Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-equol, Racemic Equol or S-equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Phytochemicals
1.2. Steroid Hormones and Estrogen Receptors: Implications for Phytochemicals
1.3. Publications of: Polyphenolic or Phytoestrogen Molecules
1.4. Resveratrol and Its Metabolism
1.5. Analogs of Resveratrol
1.6. Equol
1.7. Isomers of Equol
1.8. Equol in Plant and Food Products
1.9. Resveratrol and Equol Conjugation
1.10. Resveratrol and Equol Applications for Dermal Health
1.11. Review Topics Covered in this Overview
2. Chemical Structure Comparison of the Polyphenolic/Phytoestrogen Cosmeceuticals to 17β-Estradiol
3. ERα and ERβ Binding Characteristics of 17-βEstradiol Compared to Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, Racemic Equol, S-Equol and R-Equol
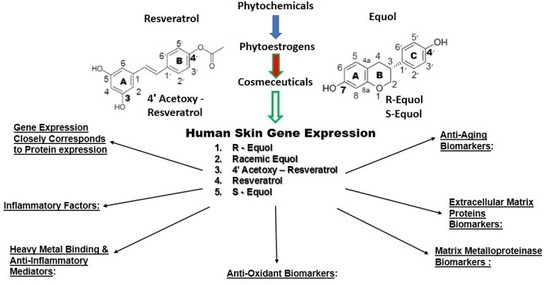
4. Human Skin Gene Expression
4.1. Gene Array (General)
4.2. Cosmeceuticals
4.3. Phase II Metabolism in Skin
4.4. Skin Gene Expression among Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-Equol, Racemic Equol or S-Equol
4.4.1. Background-Gene Arrays of the Cosmeceuticals
4.4.2. Anti-Aging Gene Expression
4.4.3. Extracellular Matrix Proteins
4.4.4. Inhibitor of MMPs (TIMP 1) and Enhancement of Fiber Assembly (LOX)
4.4.5. Matrix Metalloproteinases
4.4.6. Antioxidants
4.4.7. Heavy Metal Binding Proteins and Anti-Inflammatory Mediators
4.4.8. Inflammatory Factors
5. Summary and Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Smith, N.; Shin, D.B.; Brauer, J.A.; Mao, J.; Gelfand, J.M. Use of complementary and alternative medicine among adults with skin disease: Results from a national survey. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2009, 60, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draelos, Z.D. The art and science of new advances in cosmeceuticals. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2011, 38, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reszko, A.; Berson, D.; Lupo, M.P. Cosmeceuticals: Practical applications. Obstet. Gynecol. Clin. North Am. 2010, 37, 547–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowe, W.P.; Pugliese, S. Cosmetic benefits of natural ingredients. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2014, 13, 1021–1025. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kligman, A. The future of cosmeceuticals: An interview with Albert Kligman, MD, Ph.D. Interviewed by Dr. Zoe Diana Draelos. Dermatol. Surg. 2005, 31, 890–981. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Archer, D.F. Postmenopausal skin and estrogen. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 2012, 28, 2–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brincat, M.P.; Baron, Y.M.; Galea, R. Estrogens and skin. Climacteric 2005, 8, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wend, K.; Wend, P.; Krum, S.A. Tissue-specific effects of loss of estrogen during menopause and aging. Front. Endocrinol. 2012, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makrantonaki, E.; Zouboulis, C.C. Androgens and ageing of the skin. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2009, 16, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.O.; Simon, S.; Chae, K.; Metzler, M.; Korach, K.S. Phytoestrogens and their human metabolites show distinct agonistic and antagonistic properties on estrogen receptor α (ERα) and ERβ in human cells. Toxicol. Sci. 2004, 80, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, E.-N.; Deng, G.-F.; Guo, Y.-J.; Li, H.-B. Biological activities of polyphenols from grapes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2010, 11, 622–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuiper, G.C.; Lemmen, J.G.; Carlsson, B.; Corton, J.C.; Safe, S.H.; van der Saaq, P.T.; van der Burg, B.; Gustafsson, J.A. Interaction of estrogenic chemicals and phytoestrogens with estrogen receptor β. Endocrinology 1998, 139, 4252–4263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, M.; Cai, L.; Udeani, G.O.; Slowing, K.V.; Thomas, C.F.; Beecher, C.W.; Fong, H.H.; Farnsworth, N.R.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Mehta, R.G.; et al. Cancer chemopreventive activity of resveratrol, a natural product derived from grapes. Science 1997, 275, 218–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D. Skin aging and oxidative stress: Equol’s anti-aging effects via biochemical and molecular mechanisms. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 31, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walle, T.; Hsieh, R.; DeLegge, M.H.; Oatis, J.E., Jr.; Walle, U.K. High absorption but very low bioavailability of oral resveratrol in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2004, 32, 1377–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.R.; Clerici, C. Equol: History, chemistry, and formation. J. Nutr. 2010, 140, 1355S–1362S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, J.H.; Seok, J.K.; An, S.M.; Baek, J.H.; Koh, J.S.; Boo, Y.C. A study of the human skin-whitening effects of resveratryl triacetate. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acerson, M.J.; Fabick, K.M.; Wong, Y.; Blake, C.; Lephart, E.D.; Andrus, M.B. A new synthesis of 4′-resveratrol ester and evaluation of the potential for anti-depressent activity. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 2941–2944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, R.A. Anti-aging properties of resveratrol: Review and report of a potent new antioxidant skin care formulation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2008, 7, 2–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farris, P.A.; Krutmann, J.; Li, Y.-H.; McDaniel, D.; Krol, Y. Resveratrol: A unique antioxidant offering a multi-mechanistic approach for treating aging skin. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2013, 12, 1389–1394. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ndiaye, M.; Philippe, C.; Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. The grape antioxidant resveratrol for skin disorders: Promise, prospects and challenges. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meierhenrich, U.J. Amino Acids and the Asymmetry of Life; Springer: Heidelberg/Berlin, Germany; New York, NY, USA, 2008; ISBN 354076885. [Google Scholar]
- Strong, M. FDA policy and regulation of stereoisomers: Paradigm shift and the future of safer, more effective drugs. Food Drug Law J. 1999, 54, 463–487. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schwen, R.J.; Nguyen, L.; Jackson, R.L. Elucidation of the metabolic pathway of S-equol in rat, monkey and man. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2012, 50, 2074–2083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, A.; Bonner, M.Y.; Arbiser, J.L. Use of polyphenolic compounds in dermatologic oncology. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2016, 17, 369–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D. Modulation of aromatase by phytoestrogens. Enzyme Res. 2015, 2015, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopaul, R.; Knaggs, H.; Lephart, E.D. Biochemical investigation and gene analysis of equol: A plant and soy-derived isoflavonoid with anti-aging and anti-oxidant properties with potential human skin applications. Biofactors 2012, 38, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grace, M.H.; Esposito, D.; Dunlap, K.L.; Lila, M.A. Comparative analysis of phenolic content and profile, antioxidant capacity, and anti-inflammatory bioactivity in wild Alaskan and commercial Vaccinium berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 4007–4017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lila, M.A. The nature-versus-nurture debate of bioactive phytochemicals: The genome versus terroir. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 86, 2510–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaya, J.; Tamir, S. The relationship between the chemical structure of flavonoids and their estrogen-like activities. Curr. Med. Chem. 2004, 11, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, S.; Kim, H.; Darley-Usmar, V.; Patel, R.; Xu, J.; Boersma, B.; Luo, M. Beyond ERα and ERβ: Estrogen receptor binding is only part of the isoflavone story. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 656S–657S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enmark, E.; Gustafsson, J.