Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 and Plakins as Therapeutic Drug Targets
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Plakins and Disease
2.1. Skin, Heart, and Neurological Diseases
2.2. Cancer and Plakins
3. Microtubule-Targeted Drug Therapy
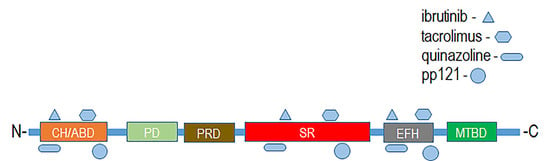
4. Therapeutic Targeting of Plakins
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bernier, G.; Mathieu, M.; De Repentigny, Y.; Vidal, S.M.; Kothary, R. Cloning and characterization of mouse ACF7, a novel member of the dystonin subfamily of actin binding proteins. Genomics 1996, 38, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawamura, D.; Nomura, K.; Sugita, Y.; Mattei, M.G.; Chu, M.L.; Knowlton, R.; Uitto, J. Bullous pemphigoid antigen (BPAG1): cDNA cloning and mapping of the gene to the short arm of human chromosome 6. Genomics 1990, 8, 722–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franke, W.W.; Moll, R.; Schiller, D.L.; Schmid, E.; Kartenbeck, J.; Mueller, H. Desmoplakins of epithelial and myocardial desmosomes are immunologically and biochemically related. Differentiation 1982, 23, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhrberg, C.; Hajibagheri, M.A.; Simon, M.; Dooley, T.P.; Watt, F.M. Envoplakin, a novel precursor of the cornified envelope that has homology to desmoplakin. J. Cell Biol. 1996, 134, 715–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aho, S.; McLean, W.H.; Li, K.; Uitto, J. cDNA cloning, mRNA expression, and chromosomal mapping of human and mouse periplakin genes. Genomics 1998, 48, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiche, G.; Herrmann, H.; Leichtfried, F.; Pytela, R. Plectin: A high-molecular-weight cytoskeletal polypeptide component that copurifies with intermediate filaments of the vimentin type. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1982, 46, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, S.; Kohno, K.; Iwamatsu, A.; Naito, I.; Shinkai, H. Identification of a 450-kDa human epidermal autoantigen as a new member of the plectin family. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 106, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, C.L.; Green, K.J.; Liem, R.K. Plakins: A family of versatile cytolinker proteins. Trends Cell Biol. 2002, 12, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouameur, J.E.; Favre, B.; Borradori, L. Plakins, a versatile family of cytolinkers: Roles in skin integrity and in human diseases. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ka, M.; Moffat, J.J.; Kim, W.Y. MACF1 Controls Migration and Positioning of Cortical GABAergic Interneurons in Mice. Cereb. Cortex 2017, 27, 5525–5538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ka, M.; Jung, E.M.; Mueller, U.; Kim, W.Y. MACF1 regulates the migration of pyramidal neurons via microtubule dynamics and GSK-3 signaling. Dev. Biol. 2014, 395, 4–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves-Silva, J.; Sánchez-Soriano, N.; Beaven, R.; Klein, M.; Parkin, J.; Millard, T.H.; Bellen, H.J.; Venken, K.J.; Ballestrem, C.; Kammerer, R.A.; et al. Spectraplakins promote microtubule-mediated axonal growth by functioning as structural microtubule-associated proteins and EB1-dependent +TIPs (tip interacting proteins). J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 9143–9158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, L.; Degenstein, L.; Dowling, J.; Yu, Q.C.; Wollmann, R.; Perman, B.; Fuchs, E. Gene targeting of BPAG1: Abnormalities in mechanical strength and cell migration in stratified epithelia and neurologic degeneration. Cell 1995, 81, 233–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalpé, G.; Leclerc, N.; Vallée, A.; Messer, A.; Mathieu, M.; De Repentigny, Y.; Kothary, R. Dystonin Is Essential for Maintaining Neuronal Cytoskeleton Organization. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 1998, 10, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruhrberg, C.; Hajibagheri, M.A.; Parry, D.A.; Watt, F.M. Periplakin, a novel component of cornified envelopes and desmosomes that belongs to the plakin family and forms complexes with envoplakin. J. Cell Biol. 1997, 139, 1835–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Loop, F.T.; Schaart, G.; Langmann, H.; Ramaekers, F.C.; Viebahn, C. Rearrangement of intercellular junctions and cytoskeletal proteins during rabbit myocardium development. