Oil Body-Bound Oleosin-rhFGF-10: A Novel Drug Delivery System that Improves Skin Penetration to Accelerate Wound Healing and Hair Growth in Mice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Stable Integration of the Oleosin-rhFGF-10 Gene in Safflowers
2.2. Oleosin-rhFGF-10 Protein Analysis
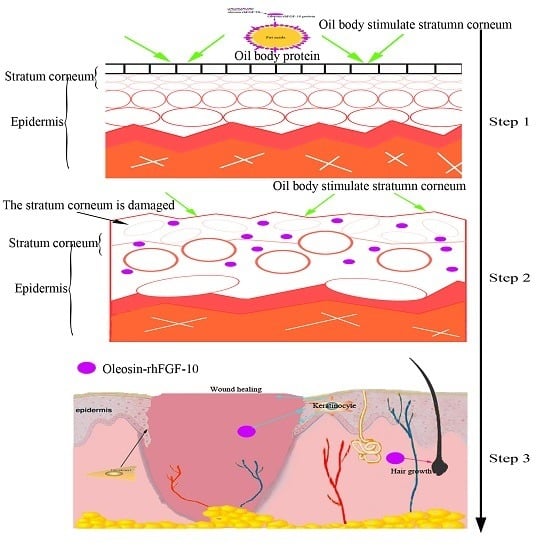
2.3. The Ability of Oleosin-rhFGF-10 to Penetrate the Skin
2.4. Oleosin-rhFGF-10 Enhances Wound Closure
2.5. Oleosin-rhFGF-10 Induces More Subcutaneous Tissue Formation
2.6. Oleosin-rhFGF-10 Promotescytokeratin-10 and IL-2 Expression
2.7. The Effect of Oleosin-rhFGF-10 on Hair Growth
2.8. Stability of Oleosin-rhFGF-10
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) and Southern Blot Detection of the Oleosin-rhFGF-10 Gene in Safflower
4.2. Identification of the Fusion Protein
4.3. Mouse Model
4.4. The Ability of Oil Body to Promote the Oleosin-rhFGF-10 to Penetrate the Skin of Mice
4.5. Effect of Oleosin-FGF-10 on Mouse Skin Wound Healing
4.6. IL-2 Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Effect of Oleosin-rhFGF-10 on Hair Growth
4.8. Effect of Oleosin on Enzymatic Hydrolysis of rhFGF-10
4.9. Histological Analysis
4.10. Immunohistochemical Staining
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCR | Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer salt |
| WT | Wild Type |
| rhFGF-10 | Recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 10 |
| Oleosin-rhFGF-10 | Oleosin-Recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 10 |
| ELISA | Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay |
| DIG | Digoxigenin |
| NBT/BCIP | Nitroblue Tetrazolium/5-Bromo-4-Chloro-3-Indolyl Phosphate |
| AP | Alkaline Phosphatase |
| HRP | Horse radish peroxidase |
| DAB | Diaminobenzidine |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene Fluoride |
References
- Emoto, H.; Tagashira, S.; Mattei, M.G.; Yamasaki, M.; Hashimoto, G.; Katsumata, T.; Negoro, T.; Nakatsuka, M.; Birnbaum, D.; Coulier, F. Structure and expression of human fibroblast growth factor-10. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 23191–231914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S. Fibroblast growth factors in epithelial repair and cytoprotection. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 753–757. [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez, P.A.; Rampy, M.A. Keratinocyte growth factor-2 accelerates wound healing in incisional wounds. J. Surg. Res. 1999, 81, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, J.H. Stimulation of human hair growth by the recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor-2 (KGF-2). Biotechnol. Lett. 2005, 27, 749–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.H.; Xiang, L.J.; Shi, H.X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, L.P.; Cai, P.T.; Lin, Z.L.; Lin, B.B.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, H.L. Fibroblast growth factors stimulate hair growth through β-catenin and Shh expression in C57BL/6 mice. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacs, D.; Cota, C.; Cardinali, G.; Aspite, N.; Bolasco, G.; Amantea, A.; Torrisi, M.R.; Picardo, M. Expression of keratinocyte growth factor and its receptor in clear cell acanthoma. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 762–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yuan, S.; Wang, P.; Liu, X.; Zhan, D.; Zhang, Z. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor-2 in Pichia pastoris. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 132, 44–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martino, M.M.; Briquez, P.S.; Ranga, A.; Lutolf, M.P.; Hubbell, J.A. Heparin-binding domain of fibrin(ogen) binds growth factors and promotes tissue repair when incorporated within a synthetic matrix. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4563–4568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z.; Ni, C.; Chu, Y.; Wang, S.; Yang, S.; Wu, X.; Wang, X.; Li, X.; Feng, W.; Lin, S. Chemical modification of recombinant human keratinocyte growth factor 2 with polyethylene glycol improves biostability and reduces animal immunogenicity. J. Biotechnol. 2009, 142, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, H.; Jing, Y.; Guan, L.; Yi, S.; Du, L.; Tian, H.; Guo, Y.; Feng, Z.; Zhen, L.; Li, H. Expression of bioactive recombinant human fibroblast growth factor 10 in Carthamus tinctorius L. seeds. Protein Expr. Purif. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Jing, Y.; Chen, Y.; Guan, L.; Du, L.N.; Guo, Y.X.; Wang, W.; Wang, L.; Li, H.; Chao, J. Expression of a functional recombinant oleosin-human hyaluronidase hPH-20 fusion in Arabidopsis thaliana. Protein Expr. Purif. 