-A. Oestrogens receptors-an overview. J. Inter. Med. 1999, 246, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robb, E.L.; Stuart, J.A. Resveratrol interacts with estrogen receptor-β to inhibit cell replicative growth and enhance stress resistance by upregulating mitochondrial superoxidase dismutase. Free Rad. Biol. Med. 2011, 50, 821–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, S.; Levenson, A.S.; Biswas, P.K. Structural insights into resveratrol’s antagonist and partial agonist actions on estrogen receptor α. BMC Struct. Biol. 2013, 13, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronghe, A.; Chatterjee, A.; Singh, B.; Dandawate, P.; Murphy, L.; Bhat, N.K.; Padhye, S.; Bhat, H.K. Differential regulation of estrogen receptors α and β by 4-E-((4-hydroxyphenylimino)-methybenzene, 1,2-diol), a novel resveratrol analog. J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2014, 144, 500–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setchell, K.D.R.; Clerici, C.; Lephart, E.D.; Cole, S.J.; Heenan, C.; Castellani, D.; Wolfe, B.E.; Nechemias-Zimmer, L.; Brown, N.M.; Lund, T.D.; et al. S-equol, a potent ligand for estrogen receptor β, is the exclusive enantiomeric form of the soy isoflavone metabolite produced by human intestinal bacterial flora. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2005, 81, 1072–1079. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Morito, K.; Hirose, T.; Kinjo, J.; Hirakawa, T.; Okawa, M.; Nohara, T.; Ogawa, S.; Inoue, S.; Muramatsu, M.; Masamune, Y. Interactions of phytoestrogens with estrogen receptors α and β. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 351–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kostelac, D.; Rechkemmer, G.; Briviba, K. Phytoestrogens modulate binding response to estrogen receptors α and β to the estrogen response element. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 7632–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthyala, R.S.; Ju, Y.H.; Sheng, S.; Williams, L.D.; Doerge, D.R.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Helferich, W.G.; Katzenenllenbogen, J.A. Equol, a natural estrogenic metabolite from soy isoflavones: Convenient preparation and resolution of R- and S-equols and their differing binding and biological activity through estrogen receptors alpha and β. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 1559–1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, J.; Gustafsson, J.A. Estrogen signaling: A subtle balance between ERα and ERβ. Mol. Inter. 2003, 3, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fox, E.M.; Davis, R.J.; Shupnik, M.A. ERβ in breast cancer-onlooker, passive player, or active protector? Steroids 2008, 73, 1039–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roger, P.; Sahla, M.E.; Makela, S.; Gustafsson, J.A.; Baldet, P.; Rochefort, H. Decreased expression of estrogen receptor β protein in proliferative preinvasive mammary tumors. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 2537–2541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Leygue, E.; Dotzlaw, H.; Watson, P.H.; Murphy, L.C. Altered estrogen receptor alpha and β messenger RNA expression during human breast tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 1998, 58, 3197–3201. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ellem, S.J.; Risbridger, G.P. The dual, opposing role of estrogens in the prostate. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2009, 1155, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thornton, M.J. Estrogens and aging skin. Dermatol. Endocrinol. 2013, 5, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier-Sevrain, S.; Bonte, F.; Gilchrest, B. Biology of estrogens in skin: Implications for skin aging. Exp. Dermatol. 2006, 15, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zouboulis, C.C.; Chen, W.-C.; Thornton, J.M.; Win, K.; Rosenfield, R. Sexual hormones in human skin. Horm. Metab. Res. 2007, 39, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blumenberg, M. DNA microarrays in dermatology and skin biology. OMICS 2006, 10, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.; Friedman, A. Skin barrier health: Regulation and repair of the stratum corneum and the role of over-the-counter skin care. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2016, 15, 1047–1051. [Google Scholar]
