Tricetin Induces Apoptosis of Human Leukemic HL-60 Cells through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Tricetin Inhibited Proliferation of Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) Cells
2.2. Tricetin Treatment Results in the Apoptosis of HL-60 AML Cells
2.3. Tricetin Induces Caspase-Dependent Apoptotic Cell Death in HL-60 Cells
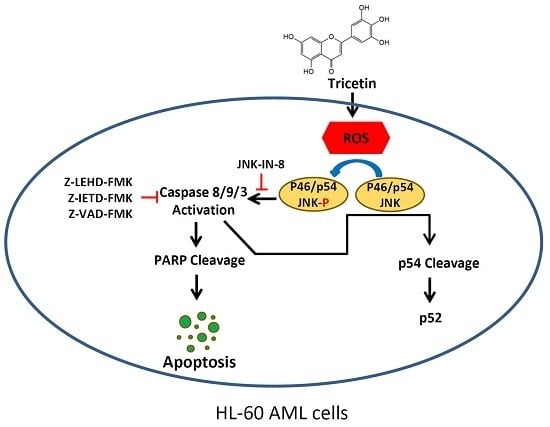
2.4. Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinases Involved in Tricetin-Regulated Apoptotic Cell Death
2.5. Tricetin-Induced Intracellular Oxidative Stress as an Initial Signal for JNK-Mediated Apoptosis in HL-60 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. In Vitro Cytotoxicity Assay
4.4. In Vitro Cell Viability Assay
4.5. Flow Cytometric Analysis of DNA Contents
4.6. 4,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) Staining
4.7. Apoptosis Assays
4.8. Preparation of Total Cell Extracts and Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Measurement of ROS Production
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| DCF | Dichlorofluorescein |
| DMSO | Dimethyl sulfoxide |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| NAC | N-Acetylcysteine |
| PARP | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| PI | Propidium iodide |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
References
- Burnett, A.K.; Hills, R.K.; Milligan, D.W.; Goldstone, A.H.; Prentice, A.G.; McMullin, M.F.; Duncombe, A.; Gibson, B.; Wheatley, K. Attempts to optimize induction and consolidation treatment in acute myeloid leukemia: Results of the MRC AML12 trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 28, 586–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tallman, M.S.; Gilliland, D.G.; Rowe, J.M. Drug therapy for acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 2005, 106, 1154–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estey, E.; Dohner, H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2006, 368, 1894–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Lee, Y.K.; Call, T.G.; Nowakowski, G.S.; Dingli, D.; Zent, C.S.; Kay, N.E. Clinical effects of oral green tea extracts in four patients with low grade B-cell malignancies. Leuk. Res. 2006, 30, 707–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, D.M.; Still, P.C.; Perez, L.B.; Grever, M.R.; Kinghorn, A.D. Potential of plant-derived natural products in the treatment of leukemia and lymphoma. Curr. Drug Targets 2010, 11, 812–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraets, L.; Moonen, H.J.; Brauers, K.; Wouters, E.F.; Bast, A.; Hageman, G.J. Dietary flavones and flavonoles are inhibitors of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 in pulmonary epithelial cells. J. Nutr. 2007, 137, 2190–2195. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Uen, Y.H.; Chen, Y.; Liang, H.L.; Kuo, P.L. Tricetin, a dietary flavonoid, inhibits proliferation of human breast adenocarcinoma MCF-7 cells by blocking cell cycle progression and inducing apoptosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 8688–8695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, Y.L.; Hou, M.F.; Tsai, E.M.; Kuo, P.L. Tricetin, a dietary flavonoid, induces apoptosis through the reactive oxygen species/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathway in human liver cancer cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 12547–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hung, J.Y.; Chang, W.A.; Tsai, Y.M.; Hsu, Y.L.; Chiang, H.H.; Chou, S.H.; Huang, M.S.; Kuo, P.L. Tricetin, a dietary flavonoid, suppresses benzo(a)pyreneinduced human nonsmall cell lung cancer bone metastasis. Int. J. Oncol. 2015, 46, 1985–1993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, P.Y.; Hsieh, M.J.; Hsieh, Y.S.; Chen, P.N.; Yang, J.S.; Lo, F.C.; Yang, S.F.; Lu, K.H. Tricetin inhibits human osteosarcoma cells metastasis by transcriptionally repressing MMP-9 via p38 and Akt pathways. Environ. Toxicol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, R.; Chow, J.M.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chen, C.K.; Lee, W.J.; Hsieh, F.K.; Yu, N.Y.; Chou, M.C.; Cheng, C.W.; Yang, S.F.; et al. Tricetin suppresses the migration/invasion of human glioblastoma multiforme cells by inhibiting matrix metalloproteinase-2 through modulation of the expression and transcriptional activity of specificity protein 1. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmore, S. Apoptosis: A review of programmed cell death. Toxicol. Pathol. 2007, 35, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Safarzadeh, E.; Sandoghchian Shotorbani, S.; Baradaran, B. Herbal medicine as inducers of apoptosis in cancer treatment. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2014, 4, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, A.S.; Hagan, S.; Rath, O.; Kolch, W. MAP kinase signalling pathways in cancer. Oncogene 2007, 26, 3279–3290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, M.; Chambers, T.C. Role of mitogen-activated protein kinases in the response of tumor cells to chemotherapy. Drug Resist. Updates 2001, 4, 253–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Meng, L.; Zhou, J.; Xing, H.; Wang, S.; Xu, G.; Zhu, H.; Wang, B.; Chen, G.; Lu, Y.P.; et al. Reversing chemoresistance in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian cancer cells: A role of c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase 1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 335, 1070–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Wang, X.M.; Liu, Z.C.; Pan, C.; Yuan, S.B.; Ma, Q.M. JNK1, JNK2, and JNK3 are involved in P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2010, 9, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lagadinou, E.D.; Ziros, P.G.; Tsopra, O.A.; Dimas, K.; Kokkinou, D.; Thanopoulou, E.; Karakantza, M.; Pantazis, P.; Spyridonidis, A.; Zoumbos, N.C. c-Jun N-terminal kinase activation failure is a new mechanism of anthracycline resistance in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 2008, 22, 1899–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouyang, L.; Shi, Z.; Zhao, S.; Wang, F.T.; Zhou, T.T.; Liu, B.; Bao, J.K. Programmed cell death pathways in cancer: A review of apoptosis, autophagy and programmed necrosis. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Afaq, F.; Mukhtar, H. Apoptosis by dietary factors: The suicide solution for delaying cancer growth. Carcinogenesis 2007, 28, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chinen, T.; Nagumo, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Imaizumi, T.; Shibuya, M.; Kataoka, T.; Kanoh, N.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Usui, T. Irciniastatin A induces JNK activation that is involved in caspase-8-dependent apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2010, 199, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, P.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Chow, J.M.; Yang, S.F.; Hsiao, M.; Hua, K.T.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, H.Y.; Chien, M.H. Hispolon induces apoptosis through JNK1/2-mediated activation of a caspase-8, -9, and -3-dependent pathway in acute myeloid leukemia (AML) cells and inhibits AML xenograft tumor growth in vivo. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 10063–10073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, P.C.; Lee, W.J.; Yang, S.F.; Tan, P.; Chen, H.Y.; Lee, L.M.; Chang, J.L.; Lai, G.M.; Chow, J.M.; Chien, M.H. Nobiletin suppresses the proliferation and induces apoptosis involving MAPKs and caspase-8/-9/-3 signals in human acute myeloid leukemia cells. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 11903–11911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCubrey, J.A.; Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Wong, E.W.; Chang, F.; Lehmann, B.; Terrian, D.M.; Milella, M.; Tafuri, A.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in cell growth, malignant transformation and drug resistance. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1773, 1263–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Yu, C.R.; Li, W.H.; Li, W.X. Induction of apoptosis by shikonin through a ROS/JNK-mediated process in Bcr/Abl-positive chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML) cells. Cell Res. 2008, 18, 879–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brodska, B.; Holoubek, A. Generation of reactive oxygen species during apoptosis induced by DNA-damaging agents and/or histone deacetylase inhibitors. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2011, 2011, 253529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Hileman, E.O.; Plunkett, W.; Keating, M.J.; Huang, P. Free radical stress in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells and its role in cellular sensitivity to ROS-generating anticancer agents. Blood 2003, 101, 4098–4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, A.T.; Wang, Y.; Chiu, J.F. Reactive oxygen species: Current knowledge and applications in cancer research and therapeutic. J. Cell. Biochem. 2008, 104, 657–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.J.; Hsiao, M.; Chang, J.L.; Yang, S.F.; Tseng, T.H.; Cheng, C.W.; Chow, J.M.; Lin, K.H.; Lin, Y.W.; Liu, C.C.; et al. Quercetin induces mitochondrial-derived apoptosis via reactive oxygen species-mediated ERK activation in HL-60 leukemia cells and xenograft. Arch. Toxicol. 2015, 89, 1103–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimoghaddam, K. A review of arsenic trioxide and acute promyelocytic leukemia. Int. J. Hematol. Oncol. Stem Cell Res. 2014, 8, 44–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yedjou, C.; Tchounwou, P.; Jenkins, J.; McMurray, R. Basic mechanisms of arsenic trioxide (ATO)-induced apoptosis in human leukemia (HL-60) cells. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2010, 3, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baysan, A.; Yel, L.; Gollapudi, S.; Su, H.; Gupta, S. Arsenic trioxide induces apoptosis via the mitochondrial pathway by upregulating the expression of Bax and Bim in human B cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2007, 30, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Lin, S.Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Wu, L.Q.; Chen, Z.Z.; Li, J.; Chen, Z.; Qian, W.B.; Jiang, J.P. Pure total flavonoids from Citrus paradisi Macfadyen act synergistically with arsenic trioxide in inducing apoptosis of Kasumi-1 leukemia cells in vitro. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B 2015, 16, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Chen, M.; Meng, J.; Yu, L.; Tu, Y.; Wan, L.; Fang, K.; Zhu, W. Arsenic trioxide and resveratrol show synergistic anti-leukemia activity and neutralized cardiotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas, E. Mitochondrial free radical production and cell signaling. Mol. Asp. Med. 2004, 25, 17–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottlieb, E.; Vander Heiden, M.G.; Thompson, C.B. Bcl-x(L) prevents the initial decrease in mitochondrial membrane potential and subsequent reactive oxygen species production during tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced apoptosis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 5680–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shim, H.Y.; Park, J.H.; Paik, H.D.; Nah, S.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Han, Y.S. Acacetin-induced apoptosis of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells involves caspase cascade, mitochondria-mediated death signaling and SAPK/JNK1/2-c-Jun activation. Mol. Cells 2007, 24, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Enomoto, A.; Suzuki, N.; Morita, A.; Ito, M.; Liu, C.Q.; Matsumoto, Y.; Yoshioka, K.; Shiba, T.; Hosoi, Y. Caspase-mediated cleavage of JNK during stress-induced apoptosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 306, 837–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steelman, L.S.; Franklin, R.A.; Abrams, S.L.; Chappell, W.; Kempf, C.R.; Basecke, J.; Stivala, F.; Donia, M.; Fagone, P.; Nicoletti, F.; et al. Roles of the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway in leukemia therapy. Leukemia 2011, 25, 1080–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cagnol, S.; Chambard, J.C. ERK and cell death: Mechanisms of ERK-induced cell death—Apoptosis, autophagy and senescence. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zelivianski, S.; Spellman, M.; Kellerman, M.; Kakitelashvilli, V.; Zhou, X.W.; Lugo, E.; Lee, M.S.; Taylor, R.; Davis, T.L.; Hauke, R.; et al. ERK inhibitor PD98059 enhances docetaxel-induced apoptosis of androgen-independent human prostate cancer cells. Int. J. Cancer 2003, 107, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Qian, C.; Shu, T.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, Z.; Liang, Y. Combination treatment of PD98059 and DAPT in gastric cancer through induction of apoptosis and downregulation of WNT/β-catenin. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2013, 14, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Natarajan, K.; Xie, Y.; Baer, M.R.; Ross, D.D. Role of breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2) in cancer drug resistance. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 83, 1084–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, K.W.; Li, Y.; Paxton, J.W.; Birch, N.P.; Scheepens, A. Identification of novel dietary phytochemicals inhibiting the efflux transporter breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP/ABCG2). Food Chem. 2013, 138, 2267–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chien, M.-H.; Chow, J.-M.; Lee, W.-J.; Chen, H.-Y.; Tan, P.; Wen, Y.-C.; Lin, Y.-W.; Hsiao, P.-C.; Yang, S.-F. Tricetin Induces Apoptosis of Human Leukemic HL-60 Cells through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081667
Chien M-H, Chow J-M, Lee W-J, Chen H-Y, Tan P, Wen Y-C, Lin Y-W, Hsiao P-C, Yang S-F. Tricetin Induces Apoptosis of Human Leukemic HL-60 Cells through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(8):1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081667
Chicago/Turabian StyleChien, Ming-Hsien, Jyh-Ming Chow, Wei-Jiunn Lee, Hui-Yu Chen, Peng Tan, Yu-Ching Wen, Yung-Wei Lin, Pei-Ching Hsiao, and Shun-Fa Yang. 2017. "Tricetin Induces Apoptosis of Human Leukemic HL-60 Cells through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 8: 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081667
APA StyleChien, M. -H., Chow, J. -M., Lee, W. -J., Chen, H. -Y., Tan, P., Wen, Y. -C., Lin, Y. -W., Hsiao, P. -C., & Yang, S. -F. (2017). Tricetin Induces Apoptosis of Human Leukemic HL-60 Cells through a Reactive Oxygen Species-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase Activation Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(8), 1667. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18081667