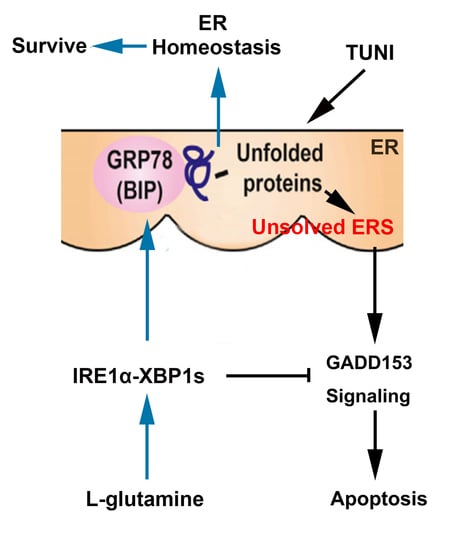
l-Glutamine Attenuates Apoptosis Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Activating the IRE1α-XBP1 Axis in IPEC-J2: A Novel Mechanism of l-Glutamine in Promoting Intestinal Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Role of Tunicamycin (TUNI) in Spontaneous Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress (ERS)
2.2. l-Glutamine Promotes Cell Proliferation in Normal Growth Medium
2.3. l-Glutamine Reduces Apoptosis and Maintains a High Level of GRP78 in Response to ERS
2.4. l-Glutamine Alleviates C/Enhancer Binding Protein Homologous Protein (CHOP)-Mediated Apoptosis and Activates IRE1α-XBP1 Axis
2.5. IRE1α-XBP1 Inhibition Reverses Protective Effect of l-Glutamine
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents
4.2. Cell Culture and Treatments
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Cell Proliferation Determination by EdU Staining
4.5. Flow Cytometry Analysis
4.6. Western Blot Analysis
4.7. Immunofluorescence
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ERS | Endoplasmic reticulum stress |
| TUNI | Tunicamycin |
| GRP78 | Glucose-regulated protein 78 |
| CHOP | C/enhancer binding protein homologous protein |
| IPEC-J2 | Intestinal porcine epithelial cell line J2 |
| DOX | Doxorubicin |
References
- Xing, S.; Zhang, B.L.; Lin, M.; Zhou, P.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F.; Zhou, G.H. Effects of alanyl-glutamine supplementation on the small intestinal mucosa barrier in weaned piglets. Asian-Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2017, 30, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.Y.; Lu, Y.; Hu, S.; Sun, D.; Yao, Y.M. Preventive effect of glutamine on intestinal barrier dysfunction induced by severe trauma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2002, 8, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sands, S.; Ladas, E.J.; Kelly, K.M.; Weiner, M.; Lin, M.; Ndao, D.H.; Dave, A.; Vahdat, L.T.; Bender, J.G. Glutamine for the treatment of vincristine-induced neuropathy in children and adolescents with cancer. Support. Care Cancer 2017, 25, 701–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sena, J.I.N.; Guimaraes, S.B.; de Vasconcelos, P.R.L. Metabolic changes induced by pre-administration of l-alanyl-glutamine and omega-3 in wistar rats subjected to sepsis. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira 2010, 25, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wu, J.; Wu, L.D.; Li, G.P.; Xiong, M.; Chen, X.; Meng, Q.Y. Effect of parenteral glutamine supplementation combined with enteral nutrition on HSP90 expression and lymphoid organ apoptosis in severely burned rats. Burns 2016, 42, 1494–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, I.R.; Ball, R.O.; Baracos, V.E.; Field, C.J. Glutamine supplementation influences immune development in the newly weaned piglet. Dev. Comp. Immunol. 2006, 30, 1191–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.H.; Lin, G.; Dai, Z.L.; Zhou, T.J.; Li, T.T.; Yuan, T.L.; Wu, Z.L.; Wu, G.Y.; Wang, J.J. l-glutamine deprivation induces autophagy and alters the mtor and mapk signaling pathways in porcine intestinal epithelial cells. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 2185–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.L.; Lin, M.; Yu, C.N.; Li, J.L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, P.; Yang, W.W.; Gao, F.; Zhou, G.H. Alanyl-glutamine supplementation regulates mtor and ubiquitin proteasome proteolysis signaling pathways in piglets. Nutrition 2016, 32, 1123–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, D.; Hou, Y.Q.; Wang, L.; Ouyang, W.J.; Long, M.H.; Zhao, D.; Ding, B.Y.; Liu, Y.L.; Wu, G.Y. l-glutamine enhances enterocyte growth via activation of the mtor signaling pathway independently of ampk. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paschen, W.; Frandsen, A. Endoplasmic reticulum dysfunction—A common denominator for cell injury in acute and degenerative diseases of the brain? J. Neurochem. 2001, 79, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duvigneau, J.C.; Miller, I.; Bahrami, S.; Redl, H.; Kozlov, A.V. ER stress markers in inflammation and ischemia. Inflamm. Res. 2010, 59, S157. [Google Scholar]
