Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) with Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Subunit VP1
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) Significantly Enhanced the Immunogenicity of Non-Replicating Enterovirus 71 VP1 Subunit (EVP1) Vaccine
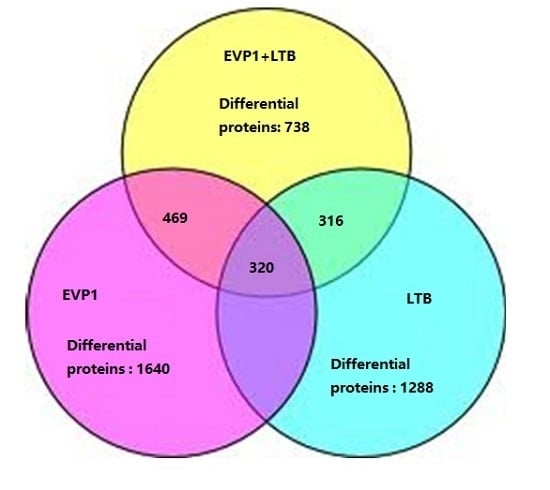
2.2. The Summarization of the Total Quantitative Proteome Profiles
2.3. Immune System Processing Proteins Summarization
2.4. The Dominant Pathways in Antigen Processing and Immunoregulation
2.5. Confocal Microscopy Assay Indicated That LTB Was Endocytosed in ENS-Lysosomal-ER System
2.6. His-LTB Pull-Down Assay
2.7. The Western Blot Confirmed the Validity of iTRAQ-LC-MS/MS Data
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. EVP1 and LTB Purification
4.2. Animal and Immunization
4.3. Immunological Assay
4.4. Cells, Cell Culture, and Cell Treatment
4.5. Cell Sample Preparation
4.6. Digestion and iTRAQ Labeling
4.7. Mass Spectrometric Analysis
4.8. Data Analysis
4.9. Confocal Microscopy Assay
4.10. His-Flag Pull-Down Assay
4.11. Western Blot Assay
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| A2MP | α-2-macroglobulin-P |
| ACAA1A | 3-ketoacyl-CoA thiolase A |
| AHCY | adenosylhomocysteinase |
| AHSA2 | activator of 90 kDa heat shock protein ATPase homolog 2 |
| AKT3 | RAC-α serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 |
| ALDH2 | aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial |
| ANAPC2 | anaphase-promoting complex subunit 2 |
| ARF6 | ADP ribosylation factor 6 |
| ARFGAP | ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein |
| ARHGEF6 | ρ guanine nucleotide exchange factor 6 |
| ASAP2 | Arf-GAP with SH3 domain, ANK repeat and PH domain-containing protein 2 |
| CALR | Calreticulin |
| CBL | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL |
| CBLB | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase CBL B |
| CCND1 | G1/S-specific cyclin-D1 |
| CCT | chaperonin containing TCP1 |
| CDK1 | cyclin-dependent kinase 1 |
| CFL1 | cofilin-1 |
| CHMP | charged multivesicular body protein |
| CHP | calcineurin B homologous protein 1 |
| CLTA | clathrin light chain A |
| CSF1R | macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor |
| DNM | dynamin |
| CTSB | cathepsin B; |
| DNM2 | dynamin 2 |
| DNM1L | dynamin-1-like protein |
| EDIL3 | EGF-like repeat and discoidin I-like domain-containing protein 3 |
| EHD | EH domain-containing protein |
| ENS | endocytosis |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| ESI | electrospray ion |
| EV71 | enterovirus 71 |
| EVP1 | EV71 VP1 subunit |
| FCGR1 | high affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc receptor I |
| FDPS | farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase |
| FLNA | filamin-A |
| FLT1 | vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 |
| GM1 | ganglioside M1 |
| GSTO1 | glutathione S-transferase ω-1 |
| HERC4 | probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HERC4 |
| HFMD | hand-foot-and-mouth disease |
| HIST1H1E | histone H1E |
| HSPA4 | heat shock 70 kDa protein 4 |
| IFI35 | interferon-induced 35 kDa protein |
| IQSEC1 | IQ motif and SEC7 domain-containing protein 1 |
| ISRE | IFN-stimulated response element |
| iTRAQ | isobaric tags for relative and absolute quantitation |
| MS | mass spectrometry |
| JAK | Janus kinase |
| KLHL9 | kelch-like protein 9 |
| LAMP-1 | Lysosome-associated membrane glycoprotein 1 |
| LC-MS | liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry |
| LT | heat-labile toxin |
| LTB | B subunits of LT |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| NFATC2 | nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic |
| NFKB1 | nuclear factor NF-κB p105 subunit |
| OAS1A | 2′-5′-oligoadenylate synthase 1A |
| PANTHER | protein annotation through evolutionary relationship |
| PIAS4 | E3 SUMO-protein ligase PIAS1 |
| PPIL2 | peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase-like 2 |
| PPM1A | protein phosphatase 1A |
| PTPN7 | tyrosine-protein phosphatase non-receptor type 7 |
