Ergostane-Type Sterols from King Trumpet Mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) and Their Inhibitory Effects on Aromatase
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
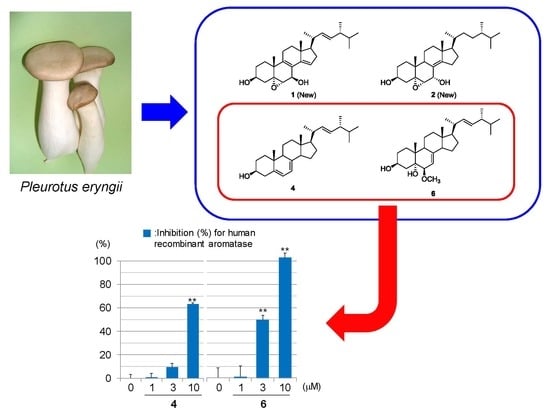
2.1. Isolation and Structure Elucidation
2.2. Evaluation for Aromatase Inhibitory Effects
3. Experimental Section
3.1. General Methods
3.2. Materials
3.3. Extraction and Isolation
3.3.1. Sample 1
3.3.2. Sample 2
3.3.3. (22E)-5α,6α-Epoxyergosta-8,14,22-triene-3β,7β-diol (1)
3.3.4. 5α,6α-Epoxyergost-8(14)-ene-3β,7α-diol (2)
3.4. Inhibitory Effects against Human Recombinant Aromatase
3.5. Statistics
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| HREIMS | High resolution electron ionization mass spectrometry |
| CDCl3 | Duterated chloroform |
| HMBC | Heteronuclear multiple bond coherence |
| COSY | Correlation spectroscopy |
| NOE | Nuclear overhauser effect |
| HSQC | Hetero nuclear single quantum coherence |
References
- Hong, Y.; Li, H.; Yuan, Y.-C.; Chen, S. Molecular characterization of aromatase. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1155, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, S.R.D.; Dowsett, M. Aromatase inhibitors for breast cancer: Lessons from the laboratory. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, K.; Yoo, H.-S.; Lamoury, G.; Boyle, F.; Rosenthal, D.S.; Oh, B. Acupuncture for aromatase inhibitor-induced arthralgia: A systematic review. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balunas, M.J.; Kinghorn, A.D. Natural compounds with aromatase inhibitory activity: An update. Planta Med. 2010, 76, 1087–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, K.; Yamanaka, M.; Gyokusen, M.; Kaneko, S.; Tsutsui, M.; Sato, J.; Sato, I.; Sato, M.; Kondo, R. Estrogen-like activity and prevention effect of bone loss in calcium deficient ovariectomized rats by the extract of Pleurotus eryngii. Phytother. Res. 2006, 20, 659–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez Estrada, A.E.; Royse, D.J. Yield, size and bacterial blotch resistance of Pleurotus eryngii grown on cottonseed hulls/oak sawdust supplemented with manganese, copper and whole ground soybean. Bioresour. Technol. 2007, 98, 1898–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.-S.; Ryoo, I.-J.; Kwon, K.-Y.; Ahn, J.S.; Yoo, I.-D. Pleurone, a novel human neutrophil elastase inhibitor from the fruiting bodies of the mushroom Pleurotus eryngii var. ferulae. J. Antibiot. 2011, 64, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.Y.; Rico, C.W.; Lee, S.C. In vitro antioxidative and antimutagenic activities of oak mushroom (Lentinus edodes) and king oyster mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) byproducts. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2012, 21, 167–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, E.H.; Hwang, Y.P.; Kim, H.G.; Choi, J.H.; Im, J.H.; Yang, J.H.; Lee, H.-U.; Chun, S.-S.; Chung, Y.C.; Jeong, H.G. Inhibitory effect of Pleurotus eryngii extracts on the activities of allergic mediators in antigen-stimulated mast cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2011, 49, 1416–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, J.; Ouchi, K.; Inatomi, S.; Andoh, T. Pleurotus eryngii ameliorates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung inflammation in mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 532389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, A.; Li, X.; Xing, C.; Yang, J.; Sun, P. Antioxidant activity of polysaccharide extracted from Pleurotus eryngii using response surface methodology. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2014, 65, 28–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Xu, J.; Fu, Q.; Fu, X.; Shu, T.; Bi, Y.; Song, B. Antitumor activity of a polysaccharide from Pleurotus eryngii on mice bearing renal cancer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 95, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaoita, Y.; Yoshihara, Y.; Kakuda, R.; Machida, K.; Kikuchi, M. New sterols from two edible mushrooms, Pleurotus eryngii and Panellus serotinus. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2002, 50, 551–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-J.; Li, Y.-X.; Bao, L.; Han, J.-J.; Yang, X.-L.; Li, H.-R.; Wang, Y.-Q.; Li, S.-J.; Liu, H.-W. Eryngiolide A, a cytotoxic macrocyclic diterpenoid with an unusual cyclododecane core skeleton produced by the edible mushroom Pleurotus eryngii. Org. Lett. 2012, 14, 3672–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, T.; Masumoto, Y.; In, Y.; Tomoo, K.; Yamada, T.; Tanaka, R. Eringiacetal A, 5,6-seco-(5S,6R,7R,9S)-5,6:5,7:6,9-triepoxyergosta-8(14),22-diene-3β,7β-diol, an unusual ergostane sterol from the fruiting bodies of Pleurotus eryngii. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2015, 2015, 4645–4649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Maekawa, Y.; Tomio, A.; Masumoto, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; In, Y.; Yamada, T.; Tanaka, R. Six new ergostane-type steroids from king trumpet mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) and their inhibitory effects on nitric oxide production. Steroids 2016, 115, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keller, A.C.; Maillard, M.P.; Hostettmann, K. Antimicrobial steroids from the fungus Fomitopsis pinicola. Phytochemistry 1996, 41, 1041–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo Hyo, W.; Hung Tran, M.; Na, M.; Jung Hyun, J.; Kim Jin, C.; Choi Jae, S.; Kim Jung, H.; Lee, H.-K.; Lee, I.; Bae, K.; et al. Steroids and triterpenes from the fruit bodies of Ganoderma lucidum and their anti-complement activity. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2009, 32, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrero, A.F.; Oltra, J.E.; Poyatos, J.A.; Jimenez, D.; Oliver, E. Phycomysterols and Other Sterols from the Fungus Phycomyces blakesleeanus. J. Nat. Prod. 1998, 61, 1491–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.-Z.; Shen, Y.-M. A rare new cleistanthane diterpene from the pericarp of Trewia nudiflora. Helv. Chim. Acta 2006, 89, 2841–2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawagishi, H.; Katsumi, R.; Sazawa, T.; Mizuno, T.; Hagiwara, T.; Nakamura, T. Cytotoxic steroids from the mushroom Agaricus blazei. Phytochemistry 1988, 27, 2777–2779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishizuka, T.; Yaoita, Y.; Kikuchi, M. Sterol constituents from the fruit bodies of Grifola frondosa (Fr.) S.F. Gray. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1997, 45, 1756–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.-H.; Liu, H.-L.; Huang, H.; Li, X.-B.; Guo, Y.-W. Steroids with Aromatic A-Rings from the Hainan Soft Coral Dendronephthya studeri Ridley. J. Nat. Prod. 2011, 74, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhou, W.; Song, S.B.; Shim, S.H.; Kim, Y.H. Sterol Fatty Acid Esters from the Mushroom Hericium erinaceum and Their PPAR Transactivational Effects. J. Nat. Prod. 2014, 77, 2611–2618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnuma, N.; Amemiya, K.; Kakuda, R.; Yaoita, Y.; Machida, K.; Kikuchi, M. Sterol constituents from two edible mushrooms, Lentinula edodes and Tricholoma matsutake. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2000, 48, 749–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, I.; Goad, L.J.; Clague, A.D.H.; Mulheirn, L.J. The 220 MHz NMR spectra of phytosterols. Phytochemistry 1976, 15, 195–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, M.; Krishna, M.M.; Haribabu, B.; Anjaneyulu, V. Marine sterols. XXV. Isolation of 23-demethylgorgost-7-ene-3β,5α,6β-triol and (24S)-ergostane-3β,5α,6β,7β,15β-pentol from soft corals of the Andaman and Nicobar coasts. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1993, 41, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninomiya, K.; Shibatani, K.; Sueyoshi, M.; Chaipech, S.; Pongpiriyadacha, Y.; Hayakawa, T.; Muraoka, O.; Morikawa, T. Aromatase Inhibitory Activity of Geranylated Coumarins, Mammeasins C and D, Isolated from the Flowers of Mammea siamensis. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 880–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, G.; Tsutsui, N.; Shibatani, K.; Marumoto, S.; Ishikawa, F.; Ninomiya, K.; Muraoka, O.; Morikawa, T. Total syntheses of the aromatase inhibitors, mammeasins C and D, from Thai medicinal plant Mammea siamensis. Tetrahedron 2017, 73, 4481–4486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| 1 | 2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Position | δH | δC | δH | δC | ||||
