Comparative Gene Mapping as a Tool to Understand the Evolution of Pest Crop Insect Chromosomes
Abstract
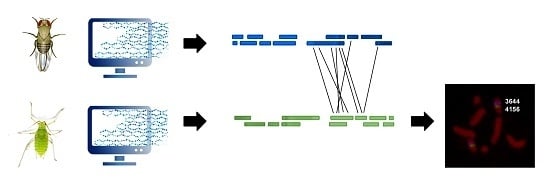
:1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Honeybee Genome Sequencing Consortium. Insights into social insects from the genome of the honey bee Apis mellifera. Nature 2006, 443, 931–949. [Google Scholar]
- Tribolium Genome Sequencing Consortium. The genome of the model beetle and pest Tribolium castaneum. Nature 2008, 452, 949–955. [Google Scholar]
- Brucker, R.M.; Funkhouser, L.J.; Setia, S.; Pauly, R.; Bordenstein, S.R. Insect innate immunity database (IIID): An annotation tool for identifying immune genes in insect genomes. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chilana, P.; Sharma, A.; Rai, A. Insect genomic resources: Status, availability and future. Curr. Sci. 2012, 102, 571–580. [Google Scholar]
- Adams, M.D.; Celniker, S.E.; Holt, R.A.; Evans, C.A.; Gocayne, J.D.; Amanatides, P.G.; Scherer, S.E.; Li, P.W.; Hoskins, R.A.; Galle, R.F.; et al. The genome sequence of Drosophila melanogaster. Science 2000, 287, 2185–2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tedeschi, R.; Monti, M.; Gonella, E.; Mandrioli, M. Molecular and cellular analysis of immunity in the phytoplasma vector Euscelidius variegatus: Exploiting immunity to improve biological control strategies. Invertebr. Surv. J. 2017, 14, 63–72. [Google Scholar]
- Meller, V.H.; Kuroda, M.I. Sex and the single chromosome. Adv. Genet. 2002, 46, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Landeen, E.L.; Presgraves, D.C. Evolution: From autosomes to sex chromosomes and back. Curr. Biol. 2013, 23, R848–R850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturtevant, A.H.; Novitski, E. The homologies of the chromosome elements in the genus Drosophila. Genetics 1941, 26, 517–541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zdobnov, E.; Mering, C.V.; Letunic, I.; Torrents, D.; Suyama, M.; Copley, R.R.; Christophides, G.K.; Thomasova, D.; Holt, R.A.; Subramanian, G.M.; et al. Comparative genome analysis of Anopheles gambiae and Drosophila melanogaster. Science 2002, 298, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severson, D.W.; de Bruyn, B.; Lovin, D.D.; Brown, S.E.; Knudson, D.L.; Morlais, I. Comparative genome analysis of the yellow fever mosquito Aedes aegypti with Drosophila melanogaster and the malaria vector mosquito Anopheles gambiae. J. Hered. 2004, 95, 103–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhutkar, A.; Schaeffer, S.W.; Russo, S.M.; Xu, M.; Smith, T.F.; Gelbart, W.M. Chromosomal rearrangement inferred from comparisons of 12 Drosophila genomes. Genetics 2008, 179, 1657–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, A.G.; Detweiler, D.; Schaeffer, S.W. Evolutionary history of the third chromosome gene arrangements of Drosophila pseudoobscura inferred from inversion breakpoints. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2011, 28, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vicoso, B.; Bachtrog, D. Reversal of an ancient sex chromosome to an autosome in Drosophila. Nature 2013, 499, 332–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sved, J.A.; Chen, Y.C.; Shearman, D.; Frommer, M.; Gichrist, A.S.; Sherwin, W.B. Extraordinary conservation of entire chromosomes in insects over long evolutionary periods. Evolution 2016, 70, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- International Aphid Genomics Consortium. Genome sequence of the pea aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. PLoS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000313. [Google Scholar]
- Oerke, E.C. Estimated crop losses in wheat. In Crop Production and Crop Protection: Estimated Losses in Major Food and Cash Crops, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 1994; pp. 179–296. [Google Scholar]
- Blackman, R.L.; Eastop, V.F. Aphids on the World’s Crops: An Identification and Information Guide, 2nd ed.; Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated: London, UK, 2000; p. 476. [Google Scholar]
- Brisson, J.A.; Davis, G.K. Pea Aphid. In Genome Mapping and Genomics in Arthropods; Hunter, W., Kole, C., Eds.; Springer-Verlag: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 59–67. [Google Scholar]