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 68, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Angst, B.D.; Khan, L.U.; Severs, N.J.; Whitely, K.; Rothery, S.; Thompson, R.P.; Magee, A.I.; Gourdie, R.G. Dissociated spatial patterning of gap junctions and cell adhesion junctions during postnatal differentiation of ventricular myocardium. Circ. Res. 1997, 80, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lechler, T.; Fuchs, E. Desmoplakin: An unexpected regulator of microtubule organization in the epidermis. J. Cell Biol. 2007, 176, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, R.; Kamiyama, M.; Arai, K.Y.; Arai, K.; Uehara, K. Expression of desmosomal proteins in rat keratinocytes during in vitro differentiation. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2002, 64, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, K.T.; Sharpe, G.R. Thapsigargin raises intracellular free calcium levels in human keratinocytes and inhibits the coordinated expression of differentiation markers. Exp. Cell Res. 1994, 210, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okada, Y.; Saika, S.; Shirai, K.; Hashizume, N.; Yamanaka, O.; Ohnishi, Y.; Senba, E. Disappearance of desmosomal components in rat corneal epithelium during wound healing. Ophthalmologica 2001, 215, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Shen, Q.T.; Oristian, D.S.; Lu, C.P.; Zheng, Q.; Wang, H.W.; Fuchs, E. Skin stem cells orchestrate directional migration by regulating microtubule-ACF7 connections through GSK3β. Cell 2011, 144, 341–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Lin, C.M.; Lin, C.S.; Perez-Olle, R.; Leung, C.L.; Liem, R.K. The role of microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1 (MACF1) in the Wnt signaling pathway. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1933–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamill, K.J.; Hopkinson, S.B.; DeBiase, P.; Jones, J.C. BPAG1e maintains keratinocyte polarity through beta4 integrin-mediated modulation of Rac1 and cofilin activities. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 2954–2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osmanagic-Myers, S.; Wiche, G. Plectin-RACK1 (receptor for activated C kinase 1) scaffolding: A novel mechanism to regulate protein kinase C activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 18701–18710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katada, K.; Tomonaga, T.; Satoh, M.; Matsushita, K.; Tonoike, Y.; Kodera, Y.; Hanazawa, T.; Nomura, F.; Okamoto, Y. Plectin promotes migration and invasion of cancer cells and is a novel prognostic marker for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. J. Proteom. 2012, 75, 1803–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrä, K.; Lassmann, H.; Bittner, R.; Shorny, S.; Fässler, R.; Propst, F.; Wiche, G. Targeted inactivation of plectin reveals essential function in maintaining the integrity of skin, muscle, and heart cytoarchitecture. Genes Dev. 1997, 11, 3143–3156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallicano, G.I.; Kouklis, P.; Bauer, C.; Yin, M.; Vasioukhin, V.; Degenstein, L.; Fuchs, E. Desmoplakin is required early in development for assembly of desmosomes and cytoskeletal linkage. J. Cell Biol. 1998, 143, 2009–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, L.H.; Mosbech, M.B.; Færgeman, N.J.; Graakjaer, J.; Jacobsen, S.V.; Schrøder, H.D. Duplication in the microtubule-actin cross-linking factor 1 gene causes a novel neuromuscular condition. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, N.; Xiong, N.; You, Q.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Qing, H.; Wang, T.; Cordell, H.J.; Isacson, O.; et al. Genetic Variants of Microtubule Actin Cross-linking Factor 1 (MACF1) Confer Risk for Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2878–2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misquitta-Ali, C.M.; Cheng, E.; O’Hanlon, D.; Liu, N.; McGlade, C.J.; Tsao, M.S.; Blencowe, B.J. Global profiling and molecular characterization of alternative splicing events misregulated in lung cancer. Mol. Cell Biol. 2011, 31, 138–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Liu, W.; Yang, J.; Qin, H. An integrated proteomics and metabolomics approach for defining oncofetal biomarkers in the colorectal cancer. Ann. Surg. 2012, 255, 720–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arai, E.; Sakamoto, H.; Ichikawa, H.; Totsuka, H.; Chiku, S.; Gotoh, M.; Mori, T.; Nakatani, T.; Ohnami, S.; Nakagawa, T.; et al. Multilayer-omics analysis of renal cell carcinoma, including the whole exome, methylome and transcriptome. Int. J. Cancer 2014, 135, 1330–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, Y.S.; Huang, H.D.; Yeh, K.T.; Chang, J.G. Identification of novel mutations in endometrial cancer patients by whole-exome sequencing. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 1778–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afghani, N.; Mehta, T.; Wang, J.; Tang, N.; Skalli, O.; Quick, Q.A. Microtubule actin cross-linking factor 1, a novel target in glioblastoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2017, 50, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.D.; Wang, Y.H.; Ye, Y.C.; Zhao, W.L.; Li, L. Prognostic factors for mortality in patients with bullous pemphigoid: A meta-analysis. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2017, 309, 335–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozzani, E.; Dal Bello, M.G.; Mastrogiacomo, A.; Drosera, M.; Parodi, A. Antidesmoplakin antibodies in pemphigus vulgaris. Br. J. Dermatol. 2006, 154, 624–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiao, D.; Bystryn, J.C. Antibodies to desmoplakin in a patient with pemphigus foliaceous. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 1998, 11, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukiwake, N.; Moroi, Y.; Urabe, K.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Furue, M. Detection of autoantibodies to desmoplakin in a patient with oral erythema multiforme. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2007, 17, 238–241. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Laffitte, E.; Burkhard, P.R.; Fontao, L.; Jaunin, F.; Saurat, J.H.; Chofflon, M.; Borradori, L. Bullous pemphigoid antigen 1 isoforms: Potential new target autoantigens in multiple sclerosis? Br. J. Dermatol. 2005, 152, 537–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, A.; Bernier, G.; Mathieu, M.; Rossant, J.; Kothary, R. The mouse dystonia musculorum gene is a neural isoform of bullous pemphigoid antigen 1. Nat. Genet. 1995, 10, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrier, A.; Sato, T.; De Repentigny, Y.; Gibeault, S.; Bhanot, K.; O’Meara, R.W.; Lynch-Godrei, A.; Kornfeld, S.F.; Young, K.G.; Kothary, R. Transgenic expression of neuronal dystonin isoform 2 partially rescues the disease phenotype of the dystonia musculorum mouse model of hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy VI. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2694–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampazzo, A.; Nava, A.; Malacrida, S.; Beffagna, G.; Bauce, B.; Rossi, V.; Zimbello, R.; Simionati, B.; Basso, C.; Thiene, G.; et al. Mutation in human desmoplakin domain binding to plakoglobin causes a dominant form of arrhythmogenic right ventricular cardiomyopathy. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2002, 71, 1200–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alcalai, R.; Metzger, S.; Rosenheck, S.; Meiner, V.; Chajek-Shaul, T. A recessive mutation in desmoplakin causes arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia, skin disorder, and woolly hair. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 42, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uzumcu, A.; Norgett, E.E.; Dindar, A.; Uyguner, O.; Nisli, K.; Kayserili, H.; Sahin, S.E.; Dupont, E.; Severs, N.J.; Leigh, I.M.; et al. Loss of desmoplakin isoform I causes early onset cardiomyopathy and heart failure in a Naxos-like syndrome. J. Med. Genet. 2006, 43, e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van der Zwaag, P.A.; Jongbloed, J.D.; van den Berg, M.P.; van der Smagt, J.J.; Jongbloed, R.; Bikker, H.; Hofstra, R.M.; van Tintelen, J.P. A genetic variants database for arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia/cardiomyopathy. Hum. Mutat. 2009, 30, 1278–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Jassar, C.; Knowles, T.; Jeeves, M.; Kami, K.; Behr, E.; Bikker, H.; Overduin, M.; Chidgey, M. The nonlinear structure of the desmoplakin plakin domain and the effects of cardiomyopathy-linked mutations. J. Mol. Biol. 2011, 411, 1049–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, G.D.; Winokur, T.S.; Cerfolio, R.J.; Van Tine, B.A.; Chow, L.T.; Okoh, V.; Garver, R.I., Jr. Differential expression and biodistribution of cytokeratin 18 and desmoplakins in non-small cell lung carcinoma subtypes. Lung Cancer 2002, 36, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayana, N.; Gist, J.; Smith, T.; Tylka, D.; Trogdon, G.; Wahl, J.K. Desmosomal component expression in normal, dysplastic, and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Dermatol. Res. Pract. 