| Q-TOF-MS | source for quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry |
| RAB5A | Ras-related protein Rab-5A |
| RAP1B | Ras-related protein Rap-1b |
| PRSS1 | protease serine 1 |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| SLC11 | solute carrier 11 |
| SLFN | schlafen |
| SRC | proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase |
| STAM2 | signal transducing adapter molecule 2 |
| STAT | signal transducers and activators of transcription |
| STAU2 | double-stranded RNA-binding protein Staufen homolog 2 |
| SWAP70 | switch-associated protein 70 |
| TCP1 | t-complex protein 1 |
| TGFB1 | transforming growth factor β-1 |
| UBE2R2 | ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 R2 |
| UBMP | ubiquitin mediated proteolysis pathway |
| VPS | vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein |
| WWP2 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP2 |
| XIAP | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase XIAP |
| ZFYVE9 | Zinc finger FYVE domain-containing protein 9 |
References
- Donaldson, D.S.; Tong, K.K.; Williams, N.A. Mucosal administration of the B subunit of E. coli heat-labile enterotoxin promotes the development of Foxp3-expressing regulatory T-cells. Mucosal Immunol. 2011, 4, 227–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, E.; Merritt, E.A.; Zhang, Z.; Pickens, J.C.; Roach, C.; Ahn, M.; Hol, W.G. Exploration of the GM1 receptor-binding site of heat-labile enterotoxin and cholera toxin by phenyl-ring-containing galactose derivatives. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2001, 57, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fingerut, E.; Gutter, B.; Meir, R.; Eliahoo, D.; Pitcovski, J. Vaccine and adjuvant activity of recombinant subunit B of E. coli enterotoxin produced in yeast. Vaccine 2005, 23, 4685–4696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freytag, L.C.; Clements, J.D. Mucosal adjuvants. Vaccine 2005, 23, 1804–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leach, S.; Clements, J.D.; Kaim, J.; Lundgren, A. The adjuvant double mutant Escherichia coli heat labile toxin enhances IL-17A production in human T-cells specific for bacterial vaccine antigens. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e51718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ong, K.W.; Wilson, A.D.; Hirst, T.R.; Morgan, A.J. The B subunit of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin enhances CD8+ cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte killing of Epstein-Barr virus-infected cell lines. J. Virol. 2003, 77, 4298–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millar, D.G.; Hirst, T.R.; Snider, D.P. Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin B subunit is a more potent mucosal adjuvant than its vlosely related homologue, the B subunit of cholera toxin. Infect. Immun. 2001, 69, 3476–3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Luo, Y.; Huang, X.; Song, F.; Liu, G. Construction of Bifidobacterium infantis as a live oral vaccine that expresses antigens of the major fimbrial subunit (CfaB) and the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin (LTB) from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Microbiology 2012, 158, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y. Recent advances in nontoxic Escherichia coli heat-labile toxin and its derivative adjuvants. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Da Hora, V.P.; Conceicao, F.R.; Dellagostin, O.A.; Doolan, D.L. Non-toxic derivatives of LT as potent adjuvants. Vaccine 2011, 29, 1538–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Iwasaki, T.; Asanuma, H.; Sato, Y.; Sata, T.; Aizawa, C.; Kurata, T.; Tamura, S. Effects of intranasal administration of cholera toxin (or Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin) B subunits supplemented with a trace amount of the holotoxin on the brain. Vaccine 2001, 19, 1652–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, J.; Bourgeois, L.; Carlin, N.; Clements, J.; Gustafsson, B.; Lundgren, A.; Nygren, E.; Tobias, J.; Walker, R.; Svennerholm, A.M. Development and preclinical evaluation of safety and immunogenicity of an oral ETEC vaccine containing inactivated E. coli bacteria overexpressing colonization factors CFA/I, CS3, CS5 and CS6 combined with a hybrid LT/CT B subunit antigen, administered alone and together with dmLT adjuvant. Vaccine 2013, 31, 2457–2464. