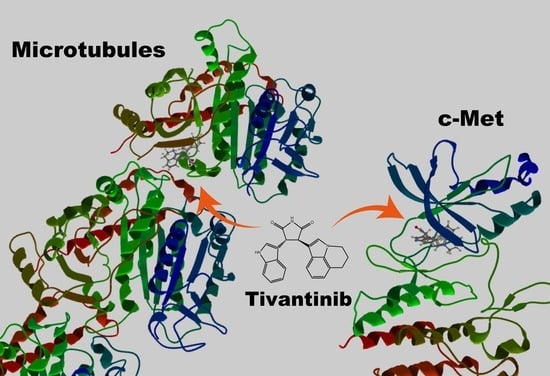
Microtubule Depolymerization by Kinase Inhibitors: Unexpected Findings of Dual Inhibitors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. A Clinically Tested c-Met Kinase Inhibitor Is Also a Microtubule Inhibitor
3. Examples of Kinase Inhibitors That Disrupt Microtubule Function
4. Image Analyses of Cellular Phenotype That Led to the Identification of Dual Inhibitors of Kinases and Microtubules
5. Examples of Microtubule Disrupting Agents That Also Inhibit Kinases
6. Disruption of Microtubules by Non-Kinase Inhibitors
7. A Simple Method to Screen Agents for Microtubule Disruption
8. Perspectives
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BPT | N-(biphenyl-2-yl) tryptoline |
| Btk | Bruton’s tyrosine kinase |
| Cdk4 | cyclin-dependent kinase 4 |
| CK1 | casein kinase-1 |
| CXCR2 | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 |
| DyrK | dual specificity tyrosine-phosphorylation-regulated kinase |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| FLT3 | FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 |
| GSK3α | glycogen synthase kinase 3α |
| HGF | hepatocyte growth factor |
| JAK2 | JUN amino-terminal kinase |
| KS99 | 5,7-dibromo-N-(p-thiocyanomethylbenzyl) isatin |
| LIMK | LIM kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| MK2 | MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 |
| MT | microtubules |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| Plk1 | polo-like kinase 1 |
References
- Parker, A.L.; Kavallaris, M.; McCarroll, J.A. Microtubules and their role in cellular stress in cancer. Front. Oncol. 2014, 4, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Giannakakou, P. Targeting microtubules for cancer chemotherapy. Curr. Med. Chem. Anti Cancer Agents 2005, 5, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumontet, C.; Jordan, M.A. Microtubule-binding agents: A dynamic field of cancer therapeutics. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2010, 9, 897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prota, A.E.; Bargsten, K.; Diaz, J.F.; Marsh, M.; Cuevas, C.; Liniger, M.; Neuhaus, C.; Andreu, J.M.; Altmann, K.-H.; Steinmetz, M.O. A new tubulin-binding site and pharmacophore for microtubule-destabilizing anticancer drugs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 13817–13821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, R.; Kaur, G.; Gill, R.K.; Soni, R.; Bariwal, J. Recent developments in tubulin polymerization inhibitors: An overview. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 87, 89–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, P.; Nielsen, T.E.; Clausen, M.H. Small-molecule kinase inhibitors: An analysis of FDA-approved drugs. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basilico, C.; Pennacchietti, S.; Vigna, E.; Chiriaco, C.; Arena, S.; Bardelli, A.; Valdembri, D.; Serini, G.; Michieli, P. Tivantinib (ARQ197) displays cytotoxic activity that is independent of its ability to bind MET. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katayama, R.; Aoyama, A.; Yamori, T.; Qi, J.; Oh-hara, T.; Song, Y.; Engelman, J.A.; Fujita, N. Cytotoxic activity of tivantinib (ARQ 197) is not due solely to c-MET inhibition. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 3087–3096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheong, J.K.; Nguyen, T.H.; Wang, H.; Tan, P.; Voorhoeve, P.M.; Lee, S.H.; Virshup, D.M. IC261 induces cell cycle arrest and apoptosis of human cancer cells via CK1δ/ɛ and Wnt/β-catenin independent inhibition of mitotic spindle formation. Oncogene 2011, 30, 2558–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurgis, F.; Åkerfeldt, M.C.; Heng, B.; Wong, C.; Adams, S.; Guillemin, G.J.; Johns, T.G.; Chircop, M.; Munoz, L. Cytotoxic activity of the {MK2} inhibitor {CMPD1} in glioblastoma cells is independent of {MK2}. Cell Death Discov. 2015, 1, 15028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Yang, N.; Yang, C.-H.; Ding, H.-S.; Luo, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, M.-J.; Zhang, X.-W.; Shen, X.; Jiang, H.-L.; et al. S9, a novel anticancer agent, exerts its anti-proliferative activity by interfering with both PI3K-Akt-mTOR signaling and microtubule cytoskeleton. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross-Macdonald, P.; de Silva, H.; Guo, Q.; Xiao, H.; Hung, C.