- Hawthorne, D.J.; Via, S. Genetic linkage of ecological specialization and reproductive isolation in pea aphids. Nature 2001, 412, 904–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braendle, C.; Caillaud, M.C.; Stern, D.L. Genetic mapping of aphicarus: A sex-linked locus controlling a wing polymorphism in the pea aphid (Acyrthosiphon pisum). Heredity 2005, 94, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrioli, M.; Bizzaro, D.; Giusti, M.; Manicardi, G.C.; Bianchi, U. The role of rDNA genes in X chromosomes association in the aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum. Genome 1999, 42, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandrioli, M.; Bizzaro, D.; Manicardi, G.C.; Gionghi, D.; Bassoli, L.; Bianchi, U. Cytogenetic and molecular characterization of a highly repeated DNA sequence in the peach potato aphid Myzus persicae. Chromosoma 1999, 108, 436–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, D.; Mandrioli, M.; Zanotti, M.; Giusti, M.; Manicardi, G.C. Chromosome analysis and molecular characterization of highly repeated DNAs in the aphid Acyrthosiphon pisum (Aphididae, Hemiptera). Genetica 2000, 108, 197–202. [Google Scholar]
- Manicardi, G.C.; Mandrioli, M.; Bizzaro, D.; Bianchi, U. Cytogenetic and molecular analysis of heterochromatic areas in the holocentric chromosomes of different aphid species. In Chromosome Structure and Function; Sobti, R.G., Obe, G., Athwal, R.S., Eds.; Narosa Publishing House: New Delhi, India, 2002; pp. 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Mandrioli, M.; Azzoni, P.; Lombardo, G.; Manicardi, G.C. Composition and epigenetic markers of heterochromatin in the aphid Aphis nerii (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Cytogenet. Genome Res. 2011, 133, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandrioli, M.; Manicardi, G.C. Unlocking holocentric chromosomes: New perspectives from comparative and functional genomics? Curr. Genom. 2012, 13, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manicardi, G.C.; Mandrioli, M.; Blackman, R.L. The cytogenetic architecture of the aphid genome. Biol. Rev. 2015, 90, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manicardi, G.C.; Nardelli, A.; Mandrioli, M. Fast chromosomal evolution and karyotype instability: Occurrence of recurrent chromosomal rearrangements in the peach potato aphid Myzus. persicae (Hemiptera, Aphididae). Biol. J. Linn. Soc. 2015, 116, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, N.A.; Kaplan, M.E.; Gelsey, M.J.; Murphy, T.G.; Scholes, E.A. Phylogenetics and evolution of the aphid genus Uroleucon based on mitochondrial and nuclear DNA sequences. System Entomol. 1999, 24, 85–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Dohlen, C.D.; TeulonM, D.A.J. Phylogeny and historical biogeography of New Zealand indigenous Aphidini aphids (Hemiptera, Aphididae): An hypothesis. Ann. Entomol. Soc. Am. 2003, 96, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, D. Using Drosophila as a model insect. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2000, 1, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arias, A.M. Drosophila melanogaster and the development of biology in the 20th century. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 420, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ashburner, M.; Bergman, C.M. Drosophila melanogaster: A case study of a model genomic sequence and its consequence. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1661–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muller, H.J. Bearings of the Drosophila work on systematics. In The New Systematics; Huxley, J., Ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1940; pp. 185–268. [Google Scholar]