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, J.; Holmgren, J. Cholera toxin—A foe & a friend. Indian J. Med. Res. 2011, 133, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Holmgren, J.; Elwing, H.; Fredman, P.; Strannegard, O.; Svennerholm, L. Gangliosides as receptors for bacterial toxins and Sendai virus. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 1980, 125, 453–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nashar, T.O.; Webb, H.M.; Eaglestone, S.; Williams, N.A.; Hirst, T.R. Potent immunogenicity of the B subunits of Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin: Receptor binding is essential and induces differential modulation of lymphocyte subsets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Haan, L.; Verweij, W.R.; Feil, I.K.; Holtrop, M.; Hol, W.G.; Agsteribbe, E.; Wilschut, J. Role of GM1 binding in the mucosal immunogenicity and adjuvant activity of the Escherichia coli heat-labile enterotoxin and its B subunit. Immunology 1998, 94, 424–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McMinn, P.C. An overview of the evolution of enterovirus 71 and its clinical and public health significance. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 26, 91–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Li, J.X.; Jin, P.F.; Wang, Y.X.; Zhu, F.C. Enterovirus 71: A whole virion inactivated enterovirus 71 vaccine. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.; Bian, L.; Xu, M.; Liang, Z. EV71 vaccine, a new tool to control outbreaks of hand, foot and mouth disease (HFMD). Expert Rev. Vaccines 2016, 15, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, S.L.; Ying, X.L.; Han, X.; Sun, X.X.; Jin, Q.; Yang, F. Characterization of the enterovirus 71 VP1 protein as a vaccine candidate. J. Med. Virol. 2015, 87, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premanand, B.; Kiener, T.K.; Meng, T.; Tan, Y.R.; Jia, Q.; Chow, V.T.; Kwang, J. Induction of protective immune responses against EV71 in mice by baculovirus encoding a novel expression cassette for capsid protein VP1. Antivir. Res. 2012, 95, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, P.; Hsieh, S.Y.; Liu, C.C.; Chou, A.H.; Chang, J.Y.; Wu, S.C.; Liu, S.J.; Chow, Y.H.; Su, I.J.; Klein, M. Production of EV71 vaccine candidates. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2012, 8, 1775–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, Z.; Ye, X.; Huang, X.; Cai, Y.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Su, Z.; Huang, Z. Neutralizing antibodies induced by recombinant virus-like particles of enterovirus 71 genotype C4 inhibit infection at pre- and post-attachment steps. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Dong, M.; Jiang, B.; Dai, X.; Meng, J. Antigenic characteristics of the complete and truncated capsid protein VP1 of enterovirus 71. Virus Res. 2012, 167, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Jiang, S.; Wang, Y. Recombinant VP1 protein expressed in Pichia pastoris induces protective immune responses against EV71 in mice. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hagiwara, Y.; Kawamura, Y.I.; Kataoka, K.; Rahima, B.; Jackson, R.J.; Komase, K.; Dohi, T.; Boyaka, P.N.; Takeda, Y.; Kiyono, H.; et al. A second generation of double mutant cholera toxin adjuvants: Enhanced immunity without intracellular trafficking. J. Immunol. 