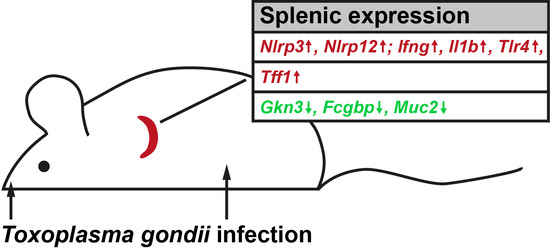
Transcriptional Responses in the Murine Spleen after Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Inflammasome and Mucus-Associated Genes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression Profiling of Mouse Spleen after Oral T. gondii Infection
2.2. Expression Profiling of Mouse Spleen after Intraperitoneal T. gondii Infection
3. Discussion
3.1. T. gondii Infection Induces the Expression of Specific Inflammasomes in the Spleen
3.2. Splenic Tff1 Expression is Induced in Two Models of T. gondii Infection
3.3. Changes of Other Secretory Genes in the Spleen after T. gondii Infection
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Murine T. gondii Infection Models
4.2. DNA and RNA Extraction, PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tarantino, G.; Savastano, S.; Capone, D.; Colao, A. Spleen: A new role for an old player? World J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 17, 3776–3784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, V.; Pittet, M.J. The spleen in local and systemic regulation of immunity. Immunity 2013, 39, 806–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gigliotti, J.C.; Okusa, M.D. The spleen: The forgotten organ in acute kidney injury of critical illness. Nephron. Clin. Pract. 2014, 127, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.J.; Ma, J.; Song, H.Q.; Zhou, D.H.; Wang, J.L.; Huang, S.Y.; Zhu, X.Q. Transcriptomic analysis of global changes in cytokine expression in mouse spleens following acute Toxoplasma gondii infection. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huston, J.M.; Ochani, M.; Rosas-Ballina, M.; Liao, H.; Ochani, K.; Pavlov, V.A.; Gallowitsch-Puerta, M.; Ashok, M.; Czura, C.J.; Foxwell, B.; et al. Splenectomy inactivates the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway during lethal endotoxemia and polymicrobial sepsis. J. Exp. Med. 2006, 203, 1623–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garraud, O.; Borhis, G.; Badr, G.; Degrelle, S.; Pozzetto, B.; Cognasse, F.; Richard, Y. Revisiting the B-cell compartment in mouse and humans: More than one B-cell subset exists in the marginal zone and beyond. BMC Immunol. 2012, 13, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, J.M.; Banks, W.A.; Kastin, A.J. Transport of CRH from mouse brain directly affects peripheral production of β-endorphin by the spleen. Am. J. Physiol. 1997, 273, E1083–E1089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Xing, L.; Li, W.; Hou, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, X. Production and secretion of calcitonin gene-related peptide from human lymphocytes. J. Neuroimmunol. 2002, 130, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite Nde, C.; Montes, E.G.; Fisher, S.V.; Cancian, C.R.; de Oliveira, J.C.; Martins-Pinge, M.C.; Kanunfre, C.C.; Souza, K.L.; Grassiolli, S. Splenectomy attenuates obesity and decreases insulin hypersecretion in hypothalamic obese rats. Metabolism 2015, 64, 1122–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barragan, A.; Sibley, L.D. Migration of Toxoplasma gondii across biological barriers. Trends Microbiol. 2003, 11, 426–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, L.; Courret, N.; Darche, S.; Luangsay, S.; Mennechet, F.; Minns, L.; Rachinel, N.; Ronet, C.; Buzoni-Gatel, D. Toxoplasma gondii and mucosal immunity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunay, I.R.; Sibley, L.D. Monocytes mediate mucosal immunity to Toxoplasma gondii. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010, 22, 461–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.B.; Jensen, K.D.C.; Saeij, J.P.J. Toxoplasma gondii effectors are master regulators of the inflammatory response. Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, T.; Znalesniak, E.B.; Kalinski, T.; Möhle, L.; Biswas, A.; Salm, F.; Dunay, I.R.; Hoffmann, W. TFF peptides play a role in the immune response following oral infection of mice with Toxoplasma gondii. Eur. J. Microbiol. Immunol. 2015, 5, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.J.