2010, 2010, 649731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papagerakis, S.; Shabana, A.H.; Pollock, B.H.; Papagerakis, P.; Depondt, J.; Berdal, A. Altered desmoplakin expression at transcriptional and protein levels provides prognostic information in human oropharyngeal cancer. Hum. Pathol. 2009, 40, 1320–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; South, A.P.; Hart, I.R. Increased keratinocyte proliferation initiated through downregulation of desmoplakin by RNA interference. Exp. Cell Res. 2007, 313, 2336–2344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Chen, Y.; Cui, T.; Knösel, T.; Zhang, Q.; Albring, K.F.; Huber, O.; Petersen, I. Desmoplakin acts as a tumor suppressor by inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway in human lung cancer. Carcinogenesis 2012, 33, 1863–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muro, Y.; Sugiura, K.; Shiraki, A.; Ishii, N.; Hashimoto, T.; Akiyama, M. Detection of autoantibodies to periplakin and envoplakin in paraneoplastic pemphigus but not idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis using full-length recombinant proteins. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 429, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Zhu, X. Detection of anti-envoplakin and anti-periplakin autoantibodies by ELISA in patients with paraneoplastic pemphigus. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2009, 301, 703–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Y.; Elgehama, A.; Sun, Y.; Li, L.; Gu, Y.; Guo, W.; Xu, Q. Loss of periplakin expression is associated with the tumorigenesis of colorectal carcinoma. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsubo, T.; Hagiwara, T.; Tamura-Nakano, M.; Sezaki, T.; Miyake, O.; Hinohara, C.; Shimizu, T.; Yamada, K.; Dohi, T.; Kawamura, Y.I. Aberrant DNA hypermethylation reduces the expression of the desmosome-related molecule periplakin in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 415–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natsuga, K. Plectin-related skin diseases. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 77, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bausch, D.; Thomas, S.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Fernández-del, C.C.; Bauer, T.W.; Williams, M.; Warshaw, A.L.; Thayer, S.P.; Kelly, K.A. Plectin-1 as a novel biomarker for pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lever, W.F. Pemphigus. Medicine 1953, 32, 1–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai Cheong, J.E.; Wessagowit, V.; McGrath, J.A. Molecular abnormalities of the desmosomal protein desmoplakin in human disease. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2005, 30, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ermakov, S.; Scheinman, M. Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy—Antiarrhythmic Therapy. Arrhythm. Electrophysiol. Rev. 2015, 4, 86–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, A.A. Paraneoplastic Pemphigus: Autoimmune-Cancer Nexus in the Skin. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2015, 15, 1215–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steele, H.A.; George, B.J. Mucocutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes associated with hematologic malignancies. Oncology 2011, 25, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Balestri, R.; Magnano, M.; La Placa, M.; Patrizi, A.; Angileri, L.; Tengattini, V.; Bardazzi, F. Malignancies in bullous pemphigoid: A controversial association. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goodnough, L.T.; Muir, W.A. Bullous pemphigoid as a manifestation of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Arch. Intern. Med. 1980, 140, 1526–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez De Pablo, M.I.; Iranzo, P.; Mascaró, J.M.; Llambrich, A.; Baradad, M.; Herrero, C. Paraneoplastic pemphigus associated with non-Hodgkin B-cell lymphoma and good response to prednisone. