Bimolecular Rate Constants for FAD-Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase from Aspergillus terreus and Organic Electron Acceptors
Abstract
:1. Introduction
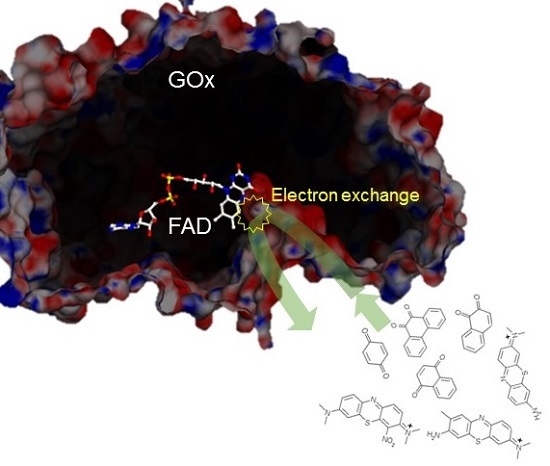
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Homogeneous Redox Reactions of FAD-GDH with the Electron Acceptors
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferri, S.; Kojima, K.; Sode, K. Review of glucose oxidase and glucose dehydrogenases: A bird’s eye view of glucose sensing enzymes. J. Diabetes Sci. Technol. 2011, 5, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsujimura, S.; Kojima, K.; Kano, K.; Ikeda, T.; Sato, M.; Sanada, H.; Omura, H. Novel FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase for a dioxygen-insensitive glucose biosensor. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 654–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.N.; Beden, N.; Leech, D.; Sygmund, C.; Ludwig, R.; Gorton, L. Characterization of different FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenases for possible use in glucose-based biosensors and biofuel cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2012, 402, 2069–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemistry in diabetes management. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Ferri, S.; Huynh, M.L.; Shimazu, H.; Yamaoka, H.; Sode, K. Direct electron transfer type disposable sensor strip for glucose sensing employing an engineered FAD glucose dehydrogenase. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2013, 52, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, I.Y.; Sode, T.; Loew, N.; Tsugawa, W.; Lowe, C.R.; Sode, K. Continuous operation of an ultra-low-power microcontroller using glucose as the sole energy source. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinyou, P.; Ruff, A.; Pöller, S.; Ma, S.; Ludwig, R.; Schuhmann, W. Design of an Os Complex-Modified Hydrogel with Optimized Redox Potential for Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronkainen, N.J.; Halsall, H.B.; Heineman, W.R. Electrochemical biosensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1747–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A.; Feldman, B. Electrochemical Glucose Sensors and Their Applications in Diabetes Management. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2482–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murata, K.; Akatsuka, W.; Sadakane, T.; Matsunaga, A.; Tsujimura, S. Glucose oxidation catalyzed by FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase within Os complex-tethered redox polymer hydrogel. Electrochim. Acta 2014, 136, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsujimura, S.; Murata, K.; Akatsuka, W. Exceptionally high glucose current on a hierarchically structured porous carbon electrode with “wired” flavin adenine dinucleotide-dependent glucose dehydrogenase. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 14432–14437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Fraser, D.M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Gratzel, M. Towards mediator design: Characterization of tris-(4,4′-substituted-2,2′-bipyridine) complexes of iron(II), ruthenium(II) and osmium(II) as mediators for glucose oxidase of Aspergillus niger and other redox proteins. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1992, 337, 253–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakabayashi, Y.; Omayu, A.; Yagi, S.; Nakamura, K.; Motonaka, J. Evaluation of osmium(II) complexes as electron transfer mediators accessible for amperometric glucose sensors. Anal. Sci. 2001, 17, 945–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heller, A. Electron-conducting redox hydrogels; design, characteristics and synthesis. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2006, 10, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zafar, M.N.; Tasca, F.; Boland, S.; Kujawa, M.; Patel, I.; Peterbauer, C.K.; Leech, D.; Gorton, L. Wiring of pyranose dehydrogenase with osmium polymers of different redox potentials. Bioelectrochemistry 2010, 80, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guschin, D.A.; Castillo, J.; Dimcheva, N.; Schuhmann, W. Redox electrodeposition polymers: Adaptation of the redox potential of polymer-bound Os complexes for bioanalytical applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 398, 1661–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milton, R.D.; Hickey, D.P.; Abdellaoui, S.; Lim, K.; Wu, F.; Tan, B.; Minteer, S.D. Rational design of quinones for high power density biofuel cells. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4867–4875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardosi, M.; Phillips, R.; Macfie, G. Electrochemical-Based Analytical Test Strip with Enzymatic Reagent Layer Containing a Naphthoquinone-Based Mediator and FAD-GDH. Patent Pub. No. WO/2016/009018, 21 January 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Takahara, Y.; Nakaminami, T.; Ikeda, S. Sensor and Concentration Measurement Method. Patent Pub. No. WO2011024487 A1, 3 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Sode, K.; Loew, N.; Ohnishi, Y.; Tsuruta, H.; Mori, K.; Kojima, K.; Tsugawa, W.; LaBelle, J.T.; Klonoff, D.C. Novel fungal FAD glucose dehydrogenase derived from Aspergillus niger for glucose enzyme sensor strips. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 87, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwasa, H.; Ozawa, K.; Sasaki, N.; Kinoshita, N.; Hiratsuka, A.; Yokoyama, K. Thermostable FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenases from thermophilic filamentous fungus thermoascus aurantiacus. Electrochemistry 2016, 84, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozawa, K.; Iwasa, H.; Sasaki, N.; Kinoshita, N.; Hiratsuka, A.; Yokoyama, K. Identification and characterization of thermostable glucose dehydrogenases from thermophilic filamentous fungi. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 101, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, K.; Nakajima, M.; Kojima, K.; Murakami, K.; Ferri, S.; Sode, K. Screening of Aspergillus-derived FAD-glucose dehydrogenases from fungal genome database. Biotechnol. Lett. 2011, 33, 2255–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satake, R.; Ichiyanagi, A.; Ichikawa, K.; Hirokawa, K.; Araki, Y.; Yoshimura, T.; Gomi, K. Novel glucose dehydrogenase from Mucor prainii: Purification, characterization, molecular cloning and gene expression in Aspergillus sojae. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 498–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Huang, L.; Wang, J.; Xu, Z. Expression, characterization and mutagenesis of an FAD-dependent glucose dehydrogenase from Aspergillus terreus. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2015, 68, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.Y.; Chang, H.W.; Tsao, M.F.; Chuang, S.M.; Ni, C.C.; Sue, J.W.; Lin, H.C.; Hsu, C.T. Evaluation of accuracy of FAD-GDH- and mutant Q-GDH-based blood glucose monitors in multi-patient populations. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 433, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulys, J.J.; Cenas, N.K. Oxidation of glucose oxidase from Penicillium vitale by one- and two-electron acceptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1983, 744, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albery, W.J.; Cass, A.E.G.; Shu, Z.X. Inhibited enzyme electrodes. Part 1: Theoretical model. Biosens. Bioelectron. 1990, 5, 367–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.A. On the theory of oxidation-reduction reactions involving electron transfer. J. Chem. Phys. 1956, 24, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battaglini, F.; Koutroumanis, M.; English, A.M.; Mikkelsen, S.R. Targeting glucose oxidase at aspartate and glutamate residues with organic two-electron redox mediators. Bioconjug. Chem. 1994, 5, 430–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskovac, V.; Trivic, S.; Wohlfahrt, G.; Kandrac, J.; Pericin, D. Glucose oxidase from Aspergillus niger: The mechanism of action with molecular oxygen, quinones, and one-electron acceptors. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2005, 37, 731–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, H.; Sakai, G.; Mori, K.; Kojima, K.; Kamitori, S.; Sode, K. Structural analysis of fungus-derived FAD glucose dehydrogenase. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okumura, N.; Abo, T.; Tsujimura, S.; Kano, K. Electron transfer between PQQ-dependent soluble glucose dehydrogenase and mediators. Electrochemistry 2006, 74, 639–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Compound | E (V vs. Ag/AgCl (sat. KCl)) | Structure | DM × 106 (cm2·s−1) | log (k2 for FAD-GDH/M−1·s−1) | log (k2 for GOx/M−1·s−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Methyl-1,4-naphthoquinone (MeNQ) | −0.20 |  | 7.0 | 5.7 ± 0.0 | 2.8 |
| Toluidine blue (TB) | −0.19 |  | 2.4 | 6.2 ± 0.1 | 4.3 ± 0.1 |
| AzureA (AA) | −0.19 |  | 3.6 | 6.2 ± 0.0 | 4.1 ± 0.1 |
| 9,10-Phenanthrenequinone (PQ) | −0.18 |  | 6.0 | 8.2 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 0.1 3.6 * |
| Methylene blue (MB) | −0.17 |  | 4.3 | 6.1 ± 0.2 | 3.5 ± 0.0 |
| 1,4-Naphthoquinone (14NQ) | −0.15 |  | 6.1 | 7.1 ± 0.2 | 3.0 ± 0.2 3.5 * |
| Thionine (TH) | −0.14 |  | 2.6 | 7.0 ± 0.0 | 5.1 ± 0.0 |
| Methylene green (MG) | −0.06 |  | 4.3 | 6.5 ± 0.1 | 4.5 ± 0.2 |
| 1,2-Naphthoquinone (12NQ) | −0.05 |  | 6.1 | 8.1 ± 0.2 | 5.5 ± 0.2 5.0 * |
| 1,2-Naphthoquinone-4-sulfonate (NQS) | 0.01 |  | 3.0 | 6.6 ± 0.1 | 4.0 ± 0.1 2.9 * |
| 1,4-Benzoquinone (BQ) | 0.09 |  | 8.4 | 7.9 ± 0.2 | 5.4 ± 0.2 5.2 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsuruoka, N.; Sadakane, T.; Hayashi, R.; Tsujimura, S. Bimolecular Rate Constants for FAD-Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase from Aspergillus terreus and Organic Electron Acceptors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030604
Tsuruoka N, Sadakane T, Hayashi R, Tsujimura S. Bimolecular Rate Constants for FAD-Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase from Aspergillus terreus and Organic Electron Acceptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(3):604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030604
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsuruoka, Nozomu, Takuya Sadakane, Rika Hayashi, and Seiya Tsujimura. 2017. "Bimolecular Rate Constants for FAD-Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase from Aspergillus terreus and Organic Electron Acceptors" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 3: 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030604
APA StyleTsuruoka, N., Sadakane, T., Hayashi, R., & Tsujimura, S. (2017). Bimolecular Rate Constants for FAD-Dependent Glucose Dehydrogenase from Aspergillus terreus and Organic Electron Acceptors. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(3), 604. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030604