- Zacharopoulou, A.; Frisardi, M.; Savakis, C.; Robinson, A.S.; Tolias, P.; Konsolaki, M. The genome of the Mediterranean fruitfly Ceratitis capitata: Localization of molecular markers by in situ hybridization to salivary gland polytene chromosomes. Chromosoma 1992, 101, 448–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariou-Papalexiou, A.; Gourzi, P.; Delprat, A.; Kritikou, D.; Rapti, K.; Chrysanthakopoulou, B. Polytene chromosomes as tools in the genetic analysis of the Mediterranean fruit fly, Ceratitis capitata. Genetica 2002, 116, 59–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoumani, K.T.; Augustinos, A.A.; Kakani, E.G.; Drosopoulou, E.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P.; Mathiopoulos, K.D. Isolation, annotation and applications of expressed sequence tags from the olive fly, Bactrocera oleae. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2011, 285, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavragani-Tsipidou, P. Genetic and cytogenetic analysis of the olive fruit fly Bactrocera oleae (Diptera: Tephritidae). Genetica 2002, 116, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drosopoulou, E.; Nakou, I.; Mavragani-Tsipidou, P. The Bactrocera. Oleae genome: Localization of nine genes on the polytene chromosomes of the olive fruit fly (Diptera: Tephritidae). Genome 2014, 57, 573–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustinos, A.A.; Drosopoulou, E.; Gariou-Papalexiou, A.; Asimakis, E.D.; Cáceres, C.; Tsiamis, G. Cytogenetic and symbiont analysis of five members of the B. dorsalis complex (Diptera, Tephritidae): No evidence of chromosomal or symbiont-based speciation events. Zookeys 2015, 540, 273–298. [Google Scholar]
- Orengo, D.J.; Puerma, E.; Papaceit, M.; Segarra, C.; Aguadé, M. Dense gene physical maps of the non-model species Drosophila subobscura. Chromosome Res. 2017, 25, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, S.; Liu, Y.; Bettencourt, B.R.; Hradecky, P.; Letovsky, S.; Nielsen, R.; Thornton, K.; Hubisz, M.J.; Chen, R.; Meisel, R.P. Comparative genome sequencing of Drosophila pseudoobscura: Chromosomal, gene, and cis-element evolution. Genome Res. 2005, 15, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foote, M.; Hunter, J.P.; Janis, C.M.; Sepkoski, J.J. Evolutionary and preservational constraints on origins of biologic groups: Divergence times of eutherian mammals. Science 1999, 283, 1310–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poletto, A.B.; Ferreira, I.A.; Cabral-de-Mello, D.C.; Nakajima, R.T.; Mazzuchelli, J.; Ribeiro, H.B.; Venere, P.C.; Nirchio, M.; Kocher, T.D.; Martins, C. Chromosome differentiation patterns during cichlid fish evolution. BMC Genet. 2010, 11, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hooper, D.M.; Price, T.D. Rates of karyotypic evolution in Estrildid finches differ between island and continental clades. Evolution 2015, 69, 890–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darlington, C.D.; Wylie, A.P. Chromosome atlas of flowering plants, 2nd ed.; Allen & Unwin: London, UK, 1955. [Google Scholar]
- Mandrioli, M.; Manicardi, G.C. Chromosomal mapping reveals a dynamic organization of the histone genes in aphids (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Entomologia 2013, 1, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blackman, R.L.; Spence, J.M.; Field, L.M.; Devonshire, A.L. Chromosomal localization of the amplified esterase genes conferring resistance to insecticides in the aphid Myzus persicae. Heredity 1995, 75, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bizzaro, D.; Manicardi, G.C.; Bianchi, U. Chromosomal localization of a highly repeated EcoRI DNA fragment in Megoura viciae (Homoptera, Aphididae) by nick translation and FISH. Chrom. Res. 1996, 4, 392–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti, V.; Manicardi, G.C.; Mandrioli, M. Distribution and molecular composition of heterochromatin in the holocentric chromosomes of the aphid Rhopalosiphum padi (Hemiptera: Aphididae). Genetica 2010, 138, 1077–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Spence, J.M.; Blackman, R.L.; Testa, J.M.; Ready, P.D. A 169 bp tandem repeat DNA marker for subtelomeric heterochromatin and chromosomal re-arrangement in aphids of the Myzus persicae group. Chrom. Res. 1998, 6, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spence, J.M.; Blackman, R.L. Orientation of the stretched univalent X chromosome during the unequal first meiotic division in male aphids. Chrom. Res. 1998, 6, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, S.B.; Marin, J.; Suleski, M.; Paymer, M.; Kumar, S. Tree of life reveals clock-like speciation and diversification. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Alençon, E.; Sezutsu, H.; Legeai, F.; Permal, E.; Bernard-Samain, S.; Gimenez, S.; Gagneur, C.; Cousserans, F.; Shimomura, M.; Brun-Barale, A.; et al. Extensive synteny conservation of holocentric chromosomes in Lepidoptera despite high rates of local genome rearrangements. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 7680–7685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manicardi, G.C.; Mandrioli, M.; Bizzaro, D.; Bianchi, U. Patterns of DNase I sensitivity in the holocentric chromosomes of the aphid Megoura viciae. Genome 1998, 41, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cammarano, R.; Costantini, M.; Bernardi, G. The isochore patterns of invertebrate genomes. BMC Genom. 2009, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Scaffold/Probe Name | Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| Scaffold 0033844156 (NW_003384156) probe 1 | 4156F1 | 5′-CTTGTATGTTTTGTATGCGTGAGAC-3′ |
| 4156R1 | 5′-AACAAATTTCAGTTAAACGCAGAAC-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033844156 (NW_003384156) probe 2 | 4156F2 | 5′-TATATGAATAAGCCATGACAAATAA-3′ |
| 4156R2 | 5′-ATTATGAATATAAAGACGAGCCTAA-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033833644 (NW_003383644) probe 1 | 3644F1 | 5′-TAGGTAGCTGTATAACCCAGTTTCG-3′ |
| 3644R1 | 5′-AACAGACGGTGTGTAGGTATGGTAT-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033833644 (NW_003383644) probe 2 | 3644F2 | 5′-CAGCATTATACGCATAGGTAGGACT-3′ |
| 3644R2 | 5′-AAAACTTGTCATGTGTTTTCTGACA-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003383818 (NW_003383818) probe 1 | 3818F1 | 5′-TTGTTCTCATTGGATTTATTTGGTT-3′ |
| 3818R1 | 5′-AAGTGAGGTACTAATTCGTGTCCAG-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033833818 (NW_003383818) probe 2 | 3818F2 | 5′-CTGGACACGAATTAGTACCTCACTT-3′ |
| 3818R2 | 5′-TTCATTGCATACAAAACATGGTATC-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003383768 (NW_003383768) probe 1 | 3768F1 | 5′-TACCAACGTCGTACATACACCATAC-3′ |
| 3768R1 | 5′-ATTATTGATGCCCATTTTACTACGA-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033833768 (NW_003383768) probe 2 | 3768F2 | 5′-TGGCTATGTGTCGTTATGAATTAGA-3′ |
| 3768R2 | 5′-CCAAGTTTGTGAAAATGGTTAAATC-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003383906 (NW_003383906) probe 1 | 3906F1 | 5′-TAGAAATCAGTGTCATGAAGGATGA-3′ |
| 3906R1 | 5′-CTAGTCAACACGGGTAATGAGAGTT-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033833906 (NW_0033838906) probe 2 | 3906F2 | 5′-ATCACTCACACATTCGTTTTCAGTA-3′ |
| 3906R2 | 5′-TTATTTTCCACCACTTTTCAATCAT-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003383512 (NW_003383512) probe 1 | 3512F1 | 5′-CGGTATCAGTTCGTTAAGCATAAGT-3′ |
| 3512R1 | 5′-ATACAATTGATGAATCGGTTGAGTT-3′ | |
| Scaffold 0033833512 (NW_0033838512) probe 2 | 3512F2 | 5′-AACCAATACATTCAAGAATTTCCAA-3′ |
| 3512R2 | 5′-CACACGACGTCATCTAGTACAAATC-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003384165 (NW_003384165) probe 1 | 4165F1 | 5′-TTTAATATTGATTGCTCCGTATGGT-3′ |
| 4165R1 | 5′-TCATTATCCAAAAGAAAGGAGACTG-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003384165 (NW_003384165) probe 2 | 4165F2 | 5′-TGATACCGATTGTGATTTTAAGGAT-3′ |
| 4165R2 | 5′-GTTCAAAGACTGATCGTACATGTTG-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003384041 (NW_003384041) probe 1 | 4041F1 | 5′-TTGTACCTGCACATTGTAGACCTAA-3′ |
| 4041R1 | 5′-ACAACTAACTGCAGGTCTTTATTGG-3′ | |
| Scaffold 003384041 (NW_003384041) probe 2 | 4041F2 | 5′-GATTTCTCATTGATACGGCTTCTAA-3′ |
| 4041R2 | 5′-CCATGGTTTGAGTGTACTTCTTCTT-3′ |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mandrioli, M.; Zambonini, G.; Manicardi, G.C. Comparative Gene Mapping as a Tool to Understand the Evolution of Pest Crop Insect Chromosomes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091919
Mandrioli M, Zambonini G, Manicardi GC. Comparative Gene Mapping as a Tool to Understand the Evolution of Pest Crop Insect Chromosomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091919
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandrioli, Mauro, Giada Zambonini, and Gian Carlo Manicardi. 2017. "Comparative Gene Mapping as a Tool to Understand the Evolution of Pest Crop Insect Chromosomes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091919
APA StyleMandrioli, M., Zambonini, G., & Manicardi, G. C. (2017). Comparative Gene Mapping as a Tool to Understand the Evolution of Pest Crop Insect Chromosomes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1919. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091919