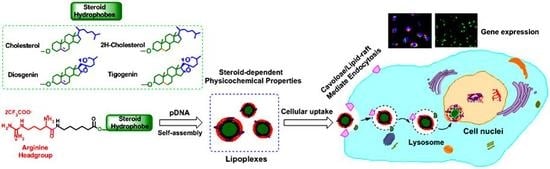
Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Synthesis Procedures of the Steroids-Based Cationic Lipids
2.3. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) and Mass Spectral Measurements
2.4. Agarose Gel Retardation Assay
2.5. Particle Sizes and ζ Potentials of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids/pDNA Lipoplexes
2.6. Morphologies of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids/pDNA Lipoplexes by TEM
2.7. Cytotoxicity of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids by MTT and CCK-8 Assays
2.8. Luciferase Gene Transfection Assay in the Presence and Absence of Serum
2.9. Intracellular Uptake of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids/Cy3-pDNA Lipoplexes Measured by Flow Cytometry
2.10. Luciferase Transfection Assays under Various Endocytosis Inhibitors [38]
2.11. Intracellular Localization of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids/Cy3-pDNA Lipoplexes Observed by Fluorescence Microscopy
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids
3.2. pDNA Binding of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids and the Stability of the Lipoplexes
3.3. Particle Size, Surface Charge and Morphology of the Lipoplexes
3.4. Cytotoxicity of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids by MTT/CCK-8 Assay
3.5. Luciferase Gene Transfection Assay of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids in the Absence/Presence of Serum
3.6. Cellular Uptake of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids/Cy3-pDNA Lipoplexes
3.7. Endocytosis Pathway Analysis of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids
3.8. Intracellular Localization of the Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Albrecht, M.A.; Evans, C.W.; Raston, C.L. Green chemistry and the health implications of nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2006, 8, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Wang, Y.; Yu, A.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhu, X.X. Cholic acid-modified dendritic multimolecular micelles and enhancement of anticancer drug therapeutic efficacy. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 1596–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Lavigueur, C.; Zhu, X.X. Aggregation and thermoresponsive properties of new star block copolymers with a cholic acid core. Langmuir 2011, 27, 11174–11179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X.; Szoka, F.C. Chemical approaches to triggerable lipid vesicles for drug and gene delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2003, 36, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niidome, T.; Huang, L. Gene therapy progress and prospects: Nonviral vectors. Gene Ther. 2002, 9, 1647–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Zhang, S.; Wang, B.; Cui, S.; Yan, J. Toxicity of cationic lipids and cationic polymers in gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2006, 114, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morille, M.; Passirani, C.; Vonarbourg, A.; Clavreul, A.; Benoit, J.P. Progress in developing cationic vectors for non-viral systemic gene therapy against cancer. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 3477–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lee, A.L.Z.; Venkataraman, S.; Sirat, S.B.M.; Gao, S.; Hedrick, J.L.; Yang, Y.Y. The use of cholesterol-containing biodegradable block copolymers to exploit hydrophobic interactions for the delivery of anticancer drugs. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 1921–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dao, K.L.; Hanson, R.N. Targeting the estrogen receptor using steroid–therapeutic drug conjugates (hybrids). Bioconjug. Chem. 2012, 23, 2139–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.J.; Wang, J.C.; Zhao, E.Y.; Gao, L.Y.; Feng, Q.; Liu, X.Y.; Zhao, Z.X.; Ma, X.F.; Hou, W.J.; Zhang, L.R.; et al. Self-assembly cationic nanoparticles based on cholesterol-grafted bioreducible poly(amidoamine) for sirna delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5303–5316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Z.Y.; Chu, B.Y.; Wei, X.W.; Li, J.; Carl, E.K.; Song, X.R.; He, G.; Xie, Y.M.; Wei, Y.Q.; Qian, Z.Y. Recent development of poly(ethylene glycol)-cholesterol conjugates as drug delivery systems. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 469, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Bajaj, A. Advances in gene delivery through molecular design of cationic lipids. Chem. Commun. 2009, 4632–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, J.; Bajaj, A.; Bhattacharya, S. Membranes of cationic gemini lipids based on cholesterol with hydroxyl headgroups and their interactions with DNA and phospholipid. J. Phys. Chem. B 2010, 115, 478–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, A.