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2005, 85, 233–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nishimori, T.; Tomonaga, T.; Matsushita, K.; Oh-Ishi, M.; Kodera, Y.; Maeda, T.; Nomura, F.; Matsubara, H.; Shimada, H.; Ochiai, T. Proteomic analysis of primary esophageal squamous cell carcinoma reveals downregulation of a cell adhesion protein, periplakin. Proteomics 2006, 6, 1011–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumoto, K.; Ikeda, M.; Sato, Y.; Kuruma, H.; Kamata, Y.; Nishimori, T.; Tomonaga, T.; Nomura, F.; Egawa, S.; Iwamura, M. Loss of periplakin expression is associated with pathological stage and cancer-specific survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the urinary bladder. Biomed. Res. 2014, 35, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimbo, T.; Tanemura, A.; Yamazaki, T.; Tamai, K.; Katayama, I.; Kaneda, Y. Serum anti-BPAG1 auto antibody is a novel marker for human melanoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadfield, J.A.; Ducki, S.; Hirst, N.; McGown, A.T. Tubulin and microtubules as targets for anticancer drugs. Prog. Cell Cycle Res. 2003, 5, 309–325. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mollinedo, F.; Gajate, C. Microtubules, microtubule-interfering agents and apoptosis. Apoptosis 2003, 8, 413–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pellegrini, F.; Budman, D.R. Review: Tubulin function, action of antitubulin drugs, and new drug development. Cancer Investig. 2005, 23, 264–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tangutur, A.D.; Kumar, D.; Krishna, K.V.; Kantevari, S. Microtubule Targeting Agents as Cancer Chemotherapeutics: An Overview of Molecular Hybrids as Stabilizing and Destabilizing Agents. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2017, 17, 2523–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingston, D.G. Tubulin-interactive natural products as anticancer agents. J. Nat. Prod. 2009, 72, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tubiana-Hulin, M. How to maximize the efficacy of taxanes in breast cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2005, 31 (Suppl. S4), S3–S9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccart-Gebhart, M.J.; Burzykowski, T.; Buyse, M.; Sledge, G.; Carmichael, J.; Lück, H.J.; Mackey, J.R.; Nabholtz, J.M.; Paridaens, R.; Biganzoli, L.; et al. Taxanes alone or in combination with anthracyclines as first-line therapy of patients with metastatic breast cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajorin, D.F. Paclitaxel in the treatment of advanced urothelial cancer. Oncology 2000, 14, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parasramka, S.; Talari, G.; Rosenfeld, M.; Guo, J.; Villano, J.L. Procarbazine, lomustine and vincristine for recurrent high-grade glioma. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 7, CD011773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundstrøm, S.; Bremnes, R.M.; Kaasa, S.; Aasebø, U.; Hatlevoll, R.; Dahle, R.; Boye, N.; Wang, M.; Vigander, T.; Vilsvik, J.; et al. Cisplatin and etoposide regimen is superior to cyclophosphamide, epirubicin, and vincristine regimen in small-cell lung cancer: Results from a randomized phase III trial with 5 years’ follow-up. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 4665–4672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flowers, C.R.; Sinha, R.; Vose, J.M. Improving outcomes for patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2010, 60, 393–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceresoli, G.L.; Zucali, P.A. Vinca alkaloids in the therapeutic management of malignant pleural mesothelioma. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2015, 41, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quasthoff, S.; Hartung, H.P. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy. J. Neurol. 2002, 249, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowinsky, E.K. The development and clinical utility of the taxane class of antimicrotubule chemotherapy agents. Annu. Rev. Med. 1997, 48, 353–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, D.; Leung, C.L.; Liem, R.K. Characterization of the microtubule binding domain of microtubule actin crosslinking factor (MACF): Identification of a novel group of microtubule associated proteins. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Henry, W.I.; Dubois, J.; Quick, Q.A. The microtubule inhibiting agent epothilone B antagonizes glioma cell motility associated with reorganization of the actin-binding protein α-actinin 4. Oncol. Rep. 2011, 25, 887–893. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- National Center for Health Statistics. Health, United States, 2016: With Chartbook on Long-term Trends in Health. Hyattsville, MD, USA, 2017; pp. 1–488. Available online: www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/leading-causes-of-death.htm (accessed on 7 November 2017).