- Farris, P.K. Innovative cosmeceuticals: Sirtuin activators and anti-glycation compounds. Semin. Cutan. Med. Surg. 2011, 30, 163–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levin, J.; del Rosso, J.Q.; Momin, S.B. How much do we really know about our favorite cosmeceutical ingredients? J. Clin. Aesthet. Dermatol. 2010, 3, 22–41. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Flamini, R.; Fulvio, M.; de Rosso, M.; Arapitsas, P.; Bavaresco, L. Advanced knowledge of three important classes of grape phenolics: Anthoxyanins, stilbenes and flavonols. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 19651–19669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bak, M.J.; Truong, V.L.; Kang, H.S.; Jun, M.; Jeong, W.S. Anti-inflammatory effect of procyanidins from wild grape (Vitis amurensis) seeds in LPS-induced RAW 264.7 cells. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2013, 2013, 409321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagas, M.K.; Akhtar, N.; Mustafa, R.; Jamshaid, M.; Khan, H.M.S.; Murtaza, G. Dermatological and cosmeceutical benefits of Glycine max (soybean) and it active components. Acta Pol. Pharam. 2015, 71, 3–11. [Google Scholar]
- Lephart, E.D. Protective effects of equol and their polyphenolic isomers against dermal aging: Microarray/protein evidence with clinical implications and unique delivery into human skin. Pharm. Biol. 2013, 51, 1393–1400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D.; Sommerfeldt, J.M.; Andrus, M.B. Resveratrol: Influences on gene expression in human skin. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lephart, E.D.; Acerson, M.J.; Andrus, M.B. Synthesis and skin gene analysis of 4′-acetoxy-resveratrol (4AR), therapeutic potential for dermal applications. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 3258–3262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manevski, N.; Swart, P.; Balavenkatraman, K.K.; Bertschi, B.; Camenisch, G.; Kretz, O.; Schiller, H.; Walles, M.; Ling, B.; Wettstein, R.; et al. Phase II metabolism in human skin: Skin explants show full coverage for glucuronidation, sulfation, N-acetylation, catechol methylation, and glutathione conjugation. Drug Metab. Dispos. 2015, 43, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polonini, H.C.; Lima, L.L.; Goncalves, K.M.; do Carmo, A.M.R.; da Silva, A.D.; Raposo, N.R.B. Photoprotective activity of resveratrol analogues. Bioorang. Med. Chem. 2013, 21, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtkooper, R.H.; Pirinen, E.; Auwerx, J. Sirtuins as regulators of metabolism and healthspan. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2012, 13, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.-C.; Guarente, L. SIRT 1 and other sirtuins in metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. 2014, 25, 138–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davinelli, S.; Nadia, S.; Visentin, M.; Zella, D.; Scapagnini, G. Enhancement of mitochondrial biogenesis with polyphenols: Combined effects of resveratrol and equol in human endothelial cells. Immun. Aging 2013, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-S.; Park, K.-Y.; Min, H.-G.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, J.-J.; Choi, J.-S.; Kim, W.-S.; Cha, H.-J. Negative regulation of stress-induced matrix metalloproteinase-9 by SIRT 1 in skin tissue. Exp. Dermatol. 2010, 19, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohguchi, K.; Itoh, T.; Akao, Y.; Inoue, H.; Nozawa, Y.; Ito, M. SIRT 1 modulates expression of matrix metalloproteinases in human dermal fibroblasts. Br. J. Dermatol. 2010, 163, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goukassian, G.; Gad, F.; Yaar, M.; Eller, M.S.; Nahal, U.S.; Gilchrest, B.A. Mechanisms and implications of the age-associated decrease in DNA repair capacity. FASEB J. 2000, 14, 1325–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takahashi, Y.; Moriwaki, S.; Sugiyama, Y.; Yamazaki, Y.E.-K.; Mori, T.; Takigawa, M. Decreased gene expression responsible for post-ultraviolet DNA repair synthesis in aging: A possible mechanism fo age-related reduction in DNA repair capacity. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 124, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schultz-Norton, J.R.; Gabisi, V.A.; Ziegler, Y.S.; McLeod, I.X.; John, R.; Yates, J.R.; Nardulli, A.M. Interaction of estrogen receptor α with proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Nucl. Acids Res. 2007, 35, 5028–5038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Yu, J.; Kallen, C.B. Two estrogen response element sequences near the PCNA gene are not responsible for its estrogen-enhance expression in MCF7 cells. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e3523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marconi, A.; Terracina, M.; Fila, C.; Franchi, J.; Bonte, F.; Romagnoli, G.; Maurelli, R.; Failla, C.M.; Dumas, M.; Pincelli, C. Expression and function of neurotrophins and their receptors in cultured human keratinocytes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2003, 121, 1515–1521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nithy, M.; Suguna, S.; Rose, C. The effect of nerve growth factor on the early responses during the process of wound healing. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2003, 1620, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaar, M.; Grossman, K.; Eller, M.; Gilchrest, B.A. Evidence for nerve growth factor-mediated paracrine effects in human epidermis. J. Cell Biol. 1991, 115, 821–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, S.; Yarr, M.; Doyle, S.M.; Gilchrest, B.A. Nerve growth factor rescues pigment cells from ultraviolet-induced apoptosis by upregulating BCL-2 levels. Exp. Cell Res. 1996, 224, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toran-Allerand, C.D. Developmental interactions of estrogens, neurotrophins and their receptors. Chapter 17. In Neurobiological Effects of Steroid Hormones; Micevych, P.E., Hammer, R.P., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995; pp. 391–411. [Google Scholar]
- Merot, Y.; Ferriere, F.; Debroas, E.; Flouriot, G.; Duval, D.; Saligaut, C. Estrogen receptor α mediates neuronal differentiation and neuroprotection in PC12 cells: Critical role of A/B domain of the receptor. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjorling, D.E.; Beckman, M.; Clayton, M.K.; Wang, Z.Y. Modulation of nerve growth factor in peripheral organs by estrogen and progesterone. Neuroscience 2002, 110, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.J.; Cha, J.H.; Lim, K.M.; Lee, O.-K.; Bae, S.; Kim, C.-H.; Lee, K.-H.; Ahn, K.J. Analysis of the microRNA expression profile of normal human dermal papilla cells treated with 5α-dihydrotestosterone. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 1205–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, R.J.; Wilson, J.D. Steroid 5α-reductase in cultured human fibroblasts. Biochemical and genetic evidence for two distinct enzyme activities. J. Biol. Chem. 1976, 251, 5895–5900. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Azzouni, F.; Godoy, A.; Li, Y.; Mohler, J. The 5α-reductase isozyme family: A review of basic biology and their role in human diseases. Adv. Urol. 2012, 2012, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lephart, E.D. Review: Anti-oxidant and anti-aging properties of equol in prostate health (BPH). Open J. Endocr. Metab. Dis. 2014, 4, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aochi, S.; Tsuji, K.; Sakaguchi, M.; Huh, N.; Tsuda, T.; Yamanishi, K.; Komine, M.; Iwatsuki, K. Markedly elevated serum levels of calcium binding S100A8/A9 proteins in psoriatic arthritis are due to activated monocytes/macrophages. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2011, 64, 879–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.; Jang, S.; Min, J.K.; Lee, K.; Sohn, K.C.; Lim, J.S.; Im, M.; Lee, H.E.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, C.D.; et al. S100A8 and S100A9 are messengers in the crosstalk between epidermis and dermis modulating a psoriatic milieu in human skin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 423, 647–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mischke, D.; Korge, B.P.; Marenholz, I.; Volz, A.; Ziegler, A. Genes encoding structural proteins of epidermal cornification and S100 calcium-binding proteins from a gene complex (“epidermal differential complex”) on human chromosome 1q21. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1996, 106, 989–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kypriotou, M.; Huber, M.; Hohl, D. The human epidermal differentiation complex: Cornified envelope precursors, S100 proteins and the “fused genes” family. Exp. Dermatol. 