-Y.; Penhallow, B.; Markwalder, J.; He, L.; Attar, R.M.; Lin, T.-A.; et al. Identification of a nonkinase target mediating cytotoxicity of novel kinase inhibitors. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 3490–3498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahale, S.; Bharate, S.B.; Manda, S.; Joshi, P.; Jenkins, P.R.; Vishwakarma, R.A.; Chaudhuri, B. Antitumour potential of BPT: A dual inhibitor of Cdk4 and tubulin polymerization. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brachmann, S.M.; Kleylein-Sohn, J.; Gaulis, S.; Kauffmann, A.; Blommers, M.J.J.; Kazic-Legueux, M.; Laborde, L.; Hattenberger, M.; Stauffer, F.; Vaxelaire, J.; et al. Characterization of the mechanism of action of the pan clAss I PI3K inhibitor NVP-BKM120 across a broad range of concentrations. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 1747–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steegmaier, M.; Hoffmann, M.; Baum, A.; Lénárt, P.; Petronczki, M.; Krššák, M.; Gürtler, U.; Garin-Chesa, P.; Lieb, S.; Quant, J.; et al. BI 2536, a potent and selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Curr. Biol. 2007, 17, 316–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K. Image-based compound profiling reveals a dual inhibitor of tyrosine kinase and microtubule polymerization. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carta, D.; Bortolozzi, R.; Hamel, E.; Basso, G.; Moro, S.; Viola, G.; Ferlin, M.G. Novel 3-substituted 7-phenylpyrrolo[3,2-f]quinolin-9(6H)-ones as single entities with multitarget antiproliferative activity. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 7991–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, M.K.; Gowda, K.; Sung, S.; Abraham, T.; Budak-Alpdogan, T.; Talamo, G.; Dovat, S.; Amin, S. A novel dual inhibitor of microtubule and Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase inhibits survival of multiple myeloma and osteoclastogenesis. Exp. Hematol. 2017, 53, 31–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, B. Comparison of cancer cell survival triggered by microtubule damage after turning Dyrk1B kinase on and off. ACS Chem. Biol. 2014, 9, 731–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirisoma, N.; Pervin, A.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, S.; Adam Willardsen, J.; Anderson, M.B.; Mather, G.; Pleiman, C.M.; Kasibhatla, S.; Tseng, B.; et al. Discovery of N-methyl-4-(4-methoxyanilino)quinazolines as potent apoptosis inducers. Structure-activity relationship of the quinazoline ring. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2010, 20, 2330–2334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, A.E.; Koyama, M.; Sowa, Y.; Elokely, K.M.; Yoshida, T.; Kim, B.Y.; Sakai, T. Molecular mechanisms of the antitumor activity of SB225002: A novel microtubule inhibitor. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, J.; Barber, D.L.; Jacobson, M.P. Intracellular pH sensors: Design principles and functional significance. Physiology 2007, 22, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.-L.; Shang, Z.-P.; Jantan, I.; Tan, O.U.; Hussain, M.A.; Sher, M.; Bukhari, S.N.A. Molecular docking studies and biological evaluation of chalcone based pyrazolines as tyrosinase inhibitors and potential anticancer agents. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 46330–46338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccaccio, C.; Comoglio, P.M. Invasive growth: A MET-driven genetic programme for cancer and stem cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2006, 6, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilkovitch-Miagkova, A.; Zbar, B. Dysregulation of Met receptor tyrosine kinase activity in invasive tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 109, 863–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munshi, N.; Jeay, S.; Li, Y.; Chen, C.-R.; France, D.S.; Ashwell, M.A.; Hill, J.; Moussa, M.M.; Leggett, D.S.; Li, C.J. ARQ 197, a novel and selective inhibitor of the human c-met receptor tyrosine kinase with antitumor activity. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2010, 9, 1544–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyama, A.; Katayama, R.; Oh-Hara, T.; Sato, S.; Okuno, Y.; Fujita, N. Tivantinib (ARQ 197) exhibits antitumor activity by directly interacting with tubulin and overcomes ABC transporter-mediated drug resistance. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2014, 13, 2978–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, S.; Reddy, H.; Caivano, M.; Cohen, P. Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem. J. 2000, 105, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bain, J.; McLauchlan, H.; Elliott, M.; Cohen, P. The specificities of protein kinase inhibitors: An update. Biochem. J. 2003, 371, 199–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrend, L.; Milne, D.M.; Stöter, M.; Deppert, W.; Campbell, L.E.; Meek, D.W.; Knippschild, U. IC261, a specific inhibitor of the protein kinases casein kinase 1-delta and -epsilon, triggers the mitotic checkpoint and induces p53-dependent postmitotic effects. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5303–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrend, L.; Stöter, M.; Kurth, M.; Rutter, G.; Heukeshoven, J.; Deppert, W.; Knippschild, U. Interaction of casein kinase 1 delta (CK1delta) with post-Golgi structures, microtubules and the spindle apparatus. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2000, 79, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockschmidt, C.; Hirner, H.; Huber, N.; Eismann, T.; Hillenbrand, A.; Giamas, G.; Radunsky, B.; Ammerpohl, O.; Bohm, B.; Henne-Bruns, D.; et al. Anti-apoptotic and growth-stimulatory functions of CK1 delta and epsilon in ductal adenocarcinoma of the pancreas are inhibited by IC261 in vitro and in vivo. Gut 2008, 57, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, W.; Frego, L.; Peet, G.W.; Kroe, R.R.; Labadia, M.E.; Lukas, S.M.; Snow, R.J.; Jakes, S.; Grygon, C.A.; Pargellis, C.; et al. Discovery and characterization of a substrate selective p38α inhibitor. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 11658–11671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, D.R.; Meyers, M.J.; Vernier, W.F.; Mahoney, M.W.; Kurumbail, R.G.; Caspers, N.; Poda, G.I.; Schindler, J.F.; Reitz, D.B.; Mourey, R.J. Pyrrolopyridine inhibitors of mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 (MK-2). J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2647–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beattie, J.F.; Breault, G.A.; Ellston, R.P.A.; Green, S.; Jewsbury, P.J.; Midgley, C.J.; Naven, R.T.; Minshull, C.A.; Pauptit, R.A.; Tucker, J.A.; et al. Cyclin-dependent kinase 4 inhibitors as a treatment for cancer. Part 1: Identification and optimisation of substituted 4,6-Bis anilino pyrimidines. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2003, 13, 2955–2960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segraves, N.L.; Robinson, S.J.; Garcia, D.; Said, S.A.; Fu, X.; Schmitz, F.J.; Pietraszkiewicz, H.; Valeriote, F.A.; Crews, P. Comparison of fascaplysin and related alkaloids: A study of structures, cytotoxicities, and sources. J. Nat. Prod. 2004, 67, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maira, S.-M.; Pecchi, S.; Huang, A.; Burger, M.; Knapp, M.; Sterker, D.; Schnell, C.; Guthy, D.; Nagel, T.; Wiesmann, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of NVP-BKM120, an orally available pan-class I PI3-kinase inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 317–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massacesi, C.; Di Tomaso, E.; Fretault, N.; Hirawat, S. Challenges in the clinical development of PI3K inhibitors. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2013, 1280, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saura, C.; Bendell, J.; Jerusalem, G.; Su, S.; Ru, Q.; de Buck, S.; Mills, D.; Ruquet, S.; Bosch, A.; Urruticoechea, A.; et al. Phase lb study of buparlisib plus trastuzumab in patients with HER2-positive advanced or metastatic breast cancer that has progressed on trastuzumab-based therapy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 1935–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohnacker, T.; Prota, A.E.; Beaufils, F.; Burke, J.E.; Melone, A.; Inglis, A.J.; Rageot, D.; Sele, A.M.; Cmiljanovic, V.; Cmiljanovic, N.; et al. Deconvolution of Buparlisib’s mechanism of action defines specific PI3K and tubulin inhibitors for therapeutic intervention. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gumireddy, K.; Reddy, M.V.R.; Cosenza, S.C.; Nathan, R.B.; Baker, S.J.; Papathi, N.; Jiang, J.; Holland, J.; Reddy, E.P. ON01910, a non-ATP-competitive small molecule inhibitor of Plk1, is a potent anticancer agent. Cancer Cell 2005, 7, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, T.; Laughton, C.A.; Wang, S.; Bradshaw, T.D. In vitro antitumor mechanism of (E)-N-(2-methoxy-5-(((2,4,6-trimethoxystyryl)sulfonyl)methyl)pyridin-3-yl)methanesulfonamide. Mol. Pharmacol. 2014, 87, 18–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oussenko, I.A.; Holland, J.F.; Reddy, E.P.; Ohnuma, T. Effect of on 01910.Na, an anticancer mitotic inhibitor, on cell-cycle progression correlates with RanGAP1 hyperphosphorylation. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 4968–4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Twarog, N.R.; Low, J.A.; Currier, D.G.; Miller, G.; Chen, T.; Shelat, A.A. Robust classification of small-molecule mechanism of action using a minimalist high-content microscopy screen and multidimensional phenotypic trajectory analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0149439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jost, M.; Chen, Y.; Gilbert, L.A.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Krenning, L.; Menchon, G.; Rai, A.; Cho, M.Y.; Stern, J.J.; Prota, A.E.; et al. Combined CRISPRi/a-based chemical genetic screens reveal that rigosertib is a microtubule-destabilizing agent. Mol. Cell 2017, 68, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Gao, F.; Ding, Q.; Cho, C.; Hur, W.; Jin, Y.; Uno, T.; Joazeiro, C.A.P.; Gray, N. Discovery of EGFR selective 4,6-disubstituted pyrimidines from a combinatorial kinase-directed heterocycle library. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 2182–2183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anastassiadis, T.; Deacon, S.W.; Devarajan, K.; Ma, H.; Peterson, J.R. Comprehensive assay of kinase catalytic activity reveals features of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Z.; Cui, B.; Jin, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, X. Novel irreversible EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor 324674 sensitizes human colon carcinoma HT29 and SW480 cells to apoptosis by blocking the EGFR pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 411, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, K.; Henmi, Y.; Satake, M. Image-based profiling can discriminate the effects of inhibitors on signaling pathways under differential ligand stimulation. bioRxiv 2017, 190637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnegowda, G.; Prakasha Gowda, A.S.; Tagaram, H.R.S.; Carroll, K.F.S.-O.; Irby, R.B.; Sharma, A.K.; Amin, S. Synthesis and biological evaluation of a novel class of isatin analogs as dual inhibitors of tubulin polymerization and Akt pathway. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2011, 19, 6006–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fabian, M.A.; Biggs, W.H.; Treiber, D.K.; Atteridge, C.E.; Azimioara, M.D.; Benedetti, M.G.; Carter, T.A.; Ciceri, P.; Edeen, P.T.; Floyd, M.; et al. A small molecule–kinase interaction map for clinical kinase inhibitors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karaman, M.W.; Herrgard, S.; Treiber, D.K.; Gallant, P.; Atteridge, C.E.; Campbell, B.T.; Chan, K.W.; Ciceri, P.; Davis, M.I.; Edeen, P.T.; et al. A quantitative analysis of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, X.; Ewton, D.Z.; Li, S.; Naqvi, A.; Mercer, S.E.; Landas, S.; Friedman, E. The kinase Mirk/Dyrk1B mediates cell survival in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 4149–4158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Hong, S.; Hong, S. Nocodazole is a high-affinity ligand for the cancer-related kinases ABL, c-KIT, BRAF, and MEK. ChemMedChem 2012, 7, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Shen, B.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J. Nocodazole increases the ERK activity to enhance MKP-1 expression which inhibits p38 activation induced by TNF-α. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 364, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marzaro, G.; Coluccia, A.; Ferrarese, A.; Brun, P.; Castagliuolo, I.; Conconi, M.T.; La Regina, G.; Bai, R.; Silvestri, R.; Hamel, E.; et al. Discovery of biarylaminoquinazolines as novel tubulin polymerization inhibitors. