Altered Leukocyte Sphingolipid Pathway in Breast Cancer
Abstract
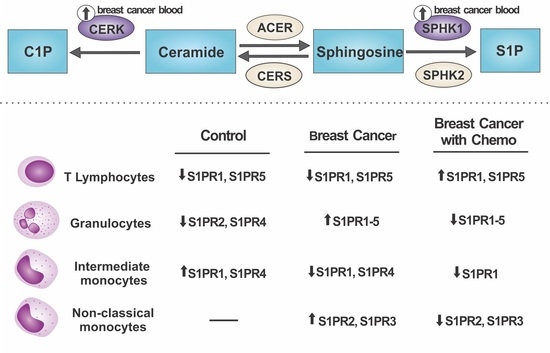
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. S1P Receptors Characterization in Leukocytes
2.2. Relative mRNA Expression of Major Genes of the Sphingolipid Pathway
2.3. Cytokine Production
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patients and Controls
4.2. Characterization of S1P Receptors by Flow Cytometry
4.3. Flow Cytometry Gating Strategy
4.4. Gene Expression Analysis for SPHK1, SPHK2, CERK, CERS2, and ACER
4.5. Cytokines Assays
4.6. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACER | ceramidase 3 |
| BC | breast cancer |
| BCC | breast cancer under chemotherapy treatment |
| C1P | ceramide 1-phosphate |
| CERK | ceramide kinase |
| CERS2 | ceramide synthase 2 |
| IDC | invasive ductal carcinoma |
| ILC | invasive lobular carcinoma |
| S1P | sphingosine 1-phosphate |
| SPHK | sphingosine kinase |
References
- Tian, T.; Olson, S.; Whitacre, J.M.; Harding, A. The origins of cancer robustness and evolvability. Integr. Biol. 2011, 3, 17–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.S.; Ma, C.D.; Chen, C.M. A study on the relationship between breast cancer molecular classification and prognosis. Zhonghua Wai Ke Za Zhi 2008, 46, 1400–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motz, G.T.; Coukos, G. Deciphering and reversing tumor immune suppression. Immunity 2013, 39, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fridman, W.H.; Pages, F.; Sautes-Fridman, C.; Galon, J. The immune contexture in human tumours: Impact on clinical outcome. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2012, 12, 298–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, D.M.; Hettinger, J.; Feuerer, M. Monocytes and macrophages in cancer: Development and functions. Cancer Microenviron. 2013, 6, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogels, M.; Braster, R.; Nijland, P.G.; Gul, N.; van de Luijtgaarden, W.; Fijneman, R.J.; Meijer, G.A.; Jimenez, C.R.; Beelen, R.H.; van Egmond, M. Carcinoma origin dictates differential skewing of monocyte function. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eruslanov, E.B.; Bhojnagarwala, P.S.; Quatromoni, J.G.; Stephen, T.L.; Ranganathan, A.; Deshpande, C.; Akimova, T.; Vachani, A.; Litzky, L.; Hancock, W.W.; et al. Tumor-associated neutrophils stimulate T cell responses in early-stage human lung cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 5466–5480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melendez, A.J. Sphingosine kinase signalling in immune cells: Potential as novel therapeutic targets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Schmelz, E.M.; Dillehay, D.L.; Spiegel, S.; Shayman, J.A.; Schroeder, J.J.; Riley, R.T.; Voss, K.A.; Wang, E. Sphingolipids—The enigmatic lipid class: Biochemistry, physiology, and pathophysiology. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1997, 142, 208–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceyka, M.; Spiegel, S. Sphingolipid metabolites in inflammatory disease. Nature 2014, 510, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takabe, K.; Paugh, S.W.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. “Inside-out” signaling of sphingosine-1-phosphate: Therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2008, 60, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maceyka, M.; Harikumar, K.B.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine-1-phosphate signaling and its role in disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2012, 22, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hla, T.; Dannenberg, A.J. Sphingolipid signaling in metabolic disorders. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 420–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanchez, T.; Hla, T. Structural and functional characteristics of S1P receptors. J. Cell. Biochem. 