- Berman, H.M.; Westbrook, J.; Feng, Z.; Gilliland, G.; Bhat, T.N.; Weissig, H.; Shindyalov, I.N.; Bourne, P.E. The Protein Data Bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crassini, K.; Mulligan, S.P.; Best, O.G. Targeting chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells in the tumor microenviroment: A review of the in vitro and clinical trials to date. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 694–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayed, A.O.; Parikh, S.A. Management of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia at high risk of relapse on ibrutinib therapy. Leuk. Lymphoma 2017, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, L.; Asklid, A.; Diels, J.; Eketorp-Sylvan, S.; Repits, J.; Søltoft, F.; Jäger, U.; Österborg, A. Ibrutinib versus previous standard of care: An adjusted comparison in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Ann. Hematol. 2017, 96, 1681–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.R. Ibrutinib (PCI-32765), the first BTK (Bruton’s tyrosine kinase) inhibitor in clinical trials. Curr. Hematol. Malig. Rep. 2013, 8, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Rattu, M.A.; Kim, S.S. A review of a novel, Bruton’s tyrosine kinase inhibitor, ibrutinib. J. Oncol. Pharm. Pract. 2016, 22, 92–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Weerdt, I.; Koopmans, S.M.; Kater, A.P.; van Gelder, M. Incidence and management of toxicity associated with ibrutinib and idelalisib: A practical approach. Haematologica 2017, 102, 1629–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fruman, D.A.; Bierer, B.E.; Benes, J.E.; Burakoff, S.J.; Austen, K.F.; Katz, H.R. The complex of FK506-binding protein 12 and FK506 inhibits calcineurin phosphatase activity and IgE activation-induced cytokine transcripts, but not exocytosis, in mouse mast cells. J. Immunol. 1995, 154, 1846–1851. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Parsons, J.N.; Wiederrecht, G.J.; Salowe, S.; Burbaum, J.J.; Rokosz, L.L.; Kincaid, R.L.; O’Keefe, S.J. Regulation of calcineurin phosphatase activity and interaction with the FK-506.FK-506 binding protein complex. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 19610–19616. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sakr, M.F.; McClain, C.J.; Gavaler, J.S.; Zetti, G.M.; Starzl, T.E.; Van Thiel, D.H. FK 506 pre-treatment is associated with reduced levels of tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 6 following hepatic ischemia/reperfusion. J. Hepatol. 1993, 17, 301–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Jordan, M.L.; Tweardy, D.J.; Wright, J.; Hoffman, R.A.; Simmons, R.L. FK-506 inhibits proliferation and IL-4 messenger RNA production by a T-helper 2 cell line. J. Surg. Res. 1992, 53, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, E.; Suzuki, H.; Tunru, I.S.; Yamashita, N.; Hori, T.; Kobayashi, M. FK506, an immunosuppressant, partially inhibits interleukin 6 production by adherent rheumatoid synovial cells. J. Rheumatol. 1994, 21, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, S.; Mukaida, N.; Yasumoto, K.; Rice, N.; Ishikawa, Y.; Horiguchi, H.; Murakami, S.; Matsushima, K. The interleukin-8 AP-1 and kappa B-like sites are genetic end targets of FK506-sensitive pathway accompanied by calcium mobilization. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 8582–8589. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.C.; Morel, P.A.; Wang, Q.; Jordan, M.L.; Simmons, R.L.; Tweardy, D.J. A dual mechanism of immunosuppression by FK-506. Differential suppression of IL-4 and IL-10 levels in T helper 2 cells. Transplantation 1993, 56, 978–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, F.J.; Koprak, S.; Staruch, M.J.; Talento, A.; Koo, G.; DaSilva, C.; Sinclair, P.J.; Wong, F.; Woods, J.; Barker, J.; et al. A tacrolimus-related immunosuppressant with reduced toxicity. Transplantation 1998, 65, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.; Xi, J.; Li, W.; Zhou, L.; Lu, J.; Lu, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, C. Efficacy and safety of tacrolimus for myasthenia gravis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neurol. 2017, 264, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciardiello, F.; Caputo, R.; Bianco, R.; Damiano, V.; Pomatico, G.; De Placido, S.; Bianco, A.R.; Tortora, G. Antitumor effect and potentiation of cytotoxic drugs activity in human cancer cells by ZD-1839 (Iressa), an epidermal growth factor receptor-selective tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Clin. Cancer Res. 2000, 6, 2053–2063. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Denny, W.A. The 4-anilinoquinazoline class of inhibitors of the erbB family of receptor tyrosine kinases. Farmaco 2001, 56, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulgaru, A.M.; Mani, S.; Goel, S.; Perez-Soler, R. Erlotinib (Tarceva): A promising drug targeting epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2003, 3, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.B.; Hesson, D.P.; Dusak, B.A.; Dexter, D.L.; Kang, G.J.; Hamel, E. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-styrylquinazolin-4(3H)-ones, a new class of antimitotic anticancer agents which inhibit tubulin polymerization. J. Med. Chem. 1990, 33, 1721–1728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apsel, B.; Blair, J.A.; Gonzalez, B.; Nazif, T.M.; Feldman, M.E.; Aizenstein, B.; Hoffman, R.; Williams, R.L.; Shokat, K.M.; Knight, Z.A. Targeted polypharmacology: Discovery of dual inhibitors of tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinases. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2008, 4, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, L.; Hu, D.; Zhou, X.; Wang, Z.; Xie, C.; Zhou, F. The anti-esophageal cancer cell activity by a novel tyrosine/phosphoinositide kinase inhibitor PP121. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Che, H.Y.; Guo, H.Y.; Si, X.W.; You, Q.Y.; Lou, W.Y. PP121, a dual inhibitor of tyrosine and phosphoinositide kinases, inhibits anaplastic thyroid carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 8659–8664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prokhorova, I.V.; Akulich, K.A.; Makeeva, D.S.; Osterman, I.A.; Skvortsov, D.A.; Sergiev, P.V.; Dontsova, O.A.; Yusupova, G.; Yusupov, M.M.; Dmitriev, S.E. Amicoumacin A induces cancer cell death by targeting the eukaryotic ribosome. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guha, G.; Lu, W.; Li, S.; Liang, X.; Kulesz-Martin, M.F.; Mahmud, T.; Indra, A.K.; Ganguli-Indra, G. Novel Pactamycin Analogs Induce p53 Dependent Cell-Cycle Arrest at S-Phase in Human Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma (HNSCC) Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zylicz, Z.; Wagener, D.J.; van Rennes, H.; van der Kleijn, E.; Lelieveld, P.; van den Broek, L.A.; Ottenheijm, H.C. In vivo antitumor activity of sparsomycin and its analogues in eight murine tumor models. Investig. New Drugs 1988, 6, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiebig, H.H.; Berger, D.P.; Köpping, K.; Ottenheijm, H.C.; Zylicz, Z. In vitro and in vivo anticancer activity of mitozolomide and sparsomycin in human tumor xenografts, murine tumors and human bone marrow. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 1990, 116, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Damlaj, M.; Lipton, J.H.; Assouline, S.E. A safety evaluation of omacetaxine mepesuccinate for the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2016, 15, 1279–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radich, J.P.; Shah, N.P.; Mauro, M.J. Integrating current treatment options for TKI-resistant chronic myeloid leukemia. Clin. Adv. Hematol. Oncol. 2014, 12 (Suppl. S13), 3–17. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.D.; Frick, M.; le Coutre, P. Omacetaxine mepesuccinate for the treatment of leukemia. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2011, 12, 2381–2392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.E.; Kantarjian, H.M.; Rea, D.; Wetzler, M.; Lipton, J.H.; Akard, L.; Khoury, H.J.; Michallet, M.; Guerci-Bresler, A.; Chuah, C.; et al. Final analysis of the efficacy and safety of omacetaxine mepesuccinate in patients with chronic-or accelerated-phase chronic myeloid leukemia: Results with 24 months of follow-up. Cancer 2015, 121, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Plakin Family Member | Associated Diseases and Disorders | Refs. |
|---|---|---|
| MACF1 | Neuromuscular disease, Parkinson’s disease, cancer | [29,30,31,32,33,34,35] |
| BPAG1 | paraneoplastic pemphigus, pemphigus foliaceus, erythema multiforme, mucosal-dominant pemphigus vulgaris, multiple sclerosis, dystonia musculorum | [36,37,38,39,40,41,42] |
| Desmoplakin | paraneoplastic pemphigus, pemphigus foliaceus, erythema multiforme, mucosal-dominant pemphigus vulgaris, cardiomyopathy, cancer | [37,38,39,43,44,45,46,47,48,49,50,51,52] |
| Envoplakin | paraneoplastic pemphigus | [53,54] |
| Periplakin | paraneoplastic pemphigus, cancer | [53,54,55,56] |
| Plectin | epidermolysis bullosa simplex, cancer | [57,58] |
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Quick, Q.A. Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 and Plakins as Therapeutic Drug Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020368
Quick QA. Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 and Plakins as Therapeutic Drug Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020368
Chicago/Turabian StyleQuick, Quincy A. 2018. "Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 and Plakins as Therapeutic Drug Targets" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020368
APA StyleQuick, Q. A. (2018). Microtubule-Actin Crosslinking Factor 1 and Plakins as Therapeutic Drug Targets. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 368. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020368