Unexpectedly Higher Morbidity and Mortality of Hospitalized Elderly Patients Associated with Rhinovirus Compared with Influenza Virus Respiratory Tract Infection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
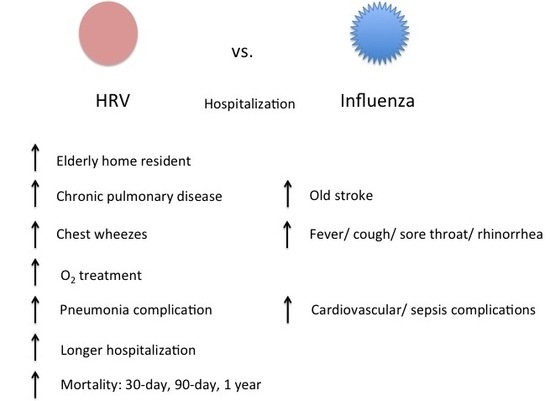
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lau, S.K.; Yip, C.C.; Tsoi, H.W.; Lee, R.A.; So, L.Y.; Lau, Y.L.; Chan, K.H.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Clinical features and complete genome characterization of a distinct human rhinovirus (HRV) genetic cluster, probably representing a previously undetected HRV species, HRV-C, associated with acute respiratory illness in children. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2007, 45, 3655–3664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, R.Y.; Chan, P.K.; Tsen, T.; Li, A.M.; Lam, W.Y.; Yeung, A.C.; Nelson, E.A. Identification of viral and atypical bacterial pathogens in children hospitalized with acute respiratory infections in Hong Kong by multiplex PCR assays. J. Med. Virol. 2009, 81, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, S.K.; Yip, C.C.; Lin, A.W.; Lee, R.A.; So, L.Y.; Lau, Y.L.; Chan, K.H.; Woo, P.C.; Yuen, K.Y. Clinical and molecular epidemiology of human rhinovirus C in children and adults in Hong Kong reveals a possible distinct human rhinovirus C subgroup. J. Infect. Dis. 2009, 200, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monto, A.S.; Fendrick, A.M.; Sarnes, M.W. Respiratory illness caused by picornavirus infection: A review of clinical outcomes. Clin. Ther. 2001, 23, 1615–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, L.; Chan, K.H.; Ip, D.K.; Fang, V.J.; Fung, R.O.; Leung, G.M.; Peiris, M.J.; Cowling, B.J. Burden, seasonal pattern and symptomatology of acute respiratory illnesses with different viral aetiologies in children presenting at outpatient clinics in Hong Kong. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mak, R.K.; Tse, L.Y.; Lam, W.Y.; Wong, G.W.; Chan, P.K.; Leung, T.F. Clinical spectrum of human rhinovirus infections in hospitalized Hong Kong children. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheuk, D.K.; Tang, I.W.; Chan, K.H.; Woo, P.C.; Peiris, M.J.; Chiu, S.S. Rhinovirus infection in hospitalized children in Hong Kong: A prospective study. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2007, 26, 995–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- To, K.K.; Lau, S.K.; Chan, K.H.; Mok, K.Y.; Luk, H.K.; Yip, C.C.; Ma, Y.K.; Sinn, L.H.; Lam, S.H.; Ngai, C.W.; et al. Pulmonary and extrapulmonary complications of human rhinovirus infection in critically ill patients. J. Clin. Virol. 2016, 77, 85–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sridhar, S.; Luk, H.K.; Lau, S.K.; Woo, P.C. First report of severe parainfluenza virus 4B and rhinovirus C coinfection in a liver transplant recipient treated with immunoglobulin. J. Clin. Virol. 2014, 61, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.L.; Chiu, S.S.; Malik, P.J.; Chan, K.H.; Wong, H.S.; Lau, Y.L. Is respiratory viral infection really an important trigger of asthma exacerbations in children? Eur. J. Pediatr. 2011, 70, 1317–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ko, F.W.; Ip, M.; Chan, P.K.; Chan, M.C.; To, K.W.; Ng, S.S.; Chau, S.S.; Tang, J.W.; Hui, D.S. Viral etiology of acute exacerbations of COPD in Hong Kong. Chest 2007, 132, 900–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hai, L.T.; Bich, V.T.N.; Ngai, L.K.; Diep, N.T.N.; Phuc, P.H.; Hung, V.P.; Taylor, W.R.; Horby, P.; Liem, N.T.; Wertheim, H.F. Fatal respiratory infections associated with rhinovirus outbreak, Vietnam. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2012, 18, 1886–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, J.K.; Yagi, S.; Nelson, F.A.; Kiang, D.; Glaser, C.A.; Rosenberg, J.; Cahill, C.K.; Schnurr, D.P. Rhinovirus outbreak in a long term care facility for elderly persons associated with unusually high mortality. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2005, 15, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, L.A.; Shepard, C.W.; Britz, P.H.; Erdman, D.D.; Fischer, M.; Flannery, B.L.; Peck, A.J.; Lu, X.; Thacker, W.L.; Benson, R.F.; et al. Two outbreaks of severe respiratory disease in nursing homes associated with rhinovirus. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2006, 54, 284–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longtin, J.; Marchand-Austin, A.; Winter, A.L.; Patel, S.; Eshaghi, A.; Jamieson, F.; Low, D.E.; Gubbay, J.B. Rhinovirus outbreaks in long-term care facilities, Ontario, Canada. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2010, 16, 1463–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reid, A.B.; Anderson, T.L.; Cooley, L.; Williamson, J.; Mcgregor, A.R. An outbreak of human rhinovirus species C infections in a neonatal intensive care unit. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2011, 30, 1096–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peltola, V.; Waris, M.; Osterback, R.; Susi, P.; Ruuskanen, O.; Hyypiä, T. Rhinovirus transmission within families with children: Incidence of symptomatic and asymptomatic infections. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, G.; Fratini, M.; Della, L.S.; Iaconelli, M.; Muscillo, M. Viral infections acquired indoors through airborne, droplet or contact transmission. Ann. Ist. Super. Sanita 2013, 49, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Savolainen-Kopra, C.; Korpela, T.; Simonen-Tikka, M.L.; Amiryousefi, A.; Ziegler, T.; Roivainen, M.; Hovi, T. Single treatment with ethanol hand rub is ineffective against human rhinovirus—Hand washing with soap and water removes the virus efficiently. J. Med. Virol. 2012, 84, 543–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.B.; Fuls, J.L.; Rodgers, N.D.; Goldfarb, H.B.; Lockhart, L.K.; Aust, L.B. A randomized trial of the efficacy of hand disinfection for prevention of rhinovirus infection. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 54, 1422–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chantzi, F.M.; Papadopoulos, N.G.; Bairamis, T.; Tsiakou, M.; Bournousouzis, N.; Constantopoulos, A.G.; Liapi, G.; Xatzipsalti, M.; Kafetzis, D.A. Human rhinoviruses in otitis media with effusion. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2006, 17, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, D.; Ganesan, S.; Comstock, A.T.; Meldrum, C.A.; Mahidhara, R.; Goldsmith, A.M.; Curtis, J.L.; Martinez, F.J.; Hershenson, M.B.; Sajjan, U. Increased cytokine response of rhinovirus-infected airway epithelial cells in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 332–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, S.E.; Lamson, D.M.; Soave, R.; Guzman, B.H.; Shore, T.B.; Ritchie, E.K.; Zappetti, D.; Satlin, M.J.; Leonard, J.P.; van Besien, K.; et al. Clinical and molecular epidemiology of human rhinovirus infections in patients with hematologic malignancy. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 71, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, J.J.; Voora, D.; Cyr, D.D.; Lucas, J.E.; Zaas, A.K.; Woods, C.W.; Newby, L.K.; Kraus, W.E.; Ginsburg, G.S. Gene expression profiles link respiratory viral infection, platelet response to aspirin, and acute myocardial infarction. PLoS ONE 2015, 20, e0132259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wark, P.A.; Tooze, M.; Powell, H.; Parsons, K. Viral and bacterial infection in acute asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease increases the risk of readmission. Respirology 2013, 18, 996–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hewson, C.A.; Jardine, A.; Edwards, M.R.; Laza-Stanca, V.; Johnston, S.L. Toll-like receptor 3 is induced by and mediates antiviral activity against rhinovirus infection of human bronchial epithelial cells. J. Virol. 