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.L.; Xu, M.J.; Zhu, X.Q. Analysis of miRNA expression profiling in mouse spleen affected by acute Toxoplasma gondii infection. Infect. Genet. Evol. 2016, 37, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.J.; Ma, J.; Li, F.C.; Song, H.Q.; Xu, M.J.; Zhu, X.Q. Transcriptional changes of mouse splenocyte organelle components following acute infection with Toxoplasma gondii. Exp. Parasitol. 2016, 167, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Guttek, K.; Händel, U.; Reinhold, D.; Hoffmann, W. Increased cerebral TFF1 expression in two murine models of neuroinflammation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2287–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, K.; Tschopp, J. The inflammasomes. Cell 2010, 140, 821–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamkanfi, M.; Dixit, V.M. Inflammasomes and their roles in health and disease. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 137–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Zoete, M.R.; Palm, N.W.; Zhu, S.; Flavell, R.A. Inflammasomes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a016287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF peptides. In Handbook of Biologically Active Peptides, 2nd ed.; Kastin, A., Ed.; Elsevier: San Diego, CA, USA, 2013; pp. 1338–1345. [Google Scholar]
- Cook, G.A.; Familari, M.; Thim, L.; Giraud, A.S. The trefoil peptides TFF2 and TFF3 are expressed in rat lymphoid tissues and participate in the immune response. FEBS Lett. 1999, 456, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, W.; Jagla, W. Cell type specific expression of secretory TFF peptides: colocalization with mucins and synthesis in the brain. Int. Rev. Cytol. 2002, 213, 147–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.-C. Pleiotropic effects of trefoil factor 1 deficiency. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2005, 62, 2916–2920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellev, S. The trefoil factor family—Small peptides with multiple functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2009, 66, 1350–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. Trefoil factor family (TFF) peptides and chemokine receptors: A promising relationship. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 6505–6510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF2, a MUC6-binding lectin stabilizing the gastric mucus barrier and more. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 47, 806–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nam, H.W.; Ahn, H.J.; Yang, H.J. Pro-inflammatory cytokine expression of spleen dendritic cells in mouse toxoplasmosis. Korean J. Parasitol. 2011, 49, 109–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, J.; Lin, X.; Lin, H.; Chen, S.; Liu, J.; Guo, Z.; Liang, Y.; Huang, S.; Lu, F. Upregulated TLR2 and TLR4 expressions in liver and spleen during acute murine T. gondii infection. Parasitol. Res. 2016, 115, 4681–4686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorgi, N.E.; Galisteo, A.J., Jr.; Sato, M.N.; do Nascimento, N.; de Andrade, H.F., Jr. Immunity in the spleen and blood of mice immunized with irradiated Toxoplasma gondii tachyzoites. Med. Microbial. Immunol. 2016, 205, 297–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gov, L.; Karimzadeh, A.; Ueno, N.; Lodoen, M.B. Human innate immunity to Toxoplasma gondii is mediated by host caspase-1 and ASC and parasite GRA15. mBio 2013, 4, e00255-13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyden, E.D.; Dietrich, W.F. Nalp1b controls mouse macrophage susceptibility to anthrax lethal toxin. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, N.A.; Poulsom, R.; Stamp, G.W.; Hall, P.A.; Jeffery, R.E.; Longcroft, J.M.; Rio, M.C.; Tomasetto, C.; Chambon, P. Epidermal growth factor (EGF/URO) induces expression of regulatory peptides in damaged human gastrointestinal tissues. J. Pathol. 1990, 162, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebert, M.P.; Hoffmann, J.; Haeckel, C.; Rutkowski, K.; Schmid, R.M.; Wagner, M.; Adler, G.; Schulz, H.U.