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Effect of the nature of the spacer on gene transfer efficacies of novel thiocholesterol derived gemini lipids in different cell lines: A structure–activity investigation. J. Med. Chem. 2008, 51, 2533–2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, A.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Synthesis and gene transfection efficacies of pei−cholesterol-based lipopolymers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2008, 19, 1640–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, A.; Kondiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Design, synthesis, and in vitro gene delivery efficacies of novel cholesterol-based gemini cationic lipids and their serum compatibility: A structure-activity investigation. J. Med. Chem. 2007, 50, 2432–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajaj, A.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. Synthesis and gene transfer activities of novel serum compatible cholesterol-based gemini lipids possessing oxyethylene-type spacers. Bioconjug. Chem. 2007, 18, 1537–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.K.; Naz, S.; Kondaiah, P.; Bhattacharya, S. A cationic cholesterol based nanocarrier for the delivery of p53-egfp-c3 plasmid to cancer cells. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 1334–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, A.; Mukherjee, K.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Y.; McCarroll, J.; Qu, J.; Swain, P.M.; Baigude, H.; Rana, T.M. Design and assembly of new nonviral rnai delivery agents by microwave-assisted quaternization (maq) of tertiary amines. Bioconjug. Chem. 2010, 21, 1581–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medvedeva, D.A.; Maslov, M.A.; Serikov, R.N.; Morozova, N.G.; Serebrenikova, G.A.; Sheglov, D.V.; Latyshev, A.V.; Vlassov, V.V.; Zenkova, M.A. Novel cholesterol-based cationic lipids for gene delivery. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6558–6568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.A.; Maslov, M.A.; Kabilova, T.O.; Puchkov, P.A.; Alekseeva, A.S.; Boldyrev, I.A.; Vlassov, V.V.; Serebrennikova, G.A.; Morozova, N.G.; Zenkova, M.A. Structure-transfection activity relationships in a series of novel cationic lipids with heterocyclic head-groups. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2013, 11, 7164–7178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov, M.A.; Kabilova, T.O.; Petukhov, I.A.; Morozova, N.G.; Serebrennikova, G.A.; Vlassov, V.V.; Zenkova, M.A. Novel cholesterol spermine conjugates provide efficient cellular delivery of plasmid DNA and small interfering rna. J. Control. Release 2012, 160, 182–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maslov, M.A.; Morozova, N.G.; Chizhik, E.I.; Rapoport, D.A.; Ryabchikova, E.I.; Zenkova, M.A.; Serebrennikova, G.A. Synthesis and delivery activity of new cationic cholesteryl glucosides. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 2438–2449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Zhu, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, S.; Sun, W.; Cao, A. The intracellular plasmid DNA localization of cationic reducible cholesterol-disulfide lipids. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 3507–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, A. Cholesterol-based cationic lipids for gene delivery: Contribution of molecular structure factors to physico-chemical and biological properties. Colloids Surf. B 2014, 116, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cline, L.L.; Janout, V.; Fisher, M.; Juliano, R.L.; Regen, S.L. A molecular umbrella approach to the intracellular delivery of small interfering rna. Bioconjug. Chem. 2011, 22, 2210–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janout, V.; Cline, L.L.; Feuston, B.P.; Klein, L.; O’Brien, A.; Tucker, T.; Yuan, Y.; O’Neill-Davis, L.A.; Peiffer, R.L.; Nerurkar, S.S.; et al. Molecular umbrella conjugate for the ocular delivery of sirna. Bioconjug. Chem. 2014, 25, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, W.J.; Zhang, Q.F.; Zhang, J.; Liu, Q.; Ren, L.; Chen, Q.M.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.Q. Cyclen-based lipidic oligomers as potential gene delivery vehicles. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1412–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.F.; Yi, W.J.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Ren, L.; Chen, Q.M.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.Q. Linear polycations by ring-opening polymerization as non-viral gene delivery vectors. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 5391–5401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.L.; Ma, Q.P.; Huang, Q.D.; Yang, W.H.; Zhang, J.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhu, W.; Yu, X.Q. Cationic lipids containing protonated cyclen and different hydrophobic groups linked by uracil-pna monomer: Synthesis and application for gene delivery. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2011, 46, 4133–4141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, A. “Click” synthesized sterol-based cationic lipids as gene carriers, and the effect of skeletons and headgroups on gene delivery. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 6366–6377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; Tong, H.; Shi, Q.; Fernandes, J.C.; Jin, T.; Dai, K.; Zhang, X. Uptake mechanisms of non-viral gene delivery. J. Control. Release 2012, 158, 371–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, Y.U.; Kim, B.K.; Park, J.W.; Seu, Y.B.; Doh, K.O. Endocytic pathway and resistance to cholesterol depletion of cholesterol derived cationic lipids for gene delivery. Mol. Pharm. 2012, 9, 3579–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pozzi, D.; Marchini, C.; Cardarelli, F.; Rossetta, A.; Colapicchioni, V.; Amici, A.; Montani, M.; Motta, S.; Brocca, P.; Cantù, L. Mechanistic understanding of gene delivery mediated by highly efficient multicomponent envelope-type nanoparticle systems. Mol. Pharm. 2013, 10, 4654–4665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, H.Y.; Kwon, S.M.; Chung, H.; Lee, S.Y.; Kwon, S.H.; Jeon, H.; Kim, Y.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.; Her, S.; et al. Cellular uptake mechanism and intracellular fate of hydrophobically modified glycol chitosan nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2009, 135, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Jung, S.; Luo, S.; Meng, F.; Zhu, X.; Park, T.G.; Zhong, Z. Co-delivery of sirna and paclitaxel into cancer cells by biodegradable cationic micelles based on PDMAEMA–PCL–PDMAEMA triblock copolymers. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2408–2416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Song, H.; Luo, K.; He, B.; Nie, Y.; Yang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gu, Z. Gene transfer efficacies of serum-resistant amino acids-based cationic lipids: Dependence on headgroup, lipoplex stability and cellular uptake. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 408, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Luo, T.; Sheng, R.; Sun, J.; Wang, Z.; Cao, A. Endoplasmic reticulum localization of poly(ω-aminohexyl methacrylamide)s conjugated with (l-)-arginines in plasmid DNA delivery. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 7923–7938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhi, D.; Zhang, S.; Cui, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, D. The headgroup evolution of cationic lipids for gene delivery. Bioconjug. Chem. 2013, 24, 487–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, R.; An, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, M.; Cao, A. Assembly of plasmid DNA with pyrene-amines cationic amphiphiles into nanoparticles and their visible lysosome localization. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 12338–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Sheng, R.; Luo, T.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Li, Y.; Cao, A. Amphiphilic cationic dendritic poly(l-lysine) -block-poly(l-lactide)-block-dendritic poly(l-lysine) s in aqueous solution: Self-aggregation and interaction with DNA as gene delivery carriers. Macromol. Biosci. 2011, 11, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moret, I.; Esteban Peris, J.; Guillem, V.M.; Benet, M.; Revert, F.; Dasí, F.; Crespo, A.; Aliño, S.F. Stability of PEI–DNA and DOTAP–DNA complexes: Effect of alkaline pH, heparin and serum. J. Control. Release 2001, 76, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheikhi Mehrabadi, F.; Fischer, W.; Haag, R. Dendritic and lipid-based carriers for gene/sirna delivery (a review). Curr. Opin. Solid Stat. Mater. Sci. 2012, 16, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehman, Z.U.; Zuhorn, I.S.; Hoekstra, D. How cationic lipids transfer nucleic acids into cells and across cellular membranes: Recent advances. J. Control. Release 2013, 166, 46–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaManna, C.M.; Lusic, H.; Camplo, M.; McIntosh, T.J.; Barthélémy, P.; Grinstaff, M.W. Charge-reversal lipids, peptide-based lipids, and nucleoside-based lipids for gene delivery. Acc. Chem. Res. 2012, 45, 1026–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Yi, W.J.; Zhang, Y.-M.; Zhang, J.; Guo, L.; Yu, X.Q. Biotinylated cyclen-contained cationic lipids as non-viral gene delivery vectors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2013, 82, 376–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggi, F.; Ciccarelli, S.; Diociaiuti, M.; Casciardi, S.; Masci, G. Chitosan nanogels by template chemical cross-linking in polyion complex micelle nanoreactors. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 3499–3507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gan, Q.; Wang, T.; Cochrane, C.; McCarron, P. Modulation of surface charge, particle size and morphological properties of chitosan–tpp nanoparticles intended for gene delivery. Colloids Surf. B 2005, 44, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunath, K.; von Harpe, A.; Fischer, D.; Petersen, H.; Bickel, U.; Voigt, K.; Kissel, T. Low-molecular-weight polyethylenimine as a non-viral vector for DNA delivery: Comparison of physicochemical properties, transfection efficiency and in vivo distribution with high-molecular-weight polyethylenimine. J. Control. Release 2003, 89, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raju, J.; Bird, R.P. Diosgenin, a naturally occurring furostanol saponin suppresses 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coa reductase expression and induces apoptosis in hct-116 human colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2007, 255, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Q.-D.; Ou, W.-J.; Chen, H.; Feng, Z.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, W.; Yu, X.Q. Novel cationic lipids possessing protonated cyclen and imidazolium salt for gene delivery. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2011, 78, 326–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.X.; Yang, B.; Chen, S.; Lei, Q.; Feng, J.; Qiu, X.F.; Dong, N.G.; Zhuo, R.X.; Zhang, X.Z. Oligoamines grafted hyperbranched polyether as high efficient and serum-tolerant gene vectors. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 111, 732–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalby, B.; Cates, S.; Harris, A.; Ohki, E.C.; Tilkins, M.L.; Price, P.J.; Ciccarone, V.C. Advanced transfection with lipofectamine 2000 reagent: Primary neurons, sirna, and high-throughput applications. Methods 2004, 33, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, F.; Liu, W. Enhanced gene transfection and serum stability of polyplexes by PDMAEMA-polysulfobetaine diblock copolymers. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 628–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Y.; Luo, T.; Peng, C.; Sheng, R.; Cao, A.; Cao, X.; Shen, M.; Guo, R.; Tomás, H.; Shi, X. Gene delivery using dendrimer-entrapped gold nanoparticles as nonviral vectors. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adler, A.F.; Leong, K.W. Emerging links between surface nanotechnology and endocytosis: Impact on nonviral gene delivery. Nano Today 2010, 5, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahay, G.; Alakhova, D.Y.; Kabanov, A.V. Endocytosis of nanomedicines. J. Control. Release 2010, 145, 182–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, C.Y.M.; Uludağ, H. Cellular uptake pathways of lipid-modified cationic polymers in gene delivery to primary cells. Biomaterials 2012, 33, 7834–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.H.; Rothberg, K.G.; Anderson, R. Mis-assembly of clathrin lattices on endosomes reveals a regulatory switch for coated pit formation. J. Cell Biol. 1993, 123, 1107–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koivusalo, M.; Welch, C.; Hayashi, H.; Scott, C.C.; Kim, M.; Alexander, T.; Touret, N.; Hahn, K.M.; Grinstein, S. Amiloride inhibits macropinocytosis by lowering submembranous pH and preventing rac1 and cdc42 signaling. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 188, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ondřej, V.; Lukášová, E.; Falk, M.; Kozubek, S. The role of actin and microtubule network in plastid DNA intracellular trafficking. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2007, 54, 657–663. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, R.; Zheng, N.; Song, Z.; Yin, L.; Cheng, J. The effect of side-chain functionality and hydrophobicity on the gene delivery capabilities of cationic helical polypeptides. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 3443–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, D.; Lin, Q.M.; Zhang, L.M.; Liang, Y.Y.; Xue, W. A star-shaped porphyrin-arginine functionalized poly (l-lysine) copolymer for photo-enhanced drug and gene co-delivery. Biomaterials 2014, 35, 4357–4367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sheng, R.; Wang, Z.; Luo, T.; Cao, A.; Sun, J.; Kinsella, J.M. Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020369
Sheng R, Wang Z, Luo T, Cao A, Sun J, Kinsella JM. Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020369
Chicago/Turabian StyleSheng, Ruilong, Zhao Wang, Ting Luo, Amin Cao, Jingjing Sun, and Joseph M. Kinsella. 2018. "Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020369
APA StyleSheng, R., Wang, Z., Luo, T., Cao, A., Sun, J., & Kinsella, J. M. (2018). Skeleton-Controlled pDNA Delivery of Renewable Steroid-Based Cationic Lipids, the Endocytosis Pathway Analysis and Intracellular Localization. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 369. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020369