Preclinical Imaging for the Study of Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancer
Abstract
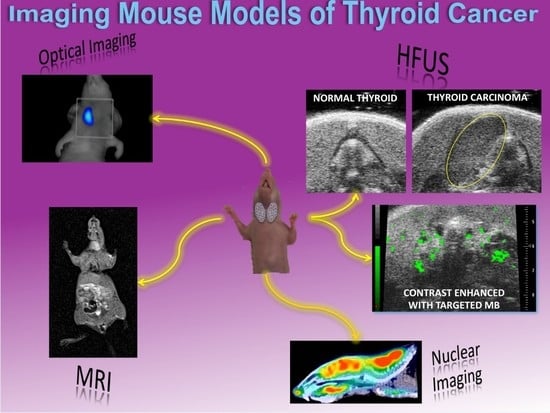
:1. Introduction
2. Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancers
2.1. Transgenic Mouse Models
2.1.1. BRAF V600E Transgenic Mouse Model
2.1.2. TRK-T1 Transgenic Mouse Model
2.1.3. TRβ-PV Transgenic Mouse Model
2.1.4. Rb+/− Transgenic Mouse Model
2.2. Xenograft and Orthotopic Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancer
2.3. Metastatic Mouse Model of Thyroid Cancer
3. In Vivo Imaging for the Molecular Characterization of Thyroid Carcinoma Mouse Models
3.1. Nuclear Imaging
3.2. Optical Imaging
3.3. High Frequency Ultrasound
3.4. Magnetic Resonance Imaging
3.5. Multimodal Imaging
3.6. Theranostic
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADC | Apparent Diffusion Coefficient |
| ATC | Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma |
| BRAF | V-raf murine sarcoma viral oncogene homolog B |
| CLI | Cerenkov luminescence imaging |
| CT | Computed tomography |
| Cy | Cyanine |
| DCE | Dynamic contrast enhanced |
| DFO | Desferrioxamine-thioureyl-phenyl-isothiocyanate |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| DW | Diffusion weighted |
| EGFR | Epithelial growth factor receptor |
| ET | Endothelin |
| FMT | Fluorescence molecular tomography |
| FTC | Follicular thyroid carcinoma |
| GFP | Green fluorescent protein |
| HFUS | High-frequency ultrasound |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| MTC | Medullary thyroid carcinoma |
| NDRG2 | N-myc downstream-regulated gene 2 |
| NIR | Near-infrared |
| NIS | Sodium/iodide symporter |
| NK | Natural killer |
| NOD | non-diabetic obese |
| NSG | NOD SCID gamma |
| NTRK1 | Neurotrophic Receptor Tyrosine Kinase 1 |
| PA | Photoacoustic tomography |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PDTX | Patients derived tumor xenografts |
| PET | Positron emission tomography |
| PTC | Papillary thyroid carcinoma |
| PTEN | Phosphatase and tensin homolog |
| RACPP | Ratiometric activatable cell-penetrating peptide |
| RAS | Rat sarcoma |
| RET | Rearranged During Transfection |
| RPMI | Roswell Park Memorial Institute |
| SCID | Severely combined immune-deficient |
| SPECT | Single photon emission tomography |
| STR | Short tandem repeat |
| TC | Thyroid cancer |
| TCGA | Cancer Genome Atlas |
| Tet/O | Tetracycline-inducible mouse model |
| TFB | Tetrafluoroborate |
| Tg | Thyroglobulin |
| THRB | Thyroid hormone receptor-β |
| TPO-Cre | Thyroid peroxidase-driven cre recombinase |
| VEGF | Vascular-endothelial growth factor |
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2017, 67, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitahara, C.M.; Sosa, J.A. The changing incidence of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2016, 12, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagin, J.A.; Wells, S.A., Jr. Biologic and Clinical Perspectives on Thyroid Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dralle, H.; Machens, A.; Basa, J.; Fatourechi, V.; Franceschi, S.; Hay, I.D.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Pasieka, J.L.; Sherman, S.I. Follicular cell-derived thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikiforov, Y.E.; Nikiforova, M.N. Molecular genetics and diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinaro, E.; Romei, C.; Biagini, A.; Sabini, E.; Agate, L.; Mazzeo, S.; Materazzi, G.; Sellari-Franceschini, S.; Ribechini, A.; Torregrossa, L.; et al. Anaplastic thyroid carcinoma: From clinicopathology to genetics and advanced therapies. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2017, 13, 644–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, B.; Ghossein, R. Genomic Landscape of poorly Differentiated and Anaplastic Thyroid Carcinoma. Endocr. Pathol. 