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W.; et al. Induction of TFF1 gene expression in pancreas overexpressing transforming growth factor α. Gut 1999, 45, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaoul, R.; Okada, Y.; Cutz, E.; Marcon, M.A. Colonic expression of MUC2, MUC5AC, and TFF1 in inflammatory bowel disease in children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2004, 38, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Oh, Y.; Ha, Y.; Ahn, Q.; Kim, S.H.; Cho, K.D.; Lee, B.H.; Chae, C. Expression of mucins in the mucosal surface of small intestines in 1 week-old pigs. J. Vet. Med. Sci. 2010, 72, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Chwieralski, C.E.; Balder, R.; Hinz, M.; Braun, A.; Krug, N.; Hoffmann, W. Induced trefoil factor family 1 expression by trans-differentiating clara cells in a murine asthma model. Am. J. Respir. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2007, 36, 286–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, W. TFF (trefoil factor family) peptides and their potential roles for differentiation processes during airway remodeling. Curr. Med. Chem. 2007, 14, 2716–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koike, T.; Shimada, T.; Fujii, Y.; Chen, G.; Tabei, K.; Namatame, T.; Yamagata, M.; Tajima, A.; Yoneda, M.; Terano, A.; et al. Upregulation of TFF1 (pS2) expression by TNF-α in gastric epithelial cells. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2007, 22, 936–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirota, M.; Awatsuji, H.; Furukawa, Y.; Hayashi, K. Cytokine regulation of PS2 gene expression in mouse astrocytes. Biochem. Mol. Biol. Int. 1994, 33, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Beck, S.; Sommer, P.; dos Santos Silva, E.; Blin, N.; Gott, P. Hepatocyte nuclear factor 3 (winged helix domain) activates trefoil factor gene TFF1 through a binding motif adjacent to the TATAA box. DNA Cell. Biol. 1999, 18, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribieras, S.; Lefebvre, O.; Tomasetto, C.; Rio, M.C. Mouse trefoil factor genes: Genomic organization, sequences and methylation analyses. Gene 2001, 266, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terada, T.; Sakagami, R.; Tabuchi, Y.; Maeda, M. Characterization of the mouse TFF1 (pS2) gene promoter region. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2001, 24, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hromas, R.; Costa, R. The hepatocyte nuclear factor-3/forkhead transcription regulatory family in development, inflammation, and neoplasia. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 1995, 20, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reeves, E.P.; Ali, T.; Leonard, P.; Hearty, S.; O’Kennedy, R.; May, F.E.; Westley, B.R.; Josenhans, C.; Rust, M.; Suerbaum, S.; et al. Helicobacter pylori lipopolysaccharide interacts with TFF1 in a pH-dependent manner. Gastroenterology 2008, 135, 2043–2054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baus-Loncar, M.; Kayademir, T.; Takaishi, S.; Wang, T. Trefoil factor family 2 deficiency and immune response. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2005, 62, 2947–2955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Cao, L.; Sandor, F.; Rogers, A.B.; Whary, M.T.; Nambiar, P.R.; Cerny, A.; Bowen, G.; Yan, J.; Takaishi, S.; et al. Trefoil family factor 2 is expressed in murine gastric and immune cells and controls both gastrointestinal inflammation and systemic immune responses. Infect. Immun. 2007, 75, 471–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westley, B.R.; Griffin, S.M.; May, F.E. Interaction between TFF1, a gastric tumor suppressor trefoil protein, and TFIZ1, a brichos domain-containing protein with homology to SP-C. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 7967–7975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kouznetsova, I.; Laubinger, W.; Kalbacher, H.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Roessner, A.; Hoffmann, W. Biosynthesis of gastrokine-2 in the human gastric mucosa: Restricted spatial expression along the antral gland axis and differential interaction with TFF1, TFF2 and mucins. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 20, 899–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, T.K.; Laubinger, W.; Muller, S.; Hanisch, F.G.; Kalinski, T.; Meyer, F.; Hoffmann, W. Human intestinal TFF3 forms disulfide-linked heteromers with the mucus-associated FCGBP protein and is released by hydrogen sulfide. J. Proteome Res. 2010, 9, 3108–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menheniott, T.R.; Peterson, A.J.; O’Connor, L.; Lee, K.S.; Kalantzis, A.; Kondova, I.; Bontrop, R.E.; Bell, K.M.; Giraud, A.S. A novel gastrokine, Gkn3, marks gastric atrophy and shows evidence of adaptive gene loss in humans. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 1823–1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, S.N.; Ahmed, R. Lymphoid stroma in the initiation and control of immune responses. Immunol. Rev. 2008, 224, 284–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobayashi, K.; Ogata, H.; Morikawa, M.; Iijima, S.; Harada, N.; Yoshida, T.; Brown, W.R.; Inoue, N.; Hamada, Y.; Ishii, H.; et al. Distribution and partial characterisation of IgG Fc binding protein in various mucin producing cells and body fluids. Gut 2002, 51, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.; Thomsson, K.A.; Hansson, G.C. Proteomic analyses of the two mucus layers of the colon barrier reveal that their main component, the MUC2 mucin, is strongly bound to the FCGBP protein. J. Proteome Res. 2009, 8, 3549–3557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, J.L. FCGBP—A potential viral trap in RV144. Open AIDS J. 2014, 8, 21–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaretsky, A.G.; Silver, J.S.; Siwicki, M.; Durham, A.; Ware, C.F.; Hunter, C.A. Infection with Toxoplasma gondii alters lymphotoxin expression associated with changes in splenic architecture. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 3602–3610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Della Valle, M.C.; Sleat, D.E.; Sohar, I.; Wen, T.; Pintar, J.E.; Jadot, M.; Lobel, P. Demonstration of lysosomal localization for the mammalian ependymin-related protein using classical approaches combined with a novel density shift method. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 35436–35445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmrich, I.; Erdmann, S.; Melchers, U.; Chtarbova, S.; Finke, U.; Hentsch, S.; Hoffmann, I.; Oertel, M.; Hoffmann, W.; Müller, O. The novel ependymin related gene UCC1 is highly expressed in colorectal tumor cells. Cancer Lett. 2001, 165, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Genes | Accession No. | Primer No. | Primer Pairs | Nucleotide Positions | Tm | Size (bp) | Intron Spanning |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fcgbp | NM_001122603.1 | MB1516 | CCAAAACCTGGAGATGAGGA | 6215–6234 | 60 °C | 621 | Yes |
| MB1517 | CAGGCTACGGCAGAGATAGG | 6835–6816 | |||||
| Gkn3 | NM_026860.1 | MB2656 MB2657 | TGGTCAGCATCCGAGACAAC CATGAGTCTGGGTCCATCGT | 270–289 612–593 | 60 °C | 343 | Yes |
| Muc2 | NM_023566.3 | MB2660 MB2661 | GCTCTTTCTTCCTACGCCCG CATGAAGGTATGGTCAGGGC | 1913–1933 2141–2122 | 60 °C | 228 | Yes |
| Nlrp12 | NM_001033431.1 | MB2606 MB2607 | CCCGTTACTTTGTCCCCCAT CACGCTGATTGGCTCTCAAAA | 184–203 536–516 | 60 °C | 353 | Yes |
| Tlr4 | NM_021297.3 | MB1687 | AGAAAATGCCAGGATGATGC | 269–288 | 60 °C | 417 | Yes |
| MB1688 | GTCTCCACAGCCACCAGATT | 685–666 | |||||
| T. g. RH repeat region | AF487550.1 | MB2066 MB2067 | ACTACAGACGCGATGCCGCTC CTCTCCGCCATCACCACGAGGAA | 107–127 328–306 | 60 °C | 222 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Znalesniak, E.B.; Fu, T.; Salm, F.; Händel, U.; Hoffmann, W. Transcriptional Responses in the Murine Spleen after Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Inflammasome and Mucus-Associated Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061245
Znalesniak EB, Fu T, Salm F, Händel U, Hoffmann W. Transcriptional Responses in the Murine Spleen after Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Inflammasome and Mucus-Associated Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(6):1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061245
Chicago/Turabian StyleZnalesniak, Eva B., Ting Fu, Franz Salm, Ulrike Händel, and Werner Hoffmann. 2017. "Transcriptional Responses in the Murine Spleen after Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Inflammasome and Mucus-Associated Genes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 6: 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061245
APA StyleZnalesniak, E. B., Fu, T., Salm, F., Händel, U., & Hoffmann, W. (2017). Transcriptional Responses in the Murine Spleen after Toxoplasma gondii Infection: Inflammasome and Mucus-Associated Genes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(6), 1245. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18061245