| 1α | 2.01 | (1H, multiplet (m)) | 31.0 | t | 1.46 | (1H, m) | 32.2 | t |
| 1β | 1.86 | (1H, m) | 1.67 | (1H, m) | ||||
| 2 | 1.68 | (2H, m) | 30.9 | t | α 1.96 | (1H, m) | 31.1 | t |
| β 1.56 | (1H, m) | |||||||
| 3 | 3.96 | (1H, tt, J = 11.5, 5.4) | 68.4 | d | 3.92 | (1H, tt, J = 11.4, 3.0) | 68.7 | d |
| 4α | 1.50 | (1H, m) | 39.0 | t | 1.42 | (1H, m) | 39.6 | t |
| 4β | 2.21 | (1H, m) | 2.13 | (1H, dd, J = 13.2, 11.4) | ||||
| 5 | 63.3 | s | 67.8 | s | ||||
| 6 | 3.24 | (1H, d, J = 2.4) | 59.5 | d | 3.15 | (1H, d, J = 3.5) | 61.3 | d |
| 7 | 4.85 | (1H, br s) | 63.8 | d | 4.43 | (1H, dd, J = 9.6, 3.5) | 65.1 | d |
| 8 | 122.2 | s | 125.1 | s | ||||
| 9 | 138.8 | s | 2.35 | (1H, m) | 38.7 | d | ||
| 10 | 38.3 | s | 35.8 | s | ||||
| 11 | 2.19 | (2H, m) | 22.2 | t | α 1.49 | (1H, m) | 19.0 | t |
| β 1.40 | (1H, m) | |||||||
| 12α | 1.47 | (1H, m) | 35.4 | t | 1.16 | (1H, m) | 36.7 | t |
| 12β | 1.99 | (1H, m) | 1.95 | (1H, m) | ||||
| 13 | 44.6 | s | 43.1 | s | ||||
| 14 | 147.7 | s | 152.7 | s | ||||
| 15 | 5.55 | (1H, br s) | 118.7 | d | α 2.65 | (1H, m) | 25.0 | t |
| β 2.30 | (1H, m) | |||||||
| 16α | 2.27 | (1H, m) | 1.89 | (1H, m) | 26.6 | t | ||
| 16β | 2.08 | (1H, m) | 36.8 | t | 1.41 | (1H, m) | ||
| 17 | 1.55 | (1H, m) | 56.4 | d | 1.21 | (1H, m) | 56.6 | d |
| 18 | 0.82 | (3H, s) | 15.6 | quartet (q) | 0.85 | (3H, s) | 17.9 | q |
| 19 | 1.30 | (3H, s) | 23.6 | q | 0.87 | (3H, s) | 16.5 | q |
| 20 | 2.24 | (1H, m) | 38.8 | d | 1.46 | (1H, m) | 34.9 | d |
| 21 | 1.04 | (3H, d, J = 6.5) | 21.0 | q | 0.93 | (3H, d, J = 6.8) | 19.1 | q |
| 22 | 5.20 | (1H, dd, J = 15.2, 7.6) | 135.1 | d | A 1.03 | (1H, m) | 33.4 | t |
| B 1.44 | (1H, m) | |||||||
| 23 | 5.28 | (1H, dd, J = 15.2, 7.9) | 132.4 | d | A 0.95 | (1H, m) | 30.4 | t |
| B 1.37 | (1H, m) | |||||||
| 24 | 1.88 | (1H, m) | 42.8 | d | 1.21 | (1H, m) | 39.1 | d |
| 25 | 1.48 | (1H, m) | 33.1 | d | 1.58 | (1H, m) | 31.5 | d |
| 26 | 0.85 | (3H, d, J = 6.8) | 19.9 | q | 0.85 | (3H, d, J = 7.1) | 20.5 | q |
| 27 | 0.83 | (3H, d, J = 6.8) | 19.6 | q | 0.78 | (3H, d, J = 7.0) | 17.6 | q |
| 28 | 0.93 | (3H, d, J = 6.8) | 17.6 | q | 0.77 | (3H, d, J = 6.9) | 15.4 | q |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kikuchi, T.; Motoyashiki, N.; Yamada, T.; Shibatani, K.; Ninomiya, K.; Morikawa, T.; Tanaka, R. Ergostane-Type Sterols from King Trumpet Mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) and Their Inhibitory Effects on Aromatase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112479
Kikuchi T, Motoyashiki N, Yamada T, Shibatani K, Ninomiya K, Morikawa T, Tanaka R. Ergostane-Type Sterols from King Trumpet Mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) and Their Inhibitory Effects on Aromatase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(11):2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112479
Chicago/Turabian StyleKikuchi, Takashi, Naoki Motoyashiki, Takeshi Yamada, Kanae Shibatani, Kiyofumi Ninomiya, Toshio Morikawa, and Reiko Tanaka. 2017. "Ergostane-Type Sterols from King Trumpet Mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) and Their Inhibitory Effects on Aromatase" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 11: 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112479
APA StyleKikuchi, T., Motoyashiki, N., Yamada, T., Shibatani, K., Ninomiya, K., Morikawa, T., & Tanaka, R. (2017). Ergostane-Type Sterols from King Trumpet Mushroom (Pleurotus eryngii) and Their Inhibitory Effects on Aromatase. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(11), 2479. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112479