2016, 27, 205–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maia, A.L.; Wajner, S.M.; Vargas, C.V. Advances and controversies in the management of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 2017, 29, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agrawal, N.; Akbani, R.; Aksoy, B.A.; Ally, A.; Arachchi, H.; Asa, S.L.; Auman, J.T.; Balasundaram, M.; Balu, S.; Baylin, S.B.; et al. Integrated genomic characterization of papillary thyroid carcinoma. Cell 2014, 159, 676–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, G.M.; Hodak, S.P.; Yip, L. RAS mutations in thyroid cancer. Oncologist 2013, 18, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raman, P.; Koenig, R.J. Pax-8-PPAR-gamma fusion protein in thyroid carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2014, 10, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asa, S.L.; Ezzat, S. The epigenetic landscape of differentiated thyroid cancer. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Accardo, G.; Conzo, G.; Esposito, D.; Gambardella, C.; Mazzella, M.; Castaldo, F.; Di Donna, C.; Polistena, A.; Avenia, N.; Colantuoni, V.; et al. Genetics of medullary thyroid cancer: An overview. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 41, S2–S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walrath, J.C.; Hawes, J.J.; Van Dyke, T.; Reilly, K.M. Genetically engineered mouse models in cancer research. Adv. Cancer Res. 2010, 106, 113–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doyle, A.; McGarry, M.P.; Lee, N.A.; Lee, J.J. The construction of transgenic and gene knockout/knockin mouse models of human disease. Transgenic Res. 2012, 21, 327–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rusinek, D.; Krajewska, J.; Jarzab, M. Mouse models of papillary thyroid carcinoma—Short review. Endokrynol. Pol. 2016, 67, 212–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirschner, L.S.; Qamri, Z.; Kari, S.; Ashtekar, A. Mouse models of thyroid cancer: A 2015 update. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 421, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitale, G.; Gaudenzi, G.; Circelli, L.; Manzoni, M.F.; Bassi, A.; Fioritti, N.; Faggiano, A.; Colao, A. Animal models of medullary thyroid cancer: State of the art and view to the future. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2017, 24, R1–R12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.D.; Zhang, Y.F.; Xu, H.X.; Zhang, X.P. The role of BRAF in the pathogenesis of thyroid carcinoma. Front. Biosci. 2015, 20, 1068–1078. [Google Scholar]
- Knauf, J.A.; Ma, X.; Smith, E.P.; Zhang, L.; Mitsutake, N.; Liao, X.H.; Refetoff, S.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Fagin, J.A. Targeted expression of BRAFV600E in thyroid cells of transgenic mice results in papillary thyroid cancers that undergo dedifferentiation. Cancer Res. 2005, 65, 4238–4245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Santos, E.; Ryder, M.; Knauf, J.A.; Liao, X.H.; West, B.L.; Bollag, G.; Kolesnick, R.; Thin, T.H.; Rosen, N.; et al. Small-molecule MAPK inhibitors restore radioiodine incorporation in mouse thyroid cancers with conditional BRAF activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 4700–4711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russell, J.P.; Powell, D.J.; Cunnane, M.; Greco, A.; Portella, G.; Santoro, M.; Fusco, A.; Rothstein, J.L. The TRK-T1 fusion protein induces neoplastic transformation of thyroid epithelium. Oncogene 2000, 19, 5729–5735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cunha, L.L.; Marcello, M.A.; Ward, L.S. The role of the inflammatory microenvironment in thyroid carcinogenesis. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2014, 21, R85–R103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, E.; Heyland, A. Evolution of thyroid hormone signaling in animals: Non-genomic and genomic modes of action. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzuki, H.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. Mice with a mutation in the thyroid hormone receptor beta gene spontaneously develop thyroid carcinoma: A mouse model of thyroid carcinogenesis. Thyroid 2002, 12, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, Y.; Ying, H.; Willingham, M.C.; Cheng, S.Y. A tumor suppressor role for thyroid hormone beta receptor in a mouse model of thyroid carcinogenesis. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 4430–4438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaneshige, M.; Kaneshige, K.; Zhu, X.; Dace, A.; Garrett, L.; Carter, T.A.; Kazlauskaite, R.; Pankratz, D.G.; Wynshaw-Boris, A.; Refetoff, S.; et al. Mice with a targeted mutation in the thyroid hormone beta receptor gene exhibit impaired growth and resistance to thyroid hormone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13209–13214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Velez-Cruz, R.; Johnson, D.G. The Retinoblastoma (RB) Tumor Suppressor: Pushing Back against Genome Instability on Multiple Fronts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, B.O.; Remington, L.; Albert, D.M.; Mukai, S.; Bronson, R.T.; Jacks, T. Cooperative tumorigenic effects of germline mutations in Rb and p53. Nat. Genet. 1994, 7, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akeno, N.; Miller, A.L.; Ma, X.; Wikenheiser-Brokamp, K.A. p53 suppresses carcinoma progression by inhibiting mTOR pathway activation. Oncogene 2015, 34, 589–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harvey, M.; Vogel, H.; Lee, E.Y.; Bradley, A.; Donehower, L.A. Mice deficient in both p53 and Rb develop tumors primarily of endocrine origin. Cancer Res. 1995, 55, 1146–1151. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.S.; Zhu, X. Lessons from mouse models of thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2009, 19, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonello, Z.A.; Nucera, C. Orthotopic mouse models for the preclinical and translational study of targeted therapies against metastatic human thyroid carcinoma with BRAF(V600E) or wild-type BRAF. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5397–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, A.; Albanese, S.; Auletta, L.; Mirabelli, P.; Zannetti, A.; D’Alterio, C.; Di Maro, G.; Orlandella, F.M.; Salvatore, G.; Soricelli, A.; et al. High-Frequency Ultrasound-Guided Injection for the Generation of a Novel Orthotopic Mouse Model of Human Thyroid Carcinoma. Thyroid 2016, 26, 552–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Park, Y.W.; Schiff, B.A.; Doan, D.D.; Yazici, Y.; Jasser, S.A.; Younes, M.; Mandal, M.; Bekele, B.N.; Myers, J.N. An orthotopic model of anaplastic thyroid carcinoma in athymic nude mice. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.H.; Henderson, Y.; Kang, Y.; Chattopadhyay, C.; Holton, P.; Wang, M.; Briggs, K.; Clayman, G.L. An orthotopic model of papillary thyroid carcinoma in athymic nude mice. Arch. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2008, 134, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nucera, C.; Nehs, M.A.; Mekel, M.; Zhang, X.; Hodin, R.; Lawler, J.; Nose, V.; Parangi, S. A novel orthotopic mouse model of human anaplastic thyroid carcinoma. Thyroid 2009, 19, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Todaro, M.; Iovino, F.; Eterno, V.; Cammareri, P.; Gambara, G.; Espina, V.; Gulotta, G.; Dieli, F.; Giordano, S.; De Maria, R.; et al. Tumorigenic and metastatic activity of human thyroid cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 8874–8885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran Cao, H.S.; Kaushal, S.; Snyder, C.S.; Ongkeko, W.M.; Hoffman, R.M.; Bouvet, M. Real-time imaging of tumor progression in a fluorescent orthotopic mouse model of thyroid cancer. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 4415–4422. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gule, M.K.; Chen, Y.; Sano, D.; Frederick, M.J.; Zhou, G.; Zhao, M.; Milas, Z.L.; Galer, C.E.; Henderson, Y.C.; Jasser, S.A.; et al. Targeted therapy of VEGFR2 and EGFR significantly inhibits growth of anaplastic thyroid cancer in an orthotopic murine model. Clin. Cancer Res. 2011, 17, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buther, K.; Compeer, M.G.; De Mey, J.G.; Schober, O.; Schafers, M.; Bremer, C.; Riemann, B.; Holtke, C. Assessment of endothelin-A receptor expression in subcutaneous and orthotopic thyroid carcinoma xenografts in vivo employing optical imaging methods. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 2907–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrison, J.A.; Pike, L.A.; Lund, G.; Zhou, Q.; Kessler, B.E.; Bauerle, K.T.; Sams, S.B.; Haugen, B.R.; Schweppe, R.E. Characterization of thyroid cancer cell lines in murine orthotopic and intracardiac metastasis models. Horm. Cancer 2015, 6, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Chen, Y.; Adachi, M.; Wen, X.; Erwin, B.; Mawlawi, O.; Lai, S.Y.; Li, C. Single agent nanoparticle for radiotherapy and radio-photothermal therapy in anaplastic thyroid cancer. Biomaterials 2015, 57, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Gunda, V.; Zhu, X.; Xu, X.; Wu, J.; Askhatova, D.; Farokhzad, O.C.; Parangi, S.; Shi, J. Theranostic near-infrared fluorescent nanoplatform for imaging and systemic siRNA delivery to metastatic anaplastic thyroid cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, 7750–7755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reeb, A.N.; Ziegler, A.; Lin, R.Y. Characterization of human follicular thyroid cancer cell lines in preclinical mouse models. Endocr. Connect. 2016, 5, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mo, J.H.; Choi, I.J.; Jeong, W.J.; Jeon, E.H.; Ahn, S.H. HIF-1alpha and HSP90: Target molecules selected from a tumorigenic papillary thyroid carcinoma cell line. Cancer Sci. 2012, 103, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nehs, M.A.; Nucera, C.; Nagarkatti, S.S.; Sadow, P.M.; Morales-Garcia, D.; Hodin, R.A.; Parangi, S. Late intervention with anti-BRAF(V600E) therapy induces tumor regression in an orthotopic mouse model of human anaplastic thyroid cancer. Endocrinology 2012, 153, 985–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.J.; Na, H.J.; Suh, M.J.; Ban, M.J.; Byeon, H.K.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, J.W.; Choi, E.C.; Kwon, H.J.; Chang, J.W.; et al. Hypoxia Induces Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Follicular Thyroid Cancer: Involvement of Regulation of Twist by Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1alpha. Yonsei Med. J. 2015, 56, 1503–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tentler, J.J.; Tan, A.C.; Weekes, C.D.; Jimeno, A.; Leong, S.; Pitts, T.M.; Arcaroli, J.J.; Messersmith, W.A.; Eckhardt, S.G. Patient-derived tumour xenografts as models for oncology drug development. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 9, 338–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauregui-Osoro, M.; Sunassee, K.; Weeks, A.J.; Berry, D.J.; Paul, R.L.; Cleij, M.; Banga, J.P.; O’Doherty, M.J.; Marsden, P.K.; Clarke, S.E.; et al. Synthesis and biological evaluation of [18F]tetrafluoroborate: A PET imaging agent for thyroid disease and reporter gene imaging of the sodium/iodide symporter. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2010, 37, 2108–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maschauer, S.; Michel, K.; Tripal, P.; Buther, K.; Kuwert, T.; Schober, O.; Kopka, K.; Riemann, B.; Prante, O. Synthesis and in vivo evaluation of an 18F-labeled glycoconjugate of PD156707 for imaging ETA receptor expression in thyroid carcinoma by positron emission tomography. Am. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2013, 3, 425–436. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- D’Alessandria, C.; Braesch-Andersen, S.; Bejo, K.; Reder, S.; Blechert, B.; Schwaiger, M.; Bartolazzi, A. Noninvasive In Vivo Imaging and Biologic Characterization of Thyroid Tumors by ImmunoPET Targeting of Galectin-3. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 3583–3592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Pang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, W.; Xi, J.; Xu, L.; Zhou, J. Construction of human single-chain variable fragment antibodies of medullary thyroid carcinoma and single photon emission computed tomography/computed tomography imaging in tumor-bearing nude mice. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 35, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, A.; Wang, C.; Sun, J.; Gao, J.; Tao, L.; Du, X.; Zhao, H.; Yang, J.; Li, Y. Overexpression of NDRG2 Increases Iodine Uptake and Inhibits Thyroid Carcinoma Cell Growth In Situ and In Vivo. Oncol. Res. 2016, 23, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, C.-C.; He, Z.-M.; Hsieh, Y.-J.; Huang, C.-W.; Li, J.-J.; Hwu, L.; Chen, Y.-A.; Yang, B.-H.; Chang, C.-W.; Huang, W.-S.; et al. Quantitative Measurement of the Thyroid Uptake Function of Mouse by Cerenkov Luminescence Imaging. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.Y.; Hwang, M.H.; Kim, J.E.; Kang, S.; Park, J.C.; Yoo, J.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, S.W.; Ahn, B.C.; Lee, J. Combined Cerenkov luminescence and nuclear imaging of radioiodine in the thyroid gland and thyroid cancer cells expressing sodium iodide symporter: Initial feasibility study. Endocr. J. 2011, 58, 575–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levi, J.; Kothapalli, S.R.; Bohndiek, S.; Yoon, J.K.; Dragulescu-Andrasi, A.; Nielsen, C.; Tisma, A.; Bodapati, S.; Gowrishankar, G.; Yan, X.; et al. Molecular photoacoustic imaging of follicular thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orosco, R.K.; Savariar, E.N.; Weissbrod, P.A.; Diaz-Perez, J.A.; Bouvet, M.; Tsien, R.Y.; Nguyen, Q.T. Molecular targeting of papillary thyroid carcinoma with fluorescently labeled ratiometric activatable cell penetrating peptides in a transgenic murine model. J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 113, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Vergara, E.; Salvatore, G.; Greco, A.; Troncone, G.; Affuso, A.; Liuzzi, R.; Salerno, P.; Scotto di Santolo, M.; Santoro, M.; et al. Morphological ultrasound microimaging of thyroid in living mice. Endocrinology 2009, 150, 4810–4815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavarello, R.J.; Ridgway, W.R.; Sarwate, S.S.; Oelze, M.L. Characterization of thyroid cancer in mouse models using high-frequency quantitative ultrasound techniques. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 2013, 39, 2333–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancini, M.; Greco, A.; Salvatore, G.; Liuzzi, R.; Di Maro, G.; Vergara, E.; Chiappetta, G.; Pasquinelli, R.; Brunetti, A.; Salvatore, M. Imaging of thyroid tumor angiogenesis with microbubbles targeted to vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 in mice. BMC Med. Imaging 2013, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Zhang, M.; Fu, Q.; Li, J.; Sun, H. Targeted near infrared hyperthermia combined with immune stimulation for optimized therapeutic efficacy in thyroid cancer treatment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 6878–6890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Zhu, H.; Huang, X.; Wang, P.; Zhang, F.; Li, W.; Chen, G.; Chen, B. Novel iodinated gold nanoclusters for precise diagnosis of thyroid cancer. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2219–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscombe, J.R. Radionuclides in the management of thyroid cancer. Cancer Imaging 2007, 7, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buscombe, J.; Hirji, H.; Witney-Smith, C. Nuclear medicine in the management of thyroid disease. Expert Rev. Anticancer Ther. 2008, 8, 1425–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perron, B.; Rodriguez, A.M.; Leblanc, G.; Pourcher, T. Cloning of the mouse sodium iodide symporter and its expression in the mammary gland and other tissues. J. Endocrinol. 2001, 170, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, B.C. Personalized Medicine Based on Theranostic Radioiodine Molecular Imaging for Differentiated Thyroid Cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groot-Wassink, T.; Aboagye, E.O.; Glaser, M.; Lemoine, N.R.; Vassaux, G. Adenovirus biodistribution and noninvasive imaging of gene expression in vivo by positron emission tomography using human sodium/iodide symporter as reporter gene. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 1723–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, B.; Zhang, R.; Li, L.; Shao, J.Y.; Wang, L.V. Photoacoustic imaging of voltage responses beyond the optical diffusion limit. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greco, A.; Albanese, S.; Auletta, L.; De Carlo, F.; Salvatore, M.; Howard, C.M.; Claudio, P.P. Advances in molecular preclinical therapy mediated by imaging. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 61, 76–94. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Padhani, A.R.; Liu, G.; Mu-Koh, D.; Chenevert, T.L.; Thoeny, H.C.; Takahara, T.; Dzik-Jurasz, A.; Ross, B.D.; Van Cauteren, M.; Collins, D.; et al. Diffusion-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging as a Cancer Biomarker: Consensus and Recommendations. Neoplasia 2009, 11, 102–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-Y.; Wang, Y.-X.; Lin, Y.; Zhang, J.-S.; Yang, F.; Zhou, Q.-L.; Liao, Y.-Y. Advance of Molecular Imaging Technology and Targeted Imaging Agent in Imaging and Therapy. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, X.; Liu, H.; Yin, B.; Xu, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Intravoxel Incoherent Motion Di usion-weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging for Monitoring the Early Response to ZD6474 from Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma in Nude Mouse. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foroutan, P.; Kreahling, J.M.; Morse, D.L.; Grove, O.; Lloyd, M.C.; Reed, D.; Raghavan, M.; Altiok, S.; Martinez, G.V.; Gillies, R.J. Diffusion MRI and Novel Texture Analysis in Osteosarcoma Xenotransplants Predicts Response to Anti-Checkpoint Therapy. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e82875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozgeyik, Z.; Coskun, S.; Dagli, A.F.; Ozkan, Y.; Sahpaz, F.; Ogur, E. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of thyroid nodules. Neuroradiology 2009, 51, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schob, S.; Voigt, P.; Bure, L.; Meyer, H.-J.; Wickenhauser, C.; Behrmann, C.; Höhn, A.; Kachel, P.; Dralle, H.; Hoffmann, K.-T.; et al. Diffusion-Weighted Imaging Using a Readout-Segmented, Multishot EPI Sequence at 3 T Distinguishes between Morphologically Differentiated and Undifferentiated Subtypes of Thyroid Carcinoma—A Preliminary Study. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 9, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.-Y.; Yao, Q.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-Y.; Lu, Q.; Suo, S.