2004, 92, 913–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pyne, N.J.; Pyne, S. Sphingosine 1-phosphate and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2010, 10, 489–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivera, J.; Proia, R.L.; Olivera, A. The alliance of sphingosine-1-phosphate and its receptors in immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 753–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahaman, M.; Costello, R.W.; Belmonte, K.E.; Gendy, S.S.; Walsh, M.T. Neutrophil sphingosine 1-phosphate and lysophosphatidic acid receptors in pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2006, 34, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaho, V.A.; Hla, T. An update on the biology of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1596–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thangada, S.; Khanna, K.M.; Blaho, V.A.; Oo, M.L.; Im, D.S.; Guo, C.; Lefrancois, L.; Hla, T. Cell-surface residence of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 on lymphocytes determines lymphocyte egress kinetics. J. Exp. Med. 2010, 207, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hla, T. Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat. 2001, 64, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Graeler, M.H.; Goetzl, E.J. Type 4 sphingosine 1-phosphate G protein-coupled receptor (S1P4) transduces S1P effects on T cell proliferation and cytokine secretion without signaling migration. FASEB J. 2005, 19, 1731–1733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mackall, C.L.; Fleisher, T.A.; Brown, M.R.; Magrath, I.T.; Shad, A.T.; Horowitz, M.E.; Wexler, L.H.; Adde, M.A.; McClure, L.L.; Gress, R.E. Lymphocyte depletion during treatment with intensive chemotherapy for cancer. Blood 1994, 84, 2221–2228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Stahnke, K.; Fulda, S.; Friesen, C.; Strauss, G.; Debatin, K.M. Activation of apoptosis pathways in peripheral blood lymphocytes by in vivo chemotherapy. Blood 2001, 98, 3066–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allende, M.L.; Bektas, M.; Lee, B.G.; Bonifacino, E.; Kang, J.; Tuymetova, G.; Chen, W.; Saba, J.D.; Proia, R.L. Sphingosine-1-phosphate lyase deficiency produces a pro-inflammatory response while impairing neutrophil trafficking. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 7348–7358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, J.; Im, D.S.; Hla, T. Inhibitory role of sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 2 in macrophage recruitment during inflammation. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 1475–1483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keul, P.; Lucke, S.; von Wnuck Lipinski, K.; Bode, C.; Graler, M.; Heusch, G.; Levkau, B. Sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 3 promotes recruitment of monocyte/macrophages in inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2011, 108, 314–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.-J.; You, H.; Tan, J.-X.; Li, F.; Qiu, Z.; Li, H.-Z.; Huang, H.-Y.; Zheng, K.; Ren, G.-S. Overexpression of sphingosine kinase 1 is predictive of poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruckhäberle, E.; Rody, A.; Engels, K.; Gaetje, R.; von Minckwitz, G.; Schiffmann, S.; Grösch, S.; Geisslinger, G.; Holtrich, U.; Karn, T.; et al. Microarray analysis of altered sphingolipid metabolism reveals prognostic significance of sphingosine kinase 1 in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2008, 112, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yagoub, D.; Wilkins, M.R.; Lay, A.J.; Kaczorowski, D.C.; Hatoum, D.; Bajan, S.; Hutvagner, G.; Lai, J.H.; Wu, W.; Martiniello-Wilks, R.; et al. Sphingosine kinase 1 isoform-specific interactions in breast cancer. Mol. Endocrinol. 2014, 28, 1899–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponnusamy, S.; Meyers-Needham, M.; Senkal, C.E.; Saddoughi, S.A.; Sentelle, D.; Selvam, S.P.; Salas, A.; Ogretmen, B. Sphingolipids and cancer: Ceramide and sphingosine-1-phosphate in the regulation of cell death and drug resistance. Future Oncol. 