High mobility group box-1 induces migration of vascular smooth muscle cells via TLR4-dependent PI3K/Akt pathway activation. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 3361–3367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Murthy, V.; Schultz, K.; Tatro, J.B.; Fitzgerald, K.A.; Beasley, D. Toll-like receptor 3 signaling evokes a proinflammatory and proliferative phenotype in human vascular smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H2334–H2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, J.E.; Navin, T.J.; Cross, A.J.; Goddard, M.E.; Alexopoulou, L.; Mitra, A.T.; Davies, A.H.; Flavell, R.A.; Feldmann, M.; Monaco, C. Unexpected protective role for Toll-like receptor 3 in the arterial wall. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2372–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, U.; Ikeda, M.; Oohara, T.; Oguchi, A.; Kamitani, T.; Tsuruya, Y.; Kano, S. Interleukin 6 stimulates growth of vascular smooth muscle cells in a PDGF-dependent manner. Am. J. Physiol. 1991, 260, H1713–H1717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kranzhofer, R.; Schmidt, J.; Pfeiffer, C.A.; Hagl, S.; Libby, P.; Kubler, W. Angiotensin induces inflammatory activation of human vascular smooth muscle cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1999, 19, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridley, A.J.; Hall, A. The small GTP-binding protein rho regulates the assembly of focal adhesions and actin stress fibers in response to growth factors. Cell 1992, 70, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridley, A.J.; Paterson, H.F.; Johnston, C.L.; Diekmann, D.; Hall, A. The small GTP-binding protein rac regulates growth factor-induced membrane ruffling. Cell 1992, 70, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C. Pivotal role of ADP-ribosylation factor 6 in Toll-like receptor 9-mediated immune signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 4323–4334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Kuo, C.C. ADP-Ribosylation factor 3 mediates cytidine-phosphate-guanosine oligodeoxynucleotide-induced responses by regulating toll-like receptor 9 trafficking. J. Innate Immun. 2015, 7, 623–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.C.; Liang, C.M.; Lai, C.Y.; Liang, S.M. Involvement of heat shock protein (Hsp)90 β but not Hsp90 α in antiapoptotic effect of CpG-B oligodeoxynucleotide. J. Immunol. 2007, 178, 6100–6108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, G.-L.; Wu, J.-Y.; Tsai, C.-S.; Lin, C.-Y.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Lin, C.-S.; Wang, Y.-F.; Yet, S.-F.; Hsu, Y.-J.; Kuo, C.-C. TLR4-Activated MAPK-IL-6 Axis Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091394
Lee G-L, Wu J-Y, Tsai C-S, Lin C-Y, Tsai Y-T, Lin C-S, Wang Y-F, Yet S-F, Hsu Y-J, Kuo C-C. TLR4-Activated MAPK-IL-6 Axis Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091394
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Guan-Lin, Jing-Yiing Wu, Chien-Sung Tsai, Chih-Yuan Lin, Yi-Ting Tsai, Chin-Sheng Lin, Yi-Fu Wang, Shaw-Fang Yet, Yu-Juei Hsu, and Cheng-Chin Kuo. 2016. "TLR4-Activated MAPK-IL-6 Axis Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091394
APA StyleLee, G. -L., Wu, J. -Y., Tsai, C. -S., Lin, C. -Y., Tsai, Y. -T., Lin, C. -S., Wang, Y. -F., Yet, S. -F., Hsu, Y. -J., & Kuo, C. -C. (2016). TLR4-Activated MAPK-IL-6 Axis Regulates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Function. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1394. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091394