-T.; Chen, J.; Zheng, W.-J.; Dai, Y.-M.; Wu, L.-M.; Xu, J.-R. Preliminary study of diffusion kurtosis imaging in thyroid nodules and its histopathologic correlation. Eur. Radiol. 2017, 27, 4710–4720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auletta, L.; Gramanzini, M.; Gargiulo, S.; Albanese, S.; Salvatore, M.; Greco, A. Advances in multimodal molecular imaging. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2017, 61, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Guernet, A.; Grumolato, L. CRISPR/Cas9 editing of the genome for cancer modeling. Methods 2017, 121–122, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Platt, R.J.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Yim, M.J.; Swiech, L.; Kempton, H.R.; Dahlman, J.E.; Parnas, O.; Eisenhaure, T.M.; Jovanovic, M.; et al. CRISPR-Cas9 knockin mice for genome editing and cancer modeling. Cell 2014, 159, 440–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Imaging | Tracer | Model (Transgene, Cell Line, Xenograft or Orthotopic Implantation) | Histotype | Focus | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | [18F]-TFB | Transgenic TRβPV/PV | FTC | NIS | [50] |
| PET | [18F]glyPD156707 | K1—Xenograft | PTC | ETAR | [51] |
| PET | 89Zr-DFO-mAb | FRO82-1—Xenograft WRO82-1—Xenograft BCPAP—Xenograft | ATC FTC PTC | Galectin-3 | [52] |
| SPECT | 131I | TT—Xenograft | MTC | Anti-MTC antibody | [53] |
| SPECT | 99mTcO4− | TT—Xenograft | MTC | NDRG2 | [54] |
| CLI | 131I 124I | Hypo-, hyper-thyroidism NIS—Xenograft | NIS | [55] [56] | |
| PA & FMT | FTC133—Xenograft | FTC | MMP | [57] | |
| RFM | RACPP | Transgenic BRAF V600E | PTC | MMP-9 | [58] |
| BLI | GFP | Orthotopic (panel) | Tumor growth and metastatization | [42] | |
| BLI | Luciferase | Orthotopic (panel) | Tumor growth and metastatization | [45] | |
| HFUS | Transgenic Tg-TRK-T1 | PTC | Tumor growth | [59] | |
| HFUS | Transgenic Rb+/− Transgenic BRAF-TRβPV/PV | MTC PTC FTC | Tumor growth | [60] | |
| HFUS | antiVEGFR2-MB | Transgenic Tg-TRK-T1 | PTC | VEGFR2 | [61] |
| HFUS | FTC-133—Orthotopic | FTC | Orthotopic implantation | [34] | |
| FRI & FMT & HFUS | Cy5.5-PD156707 | K1—Xenograft | PTC | ETAR Tumor growth | [41] |
| BLI & DCE-MRI | Luciferase PG-Gd-DTPA | 8505C—Orthotopic Hth83—Orthotopic | ATC ATC | EGFR VEGFR2 | [40] |
| FMT | AG-IR820 | TT—Xenograft | MTC | Glucose-transporter 1 | [62] |
| FMT | 8505C-BRAF V600E—Xenograft 8505C-BRAF V600E—Orthotopic | ATC | Therapy effect | [44] | |
| FMT & CT | AuNCs@BSA-I | Human derived poorly differentiate PTC—Xenograft | PTC | Differentiating malignant tissues | [63] |
| PET & BLI | PEG-[64Cu]CuS NPs | Hth83—Orthotopic | ATC | Therapy effect | [43] |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Greco, A.; Auletta, L.; Orlandella, F.M.; Iervolino, P.L.C.; Klain, M.; Salvatore, G.; Mancini, M. Preclinical Imaging for the Study of Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122731
Greco A, Auletta L, Orlandella FM, Iervolino PLC, Klain M, Salvatore G, Mancini M. Preclinical Imaging for the Study of Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(12):2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122731
Chicago/Turabian StyleGreco, Adelaide, Luigi Auletta, Francesca Maria Orlandella, Paola Lucia Chiara Iervolino, Michele Klain, Giuliana Salvatore, and Marcello Mancini. 2017. "Preclinical Imaging for the Study of Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 12: 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122731
APA StyleGreco, A., Auletta, L., Orlandella, F. M., Iervolino, P. L. C., Klain, M., Salvatore, G., & Mancini, M. (2017). Preclinical Imaging for the Study of Mouse Models of Thyroid Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(12), 2731. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18122731