2006, 177, 3045–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, L.; Xu, M.; Yin, Z. Antiviral drug discovery for the treatment of enterovirus 71 infections. Antivir. Res. 2013, 97, 183–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, I.; Katyal, A. Modification of mouse A2M B (620–792) and A2M N (168–230) by malondialdehyde and acetaldehyde attenuates the proteinase and TGF-β1 binding ability of A2MB. FEBS Lett. 2011, 585, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murshid, A.; Gong, J.; Calderwood, S.K. Hsp90-peptide complexes stimulate antigen presentation through the class II pathway after binding scavenger receptor SREC-I. Immunobiology 2014, 219, 924–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Missy, K.; Hu, B.; Schilling, K.; Harenberg, A.; Sakk, V.; Kuchenbecker, K.; Kutsche, K.; Fischer, K.D. αPIX ρ GTPase guanine nucleotide exchange factor regulates lymphocyte functions and antigen receptor signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2008, 28, 3776–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, E.Y.; Chavakis, E.; Czabanka, M.A.; Langer, H.F.; Fraemohs, L.; Economopoulou, M.; Kundu, R.K.; Orlandi, A.; Zheng, Y.Y.; Prieto, D.A.; et al. Del-1, an endogenous leukocyte-endothelial adhesion inhibitor, limits inflammatory cell recruitment. Science 2008, 322, 1101–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Poel, C.E.; Spaapen, R.M.; van de Winkel, J.G.; Leusen, J.H. Functional characteristics of the high affinity IgG receptor, FcγRI. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 2699–2704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guyre, C.A.; Barreda, M.E.; Swink, S.L.; Fanger, M.W. Colocalization of FcγRI-targeted antigen with class I MHC: Implications for antigen processing. J. Immunol. 2001, 166, 2469–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stocki, P.; Morris, N.J.; Preisinger, C.; Wang, X.N.; Kolch, W.; Multhoff, G.; Dickinson, A.M. Identification of potential HLA class I and class II epitope precursors associated with heat shock protein 70 (HSPA). Cell Stress Chaperones 2010, 15, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, A.; Dinh, P.X.; Panda, D.; Pattnaik, A.K. Interferon-inducible protein IFI35 negatively regulates RIG-I antiviral signaling and supports vesicular stomatitis virus replication. J. Virol. 2014, 88, 3103–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, M.; Wakita, T.; Esumi, M. 2′,5′-Oligoadenylate synthetase-like gene highly induced by hepatitis C virus infection in human liver is inhibitory to viral replication in vitro. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2010, 392, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogden, K.M.; Hu, L.; Jha, B.K.; Sankaran, B.; Weiss, S.R.; Silverman, R.H.; Patton, J.T.; Prasad, B.V. Structural basis for 2′,5′-oligoadenylate binding and enzyme activity of a viral RNase L antagonist. J. Virol. 2015, 89, 6633–6645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, L.; Howell, M.D.; Kim, B.E.; Hall, C.F.; Streib, J.E.; Leung, D.Y. Inhibition of S100A11 gene expression impairs keratinocyte response against vaccinia virus through downregulation of the IL-10 receptor 2 chain. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 124, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nairz, M.; Fritsche, G.; Crouch, M.L.; Barton, H.C.; Fang, F.C.; Weiss, G. Slc11a1 limits intracellular growth of Salmonella enterica sv. Typhimurium by promoting macrophage immune effector functions and impairing bacterial iron acquisition. Cell. Microbiol. 2009, 11, 1365–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavrommatis, E.; Fish, E.N.; Platanias, L.C. The schlafen family of proteins and their regulation by interferons. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 2013, 33, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, M.; Krebs, P.; Crozat, K.; Li, X.; Croker, B.A.; Siggs, O.M.; Popkin, D.; Du, X.; Lawson, B.R.; Theofilopoulos, A.N.; et al. An Slfn2 mutation causes lymphoid and myeloid immunodeficiency due to loss of immune cell quiescence. Nat. Immunol. 