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 4598–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, J.R.; Lee, J.M.; Young, P.R.; Hertzberg, R.P.; Jurewicz, A.J.; Chaikin, M.A.; Widdowson, K.; Foley, J.J.; Martin, L.D.; Griswold, D.E.; et al. Identification of a potent, selective non-peptide CXCR2 antagonist that inhibits interleukin-8-induced neutrophil migration. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 10095–10098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meisner, H.M.; Sorensen, L. Metaphase arrest of Chinese hamster cells with rotenone. Exp. Cell Res. 1966, 42, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinkley, B.R.; Barham, S.S.; Barranco, S.C.; Fuller, G.M. Rotenone inhibition of spindle microtubule assembly in mammalian cells. Exp. Cell Res. 1974, 85, 41–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelanski, M.L.; Gaskin, F.; Cantor, C.R. Microtubule assembly in the absence of added nucleotides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1973, 70, 765–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.C.; Timasheff, S.N. In vitro reconstitution of calf brain microtubules: Effects of solution variables. Biochemistry 1977, 16, 1754–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vale, R. The molecular motor toolbox for intracellular transport. Cell 2003, 112, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, A.J.; Kon, T.; Knight, P.J.; Sutoh, K.; Burgess, S.A. Functions and mechanics of dynein motor proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2013, 14, 713–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanabe, K.; Takei, K. Dynamic instability of microtubules requires dynamin 2 and is impaired in a Charcot-Marie-Tooth mutant. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 939–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohban, M.H.; Singh, S.; Wu, X.; Berthet, J.B.; Bray, M.; Shrestha, Y.; Varelas, X.; Boehm, J.S.; Carpenter, A.E. Systematic morphological profiling of human gene and allele function via cell painting. eLife 2017, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Group | Compound | Target | Order 1 | Evidence 2 | Phenoytpe 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kinase inhibitor | Tivantiniv [7,8] | c-met | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M |
| IC261 [9] | CK1 | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M | |
| CMPD1 [10] | MK2 | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M | |
| S9 [11] | Akt | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M | |
| LIMK inhibitor [12] | LIMK | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M | |
| BPT [13] | Cdk4 | Kinase → MT | Known function | M | |
| BKM120 [14] | PI3K | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M | |
| Rigosertib [15] | Plk1 | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M | |
| CAS 879127-08 [16] | EGFR | Kinase → MT | Other inhibitor | T | |
| 3-substituted 7-Phenylpyrrolo [3,2-f]quinolin-9(6H)-ones [17] | multi-kinase | MT → Kinase | Akt inactivation | M | |
| KS99 [18] | Btk | MT → Kinase | Akt inactivation | M | |
| Tubulin/DyrK inhibitor [19] | DyrK | MT → Kinase | Other inhibitor | M | |
| Biarylaminoquinazolines [20] | Tyr. kinase | Predesigned | Predesigned | M | |
| Non-kinase inhibitor | SB225002 [21] | CXCR2 | GPCR → MT | Other inhibitor | M |
| Rotenone [22] | Mitochondria | Mito. → MT | Concentration | M | |
| Tyrosinase inhibitor [23] | Tyrosinase | Tyrosinase → MT | Other inhibitor | M |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tanabe, K. Microtubule Depolymerization by Kinase Inhibitors: Unexpected Findings of Dual Inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122508
Tanabe K. Microtubule Depolymerization by Kinase Inhibitors: Unexpected Findings of Dual Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122508
Chicago/Turabian StyleTanabe, Kenji. 2017. "Microtubule Depolymerization by Kinase Inhibitors: Unexpected Findings of Dual Inhibitors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122508
APA StyleTanabe, K. (2017). Microtubule Depolymerization by Kinase Inhibitors: Unexpected Findings of Dual Inhibitors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2508. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122508