2005, 79, 12273–12279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, L.; Crump, C.E.; Hayden, F.G. In vitro activity of pleconaril and AG7088 against selected serotypes and clinical isolates of human rhinoviruses. Antivir. Res. 2000, 47, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tijsma, A.; Franco, D.; Tucker, S.; Hilgenfeld, R.; Froeyen, M.; Leyssen, P.; Neyts, J. The capsid binder vapendavir and the novel protease inhibitor SG85 inhibit enterovirus 71 replication. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2014, 58, 6990–6992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djukanović, R.; Harrison, T.; Johnston, S.L.; Gabbay, F.; Wark, P.; Thomson, N.C.; Niven, R.; Singh, D.; Reddel, H.K.; Davies, D.E.; et al. The effect of inhaled IFN-β on worsening of asthma symptoms caused by viral infections. A randomized trial. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glanville, N.; Johnston, S.L. Challenges in developing a cross-serotype rhinovirus vaccine. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2015, 11, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Baseline Demographics | Rhinovirus (n = 728) % (Unless Stated) | Influenza (n = 1218) % (Unless Stated) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age; Mean (S.D.) | 71.6 (20.2) | 73.7 (18.6) | 0.06 |
| Male sex | 44.6 | 44.7 | 0.97 |
| Elderly home resident | 31.3 | 23.5 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| Charlson comorbidity index; Mean (S.D.) | 0.8 (0.8) | 0.8 (0.9) | 0.14 |
| Pulmonary diseases | 22.9 | 15.7 | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 21.6 | 19.9 | 0.37 |
| Stroke | 9.5 | 13 | 0.02 |
| Malignancy | 7.6 | 6.2 | 0.22 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 26.4 | 27.7 | 0.53 |
| Smoker | 21.3 | 19.8 | 0.35 |
| Influenza vaccination | 8.4 | 9.2 | 0.54 |
| Pneumococcal vaccination | 8.1 | 12.2 | 0.06 |
| Presenting Symptoms | |||
| Days of symptom onset to admission; Mean (S.D.) | 2.8 (4.8) | 2.4 (4.2) | 0.10 |
| Fever (>37.8) | 42.2 | 65.6 | <0.001 |
| Cough | 57 | 67.6 | <0.001 |
| Sputum production | 53 | 49.6 | 0.15 |
| Sore throat | 5.1 | 14.4 | <0.001 |
| Chest wheezes | 15.4 | 11.2 | 0.007 |
| Rhinorrhea | 6.6 | 11.2 | 0.001 |
| Complications | |||
| Pneumonia | 32.6 | 28 | 0.03 |
| Cardiovascular | 3.8 | 7.6 | 0.001 |
| Sepsis | 2.2 | 4.1 | 0.03 |
| Treatment | |||
| Oxygen therapy | 33.1 | 25.4 | <0.001 |
| Invasive ventilation | 0.68 | 0.74 | 0.90 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | 2.6 | 3.1 | 0.52 |
| Hospitalization days; Mean (S.D.) | 8.7 (13) | 6.8 (12) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization frequency; Mean (S.D.) | 2.2 (2.4) | 1.9 (1.9) | 0.36 |
| ICU admission | 1.8 | 2.4 | 0.38 |
| Upon Admission with abnormal value | |||
| Hemoglobin (<13.3 g/dL) | 75.4 | 69.7 | 0.01 |
| Neutrophil (>7.42 × 109 /L) | 42.3 | 26 | <0.001 |
| Lymphocyte (<1.06 × 109 /L) | 1.8 | 0.9 | 0.11 |
| Creatinine (>109 μmol/L) | 25.5 | 27.5 | 0.37 |
| ALT (>58 U/L) | 6 | 5.7 | 0.76 |
| AST (>38 U/L) | 19.5 | 28.4 | <0.001 |
| Creatine kinase (>174 IU/L) | 21.8 | 8.7 | 0.01 |
| Mortality | |||
| 30-day | 9.6 | 7.1 | 0.04 |
| 90-day | 14.2 | 10 | 0.006 |
| 1-year | 17.2 | 11.7 | 0.004 |
| Cause of death | |||
| Pneumonia | 81.6 | 81.1 | 0.92 |
| Stroke | 3.2 | 3.5 | 0.89 |
| Malignancy | 10.4 | 12.7 | 0.56 |
| Chronic renal failure | 2.4 | 5.6 | 0.19 |
| Acute myocardial infarction | 4.8 | 2.8 | 0.66 |
| Congestive heart failure | 2.4 | 5.6 | 0.19 |
| COPD | 20.8 | 15.4 | 0.39 |
| Other | 1.6 | 4.2 | 0.21 |