2010, 11, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Zuylen, W.J.; Garceau, V.; Idris, A.; Schroder, K.; Irvine, K.M.; Lattin, J.E.; Ovchinnikov, D.A.; Perkins, A.C.; Cook, A.D.; Hamilton, J.A.; et al. Macrophage activation and differentiation signals regulate schlafen-4 gene expression: Evidence for schlafen-4 as a modulator of myelopoiesis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e15723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold Wager, C.M.; Hole, C.R.; Wozniak, K.L.; Olszewski, M.A.; Wormley, F.L., Jr. STAT1 signaling is essential for protection against Cryptococcus neoformans infection in mice. J. Immunol. 2014, 193, 4060–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, G.; Angeli, V.; Randolph, G.J.; Junt, T.; von Andrian, U.; Schnittler, H.J.; Jessberger, R. Signaling protein SWAP-70 is required for efficient B cell homing to lymphoid organs. Nat. Immunol. 2006, 7, 827–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ocana-Morgner, C.; Gotz, A.; Wahren, C.; Jessberger, R. SWAP-70 restricts spontaneous maturation of dendritic cells. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5545–5558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeoni, L.; Bogeski, I. Redox regulation of T-cell receptor signaling. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 555–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaihami, G.H.; Almeida, J.R.; Santos, S.S.; Netto, L.E.; Almeida, S.R.; Baldini, R.L. Involvement of a 1-Cys peroxiredoxin in bacterial virulence. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1004442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Menon, D.; Coll, R.; O’Neill, L.A.; Board, P.G. Glutathione transferase ω 1 is required for the lipopolysaccharide-stimulated induction of NADPH oxidase 1 and the production of reactive oxygen species in macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menon, D.; Coll, R.; O’Neill, L.A.; Board, P.G. GSTO1-1 modulates metabolism in macrophages activated through the LPS and TLR4 pathway. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 1982–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heraud-Farlow, J.E.; Kiebler, M.A. The multifunctional Staufen proteins: Conserved roles from neurogenesis to synaptic plasticity. Trends Neurosci. 2014, 37, 470–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kambayashi, T.; Kraft-Leavy, J.R.; Dauner, J.G.; Sullivan, B.A.; Laur, O.; Jensen, P.E. The nonclassical MHC class I molecule Qa-1 forms unstable peptide complexes. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 1661–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mester, G.; Hoffmann, V.; Stevanovic, S. Insights into MHC class I antigen processing gained from large-scale analysis of class I ligands. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2011, 68, 1521–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gleeson, P.A. The role of endosomes in innate and adaptive immunity. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 31, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Wijk, S.J.; Timmers, H.T. The family of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes (E2s): Deciding between life and death of proteins. FASEB J. 2010, 24, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bessat, M.; Knudsen, G.; Burlingame, A.L.; Wang, C.C. A minimal anaphase promoting complex/cyclosome (APC/C) in Trypanosoma brucei. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, M.; Blanc, C.; Thazar-Poulot, N.; Ben Larbi, S.; Cosson, P.; Letourneur, F. Dictyostelium ACAP-A is an ArfGAP involved in cytokinesis, cell migration and actin cytoskeleton dynamics. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seuter, S.; Ryynanen, J.; Carlberg, C. The ASAP2 gene is a primary target of 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 in human monocytes and macrophages. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjay, A.; Horne, W.C.; Baron, R. The Cbl family: Ubiquitin ligases regulating signaling by tyrosine kinases. Sci. STKE 2001, 2001, pe40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liyasova, M.S.; Ma, K.; Lipkowitz, S. Molecular pathways: Cbl proteins in tumorigenesis and antitumor immunity-opportunities for cancer treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 1789–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Zhou, H.; Langdon, W.Y.; Zhang, J. E3 ubiquitin ligase Cbl-b in innate and adaptive immunity. Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 1875–1884. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Spang, N.; Feldmann, A.; Huesmann, H.; Bekbulat, F.; Schmitt, V.; Hiebel, C.; Koziollek-Drechsler, I.; Clement, A.M.; Moosmann, B.; Jung, J.; et al. RAB3GAP1 and RAB3GAP2 modulate basal and rapamycin-induced autophagy. Autophagy 2014, 10, 2297–2309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochrainer, K.; Kroismayr, R.; Baranyi, U.; Binder, B.R.; Lipp, J. Highly homologous HERC proteins localize to endosomes and exhibit specific interactions with hPLIC and Nm23B. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2008, 65, 2105–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goueli, B.S.; Powell, M.B.; Finger, E.C.; Pfeffer, S.R. TBC1D16 is a Rab4A GTPase activating protein that regulates receptor recycling and EGF receptor signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 15787–15792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Jiang, X.; Luo, Z. WWP2: A multifunctional ubiquitin ligase gene. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanoa, B.S.; Cogliati, T.; Satish, A.G.; Bruford, E.A.; Friedman, J.S. Update on the Kelch-like (KLHL) gene family. Hum. Genom. 2013, 7, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willinger, T.; Staron, M.; Ferguson, S.M.; de Camilli, P.; Flavell, R.A. Dynamin 2-dependent endocytosis sustains T-cell receptor signaling and drives metabolic reprogramming in T lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 4423–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, J.H.; Xiao, C.; Hayden, M.S.; Lee, K.Y.; Trombetta, E.S.; Pypaert, M.; Nara, A.; Yoshimori, T.; Wilm, B.; Erdjument-Bromage, H.; et al. CHMP5 is essential for late endosome function and down-regulation of receptor signaling during mouse embryogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 2006, 172, 1045–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Posey, A.D., Jr.; Swanson, K.E.; Alvarez, M.G.; Krishnan, S.; Earley, J.U.; Band, H.; Pytel, P.; McNally, E.M.; Demonbreun, A.R. EHD1 mediates vesicle trafficking required for normal muscle growth and transverse tubule development. Dev. Biol. 2014, 387, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galletta, B.J.; Mooren, O.L.; Cooper, J.A. Actin dynamics and endocytosis in yeast and mammals. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2010, 21, 604–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirchhausen, T.; Owen, D.; Harrison, S.C. Molecular structure, function, and dynamics of clathrin-mediated membrane traffic. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moravec, R.; Conger, K.K.; D’Souza, R.; Allison, A.B.; Casanova, J.E. BRAG2/GEP100/IQSec1 interacts with clathrin and regulates α5β1 integrin endocytosis through activation of ADP ribosylation factor 5 (Arf5). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 31138–31147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raymond, C.K.; Howald-Stevenson, I.; Vater, C.A.; Stevens, T.H. Morphological classification of the yeast vacuolar protein sorting mutants: Evidence for a prevacuolar compartment in class E vps mutants. Mol. Biol. Cell 1992, 3, 1389–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feyder, S.; De Craene, J.O.; Bar, S.; Bertazzi, D.L.; Friant, S. Membrane trafficking in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 1509–1525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrizzo, A.; Conte, C.; Tagliamonte, M.; Napolitano, M.; Bifulco, K.; Carriero, V.; de Stradis, A.; Tornesello, M.L.; Buonaguro, F.M.; Quaglia, F.; et al. Functional characterization of biodegradable nanoparticles as antigen delivery system. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 34, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.P.; Chang, K.S.; Hsu, J.L.; Tsai, I.F.; Lin, A.B.; Wei, T.Y.; Wu, C.L.; Lu, Y.T. Analysis of the immune response of human dendritic cells to Mycobacterium tuberculosis by quantitative proteomics. Proteome Sci. 2016, 14, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagafuku, M.; Okuyama, K.; Onimaru, Y.; Suzuki, A.; Odagiri, Y.; Yamashita, T.; Iwasaki, K.; Fujiwara, M.; Takayanagi, M.; Ohno, I.; et al. CD4 and CD8 T-cells require different membrane gangliosides for activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E336–E342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, T.; Honda, T.; Miwatani, T.; Wakabayashi, S.; Matsubara, H. Analysis of receptor-binding site in Escherichia coli enterotoxin. J. Biol. Chem. 1985, 260, 8552–8558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Xu, N.; Yuan, H.; Li, S.; Liu, L.; Pu, Z.; Wan, J.; Wang, H.; Chang, Y.; Li, R. Immunomodulatory activity of recombinant ricin toxin binding subunit B (RTB). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 12401–12410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adhya, D.; Dutta, K.; Kundu, K.; Basu, A. Histone deacetylase inhibition by Japanese encephalitis virus in monocyte/macrophages: A novel viral immune evasion strategy. Immunobiology 2013, 218, 1235–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cafri, G.; Amram, E.; Rinott, G.; Koifman, G.; Fishman, S.; Keisari, Y.; Tzehoval, E.; Margalit, A.; Eisenbach, L.; Gross, G. Coupling presentation of MHC class I peptides to constitutive activation of antigen-presenting cells through the product of a single gene. Int. Immunol. 2011, 23, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wang, F.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, Y.; Yin, Y.; Sun, S. Enhanced capacity of antigen presentation of HBc-VLP-pulsed RAW264.7 cells revealed by proteomics analysis. J. Proteome Res. 2008, 7, 4898–4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Preshaw, P.M.; Taylor, J.J. How has research into cytokine interactions and their role in driving immune responses impacted our understanding of periodontitis? J. Clin. Periodontol. 2011, 38, 60–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peti, W.; Page, R. Molecular basis of MAP kinase regulation. Protein Sci. 2013, 22, 1698–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Davis, R.J.; Flavell, R.A. MAP kinases in the immune response. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 20, 55–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Ren, J.; Xiao, X.; Tang, Y.Y.; Weng, H.Q.; Yang, Q.; Wu, M.J.; Tang, W. Proteomic analysis of bladder cancer by iTRAQ after Bifidobacterium infantis-mediated HSV-TK/GCV suicide gene treatment. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 1333–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, H.; Muruganujan, A.; Casagrande, J.T.; Thomas, P.D. Large-scale gene function analysis with the PANTHER classification system. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1551–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franceschini, A.; Szklarczyk, D.; Frankild, S.; Kuhn, M.; Simonovic, M.; Roth, A.; Lin, J.; Minguez, P.; Bork, P.; von Mering, C.; et al. STRING v9.1: Protein-protein interaction networks, with increased coverage and integration. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D808–D815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Protein (Acc.#) | LTB | EVP1 | LTB + EVP1 | Functions |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A2MP (Q6GQT1) | 12.2462 | 2.1478 | 0.6607 | It is able to bind endogenous or foreign peptides, providing a barrier against pathogens. |
| * ARHGEF6 (Q8K4I3) | 1.6904 | 1.2474 | 1.6904 | Acts as a RAC1 guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) and positive regulates immune responses. |
| AHSA2 (Q8N9S3) | 2.1677 | 2.1281 | 1.5704 | Cochaperone that stimulates HSP90 ATPase activity and stimulates antigen presentation through the class II pathway. |
| * EDIL3 (O35474) | 2.2699 | 0.4742 | 1.7219 | An important endogenous inhibitor of inflammatory cell adhesion and homing. |
| FCGR1 (P26151) | 2.0512 | 3.1046 | 2.1086 | Functions in both innate and adaptive immune responses. |