2010, 6, 1603–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.; Deng, J.; Kujawski, M.; Yang, C.; Liu, Y.; Herrmann, A.; Kortylewski, M.; Horne, D.; Somlo, G.; Forman, S.; et al. STAT3-induced S1PR1 expression is crucial for persistent STAT3 activation in tumors. Nat. Med. 2010, 16, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarkar, S.; Maceyka, M.; Hait, N.C.; Paugh, S.W.; Sankala, H.; Milstien, S.; Spiegel, S. Sphingosine kinase 1 is required for migration, proliferation and survival of MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 5313–5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pchejetski, D.; Golzio, M.; Bonhoure, E.; Calvet, C.; Doumerc, N.; Garcia, V.; Mazerolles, C.; Rischmann, P.; Teissie, J.; Malavaud, B.; et al. Sphingosine kinase-1 as a chemotherapy sensor in prostate adenocarcinoma cell and mouse models. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 11667–11675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boath, A.; Graf, C.; Lidome, E.; Ullrich, T.; Nussbaumer, P.; Bornancin, F. Regulation and traffic of ceramide 1-phosphate produced by ceramide kinase: Comparative analysis to glucosylceramide and sphingomyelin. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 8517–8526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patwardhan, G.A.; Liu, Y.Y. Sphingolipids and expression regulation of genes in cancer. Prog. Lipid Res. 2011, 50, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangoiti, P.; Arana, L.; Ouro, A.; Granado, M.H.; Trueba, M.; Gomez-Munoz, A. Activation of mTOR and RhoA is a major mechanism by which Ceramide 1-phosphate stimulates macrophage proliferation. Cell. Signal. 2011, 23, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippitz, B.E. Cytokine patterns in patients with cancer: A systematic review. Lancet. Oncol. 2013, 14, e218–e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiner, H.L.; Cohen, J.A. Treatment of multiple sclerosis with cyclophosphamide: Critical review of clinical and immunologic effects. Mult. Scler. 2002, 8, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Simone, V.; Franze, E.; Ronchetti, G.; Colantoni, A.; Fantini, M.C.; di Fusco, D.; Sica, G.S.; Sileri, P.; MacDonald, T.T.; Pallone, F.; et al. Th17-type cytokines, IL-6 and TNF-α synergistically activate STAT3 and NF-κB to promote colorectal cancer cell growth. Oncogene 2014, 34, 3493–3503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, P.; Wang, L.; Moretti, P.A.; Albanese, N.; Chai, F.; Pitson, S.M.; D’Andrea, R.J.; Gamble, J.R.; Vadas, M.A. Sphingosine kinase interacts with TRAF2 and dissects tumor necrosis factor-α signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 7996–8003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankaran, V.; Ikeda, H.; Bruce, A.T.; White, J.M.; Swanson, P.E.; Old, L.J.; Schreiber, R.D. IFN-γ and lymphocytes prevent primary tumour development and shape tumour immunogenicity. Nature 2001, 410, 1107–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchanathan, R.; Shen, H.; Zhang, X.; Ho, S.M.; Choubey, D. Mutually positive regulatory feedback loop between interferons and estrogen receptor-α in mice: Implications for sex bias in autoimmunity. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zitvogel, L.; Apetoh, L.; Ghiringhelli, F.; Kroemer, G. Immunological aspects of cancer chemotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 59–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, K.; Anada, Y.; Tani, M.; Ikeda, M.; Sano, T.; Kihara, A.; Igarashi, Y. Lack of sphingosine 1-phosphate-degrading enzymes in erythrocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 357, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Książek, M.; Chacińska, M.; Chabowski, A.; Baranowski, M. Sources, metabolism, and regulation of circulating sphingosine-1-phosphate. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 1271–1281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryland, L.K.; Fox, T.E.; Liu, X.; Loughran, T.P.; Kester, M. Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism in cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giussani, P.; Tringali, C.; Riboni, L.; Viani, P.; Venerando, B. Sphingolipids: Key regulators of apoptosis and pivotal players in cancer drug resistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 4356–4392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saddoughi, S.A.; Song, P.; Ogretmen, B. Roles of bioactive sphingolipids in cancer biology and therapeutics. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2008, 49, 413–440. [Google Scholar]