- McGuckin, M.A.; Eri, R.D.; Das, I.; Lourie, R.; Florin, T.H. Intestinal secretory cell ER stress and inflammation. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2011, 39, 1081–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuckin, M.A.; Eri, R.D.; Das, I.; Lourie, R.; Florin, T.H. Er stress and the unfolded protein response in intestinal inflammation. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2010, 298, G820–G832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, A. Unresolved er stress inflames the intestine. Cell 2008, 134, 724–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hetz, C.; Papa, F.R. The Unfolded Protein Response and Cell Fate Control. Mol. Cell 2017, 17, S1097–S2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, A.; Ordonez, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Mauriz, J.L. Melatonin and endoplasmic reticulum stress: Relation to autophagy and apoptosis. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, H.O.; Yadav, R.K.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. ER stress: Autophagy induction, inhibition, and selection. Autophagy 2015, 11, 1956–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ron, D.; Hubbard, S.R. How IRE1 reacts to ER stress. Cell 2008, 132, 24–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, I.; San Miguel, B.; Prause, C.; Marroni, N.; Cuevas, M.J.; Culebras, J.; Gonzalez-Gallego, J.; Tunon, M.J. Glutamine treatment attenuates endoplasmic reticulum stress and inflammation in TNBS-induced colitis. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; Chen, S.; Ren, W.K.; Liu, G.; Yao, K.; Wu, G.Y.; Yin, Y.L. Escherichia coli aggravates endoplasmic reticulum stress and triggers CHOP-dependent apoptosis in weaned pigs. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 2073–2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ringseis, R.; Kynast, A.M.; Couturier, A.; Most, E.; Eder, K. Ingestion of frying fat leads to activation of the endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced unfolded protein response in the duodenal mucosa of pigs. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2016, 60, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakrzewski, S.S.; Richter, J.F.; Krug, S.M.; Jebautzke, B.; Lee, I.F.; Rieger, J.; Sachtleben, M.; Bondzio, A.; Schulzke, J.D.; Fromm, M.; et al. Improved cell line IPEC-J2, characterized as a model for porcine jejunal epithelium. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.H.; Yang, J.C.; Yang, G.Y.; Zhou, D.; Wang, J.F. A selected lactobacillus rhamnosus strain promotes egfr-independent akt activation in an enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli K88-infected IPEC-J2 cell model. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.J.; Wang, A.N.; Zeng, X.F.; Hou, C.L.; Liu, H.; Qiao, S.Y. Lactobacillus reuteri i5007 modulates tight junction protein expression in IPEC-J2 cells with LPS stimulation and in newborn piglets under normal conditions. BMC Microbiol. 2015, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paszti-Gere, E.; Barna, R.F.; Kovago, C.; Szauder, I.; Ujhelyi, G.; Jakab, C.; Meggyeshazi, N.; Szekacs, A. Changes in the distribution of type II transmembrane serine protease, tmprss2 and in paracellular permeability in IPEC-J2 cells exposed to oxidative stress. Inflammation 2015, 38, 775–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauchart-Thevret, C.; Cui, L.; Wu, G.; Burrin, D.G. Arginine-induced stimulation of protein synthesis and survival in IPEC-J2 cells is mediated by mtor but not nitric oxide. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 299, E899–E909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, C.; Wu, G.Y.; Sun, Y.L.; Wang, B.; He, B.B.; Dai, Z.L.; Wu, Z.L. Glutamine enhances tight junction protein expression and modulates corticotropin-releasing factor signaling in the jejunum of wean ling piglets. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaser, A.; Lee, A.H.; Franke, A.; Glickman, J.N.; Zeissig, S.; Tilg, H.; Nieuwenhuis, E.E.S.; Higgins, D.E.; Schreiber, S.; Glimcher, L.H.; et al. XBP1 links er stress to intestinal inflammation and confers genetic risk for human inflammatory bowel disease. Cell 2008, 134, 743–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rhoads, J.M.; Keku, E.O.; Woodard, J.P.; Bangdiwala, S.I.; Lecce, J.G.; Gatzy, J.T. l-glutamine with d-glucose stimulates oxidative-metabolism and nacl absorption in piglet jejunum. Am. J. Physiol. 1992, 263, G960–G966. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pardo, L.P.; Poveda, P.A.; da Silva, C.; dos Santos, A.; Venancio, E.; Arantes, V.; Nogueira, E. Effect of l-glutamine levels in piglets diets challenged with escherichia coli lipopolysacharides. Revista MVZ Córdoba 2014, 19, 4328–4337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molino, J.P.; Donzele, J.L.; de Oliveira, R.F.M.; Saraiva, A.; Haese, D.; Fortes, E.I.; de Souza, M.F. l-glutamine and l-glutamate in diets with different lactose levels for piglets weaned at 21 days of age. Revista Brasileira de Zootecnia 2012, 41, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.Y.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, I.O. Tunicamycin inhibits toll-like receptor-activated inflammation in raw264.7 cells by suppression of nf-kappa 13 and c-jun activity via a mechanism that is independent of er-stress and n-glycosylation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 721, 294–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, E.