2012, 21, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Y.I.; Wang, A.; Mo, J. S100A8/A9 is associated with estrogen receptor loss in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarvari, M.; Hrabovszky, E.; Kallo, I.; Solymosi, N.; Toth, K.; Liko, I.; Szeles, J.; Maho, S.; Molnar, B.; Liposits, Z. Estrogens regulate neuroinflammatory genes via estrogen receptors α and β in the frontal cortex of middle-aged rats. J. Neuroinflam. 2011, 8, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.K.; Simpson, A.; Steer, R.; Cain, S.A.; Kielty, C.M. Elastic fibrers in health and disease. Expert Rev. Mol. Med. 2013, 15, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Draelos, Z.D.; Puglises, P.T. Physiology of the Skin, 3rd ed.; Allurebooks: Carol Stream, IL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Maibach, H.I. Degenerative changes in aging skin. In Textbook of Skin Aging; Farage, M.A., Miller, K.W., Mailbach, H.I., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 225–235. [Google Scholar]
- Hornebeck, W. Down-regulation of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP 1) in aged human skin contributes to matrix degeneration and impaired cell growth and survival. Pathol. Biol. 2003, 51, 569–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, L.D.; Abe, M.; Yokoyama, Y.; Ishikawa, O. Effects of 17β-estradiol on matrix metalloproteinase-1 synthesis by human dermal fibroblasts. Maturitas 2006, 54, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilsson, U.; Garvin, S.; Dabrosin, C. MMP-2 and MMP-9 activity is regulated by estradiol and tamoxifen in cultured human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. 2007, 102, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breckon, J.J.W.; Papaioannou, S.; Kon, L.W.M.; Tumber, A.; Hembry, R.M.; Murphy, G.; Reynolds, J.J.; Meikle, M.C. Stromelysin (MMP-3) synthesis is up-regulated in estrogen-deficient mouse osteoblasts in vivo and in vitro. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1999, 14, 1880–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voloshenyuk, T.G.; Gardner, J.D. Estrogen improves TIMP-MMP balance and collagen distribution in volume-overloaded hearts of ovariectomized females. Am. J. Physiol. Reg. Integr. Comp. 2010, 299, R683–R693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gold, S.M.; Sasidhar, M.V.; Morales, L.B.; Du, S.; Sicotte, N.L.; Tiwari-Woodruf, S.K.; Voshuhl, R.R. Estrogen treatment decreases matrix metalloproteinase (MMP-9) in autoimmune demyelinating disease through estrogen receptor alpha (ERα). Lab. Investig. 2009, 89, 1076–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noblesse, E.; Cenizo, V.; Bouez, C.; Borel, A.; Gleyzal, C.; Peyrol, S.; Jacob, M.P.; Sommer, P.; Damour, O. Lysyl oxidase-like and lysyl oxidase are present in the dermis and epidermis of a skin equivalent and in human skin and are associated to elastic fibers. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2004, 122, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucero, H.A.; Kagan, H.M. Lysyl oxidase: An oxidative enzyme and effector of cell function. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 2304–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenizo, V.; Andre, V.; Reymermier, C.; Sommer, P.; Damour, O.; Perrier, E. LOXL as a target to increase the elastin content in adult skin: A dill extract induces the LOXL gene expression. Exp. Derm. 2006, 15, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohm, B.; Cenizo, V.; Andre, V.; Zahouani, H.; Pailler-Mattei, C.; Vogelgesang, B. Evaluation of the efficacy of a dill extract in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Cosmet. 2011, 33, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zong, W.; Jiang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, J.; Gao, J.-G. Estradiol plays a role in regulating the expression of lysyl oxidase family genes in mouse urogenital tissues and human Ishikawa cells. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 857–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seltzer, J.L.; Eisen, A.Z. The role of extracellular matrix metalloproteinases in connective tissue remodeling. Chapter 17. In Fitzpatrick’s Dermatology in General Medicine, 6th ed.; Freedberg, I.M., Eisen, A.Z., Wolff, K., Austen, K.F., Goldsmith, L.A., Katz, S.I., Eds.; McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2003; Volume 1, pp. 200–209. [Google Scholar]