- Struckhoff, A.P.; Bittman, R.; Burow, M.E.; Clejan, S.; Elliott, S.; Hammond, T.; Tang, Y.; Beckman, B.S. Novel ceramide analogs as potential chemotherapeutic agents in breast cancer. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 309, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieberich, E.; Kawaguchi, T.; Yu, R.K. N-acylated serinol is a novel ceramide mimic inducing apoptosis in neuroblastoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samsel, L.; Zaidel, G.; Drumgoole, H.M.; Jelovac, D.; Drachenberg, C.; Rhee, J.G.; Brodie, A.M.; Bielawska, A.; Smyth, M.J. The ceramide analog, B13, induces apoptosis in prostate cancer cell lines and inhibits tumor growth in prostate cancer xenografts. Prostate 2004, 58, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Cheng, J.C.; Turner, L.S.; Elojeimy, S.; Beckham, T.H.; Bielawska, A.; Keane, T.E.; Hannun, Y.A.; Norris, J.S. Acid ceramidase upregulation in prostate cancer: Role in tumor development and implications for therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2009, 13, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sweeney, E.A.; Sakakura, C.; Shirahama, T.; Masamune, A.; Ohta, H.; Hakomori, S.; Igarashi, Y. Sphingosine and its methylated derivative N,N-dimethylsphingosine (DMS) induce apoptosis in a variety of human cancer cell lines. Int. J. Cancer 1996, 66, 358–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickson, M.A.; Carvajal, R.D.; Merrill, A.H., Jr.; Gonen, M.; Cane, L.M.; Schwartz, G.K. A phase I clinical trial of safingol in combination with cisplatin in advanced solid tumors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2484–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkwood, J.M.; Butterfield, L.H.; Tarhini, A.A.; Zarour, H.; Kalinski, P.; Ferrone, S. Immunotherapy of cancer in 2012. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 309–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler-Heitbrock, L.; Ancuta, P.; Crowe, S.; Dalod, M.; Grau, V.; Hart, D.N.; Leenen, P.J.; Liu, Y.J.; MacPherson, G.; Randolph, G.J.; et al. Nomenclature of monocytes and dendritic cells in blood. Blood 2010, 116, e74–e80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Variable | SPHK1 | |
|---|---|---|
| Pearson Correlation | Sig. (2-Tailed) | |
| TNF-α | 0.5287 * | 0.0352 |
| IFN-γ | 0.4061 | 0.1185 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maia, L.P.; Santos, P.S.; Alves, P.T.; Rodrigues, C.M.; Araújo, T.G.; Maia, Y.C.P.; Câmara, A.T.F.; Santos, D.W.; Goulart, L.R. Altered Leukocyte Sphingolipid Pathway in Breast Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122521
Maia LP, Santos PS, Alves PT, Rodrigues CM, Araújo TG, Maia YCP, Câmara ATF, Santos DW, Goulart LR. Altered Leukocyte Sphingolipid Pathway in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122521
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaia, Larissa P., Paula S. Santos, Patrícia T. Alves, Cláudia M. Rodrigues, Thaíse G. Araújo, Yara Cristina P. Maia, Alinne Tatiane F. Câmara, Donizeti W. Santos, and Luiz Ricardo Goulart. 2017. "Altered Leukocyte Sphingolipid Pathway in Breast Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122521
APA StyleMaia, L. P., Santos, P. S., Alves, P. T., Rodrigues, C. M., Araújo, T. G., Maia, Y. C. P., Câmara, A. T. F., Santos, D. W., & Goulart, L. R. (2017). Altered Leukocyte Sphingolipid Pathway in Breast Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2521. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122521