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Seong, S.; Cho, W.; Ahn, J.S.; Cho, H.S. Inhibitory effects of verrucarin a on tunicamycin-induced er stress in fao rat liver cells. Molecules 2015, 20, 8988–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, R.O.; Ferreiro, E.; Cardoso, S.M.; Oliveira, C.R.; Pereira, C.M.F. ER stress-mediated apoptotic pathway induced by a β peptide requires the presence of functional mitochondria. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2010, 20, 625–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taishiro, J.; Kikuchi, S.; Shinpo, K.; Kishirnoto, R.; Tsuji, S.; Sasaki, H. Role of p53 in neurotoxicity induced by the endoplasmic reticulum stress agent tunicamycin in cultures of rat organotypic slice spinal cord. J. Neurosci. Res. 2007, 85, 395–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suganya, N.; Bhakkiyalakshmi, E.; Suriyanarayanan, S.; Paulmurugan, R.; Ramkumar, K.M. Quercetin ameliorates tunicamycin-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in endothelial cells. Cell Prolif. 2014, 47, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, H.; Shimoke, K.; Isosaki, M.; Satoh, H.; Yoshizumi, M.; Ikeuchi, T. Comprison of polyglutamine-, tunicamycin- and thapsigargin-induced er stress in pc12 cells. J. Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 100, 107. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Jiang, K.; Gao, D.M.; Kang, X.N.; Sun, C.; Zhang, Q.L.; Li, Y.; Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Guo, K.; et al. Clusterin protects hepatocellular carcinoma cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress induced apoptosis through grp78. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e55981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, S.H.M.; Parveen, A.; Ahmad, I.; Ahmad, I.; Arshad, M.D.; Verma, A.K.; Mahdi, A.A. Aluminum induces er stress-mediated neuro-inflammation in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells: Implication of oxidative stress and apoptosis. Int. J. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 54–55. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, S.T.; Tian, H.; Miao, C.; Zhang, D.W.; Zhao, L.; Li, Y.Y.; Yang, N.N.; Jiao, P.; Sang, H.; Guo, S.D.; et al. D4f alleviates macrophage-derived foam cell apoptosis by inhibiting CD36 expression and er stress-chop pathway. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 836–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubillos-Ruiz, J.R.; Silberman, P.C.; Rutkowski, M.R.; Chopra, S.; Perales-Puchalt, A.; Song, M.; Zhang, S.; Bettigole, S.E.; Gupta, D.; Holcomb, K.; et al. ER stress sensor XBP1 controls anti-tumor immunity by disrupting dendritic cell homeostasis. Cell 2015, 161, 1527–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurel, M.; Chevet, E.; Tavernier, J.; Gerlo, S. Getting RIDD of RNA: IRE1 in cell fate regulation. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2014, 39, 245–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, D.D.; Lynch, C.; Medeiros, B.C.; Liedtke, M.; Bam, R.; Tam, A.B.; Yang, Z.F.; Alagappan, M.; Abidi, P.; Le, Q.T.; et al. Identification of doxorubicin as an inhibitor of the IRE1 α-xbp1 axis of the unfolded protein response. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Q.; He, L.Q.; Hou, Y.Q.; Chen, J.S.; Duan, Y.H.; Deng, D.; Wu, G.Y.; Yin, Y.L.; Yao, K. ρ-ketoglutarate enhances milk protein synthesis by porcine mammary epithelial cells. Amino Acids 2016, 48, 2179–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jiang, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, G.; Yao, K.; Yin, Y. l-Glutamine Attenuates Apoptosis Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Activating the IRE1α-XBP1 Axis in IPEC-J2: A Novel Mechanism of l-Glutamine in Promoting Intestinal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122617
Jiang Q, Chen J, Liu S, Liu G, Yao K, Yin Y. l-Glutamine Attenuates Apoptosis Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Activating the IRE1α-XBP1 Axis in IPEC-J2: A Novel Mechanism of l-Glutamine in Promoting Intestinal Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122617
Chicago/Turabian StyleJiang, Qian, Jiashun Chen, Shaojuan Liu, Gang Liu, Kang Yao, and Yulong Yin. 2017. "l-Glutamine Attenuates Apoptosis Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Activating the IRE1α-XBP1 Axis in IPEC-J2: A Novel Mechanism of l-Glutamine in Promoting Intestinal Health" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122617
APA StyleJiang, Q., Chen, J., Liu, S., Liu, G., Yao, K., & Yin, Y. (2017). l-Glutamine Attenuates Apoptosis Induced by Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress by Activating the IRE1α-XBP1 Axis in IPEC-J2: A Novel Mechanism of l-Glutamine in Promoting Intestinal Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122617