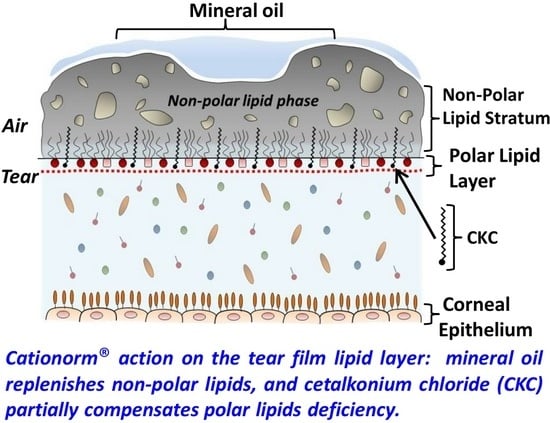
Surface Chemistry Interactions of Cationorm with Films by Human Meibum and Tear Film Compounds
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Surface Pressure/Area Isotherms and Macroscopic Evaluation of CN/Tear Lipid Film Structure
2.2. Quantitative Analysis of MGS/CN Miscibility
2.3. Dilatational Rheology
3. Discussion
3.1. Interaction of CN with MGS Layers at Film Compression. Correlation with CN/TFLL Interactions In Vivo
3.2. Analysis of CN/MGS Films Viscoelasticity
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Langmuir Trough Studies
4.2.1. Compression Isotherms
4.2.2. Stress-Relaxation Studies via the Small Deformations Method
4.3. TFLL Observations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| TF | Tear film |
| TFLL | Tear film lipid layer |
| MGS | Meibomian gland secretion (or simply meibum) |
| CKC | Cetalkonium chloride (C16) |
| BAK | Benzalkonium chloride (C12) |
| CN | Cationorm |
| CNE | Cationic nanoemulsion |
| DES | Dry eye syndrome |
| AT | Aqueous tear |
| PL | Polar lipid |
| NPL | Nonpolar lipid |
| MO | Mineral oil |
| BAM | Brewster angle microscopy |
References
- Gayton, J.L. Etiology, prevalence, and treatment of dry eye disease. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2009, 3, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Asche, C.V.; Fairchild, C.J. The economic burden of dry eye disease in the United States: A decision tree analysis. Cornea 2011, 30, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDonald, M.; Patel, D.A.; Keith, M.S.; Snedecor, S.J. Economic and Humanistic Burden of Dry Eye Disease in Europe, North America, and Asia: A Systematic Literature Review. Ocul. Surf. 2016, 14, 144–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lemp, M.A.; Crews, L.A.; Bron, A.J.; Foulks, G.N.; Sullivan, B.D. Distribution of aqueous-deficient and evaporative dry eye in a clinic-based patient cohort: A retrospective study. Cornea 2012, 31, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, S.M.; Tong, L.; Duan, X.; Petznick, A.; Wenk, M.R.; Shui, G. Extensive characterization of human tear fluid collected using different techniques unravels the presence of novel lipid amphiphiles. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butovich, I.A.; Lu, H.; McMahon, A.; Eule, J.C. Toward an Animal Model of the Human Tear Film: Biochemical Comparison of the Mouse, Canine, Rabbit, and Human Meibomian Lipidomes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 6881–6896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mochizuki, H.; Yamada, M.; Hatou, S.; Tsubota, K. Turnover rate of tear-film lipid layer determined by fluorophotometry. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2009, 93, 1535–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, E. Quantification of tear interference image: Tear fluid surface nanotechnology. Cornea 2004, 23, S20–S24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The definition and classification of dry eye disease: Report of the definition and classification subcommittee of the international dry eye workshop. Ocul. Surf. 2007, 5, 75–92.