- Beyer, T.A.; Keller, U.; Braun, S.; Schafer, M.; Werner, S. Roles and mechanisms of action of the Nrf2 transcription factor in skin morphogenesis, wound repair and skin cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2007, 14, 1250–1554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenwald, M.B.Y.; Frusic-Zlotkin, M.; Soroka, Y.; Sasson, S.B.; Bianco-Peled, H.; Bitton, R.; Kohen, R. Nitroxide delivery system for Nrf2 activation and skin protection. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 94, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekhar, K.R.; Freeman, M.L. Nrf2 promotes survival following exposure to ionizing radiation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 88, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liang, X.Y.; Shi, L.Y.; Wang, L.; Chen, J.L.; Kang, C.; Zhu, J.D.; Mi, M.T. Estrogen receptor and PI3K/Akt signaling pathway involvement in S-equol-induced activation of Nrf2/ARE in endothelia cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, P.; Wadhwani, A. Antioxidant Enzymes and Human Health, chapter 1. In Antioxidant Enzyme; El-Missiry, M.A., Ed.; In Tech Science, Technology and Medicine: Vienna, Austria, 2012; pp. 4–18. [Google Scholar]
- Shindo, Y.; Witt, E.; Han, D.; Epstein, W.; Packer, L. Enzymic and non-enzymic antioxidants in epidermis and dermis in human skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1994, 102, 122–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigel, H.; Sigel, A. Metallothioneins and Related Chelators. In Metal Ions in Life Sciences; Sigel, H., Sigel, A., Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Inoue, K.-I.; Takano, H.; Shimada, A.; Satoh, M. Metallothionein as an anti-inflammatory mediator. Med. Inflam. 2009, 2009, 101659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Or, D.; Bar-Or, R.; Rael, L.T.; Brody, E.N. Oxidative stress in severe acute illness. Redox Biol. 2015, 4, 340–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bickers, D.R.; Athar, M. Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of skin disease. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 2565–2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Mazur, M.T.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Intern. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strickland, I.; Rhodes, L.E.; Flanagan, B.F.; Friedmann, P.S. TNFα and IL-8 are upregulated in the epidermis of normal human skin after UVB exposure: Correlation with neurtrophil accumulation and E-selection expression. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1997, 108, 763–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abd-El-Aleem, S.A.; Ferguson, M.A.; Appleton, I.; Bhowmick, A.; McCollum, C.N.; Ireland, G.W. Expression of cyclooxygenase isoforms in normal human skin and chronic venous ulcers. J. Pathol. 2001, 195, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y.; Kanekura, T.; Kanzaki, T. Enhanced expression of cyclooxygenase (COX)-2 in human skin epidermal cancer cells: Evidence for growth suppression by inhibiting COX-2 expression. Intern. J. Cancer 2000, 86, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koussounadis, A.; Langdon, S.P.; Um, I.H.; Harrison, D.J.; Smith, V.A. Relationship between differentially expressed mRNA and mRNA-protein correlations in a xenograft model system. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance form proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2013, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar]
- Lephart, E.D. Human skin gene expression doesn’t correlate with protein expression? Unless both parameters are quantified. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Test Compound | Estrogen Receptor α | Estrogen Receptor β | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| 17β-Estradiol | IC50 = 4.3 nM | IC50 = 5.7 nM | [10] |
| Resveratrol | IC50 = 7.7 µM | IC50 = 29.0 µM | [10] |
| 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | Has not been studied, to date, for ER binding | ||
| Racemic Equol | IC50 = 1.5 µM | IC50 = 0.2 µM | [10] |
| 17β-Estradiol | Kd = 0.13 nM | Kd = 0.15 nM | [36] |
| S-Equol | Ki = 6.4 nM | Ki = 0.7 nM | [36] |
| R-Equol | Ki = 27.4 nM | Ki = 15.4 nM | [36] |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SIRT 1 | Sirtuin 1 | Anti-aging factor | +180 | +335 | NA | ↑ with resveratrol ● | NA |
