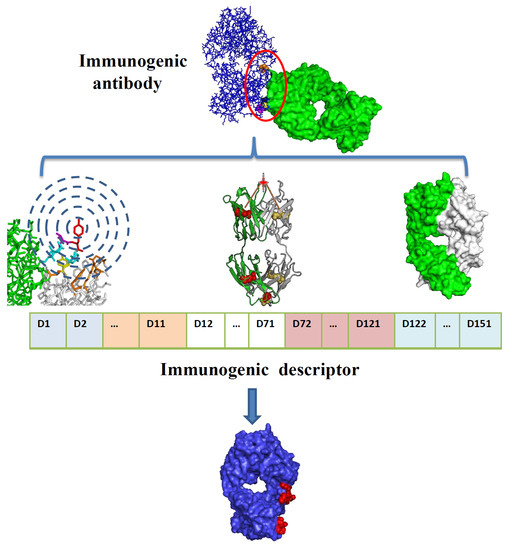
Identifying the Epitope Regions of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Structure Descriptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Difference Exists between Antibody Epitope Regions and Common Antigen Epitope Areas
2.2. Residue Character of Epitope Region on Immunogenic Antibodies
2.3. Model Construction and Performance
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Source
4.2. Disulfide Bond-Based Spatial Location Descriptor
4.3. Spatial Environment Descriptor through Neighboring Layers
4.4. Surface Exposure Descriptor
4.5. Integrated Descriptors for Structure Information and Physio-Chemical Properties
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tansey, E.M.; Catterall, P.P. Monoclonal antibodies: A witness seminar in contemporary medical history. Med. Hist. 1994, 38, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Riechmann, L.; Clark, M.; Waldmann, H.; Winter, G. Reshaping human antibodies for therapy. Nature 1988, 332, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maiese, A.; Del Nonno, F.; Dell’Aquila, M.; Moauro, M.; Baiocchini, A.; Mastracchio, A.; Bolino, G. Postmortem diagnosis of sepsis: A preliminary immunohistochemical study with an anti-procalcitonin antibody. Leg. Med. 2017, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Yu, C.F.; Yang, Y.L.; Gao, K.; Wang, J.Z. Development of a robust reporter gene assay to measure the bioactivity of anti-PD-1/anti-PD-L1 therapeutic antibodies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2017, 145, 447–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Shen, M.H. Polyethylene glycol-mediated cell fusion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2006, 325, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chaigne, B.; Watier, H. Monoclonal antibodies in excess: A simple way to avoid immunogenicity in patients? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 814–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deehan, M.; Garces, S.; Kramer, D.; Baker, M.P.; Rat, D.; Roettger, Y.; Kromminga, A. Managing unwanted immunogenicity of biologicals. Autoimmun. Rev. 2015, 14, 569–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.L.; Dhimolea, E.; Reichert, J.M. Development trends for human monoclonal antibody therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 767–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laffleur, B.; Pascal, V.; Sirac, C.; Cogne, M. Production of human or humanized antibodies in mice. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 901, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Clark, M. Antibody humanization: A case of the ‘Emperor’s new clothes’? Immunol. Today 2000, 21, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olimpieri, P.P.; Marcatili, P.; Tramontano, A. Tabhu: Tools for antibody humanization. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 434–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefranc, M.P.; Ehrenmann, F.; Ginestoux, C.; Giudicelli, V.; Duroux, P. Use of IMGT® databases and tools for antibody engineering and humanization. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 907, 3–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Fu, H.; Hewitt, S.M.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Ho, M. Therapeutically targeting glypican-2 via single-domain antibody-based chimeric antigen receptors and immunotoxins in neuroblastoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6623–E6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimori, A.; Konnai, S.; Okagawa, T.; Maekawa, N.; Ikebuchi, R.; Goto, S.; Sajiki, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Kohara, J.; Ogasawara, S.; et al. In vitro and in vivo antivirus activity of an anti-programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) rat-bovine chimeric antibody against bovine leukemia virus infection. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0174916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agadjanyan, M.G.; Zagorski, K.; Petrushina, I.; Davtyan, H.; Kazarian, K.; Antonenko, M.; Davis, J.; Bon, C.; Blurton-Jones, M.; Cribbs, D.H.; et al. Humanized monoclonal antibody armanezumab specific to N-terminus of pathological tau: Characterization and therapeutic potency. Mol. Neurodegener. 2017, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, F.; Wang, T.; Jiang, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, Z.; Li, Z.; Han, Y.; Pan, M.; Cai, J.; Wang, M.; et al. Engineering a high-affinity humanized anti-CD24 antibody to target hepatocellular carcinoma by a novel CDR grafting design. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 51238–51252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, W.Y.; Foote, J. Immunogenicity of engineered antibodies. Methods 2005, 36, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makabe, K.; Nakanishi, T.; Tsumoto, K.; Tanaka, Y.; Kondo, H.; Umetsu, M.; Sone, Y.; Asano, R.; Kumagai, I. Thermodynamic consequences of mutations in vernier zone residues of a humanized anti-human epidermal growth factor receptor murine antibody, 528. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 1156–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, J.; Winter, G. Antibody framework residues affecting the conformation of the hypervariable loops. J. Mol. Biol. 1992, 224, 487–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, C.F.; Zhao, B.B.; Gong, L.L.; Jin, W.J.; Liu, J.J.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, T.T.; Yuan, X.H.; He, Y.W. A novel antibody humanization method based on epitopes scanning and molecular dynamics simulation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e80636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiu, W.C.; Lai, Y.P.; Chou, M.Y. Humanization and characterization of an anti-human TNF-α murine monoclonal antibody. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roguska, M.A.; Pedersen, J.T.; Keddy, C.A.; Henry, A.H.; Searle, S.J.; Lambert, J.M.; Goldmacher, V.S.; Blattler, W.A.; Rees, A.R.; Guild, B.C. Humanization of murine monoclonal antibodies through variable domain resurfacing. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 969–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowers, P.M.; Neben, T.Y.; Tomlinson, G.L.; Dalton, J.L.; Altobell, L.; Zhang, X.; Macomber, J.L.; Wu, B.F.; Toobian, R.M.; McConnell, A.D.; et al. Humanization of antibodies using heavy chain complementarity-determining region 3 grafting coupled with in vitro somatic hypermutation. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 7688–7696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Gripon, P.; Bouezzedine, F.; Jeong, M.S.; Chi, S.W.; Ryu, S.E.; Hong, H.J. Enhanced humanization and affinity maturation of neutralizing anti-hepatitis B virus preS1 antibody based on antigen-antibody complex structure. FEBS Lett. 2015, 589, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tsumura, H. Production of human antibodies in TransChromo animals. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2004, 40, 8A. [Google Scholar]
- Pruzina, S.; Williams, G.T.; Kaneva, G.; Davies, S.L.; Martin-Lopez, A.; Bruggemann, M.; Vieira, S.M.; Jeffs, S.A.; Sattentau, Q.J.; Neuberger, M.S. Human monoclonal antibodies to HIV-1 gp140 from mice bearing YAC-based human immunoglobulin transloci. Protein Eng. Des. Sel. 2011, 24, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, A.S.; Terry, F.; Cousens, L.; Martin, W. Beyond humanization and de-immunization: Tolerization as a method for reducing the immunogenicity of biologics. Expert Rev. Clin. Pharmacol. 2013, 6, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Pantazes, R.J.; Maranas, C.D. OptMAVEn—A new framework for the de novo design of antibody variable region models targeting specific antigen epitopes. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Nair, S.; Sen, N.; Soni, N.; Madhusudhan, M.S. In silico methods for design of biological therapeutics. Methods 2017, 131, 33–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazar, G.A.; Desjarlais, J.R.; Jacinto, J.; Karki, S.; Hammond, P.W. A molecular immunology approach to antibody humanization and functional optimization. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1986–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.H.; Huang, K.X.; Tu, H.; Adler, A.S. Monoclonal antibody humanness score and its applications. BMC Biotechnol. 2013, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abhinandan, K.R.; Martin, A.C.R. Analyzing the “Degree of humanness” of antibody sequences. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 369, 852–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roitt, I.; Brostoff, J.; Male, D. Immunology; Mosby: London, UK, 1996. [Google Scholar]
- Goldsby, R.A.; Kindt, T.K.; Osborne, B.A.; Kuby, J. Immunology, 5th ed.; W.H. Freeman and Company: New York, NY, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Qi, T.; Qiu, T.; Zhang, Q.; Tang, K.; Fan, Y.; Qiu, J.; Wu, D.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Gao, J.; et al. SEPPA 2.0—More refined server to predict spatial epitope considering species of immune host and subcellular localization of protein antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W59–W63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Xu, T.; Wang, S.; Li, G.; Wu, D.; Cao, Z. Does difference exist between epitope and non-epitope residues? Analysis of the physicochemical and structural properties on conformational epitopes from B-cell protein antigens. Immunme Res. 2011, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kabat, E.A.; Wu, T.T.; Foeller, C.; Perry, H.M.; Gottesman, K.S. Sequence of Proteins of Immunological Interests, 5th ed.; National Institutes of Health, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima, S.; Pokarowski, P.; Pokarowska, M.; Kolinski, A.; Katayama, T.; Kanehisa, M. AAindex: Amino acid index database, progress report 2008. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, D202–D205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moise, L.; Song, C.; Martin, W.D.; Tassone, R.; De Groot, A.S.; Scott, D.W. Effect of HLA DR epitope de-immunization of Factor VIII in vitro and in vivo. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 142, 320–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Argos, P.; Rao, J.K.; Hargrave, P.A. Structural prediction of membrane-bound proteins. Eur. J. Biochem. 1982, 128, 565–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fauchere, J.L.; Charton, M.; Kier, L.B.; Verloop, A.; Pliska, V. Amino acid side chain parameters for correlation studies in biology and pharmacology. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1988, 32, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubbard, S.; Thornton, J. Naccess. Available online: http://www.bioinf.manchester.ac.uk/naccess/ (accessed on 14 November 2017).





| AAindex | Property Description | t-Test p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| ARGP820101 | Hydrophobicity index | 0.018 |
| FAUJ880108 | Localized electrical effect | 0.421 |
| FAUJ880109 | Number of hydrogen bond donors | 0.002 |
| FAUJ880103 | Normalized van der Waals volume | 2.0 × 10−4 |
| LEVM760101 | Hydrophobic parameter | 0.404 |
| ZIMJ680104 | Isoelectric point | 0.055 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qiu, J.; Qiu, T.; Huang, Y.; Cao, Z. Identifying the Epitope Regions of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Structure Descriptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122457
Qiu J, Qiu T, Huang Y, Cao Z. Identifying the Epitope Regions of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Structure Descriptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122457
Chicago/Turabian StyleQiu, Jingxuan, Tianyi Qiu, Yin Huang, and Zhiwei Cao. 2017. "Identifying the Epitope Regions of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Structure Descriptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122457
APA StyleQiu, J., Qiu, T., Huang, Y., & Cao, Z. (2017). Identifying the Epitope Regions of Therapeutic Antibodies Based on Structure Descriptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2457. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122457