- Sall, K.; Stevenson, O.D.; Mundorf, T.K.; Reis, B.L. Two multicenter, randomized studies of the efficacy and safety of cyclosporine ophthalmic emulsion in moderate to severe dry eye disease. CsA Phase 3 Study Group. Ophthalmology 2000, 107, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonardi, A.; VanSetten, G.; Amrane, M.; Ismail, D.; Garrigue, J.S.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Baudouin, C. Efficacy and safety of 0.1% cyclosporine A cationic emulsion in the treatment of severe dry eye disease: A multicenter randomized trial. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 26, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fogt, J.S.; Kowalski, M.J.; King-Smith, P.E.; Epitropolous, A.T.; Hendershot, A.J.; Lembach, C.; Maszczak, J.P.; Jones-Jordan, L.A.; Barr, J.T. Tear lipid layer thickness with eye drops in meibomian gland dysfunction. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2016, 10, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lallemand, F.; Daull, P.; Benita, S.; Buggage, R.; Garrigue, J.S. Successfully Improving Ocular Drug Delivery Using the Cationic Nanoemulsion. J. Drug Deliv. 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daull, P.; Lallemand, F.; Philips, B.; Lambert, G.; Buggage, R.; Garrigue, J.S. Distribution of cyclosporine A in ocular tissues after topical administration of cyclosporine A cationic emulsions to pigmented rabbits. Cornea 2014, 32, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daull, P.; Feraille, L.; Barabino, S.; Cimbolini, N.; Antonelli, S.; Mauro, V.; Garrigue, J.S. Efficacy of a new topical cationic emulsion of cyclosporine A on dry eye clinical signs in an experimental mouse model of dry eye. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 153, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daull, P.; Lallemand, F.; Garrigue, J.S. Benefits of cetalkonium chloride cationic oil-in-water nanoemulsions for topical ophthalmic drug delivery. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2014, 66, 531–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudouin, C.; Figueiredo, F.C.; Messmer, E.M.; Ismail, D.; Amrane, M.; Garrigue, J.S.; Bonini, S.; Leonardi, A. A randomized study of the efficacy and safety of 0.1% cyclosporine A cationic emulsion in treatment of moderate to severe dry eye. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 26, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baudouin, C.; Labbé, A.; Liang, H.; Pauly, A.; Brignole-Baudouin, F. Preservatives in eyedrops: The good, the bad and the ugly. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2010, 29, 312–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Yokoi, N.; Koev, K.; Kutsarova, E.; Ivanova, S.; Kyumurkov, A.; Jordanova, A.; Krastev, R.; Lalchev, Z. Surface Chemistry Study of theInteractions of Benzalkonium Chloride with Films of Meibum, Corneal Cells Lipids and Whole Tears. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 4645–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Yokoi, N.; Ivanova, S.; Krastev, R.; Lalchev, Z. Surface Chemistry Study of the Interactions of Pharmaceutical Ingredients and Whole Eyedrops with Films of Human Meibum. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4605–4615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Yokoi, N.; Ivanova, S.; Dimitrov, T.; Andreev, K.; Krastev, R.; Lalchev, Z. Surface chemistry study of the interactions of hyaluronic acid and benzalkonium chloride with meibomian and corneal cell lipids. Soft Matter 2013, 9, 10841–10856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wollmer, P. Air pollutants and tear film stability—A method for experimental evaluation. Clin. Physiol. 2001, 21, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amrane, M.; Creuzot-Garcher, C.; Robert, P.Y.; Ismail, D.; Garrigue, J.S.; Pisella, P.J.; Baudouin, C. Ocular tolerability and efficacy of a cationic emulsion in patients with mild to moderate dry eye disease—Arandomised comparative study. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2014, 37, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robert, P.Y.; Cochener, B.; Amrane, M.; Ismail, D.; Garrigue, J.S.; Pisella, P.J.; Baudouin, C. Efficacy and safety of a cationic emulsion in the treatment of moderate to severe dry eye disease: A randomized controlled study. Eur. J. Ophtalmol. 2016, 26, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Yokoi, N.; Ivanova, S.; Tonchev, V.; Nencheva, Y.; Krastev, R. Surface relaxations as a tool to distinguish the dynamic interfacial properties of films formed by normal and diseased meibomian lipids. Soft Matter 2014, 10, 5579–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, S.; Tonchev, V.; Yokoi, N.; Yappert, M.C.; Borchman, D.; Georgiev, G.A. Surface Properties of Squalene/Meibum Films and NMR Confirmation of Squalene in Tears. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 21813–21831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrov, P.G.; Thompson, J.M.; Rahman, I.B.; Ellis, R.E.; Green, E.M.; Miano, F.; Winlove, C.P. Two-dimensional order in mammalian pre-ocular tear film. Exp. Eye Res. 2007, 84, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arciniega, J.C.; Nadji, E.J.; Butovich, I.A. Effects of free fatty acids on meibomian lipid films. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butovich, I.A. Tear film lipids. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 117, 4–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, E.; Dogru, M.; Kojima, T.; Tsubota, K. Computer-Synthesis of an Interference Color Chart of Human Tear Lipid Layer, by a Colorimetric Approach. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 4693–4697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokoi, N.; Yamada, H.; Mizukusa, Y.; Bron, A.J.; Tiffany, J.M.; Kato, T.; Kinoshita, S. Rheology of tear film lipid layer spread in normal and aqueous tear-deficient dry eyes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 5319–5324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, N.; Bron, A.J.; Georgiev, G.A. The precorneal tear film as a fluid shell: The effect of blinking and saccades on tear film distribution and dynamics. Ocul. Surf. 2014, 12, 252–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, K.S.; Cole, R.H. Dispersion and Absorption in Dielectrics I. Alternating Current Characteristics. J. Chem. Phys. 1941, 9, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cárdenas-Valera, A.E.; Bailey, A.I. The interfacial rheological behaviour of monolayers of PEO/PMMA graft copolymers spread at the air/water and oil/water interfaces. Colloids Surf. A 1993, 19, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschoegl, N. The Modelling of Multimodal Distributions of Respondance Times. In The Phenomenological Theory of Linear Viscoelastic Behavior; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1989; pp. 489–507. [Google Scholar]
- Ferry, J. Viscoelastic Properties of Polymers; Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1981. [Google Scholar]
- Murata, H. Rheology—Theory and Application to Biomaterials. In Polymerization; De Souza Gomes, A., Ed.; InTechOpen: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012; pp. 404–424. [Google Scholar]
- Butovich, I.A. On the lipid composition of human meibum and tears: Comparative analysis of nonpolar lipids. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3779–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green-Church, K.; Butovich, I.; Willcox, M.; Borchman, D.; Paulsen, F.; Barabino, S.; Glasgow, B.J. The international workshop on meibomian gland dysfunction: Report of the subcommittee on tear film lipids and lipid-protein interactions in health and disease. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 1979–1993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Kutsarova, E.; Jordanova, A.; Krastev, R.; Lalchev, Z. Interactions of Meibomian gland secretion with polar lipids in Langmuir monolayers. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 78, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgiev, G.A. Controversies Regarding the Role of Polar Lipids in Human and Animal Tear Film Lipid Layer. Ocul. Surf. 2015, 13, 176–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenfeld, L.; Cerretani, C.; Leiske, D.L.; Toney, M.F.; Radke, C.J.; Fuller, G.G. Structural and rheological properties of meibomian lipid. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 2720–2732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cwiklik, L.; Melcrova, A.; Daull, P.; Garrigue, J.-S. Tear Film Break-Up: A Molecular Level in Silico Approach; 472-A0397; ARVO: Baltimor, MD, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mouritsen, O.G. Thermodynamics of Lipid Interactions. In Encyclopedia of Biophysics; Roberts, G.C.K., Ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 2606–2613. [Google Scholar]
- Georgiev, G.A.; Gurov, R.; Jordanova, A.; Vassilieff, C.S.; Lalchev, Z. Properties of Alkyl-Phosphatidylcholine Monolayers in the Presence of Surface-Active Three-Block Copolymers. Colloids Surf. B 2010, 80, 40–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, B.; Halliday, H.L. Principles of surfactant replacement. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1998, 1408, 346–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daull, P.; Yokoi, N.; Nencheva, Y.; Georgiev, G.A. Surface chemistry of the interactions of cationic nanoemulsions with human meibum films. Acta Opthalmol. 2016, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiffany, J.M.; Winter, N.; Bliss, G. Tear film stability and tear surface tension. Curr. Eye Res. 1989, 8, 507–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, H.; Amaral, M.H.; Lobão, P.; Sousa Lobo, J.M. Applications of poloxamers in ophthalmic pharmaceutical formulations: An overview. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2013, 10, 1223–1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souto, E.B.; Doktorovova, S.; Gonzalez-Mira, E.; Egea, M.A.; Garcia, M.L. Feasibility of lipid nanoparticles for ocular delivery of anti-inflammatory drugs. Curr. Eye Res. 2010, 35, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kinnunen, K.; Kauppinen, A.; Piippo, N.; Koistinen, A.; Toropainen, E.; Kaarniranta, K. Cationorm shows good tolerability on human HCE-2 corneal epithelial cell cultures. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 120, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loglio, G.; Tesei, U.; Cini, R. Viscoelastic dilatation processes of fluid/fluid interfaces: Time-domain representation. Colloid Poly. Sci. 1986, 264, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroy, F.; Ortega, F.; Rubio, R.G. Dilatational rheology of insoluble polymer monolayers: Poly (vinylacetate). Phys. Rev. E Stat. Phys. Plasmas Fluids Relat. Interdiscip. Top. 1998, 58, 7629–7641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skrzypieca, M.; Georgiev, G.A.; Rojewska, M.; Prochaska, K. Interaction of polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxanes and dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine at the air/water interface: Thermodynamic and rheological study. Biochim. Biophysic Acta Binmembr. 2017, 1859, 1838–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, A.; Ruckenstein, E. Mechanism of tear-film rupture and formation of dry spots on cornea. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1985, 106, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svitova, T.F.; Lin, M.C. Racial Variations in Interfacial Behavior of Lipids Extracted from Worn Soft Contact Lenses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2013, 90, 1361–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bron, A.J.; Tiffany, J.M.; Gouveia, S.M.; Yokoi, N.; Voon, L.W. Functional aspects of the tear film lipid layer. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 78, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, N.; Georgiev, G.A.; Kato, H.; Komuro, A.; Sonomura, Y.; Sotozono, C; Tsubota, K.; Kinoshita, S. Classification of Fluorescein Breakup Patterns: A Novel Method of Differential Diagnosis for Dry Eye. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, H.; Fatt, I.; Radke, C.J. Deposition and thinning of the human tear film. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1996, 184, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, E.; Tseng, S.C. Differentiation of lipid tear deficiency dry eye by kinetic analysis of tear interference images. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2003, 121, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eftimov, P.; Yokoi, N.; Tonchev, V.; Nencheva, Y.; Georgiev, G.A. Surface properties and exponential stress relaxations of mammalian meibum films. Eur. Biophys. J. 2016, 46, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagano, R.E.; Gershfeld, N.L. Physical chemistry of lipid films at the air–water interface. II. Binary lipid mixtures. The principles governing miscibility of lipids in surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. 1972, 76, 1238–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barger, W.R.; Means, J.C. Clues to the structure of marine organic material from the study of physical properties of surface films. In Marine and Estuarine Chemistry; Sigleo, A.C., Hattori, A., Eds.; Lewis Publishers: Chelsea, MI, USA, 1985; pp. 47–67. [Google Scholar]
- Flannery, B.P.; Teukolsky, S.; Press, W.H.; Vetterling, W.T. Fast Fourier Transform. In Numerical Recipes in C++; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 501–537. [Google Scholar]
- Erni, P.; Fischer, P.; Windhab, E.J. Sorbitan Tristearate Layers at the Air/Water Interface Studied by Shear and Dilatational Interfacial Rheology. Langmuir 2005, 21, 10555–10563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoi, N.; Takehisa, Y.; Kinoshita, S. Correlation of tear lipid layer interference patterns with the diagnosis and severity of dry eye. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1996, 122, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









| Composition% w/w (µg/µL) | Novasorb Cationic Emulsions(Cationorm) | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Excipients (oil phase) | ||
| Mineral oil (light & heavy) | 0.50 (5 µg/µL) | Oily agent |
| 0.50 (5 µg/µL) | ||
| Cetalkonium chloride | 0.002 (0.02 µg/µL) | Cationic surfactant |
| Excipients (water phase) | ||
| Tyloxapol | 0.30 (3 µg/µL) | Non-ionic surfactant |
| Poloxamer 188 | 0.10 (1 µg/µL) | Non-ionic surfactant |
| Glycerin | 1.60 | Osmotic agent |
| Buffer system (tris-HCl/trometamine) | (0.071/0.006) | Buffer |
| Water for injection | q.s.* | Diluent |
| TOTAL | 100 | |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Georgiev, G.A.; Yokoi, N.; Nencheva, Y.; Peev, N.; Daull, P. Surface Chemistry Interactions of Cationorm with Films by Human Meibum and Tear Film Compounds. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071558
Georgiev GA, Yokoi N, Nencheva Y, Peev N, Daull P. Surface Chemistry Interactions of Cationorm with Films by Human Meibum and Tear Film Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(7):1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071558
Chicago/Turabian StyleGeorgiev, Georgi As., Norihiko Yokoi, Yana Nencheva, Nikola Peev, and Philippe Daull. 2017. "Surface Chemistry Interactions of Cationorm with Films by Human Meibum and Tear Film Compounds" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 7: 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071558
APA StyleGeorgiev, G. A., Yokoi, N., Nencheva, Y., Peev, N., & Daull, P. (2017). Surface Chemistry Interactions of Cationorm with Films by Human Meibum and Tear Film Compounds. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(7), 1558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18071558