Dual Strands of Pre-miR-149 Inhibit Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Targeting FOXM1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression Levels of miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p in ccRCC Specimens and Cell Lines
2.2. Effects of Ectopic Expression of miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p on Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Assays in RCC Cell Lines
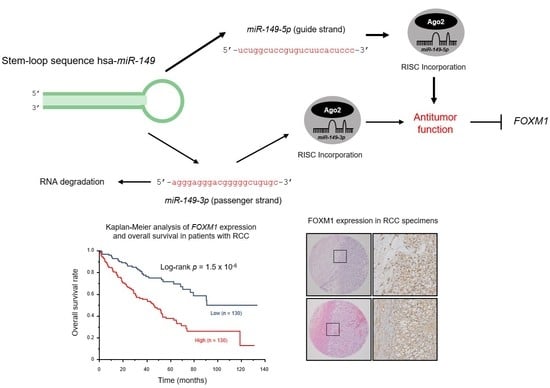
2.3. Both miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p Bind to Ago2
2.4. Screening of Target Genes Regulated by miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p in RCC Cells
2.5. Analysis of FOXM1 Expression in ccRCC Clinical Specimens by qRT-PCR and Immunohistochemistry
2.6. TCGA Database Analysis of Dual Strands of Pre-miR-149 and FOXM1
2.7. Regulation of FOXM1 Expression by miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p in RCC Cells
2.8. Effects of Silencing FOXM1 on Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion in RCC Cells
2.9. Kaplan–Meier Survival Curves and Genes Affected by miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Clinical ccRCC Specimens
4.2. Tissue Collection and Cell Culture
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
4.4. Cell Proliferation, Migration, and Invasion Assays
4.5. miRNA Incorporated into RISC by Ago2 Immunoprecipitation
4.6. Selection of Putative Target Genes Regulated by miR-149-5p and miR-149-3p in RCC Cells
4.7. TCGA Database Analysis of ccRCC
4.8. Western Blot Analysis
4.9. Immunohistochemistry Using Tissue Microarrays
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ljungberg, B.; Campbell, S.C.; Choi, H.Y.; Jacqmin, D.; Lee, J.E.; Weikert, S.; Kiemeney, L.A. The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur. Urol. 2011, 60, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patard, J.J.; Leray, E.; Rioux-Leclercq, N.; Cindolo, L.; Ficarra, V.; Zisman, A.; de la Taille, A.; Tostain, J.; Artibani, W.; Abbou, C.C.; et al. Prognostic value of histologic subtypes in renal cell carcinoma: A multicenter experience. J. Clin. Oncol. 2005, 23, 2763–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephenson, A.J.; Chetner, M.P.; Rourke, K.; Gleave, M.E.; Signaevsky, M.; Palmer, B.; Kuan, J.; Brock, G.B.; Tanguay, S. Guidelines for the surveillance of localized renal cell carcinoma based on the patterns of relapse after nephrectomy. J. Urol. 2004, 172, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Figlin, R.; Sternberg, C.; Wood, C.G. Novel agents and approaches for advanced renal cell carcinoma. J. Urol. 2012, 188, 707–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia, J.A.; Rini, B.I. Recent progress in the management of advanced renal cell carcinoma. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2007, 57, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Micrornas: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 2004, 116, 281–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carthew, R.W.; Sontheimer, E.J. Origins and mechanisms of mirnas and sirnas. Cell 2009, 136, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, D.P. Micrornas: Target recognition and regulatory functions. Cell 2009, 136, 215–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Nohata, N.; Kojima, S.; Matsushita, R.; Yoshino, H.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishida, Y.; Ichikawa, T.; Naya, Y.; et al. The microrna signature of patients with sunitinib failure: Regulation of uhrf1 pathways by microrna-101 in renal cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 59070–59086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Arai, T.; Nohata, N.; Kojima, S.; Okato, A.; Kato, M.; Yamazaki, K.; Ishida, Y.; Naya, Y.; et al. Impact of novel mir-145–3p regulatory networks on survival in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, K.; Mataki, H.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Kamikawaji, K.; Kumamoto, T.; Hiraki, T.; Hatanaka, K.; Inoue, H.; Seki, N. The microrna expression signature of small cell lung cancer: Tumor suppressors of mir-27a-5p and mir-34b-3p and their targeted oncogenes. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 62, 671–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koshizuka, K.; Nohata, N.; Hanazawa, T.; Kikkawa, N.; Arai, T.; Okato, A.; Fukumoto, I.; Katada, K.; Okamoto, Y.; Seki, N. Deep sequencing-based microrna expression signatures in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Dual strands of pre-mir-150 as antitumor mirnas. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 30288–30304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gregory, R.I.; Chendrimada, T.P.; Cooch, N.; Shiekhattar, R. Human risc couples microrna biogenesis and posttranscriptional gene silencing. Cell 2005, 123, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chendrimada, T.P.; Gregory, R.I.; Kumaraswamy, E.; Norman, J.; Cooch, N.; Nishikura, K.; Shiekhattar, R. Trbp recruits the dicer complex to ago2 for microrna processing and gene silencing. Nature 2005, 436, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutvagner, G.; Zamore, P.D. A microrna in a multiple-turnover rnai enzyme complex. Science 2002, 297, 2056–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matranga, C.; Tomari, Y.; Shin, C.; Bartel, D.P.; Zamore, P.D. Passenger-strand cleavage facilitates assembly of sirna into ago2-containing rnai enzyme complexes. Cell 2005, 123, 607–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, R.; Seki, N.; Chiyomaru, T.; Inoguchi, S.; Ishihara, T.; Goto, Y.; Nishikawa, R.; Mataki, H.; Tatarano, S.; Itesako, T.; et al. Tumour-suppressive microrna-144–5p directly targets ccne1/2 as potential prognostic markers in bladder cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2015, 113, 282–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mataki, H.; Seki, N.; Mizuno, K.; Nohata, N.; Kamikawaji, K.; Kumamoto, T.; Koshizuka, K.; Goto, Y.; Inoue, H. Dual-strand tumor-suppressor microrna-145 (mir-145–5p and mir-145–3p) coordinately targeted mtdh in lung squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 72084–72098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okato, A.; Arai, T.; Kojima, S.; Koshizuka, K.; Osako, Y.; Idichi, T.; Kurozumi, A.; Goto, Y.; Kato, M.; Naya, Y.; et al. Dual strands of pre-mir150 (mir1505p and mir1503p) act as antitumor mirnas targeting spock1 in naive and castration-resistant prostate cancer. Int J. Oncol. 2017, 51, 245–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jordan, A. Oncolnc: Linking tcga survival data to mrnas, mirnas, and lncrnas. PeerJ Comp. Sci. 2016, 2, e67. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cbioportal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jordan, A. Oncorank: A pan-cancer method of combining survival correlations and its application to mrnas, mirnas, and lncrnas. PeerJ Prepr. 2016, 4, e2574v2571. [Google Scholar]
- Duran, I.; Lambea, J.; Maroto, P.; Gonzalez-Larriba, J.L.; Flores, L.; Granados-Principal, S.; Graupera, M.; Saez, B.; Vivancos, A.; Casanovas, O. Resistance to targeted therapies in renal cancer: The importance of changing the mechanism of action. Target Oncol. 2017, 12, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurozumi, A.; Kato, M.; Goto, Y.; Matsushita, R.; Nishikawa, R.; Okato, A.; Fukumoto, I.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Regulation of the collagen cross-linking enzymes loxl2 and plod2 by tumor-suppressive microrna-26a/b in renal cell carcinoma. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1837–1846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.H.; Huang, W.C.; Chang, J.W.; Chang, K.J.; Kuo, W.H.; Wang, M.Y.; Lin, K.Y.; Uen, Y.H.; Hou, M.F.; Lin, C.M.; et al. Microrna-149 targets git1 to suppress integrin signaling and breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 4496–4507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, G.; Chao, Y.L.; Tang, B.; Li, B.S.; Xiao, Y.F.; Xie, R.; Wang, S.M.; Wu, Y.Y.; Dong, H.; Liu, X.D.; et al. Mir-149 represses metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting actin-regulatory proteins ppm1f. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 37808–37823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, D.X.; Gu, X.T.; Li, Y.R.; Jiang, L.; Jin, J.; Ma, X. Methylation-regulated mir-149 modulates chemoresistance by targeting glcnac n-deacetylase/n-sulfotransferase-1 in human breast cancer. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 4718–4730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Liu, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Liang, H.; Li, K.; Li, L.; Chen, C.; Sun, W.; Ren, S.; et al. Ephb3-targeted regulation of mir-149 in the migration and invasion of human colonic carcinoma hct116 and sw620 cells. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 408–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, L.; Xu, L.; Yin, L.; Qi, Y.; Han, X.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, K.; Peng, J. Potent effects of dioscin against pancreatic cancer via mir-149-3p-mediated inhibition of the akt1 signalling pathway. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, P.; Zhao, W.; Su, W.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Liu, J.; Ren, G.; Yin, Z.; Wang, X. 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma development by reversing hepatic stellate cell-mediated immunosuppression in mice. Int. J. Cancer 2013, 132, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, A.V.; Thirugnanam, S.; Dakshinamoorthy, G.; Samykutty, A.; Zheng, G.; Chen, A.; Bosland, M.C.; Kajdacsy-Balla, A.; Gnanasekar, M. 18alpha-glycyrrhetinic acid targets prostate cancer cells by down-regulating inflammation-related genes. Int. J. Oncol. 