2014, 103, 23–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moloney, M.M.; van Rooijen, G. Expression of epidermal growth factor in plant seeds. U.S. Patent 7091401, 15 August 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nykiforuk, C.L.; Boothe, J.G.; Murray, E.W.; Keon, R.G.; Goren, H.J.; Markley, N.A.; Moloney, M.M. Transgenic expression and recovery of biologically active recombinant human insulin from Arabidopsis thaliana seeds. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2006, 4, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parmenter, D.L.; Boothe, J.G.; van Rooijen, G.J.; Yeung, E.C.; Moloney, M.M. Production of biologically active hirudin in plant seeds using oleosin partitioning. Plant Mol. Biol. 1995, 29, 1167–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldberg, R.B.; Barker, S.J.; Perez-Grau, L. Regulation of gene expression during plant embryogenesis. Cell 1989, 56, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, X.; Ma, J.; Tian, H.; Jiao, Y.; Zhang, R.; Huang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Zhao, B.; Qian, H. Effects of keratinocyte growth factor-2 on corneal epithelial wound healing in a rabbit model of carbon dioxide laser injury. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2010, 33, 971–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.; Zhou, J.; Rong, L.; Seeley, E.J.; Pan, J.; Zhu, X.; Liu, J.; Wang, Q.; Tang, X.; Qu, J. Fibroblast growth factor-10 (FGF-10) mobilizes lung-resident mesenchymal stem cells and protects against acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21642. [Google Scholar]
- Frandsen, G.I.; Mundy, J.; Tzen, J.T.C. Oil bodies and their associated proteins, oleosin and caleosin. Physiol. Plant 2001, 112, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Čižinauskas, V.; Elie, N.; Brunelle, A.; Briedis, V. In TOF-SIMS analysis of sea buckthorn oil fatty acids skin penetration. In Proceedings of the Bbbb Conference on Pharmaceutical Sciences Strategies To Improve the Quality and PERFORMANCE of Modern Drug Delivery Systems, Helsniki, Finland, 10–12 September 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Ghyczy, M. Chemical Composition of Liposomes and Its Influence on the Humidity of Normal Skin; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1992; pp. 308–314. [Google Scholar]
- Betz, G.; Imboden, R.; Imanidis, G. Interaction of liposome formulations with human skin in vitro. Int. J. Pharm. 2001, 229, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowalvern, A.; Walenga, J.M.; Hoppensteadt, D.; Sharppucci, M.; Gamelli, R. L Interleukin-2 and interleukin-6 in relation to burn wound size in the acute phase of thermal injury. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 1994, 178, 357–362. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, X.; Tian, H.; Tang, L.; Zheng, L.; Zheng, L.; Yang, T.; Yu, B.; Wang, Z.; Lin, P.; Li, X. High-efficiency expression of TAT-bFGF fusion protein in escherichia coli and the effect on hypertrophic scar tissue. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, C.; Wei, H.U.; Wei, W.G.; Yan, S.; Yan, C.; Yang, S.L.; Yi, G. Effects of keratinocyte growth factor 2(KGF-2) on keratinocyte growth, migration and on excisional wound healing. Prog. Biochem. Biophys. 2009, 36, 854–862. [Google Scholar]













© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, W.; Yang, J.; Cai, J.; Wang, H.; Tian, H.; Huang, J.; Qiang, W.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Li, X.; et al. Oil Body-Bound Oleosin-rhFGF-10: A Novel Drug Delivery System that Improves Skin Penetration to Accelerate Wound Healing and Hair Growth in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102177
Li W, Yang J, Cai J, Wang H, Tian H, Huang J, Qiang W, Zhang L, Li H, Li X, et al. Oil Body-Bound Oleosin-rhFGF-10: A Novel Drug Delivery System that Improves Skin Penetration to Accelerate Wound Healing and Hair Growth in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(10):2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102177
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Wenqing, Jing Yang, Jingbo Cai, Hongyu Wang, Haishan Tian, Jian Huang, Weidong Qiang, Linbo Zhang, Haiyan Li, Xiaokun Li, and et al. 2017. "Oil Body-Bound Oleosin-rhFGF-10: A Novel Drug Delivery System that Improves Skin Penetration to Accelerate Wound Healing and Hair Growth in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 10: 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102177
APA StyleLi, W., Yang, J., Cai, J., Wang, H., Tian, H., Huang, J., Qiang, W., Zhang, L., Li, H., Li, X., & Jiang, C. (2017). Oil Body-Bound Oleosin-rhFGF-10: A Novel Drug Delivery System that Improves Skin Penetration to Accelerate Wound Healing and Hair Growth in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(10), 2177. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18102177