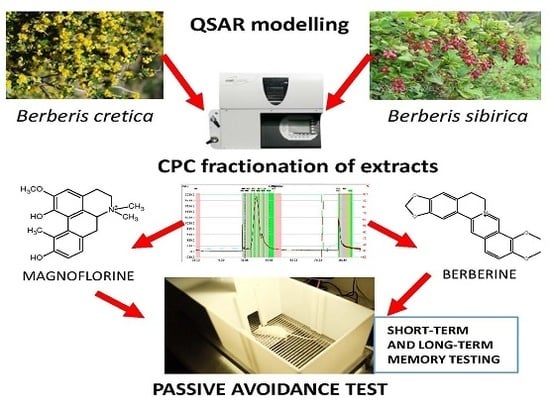
The Evaluation of Pro-Cognitive and Antiamnestic Properties of Berberine and Magnoflorine Isolated from Barberry Species by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC), in Relation to QSAR Modelling
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship (QSAR) Studies
Applicability Domain
2.2. HPLC and HPLC-MS Analysis of the Extract Composition
2.3. Purification of Magnoflorine and Berberine from Plant Extracts by CPC Chromatography
2.4. Locomotor-Activity
2.4.1. The Influence of Berberine on the Locomotor Activity of Mice
2.4.2. The Influence of Magnoflorine on the Locomotor Activity of Mice
2.5. Memory-Related Responses
2.5.1. The Influence of Berberine on the Short- and Long-Term Memory Acquisition in the Passive Avoidance (PA) Test in Mice
2.5.2. The Influence of Magnoflorine on the Short- and Long-Term Memory Acquisition in the PA Test in Mice
2.5.3. Influence of an Acute Administration of Noneffective and Effective Dose of Berberine on the Memory Impairment Induced by an Acute Administration of Scopolamine in the PA Test in Mice
2.5.4. Influence of the Non-Effective and Effective dose of Magnoflorine on the Memory Impairment Induced by an Acute Administration of Scopolamine in the PA Test in Mice
3. Discussion
3.1. QSAR Studies
- BR—the biological response in a constant time interval;
- C—the molar concentration of compound producing a standard response in a constant time interval;
- k1—the coefficient determined by the method of least squares;
- a, b—the constants;
- logPo/w—the logarithm of n-octanol/water partition coefficient of a derivative dlog(1/C)/dlogP = 0.
3.2. The Purification of Alkaloids by CPC Chromatography
3.3. In Vivo Studies
4. Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. Plant Material
4.3. Extraction of Plant Material
4.4. Identification of Major Constituents of the Extracts by HPLC and HPLC-MS
4.5. Purification of Alkaloids by Means of Hydrostatic Counter-Current Chromatography
4.5.1. Purification of Magnoflorine
4.5.2. Separation of Berberine
4.6. Animals
4.7. Drugs
4.8. Experimental Procedures
4.8.1. Locomotor Activity
4.8.2. Memory Related Responses
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AChE | Acetylcholinesterase |
| AD | Alzheimer’s Disease |
| ASE | Accelerated Solvent Extraction |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| CC | Column Chromatography |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CPC | Centrifugal Partition Chromatography |
| ESI | Electrospray Ionization |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| i.p. | Intraperitoneally |
| iNOS | Nitric Oxide Synthase |
| K | Partition Coefficient |
| LI | Latency Index |
| LSER | Linear Solvation Energy Relationship |
| MS | Mass Spectrometry |
| PA | Passive Avoidance Test |
| QSAR | Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationship |
| TEA | Trimethylamine |
| TL | Latency Time |
| TPSA | Topological Polar Surface Area |
References
- Kukula-Koch, W.; Mroczek, T. Application of hydrostatic CCC-TLC-HPLC-ESI-TOF-MS for the bioguided fractionation of anticholinesterase alkaloids from Argemone mexicana L. roots. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 407, 2581–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argyropoulou, A.; Aligiannis, N.; Trougakos, I.P.; Skaltsounis, A.L. Natural compounds with anti-ageing activity. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2013, 30, 1412–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libro, R.; Giacoppo, S.; Rajan, T.S.L.; Bramanti, P.L.; Mazzon, E. Natural phytochemicals in the treatment and prevention of dementia: An overview. Molecules 2016, 21, 518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.C.; Hung, T.H.; Lee, C.Y.; Wang, L.F.; Wu, C.H.; Ke, C.H.; Chen, S.F. Berberine protects against neuronal damage via supression of glia-mediated inflammation in traumatic brain injury. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsieh, M.T.; Peng, W.H.; Wu, C.R.; Wang, W.H. The ameliorating effect of the cognitive-enhancing chinese herbs on scopolamine-induced amnesia in rats. Phytother. Res. 2000, 14, 375–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Qian, C. Berberine chloride can ameliorate the spatial memory impairment and increase the expression of interleukin-1β and inducible nitric oxide synthase in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurosci. 2006, 7, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, A.M.; Heo, H.; Kwon, Y.K. Berberine promotes axonal regeneration in injured nerves of the peripheral nervous system. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 413–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schiff, P.L. The Thalictrum Alkaloids: Chemistry and Pharmacology. In Alkaloids: Chemical and Biological Perspectives; Pelletier, S.W., Ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1996; Volume 11, pp. 1–237. ISBN 0080427979. [Google Scholar]