| PCNA | Proliferating cell nuclear factor | DNA repair | +780 | +540 | +235 | +285 to +300 | +325 |
| NGF | Nerve growth factor | Skin/tissue repair and neurotrophic factor | +800 | +672 | +3350 | +2860 | +1620 |
| 5α-reductase 1 | 5α-reductase type 1 | Converts T to DHT and inhibits dermal health | NSA | NSA | NA | −180 | NA |
| S100 A8 | Calcium-binding protein A8 | Skin aging, inflammation and photoaging | −340 | −270 | −2050 | −2200 | −580 |
| S100 A9 | Calcium-binding protein A9 | Skin aging, inflammation and photoaging | −290 | −160 | −1850 | −2250 | −525 |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| COL I alpha 1 | Collagen type I α1 | Dermal fiber- structural support (most abundant in skin) | +225 | NSA | +210 | +235 | +185 |
| COL III alpha 1 | Collagen type III α1 | Abundant in youth | +230 | +220 | NSA | NSA | NSA |
| COL IV alpha 1 | Collagen type IV α1 | Separates/supports basement membranes | +160 | +170 | NSA | NSA | NSA |
| ELN | Elastin | Fiber-elastic/bounce-back properties | +180 | +280 | +175 | +175 to +190 | +1 |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TIMP 1 | Tissue inhibitor of matrix metallo-proteinase 1 | Enzyme that inhibits actions of MMPs | +215 | +250 | +2 | +200 to +540 | +150 |
| LOX | Lysyl oxidase | Cross links collagen and elastin fibers | +180 | +190 | NA | NA | NA |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MMP 1 | Matrix metallo-proteinase 1 | Breaks down collagens I, II and III | −180 | NA | −890 | −540 | −325 |
| MMP 3 | Matrix metallo-proteinase 3 | Breaks down collagens and elastin | NSA | NA | −885 | −800 | −330 |
| MMP 9 | Matrix metallo-proteinase 9 | Remodels extracellular matrix | −485 | NA | −1375 | −1010 to −1080 | −710 |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAT | Catalase | Antioxidant enzyme protects against oxidative stress and ROS formation | +180 | +160 | NA | NA | NA |
| SOD 1 | Superoxidase dismutase | Antioxidant enzyme protects against oxidative stress and ROS formation | +160 | +160 | NA | NA | NA |
| SOD 2 | Superoxidase dismutase | Same as SOD 1 | +160 | +170 | NA | +200 | NA |
| TXNRD1 | Thioredoxin reductase 1 | Same as SOD 1 and 2; and anti-apoptotic | NSA | NSA | NA | +215 | NA |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MTH 1 | Metallothionein 1 | Heavy metal binding protein and anti-inflammatory mediator | +4100 | +6400 | +2100 | +1800 to +2310 | +3840 |
| MTH 2 | Metallothionein 2 | Same as MTH 1 | +200 | +340 | NA | +510 | NA |
| Gene | Gene Name | Function | Resveratrol | 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol | R-Equol | Racemic Equol | S-Equol |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1A | Interleukin-1A | Inflammatory factor | −2200 | −1010 | −1385 | −1700 | −990 |
| IL-1R2 | Interleukin-1 receptor II | Inflammatory factor | −590 | −190 | −1730 | −2250 | −1675 |
| IL-6 | Interleukin-6 | Inflammatory factor | −3200 | −3520 | −550 | −455 | −375 |
| IL-8 | Interleukin-8 | Inflammatory factor | −790 | −380 | −295 | −345 | −445 |
| TNFR SF 1A | Tumor necrosis factor super family 1A | Inflammatory factor that can activate NF-κB | −160 | −140 | −310 | −250 | −205 |
| COX 1 | Cyclo-oxygenase 1 or prostaglandin- endoperoxide synthase 1 (PTGS1) | Inflammatory factor, prostaglandin production (constitutive) | NSA | NSA | −360 | −265 | −200 |
| COX 2 | Cyclo-oxygenase 2 or prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (PTGS2) | Inflammatory factor (inducible) | NSA | −170 | NA | NA | NA |
© 2017 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lephart, E.D. Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-equol, Racemic Equol or S-equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061193
Lephart ED. Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-equol, Racemic Equol or S-equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061193
Chicago/Turabian StyleLephart, Edwin D. 2017. "Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-equol, Racemic Equol or S-equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061193
APA StyleLephart, E. D. (2017). Resveratrol, 4′ Acetoxy Resveratrol, R-equol, Racemic Equol or S-equol as Cosmeceuticals to Improve Dermal Health. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1193. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061193