| GSTO1 (O09131) | 0.3981 | 0.2858 | 0.6427 | Exhibits glutathione-dependent thiol transferase and dehydroascorbate reductase activities. |
| HSPA4 (Q3U2G2) | 0.4487 | 0.1754 | 0.7178 | Involved in the antigen presentation and cross-presentation for specific triggering of the acquired immune response. |
| IFI35 (Q9D8C4) | 1.3932 | 0.6081 | 0.4246 | Interferon-induced protein 35 and negatively regulated RIG-I antiviral signaling. |
| OASL1 (Q8VI94) | 3.3113 | 3.1623 | 2.0701 | May play a role in mediating resistance to virus infection, control of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. |
| OASL2 (Q9Z2F2) | 2.466 | 2.3768 | 1.4322 | May play a role in mediating resistance to virus infection, control of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. |
| OAS1A (P11928) | 1.977 | 1.6293 | 1.556 | May play a role in mediating resistance to virus infection, control of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. |
| OAS3 (Q8VI93) | 1.7061 | 1.3305 | 1.2023 | May play a role in mediating resistance to virus infection, control of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis. |
| PRDX1 (P35700) | 0.1888 | 0.0738 | 0.4699 | Reduces peroxides with reducing equivalents provided through the thioredoxin system but not from glutaredoxin. |
| S100A11 (P50543) | 0.1445 | 0.0649 | 0.2228 | Facilitates the differentiation and the cornification of keratinocytes and resists to virus infection. |
| * SLFN2 (Q9Z0I6) | 2.208 | 1.2023 | 1.6144 | May have a role in hematopoeitic cell differentiation, induction of immune responses. |
| SLFN5 (Q8CBA2) | 7.8705 | 6.6681 | 3.8371 | May have a role in hematopoeitic cell differentiation, induction of immune responses. |
| SLC11A2 (P49282) | 1.3183 | 2.421 | 1.4322 | May play an important role in hepatic iron accumulation and tissue iron distribution. |
| SLC27A4 (Q91VE0) | 1.1695 | 1.977 | 1.5704 | Plays a role in the formation of the epidermal barrier. Required for fat absorption in early embryogenesis. |
| STAU2 (Q8CJ67) | 1.0864 | 1.4723 | 1.8535 | RNA-binding protein, mRNA stability, translation. |
| STAT1 (Q8C3V4) | 2.466 | 2.2284 | 1.8197 | Transcription factor that binds to the IFN-stimulated response element (ISRE) and to the GAS element. |
| SWAP70 (Q6A028) | 1.5996 | 0.8872 | 1.3428 | Restricts spontaneous maturation of dendritic cells. |
| GO_ID | Pathway | EVP1 | LTB | LTB + EVP1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| p-Value | p-Value | p-Value | ||
| mmu04144 | Endocytosis | * 7.17 × 10−5 | * 4.39 × 10−4 | * 4.80 × 10−5 |
| mmu04120 | Ubiquitin mediated proteolysis | * 5.72 × 10−6 | * 1.17 × 10−3 | * 2.27 × 10−3 |
| mmu04141 | Protein processing in endoplasmic reticulum | 2.02 × 10−1 | 7.21 × 10−1 | * 2.11 × 10−2 |
| mmu04010 | MAPK signaling pathway | 6.26 × 10−1 | 4.07 × 10−1 | * 1.05 × 10−2 |
| mmu04612 | Antigen processing and presentation | * 3.21 × 10−2 | 2.34 × 10−1 | 1.00 × 100 |
© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, L.; Ma, Y.; Zhou, H.; Wu, M. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) with Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Subunit VP1. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091419
Liu L, Ma Y, Zhou H, Wu M. Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) with Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Subunit VP1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2016; 17(9):1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091419
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Lin, Yongping Ma, Huicong Zhou, and Mingjun Wu. 2016. "Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) with Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Subunit VP1" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17, no. 9: 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091419
APA StyleLiu, L., Ma, Y., Zhou, H., & Wu, M. (2016). Quantitative Proteomic Analysis of Escherichia coli Heat-Labile Toxin B Subunit (LTB) with Enterovirus 71 (EV71) Subunit VP1. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 17(9), 1419. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091419