- Angelis, A.; Hamzaoui, M.; Aligiannis, N.; Nikou, T.; Michailidis, D.; Gerolimatos, P.; Termentzi, A.; Hubert, J.; Halabalaki, M.; Renault, J.H.; et al. An integrated process for the recovery of high added-value compounds from olive oil using solid support free liquid-liquid extraction and chromatography techniques. J. Chromatogr. A 2017, 1491, 126–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipinski, C.A.; Lombardo, F.; Dominy, B.W.; Feeney, P.J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2001, 46, 3–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukula-Koch, W.; Koch, W.; Angelis, A.; Halabalaki, M.; Aligiannis, N. Application of pH-zone refining hydrostatic countercurrent chromatography (hCCC) for the recovery of antioxidant phenolics and the isolation of alkaloids from Siberian barberry herb. Food Chem. 2016, 203, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthod, A.; Hassoun, M.; Ruiz-Angel, M.J. Alkane effect in the Arizona liquid systems used in countercurrent chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 327–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthod, A.; García-Alvarez-Coque, M.C. Micellar Liquid Chromatography; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Platts, J.A.; Abraham, M.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Hersey, A.; Ijaz, L.; Butina, D. Correlation and prediction of a large blood-brain distribution data set—An LFER study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 36, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abraham, M.H. The factors that influence permeation the blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2004, 39, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansch, C.; Maloney, P.P.; Fujita, T.; Muir, R.M. Correlation of biological activity of phenoxyacetic acids with hammett substituent constants and partition coefficients. Nature 1962, 194, 178–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, O.R. Hammett series with biological activity. Acta Chem. Scand. 1962, 16, 1593–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C. Quantitative approach to biochemical structure-activity relationships. Acc. Chem. Res. 1969, 2, 232–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C. Quantitative Structure-Activity Relationships. In Drug Design; Ariens, E.J., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1971; Volume 1, ISBN 0120603063. [Google Scholar]
- Hansch, C. Quantitative structure-activity relationships and the unnamed science. Acc. Chem. Res. 1993, 26, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Fujita, T. p-σ-π analysis. A Method for the correlation of biological activity and chemical structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1964, 86, 1616–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Quinlan, J.E.; Gary, L.L. Linear free-energy relationship between partition coefficients and the aqueous solubility of organic liquids. J. Org. Chem. 1968, 33, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubinyi, H. QSAR: Hansch Analysis and Related Approach, Methods and Principles in Medicinal Chemistry; VCH Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 1961; Volume 1, pp. 1–240. ISBN 978–3527300358. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.H.; Chadha, H.S.; Mitchell, R.C. Hydrogen bonding. 33. Factors that influence the distribution of solutes between blood and brain. J. Pharm. Sci. 1994, 83, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.H.; Chadha, H.S.; Martins, F.; Mitchell, R.C.; Bradbury, M.W.; Gratton, J.A. Hydrogen bonding part 46: A review of the correlation and prediction of transport properties by an LFER method: Physicochemical properties, brain penetration and skin permeability. Pest Manag. Sci. 1999, 55, 78–88. [Google Scholar]