| Baseline Demographics | Survived (n = 603) % (Unless Stated) | Succumbed (n = 125) % (Unless Stated) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age; Mean (S.D.) | 69.4 (20.7) | 81.9 (13.6) | <0.001 |
| Male sex | 45.4 | 40.8 | 0.34 |
| Elderly home resident | 25.2 | 60.8 | <0.001 |
| Comorbidity | |||
| Charlson comorbidity index; Mean (S.D.) | 0.81 (0.81) | 0.95 (0.76) | 0.04 |
| Pulmonary diseases | 21.1 | 32 | 0.008 |
| Cardiovascular diseases | 21.2 | 23.2 | 0.63 |
| Stroke | 9.1 | 11.2 | 0.47 |
| Malignancy | 7.1 | 10.4 | 0.21 |
| Diabetes mellitus | 27 | 23.2 | 0.38 |
| Smoker | 20.7 | 24 | 0.42 |
| Influenza vaccination | 8.8 | 6.4 | 0.38 |
| Pneumococcal vaccination | 11.4 | 14.4 | 0.35 |
| Presenting Symptoms | |||
| Days of symptom onset to admission; Mean (S.D.) | 2.8 (5) | 2.7 (4) | 0.69 |
| Fever (>37.8) | 41.5 | 45.6 | 0.39 |
| Cough | 55.7 | 63.2 | 0.12 |
| Sputum production | 48.1 | 56.8 | 0.08 |
| Sore-throat | 7.8 | 0.8 | 0.004 |
| Chest wheezes | 15.1 | 16.8 | 0.63 |
| Rhinorrhea | 15.6 | 4 | 0.001 |
| Complications | |||
| Pneumonia | 27.5 | 56.8 | <0.001 |
| Cardiovascular | 3 | 8 | 0.008 |
| Sepsis | 1.7 | 4.8 | 0.03 |
| Bacterial co-infection | 1.0 | 2.4 | 0.20 |
| Treatment | |||
| Oxygen therapy | 27 | 62.4 | <0.001 |
| Invasive ventilation | 0.5 | 1.6 | 0.17 |
| Non-invasive ventilation | 1.8 | 6.4 | 0.003 |
| Hospitalization days; Mean (S.D.) | 7.6 (11.1) | 13.8 (18.6) | <0.001 |
| Hospitalization frequency; Mean (S.D.) | 2 (2.2) | 2.9 (3.4) | 0.02 |
| ICU admission | 1.1 | 4.8 | 0.005 |
| Upon Admission with abnormal value | |||
| Hemoglobin (<13.3 g/dL) | 77.6 | 90.4 | 0.001 |
| Neutrophil (>7.42 × 109 /L) | 43 | 53.6 | 0.03 |
| Lymphocyte (<1.06 × 109 /L) | 2.1 | 0.8 | 0.37 |
| Creatinine (>109 μmol/L) | 25.4 | 35.2 | 0.03 |
| ALT (>58 U/L) | 6.1 | 8 | 0.41 |
| AST (>38 U/L) | 18.6 | 30.4 | 0.003 |
| Creatine kinase (>174 IU/L) | 9.1 | 9.6 | 0.99 |
| Variable | Odds Ratio | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rhinorrea | 0.31 | 0.11–0.86 | 0.024 |
| Elderly home resident | 2.60 | 1.56–4.33 | <0.001 |
| ICU admission | 9.56 | 2.17–42.18 | 0.003 |
| Oxygen therapy | 2.62 | 1.62–4.24 | <0.001 |
| Hemoglobin level <13.3 g/dL upon admission | 2.43 | 1.16–5.12 | 0.019 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hung, I.F.N.; Zhang, A.J.; To, K.K.W.; Chan, J.F.W.; Zhu, S.H.S.; Zhang, R.; Chan, T.-C.; Chan, K.-H.; Yuen, K.-Y. Unexpectedly Higher Morbidity and Mortality of Hospitalized Elderly Patients Associated with Rhinovirus Compared with Influenza Virus Respiratory Tract Infection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020259
Hung IFN, Zhang AJ, To KKW, Chan JFW, Zhu SHS, Zhang R, Chan T-C, Chan K-H, Yuen K-Y. Unexpectedly Higher Morbidity and Mortality of Hospitalized Elderly Patients Associated with Rhinovirus Compared with Influenza Virus Respiratory Tract Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(2):259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020259
Chicago/Turabian StyleHung, Ivan F. N., Anna Jinxia Zhang, Kelvin K. W. To, Jasper F. W. Chan, Shawn H. S. Zhu, Ricky Zhang, Tuen-Ching Chan, Kwok-Hung Chan, and Kwok-Yung Yuen. 2017. "Unexpectedly Higher Morbidity and Mortality of Hospitalized Elderly Patients Associated with Rhinovirus Compared with Influenza Virus Respiratory Tract Infection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 2: 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020259
APA StyleHung, I. F. N., Zhang, A. J., To, K. K. W., Chan, J. F. W., Zhu, S. H. S., Zhang, R., Chan, T. -C., Chan, K. -H., & Yuen, K. -Y. (2017). Unexpectedly Higher Morbidity and Mortality of Hospitalized Elderly Patients Associated with Rhinovirus Compared with Influenza Virus Respiratory Tract Infection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(2), 259. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18020259