2011, 39, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Shen, Y.; Qiu, R.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Z.; Chen, W. 18 beta-glycyrrhetinic acid exhibits potent antitumor effects against colorectal cancer via inhibition of cell proliferation and migration. Int. J. Oncol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, D.; Jia, Z.; You, L.; Wu, Y.; Hou, Z.; Suo, Y.; Zhang, H.; Wen, S.; Tsukamoto, T.; Oshima, M.; et al. 18beta-glycyrrhetinic acid suppresses gastric cancer by activation of mir-149-3p-wnt-1 signaling. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 71960–71973. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsushita, R.; Yoshino, H.; Enokida, H.; Goto, Y.; Miyamoto, K.; Yonemori, M.; Inoguchi, S.; Nakagawa, M.; Seki, N. Regulation of uhrf1 by dual-strand tumor-suppressor microrna-145 (mir-145-5p and mir-145-3p): Inhibition of bladder cancer cell aggressiveness. Oncotarget 2016, 196, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yonemori, M.; Seki, N.; Yoshino, H.; Matsushita, R.; Miyamoto, K.; Nakagawa, M.; Enokida, H. Dual tumor-suppressors mir-139-5p and mir-139-3p targeting matrix metalloprotease 11 in bladder cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 1233–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, K.; Liu, X.; Mao, X.; Xue, L.; Wang, R.; Chen, L.; Chu, X. Microrna-149 suppresses colorectal cancer cell migration and invasion by directly targeting forkhead box transcription factor foxm1. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 35, 499–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ke, Y.; Zhao, W.; Xiong, J.; Cao, R. Mir-149 inhibits non-small-cell lung cancer cells emt by targeting foxm1. Biochem. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 506731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Du, J.; Xie, K. Foxm1 and its oncogenic signaling in pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. Bioch. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1845, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocarslan, S.; Guldur, M.E.; Ekinci, T.; Ciftci, H.; Ozardali, H.I. Comparison of clinicopathological parameters with foxm1 expression in renal cell carcinoma. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2014, 10, 1076–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halasi, M.; Gartel, A.L. Targeting foxm1 in cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2013, 85, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.R.; Chen, Y.H.; Liu, D.M.; Sha, J.J.; Xuan, H.Q.; Bo, J.J.; Huang, Y.R. Increased expression of forkhead box m1 protein is associated with poor prognosis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, N.; Wang, Y.; Wen, L.; Zhao, S.H.; Ai, Z.H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, B.; Lu, H.X.; Yang, H.; Liu, W.C.; et al. Overexpression of foxm1 predicts poor prognosis and promotes cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion in epithelial ovarian cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Wei, P.; Peng, Z.; Huang, C.; Tang, H.; Jia, Z.; Cui, J.; Le, X.; Huang, S.; Xie, K. The critical role of dysregulated foxm1-plaur signaling in human colon cancer progression and metastasis. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Associ. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 62–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobin, L.; Gospodarowicz, M.; Wittekind, C. Tnm Classification of Malignant Tumours, 7th ed.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chichester, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Okato, A.; Goto, Y.; Kurozumi, A.; Kato, M.; Kojima, S.; Matsushita, R.; Yonemori, M.; Miyamoto, K.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Direct regulation of lamp1 by tumor-suppressive microrna-320a in prostate cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurozumi, A.; Goto, Y.; Matsushita, R.; Fukumoto, I.; Kato, M.; Nishikawa, R.; Sakamoto, S.; Enokida, H.; Nakagawa, M.; Ichikawa, T.; et al. Tumor-suppressive microrna-223 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion by targeting itga3/itgb1 signaling in prostate cancer. Cancer Sci. 2016, 107, 84–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goto, Y.; Kojima, S.; Kurozumi, A.; Kato, M.; Okato, A.; Matsushita, R.; Ichikawa, T.; Seki, N. Regulation of e3 ubiquitin ligase-1 (wwp1) by microrna-452 inhibits cancer cell migration and invasion in prostate cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2016, 114, 1135–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| No. | Age | Sex | Pathology | Grade | pT | N | M | INF | v | ly | eg/ig | fc | im | rc | rp | s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 71 | F | clear cell | G2 | T1a | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 74 | M | clear cell | G1 > G2 | T1b | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | 59 | M | clear cell | G3 > G2 | T1b | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | 79 | M | clear cell | G2 > G3 > G1 | T1a | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | 52 | M | clear cell | G2 > G3 | T1b | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | 76 | F | clear cell | G2 > G3 | T3a | 0 | 0 | a | 1 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | 64 | M | clear cell | G2 > G3 > G1 | T3a | 0 | 1 | b | 1 | 0 | ig | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | 67 | M | clear cell | G2 > G3 > G1 | T3a | 0 | 0 | b | 1 | 0 | ig | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 9 | 59 | M | clear cell | G3 | T3a | 0 | 0 | b | 1 | 0 | ig | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 10 | 73 | M | clear cell | G1 >> G3 | T2a | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 1 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 11 | 77 | M | clear cell | G1 > G2 | T1b | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 12 | 51 | F | clear cell | G2 > G1 > G3 | T3b | 0 | 0 | b | 1 | 0 | ig | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 13 | 84 | F | clear cell | G2 | T1a | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 14 | 78 | M | clear cell | G2 > G1 >> G3 | T1b | 0 | 0 | b | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 15 | 44 | M | clear cell | G2 > G1 | T1a | 0 | 0 | b | 0 | 0 | eg | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 16 | 57 | M | clear cell | G2 | T1b | 0 | 0 | a | 0 | 0 | eg | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Gene Symbol | Gene Name | Site Counts | Microarray (log2 Ratio) | GEO | TCGA | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miR-149-5p | miR-149-3p | miR-149-5p | miR-149-3p | Fold Change | p Value | ||
| FOXM1 | forkhead box M1 | 1 | 1 | −1.359 | −0.834 | 1.533 | 1.5 × 10−6 |
| SIPA1 | signal-induced proliferation-associated 1 | 1 | 3 | −2.022 | −0.732 | 1.071 | 6.4 × 10−6 |
| CXCL5 | chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 5 | 1 | 1 | −1.032 | −0.650 | 1.961 | 2.39 × 10−6 |
| LMNB2 | lamin B2 | 1 | 4 | −0.767 | −0.909 | 1.438 | 3.67 × 10−6 |
| GBP2 | guanylate binding protein 2, interferon-inducible | 1 | 4 | −2.484 | −1.278 | 1.664 | 8.57 × 10−6 |
| FBXL16 | F-box and leucine-rich repeat protein 16 | 2 | 4 | −2.451 | −0.685 | 2.203 | 0.00927 * |
| BTNL9 | butyrophilin-like 9 | 1 | 3 | −1.161 | −0.519 | 1.255 | 0.0187 * |
| APOBEC3C | apolipoprotein B mRNA editing enzyme, catalytic polypeptide-like 3C | 2 | 1 | −1.086 | −0.672 | 1.805 | 0.0424 |
| MARVELD1 | MARVEL domain containing 1 | 2 | 4 | −0.902 | −2.176 | 1.019 | 0.188 |
| IKZF1 | IKAROS family zinc finger 1 (Ikaros) | 1 | 2 | −1.133 | −0.742 | 1.350 | 0.401 |
| TTYH3 | tweety family member 3 | 1 | 7 | −1.933 | −1.480 | 1.096 | 0.57 |
| SLC29A4 | solute carrier family 29 (equilibrative nucleoside transporter), member 4 | 1 | 11 | −1.115 | −0.868 | 2.936 | 0.62 |
| DDB2 | damage-specific DNA binding protein 2, 48kDa | 2 | 1 | −0.760 | −1.295 | 2.209 | 0.757 |
| PHKA2 | phosphorylase kinase, alpha 2 (liver) | 2 | 3 | −0.550 | −1.281 | 1.872 | 0.943 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Okato, A.; Arai, T.; Yamada, Y.; Sugawara, S.; Koshizuka, K.; Fujimura, L.; Kurozumi, A.; Kato, M.; Kojima, S.; Naya, Y.; et al. Dual Strands of Pre-miR-149 Inhibit Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Targeting FOXM1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091969
Okato A, Arai T, Yamada Y, Sugawara S, Koshizuka K, Fujimura L, Kurozumi A, Kato M, Kojima S, Naya Y, et al. Dual Strands of Pre-miR-149 Inhibit Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Targeting FOXM1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091969
Chicago/Turabian StyleOkato, Atsushi, Takayuki Arai, Yasutaka Yamada, Sho Sugawara, Keiichi Koshizuka, Lisa Fujimura, Akira Kurozumi, Mayuko Kato, Satoko Kojima, Yukio Naya, and et al. 2017. "Dual Strands of Pre-miR-149 Inhibit Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Targeting FOXM1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091969
APA StyleOkato, A., Arai, T., Yamada, Y., Sugawara, S., Koshizuka, K., Fujimura, L., Kurozumi, A., Kato, M., Kojima, S., Naya, Y., Ichikawa, T., & Seki, N. (2017). Dual Strands of Pre-miR-149 Inhibit Cancer Cell Migration and Invasion through Targeting FOXM1 in Renal Cell Carcinoma. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1969. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091969