- Abraham, M.H.; Ibrahim, A.; Zissimos, A.N. Determination of sets of solute descriptors from chromatographic measurements. J. Chromatogr. A 2004, 1037, 29–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chico, L.K.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Watterson, D.M. Targeting protein kinases in central nervous system disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2009, 8, 892–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vastag, M.; Keserű, G. Current in vitro and in silico models of blood-brain barrier penetration: A practical view. Curr. Opin. Drug Discov. Dev. 2009, 12, 115–124. [Google Scholar]
- Bickel, U. How to measure drug transport across the blood-brain barrier. Neurotherapeutics 2005, 2, 15–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrard, I. Simple approach to the development of a CCC Solvent Selection Protocol Suitable for Automation. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2005, 28, 1923–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marston, A.; Hostettmann, K. Separation and quantification of flavonoids. In Chemistry, Biochemistry and Application; Oyvind, M.A., Markham, K.R., Eds.; CRC Press Taylor and Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 2–20. ISBN 9780849320217. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; Li, F.; An, L. Berberine alleviates postoperative cognitive dysfunction by suppressing neuroinflammation in aged mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kruk-Słomka, M.; Budzyńska, B.; Biała, G. Involvement of cholinergic receptors in the different stages of memory measured in the modified elevated plus maze test in mice. Pharmacol. Rep. 2012, 64, 1066–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Feng, X.; Chai, L.; Cao, S.; Qiu, F. The metabolism of berberine and its contribution to the pharmacological effects (Review). Drug Metab. Rev. 2017, 49, 139–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukula-Koch, W.; Aligiannis, N.; Halabalaki, M.; Skaltsounis, A.L.; Glowniak, K.; Kalpoutzakis, E. Influence of extraction procedures on phenolic content and antioxidant activity of Cretan barberry herb. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejar, C.; Wang, R.H.; Weinstock, M. Effect of rivstigmine on scopolamine-induced memory impairment in rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 1999, 383, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Compound | logBB | logPS | logPS*fu,brain | Fraction Unbound in Plasma | Fraction Unbound in Brain | Molar Mass (M) | Topological Polar Surface Area (TPSA) | Logarithm of n-Octanol-Water Partition Coefficient (logPo/w) | Abraham LSER Descriptors | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | B | S | E | V | |||||||||
| Berberine | −0.35 | −3.9 | −3.95 | 0.44 | 0.98 | 336.366 | 40.80 | −1.33 | 0 | 1.09 | 2.25 | 2.25 | 3957 |
| Magnoflorine | −0.23 | −4.4 | −4.4 | 0.58 | 0.98 | 342.414 | 58.92 | −1.38 | 0.55 | 0.94 | 1.62 | 1.62 | 2.5903 |
| Parameter | Aporphines | Protoberberines | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| logPo/w | 94.87 | 0.001 | 1010.13 | 0.000 |
| M | 1.50 | 0.288 | 1405.09 | 0.000 |
| TPSA | 1.86 | 0.245 | 46.28 | 0.0006 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kukula-Koch, W.; Kruk-Słomka, M.; Stępnik, K.; Szalak, R.; Biała, G. The Evaluation of Pro-Cognitive and Antiamnestic Properties of Berberine and Magnoflorine Isolated from Barberry Species by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC), in Relation to QSAR Modelling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122511
Kukula-Koch W, Kruk-Słomka M, Stępnik K, Szalak R, Biała G. The Evaluation of Pro-Cognitive and Antiamnestic Properties of Berberine and Magnoflorine Isolated from Barberry Species by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC), in Relation to QSAR Modelling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122511
Chicago/Turabian StyleKukula-Koch, Wirginia, Marta Kruk-Słomka, Katarzyna Stępnik, Radosław Szalak, and Grażyna Biała. 2017. "The Evaluation of Pro-Cognitive and Antiamnestic Properties of Berberine and Magnoflorine Isolated from Barberry Species by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC), in Relation to QSAR Modelling" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122511
APA StyleKukula-Koch, W., Kruk-Słomka, M., Stępnik, K., Szalak, R., & Biała, G. (2017). The Evaluation of Pro-Cognitive and Antiamnestic Properties of Berberine and Magnoflorine Isolated from Barberry Species by Centrifugal Partition Chromatography (CPC), in Relation to QSAR Modelling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2511. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122511