Evolution of RAD- and DIV-Like Genes in Plants
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. RAD-Like Genes from Solanaceae
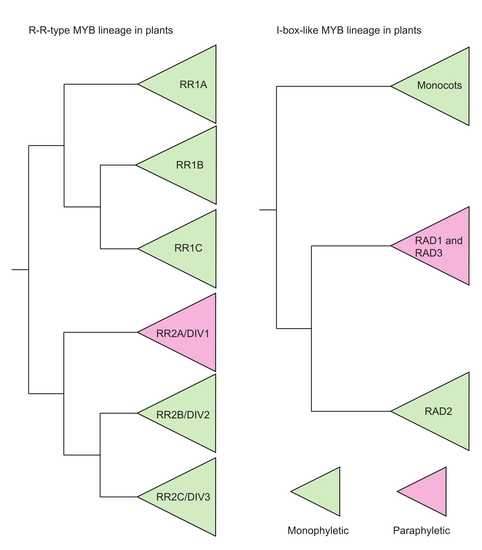
2.2. Diversity and Phylogeny of I-Box-Like MYB Genes
2.3. Diversity and Phylogeny of R-R-Type MYB Genes
2.4. Testing the Tree Topology for R-R-Type Genes
2.5. Motif Analyses
3. Discussion
3.1. Phylogenetic Positions of RAD- and DIV-Like Genes in the Plant MYB Lineage.
3.2. Evolution of the I-Box-Like Subfamily
3.3. Evolution of the R-R-Type Subfamily
3.4. Evolution of the Antagonism among RAD-DRIF-DIV and FSM1-FSB1-MYBI in An. majus and So. lycopersicum, Respectively
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cloning RAD-Like Genes from Species of Solanaceae and Convolvulaceae
4.2. Gene Mining
4.3. Alignment and Phylogenetic Analyses
4.4. Phylogeny Assessment for R-R-Type Genes
4.5. Motif Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klempnauer, K.H.; Gonda, T.J.; Bishop, J.M. Nucleotide-sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-MYB and its cellular progenitor c-MYB-the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell 1982, 31, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nomura, N.; Takahashi, M.; Matsui, M.; Ishii, S.; Date, T.; Sasamoto, S.; Ishizaki, R. Isolation of human cDNA clones of MYB-related genes, a-MYB and b-MYB. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988, 16, 11075–11089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weston, K. MYB Proteins in life, death and differentiation. Curr. Opin. Genet. Dev. 1998, 8, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipsick, J.S. One billion years of MYB. Oncogene 1996, 13, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Paz-Ares, J.; Ghosal, D.; Wienand, U.; Peterson, P.A.; Saedler, H. The regulatory c1 locus of Zea mays encodes a protein with homology to MYB proto-oncogene products and with structural similarities to transcriptional activators. EMBO J. 1987, 6, 3553–3558. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cominelli, E.; Tonelli, C. A new role for plant R2R3-MYB transcription factors in cell cycle regulation. Cell Res. 2009, 19, 1231–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, C.; PazAres, J. MYB transcription factors in plants. Trends Genet. 1997, 13, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oppenheimer, D.G.; Herman, P.L.; Sivakumaran, S.; Esch, J.; Marks, M.D. A MYB gene required for leaf trichome differentiation in arabidopsis is expressed in stipules. Cell 1991, 67, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, R.; Wang, Z.M.; Zhang, S.W.; Meng, G.; Song, L.Y.; Wang, Z.G.; Li, P.M.; Ma, F.W.; Xu, L.F. Two MYB transcription factors regulate flavonoid biosynthesis in pear fruit (pyrus bretschneideri REHD.). J. Exp. Bot. 2016, 67, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raimundo, J.; Sobral, R.; Bailey, P.; Azevedo, H.; Galego, L.; Almeida, J.; Coen, E.; Costa, M.M.R. A subcellular tug of war involving three MYB-like proteins underlies a molecular antagonism in Antirrhinum flower asymmetry. Plant J. 2013, 75, 527–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Carpenter, R.; Vincent, C.; Copsey, L.; Coen, E. Origin of floral asymmetry in Antirrhinum. Nature 1996, 383, 794–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, D.; Carpenter, R.; Copsey, L.; Vincent, C.; Clark, J.; Coen, E. Control of organ asymmetry in flowers of Antirrhinum. Cell 1999, 99, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, D.G.; Donoghue, M.J. Phylogenetic analysis of the “ECE” (cyc/tb1) clade reveals duplications predating the core eudicots. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 9101–9106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cubas, P.; Lauter, N.; Doebley, J.; Coen, E. The TCP domain: A motif found in proteins regulating plant growth and development. Plant J. 1999, 18, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baxter, C.E.L.; Costa, M.M.R.; Coen, E.S. Diversification and co-option of rad-like genes in the evolution of floral asymmetry. Plant J. 2007, 52, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corley, S.B.; Carpenter, R.; Copsey, L.; Coen, E. Floral asymmetry involves an interplay between TCP and MYB transcription factors in Antirrhinum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 5068–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, M.M.R.; Fox, S.; Hanna, A.I.; Baxter, C.; Coen, E. Evolution of regulatory interactions controlling floral asymmetry. Development 2005, 132, 5093–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almeida, J.; Rocheta, M.; Galego, L. Genetic control of flower shape in Antirrhinum majus. Development 1997, 124, 1387–1392. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galego, L.; Almeida, J. Role of divaricata in the control of dorsoventral asymmetry in Antirrhinum flowers. Genes Dev. 2002, 16, 880–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machemer, K.; Shaiman, O.; Salts, Y.; Shabtai, S.; Sobolev, I.; Belausov, E.; Grotewold, E.; Barg, R. Interplay of MYB factors in differential cell expansion, and consequences for tomato fruit development. Plant J. 2011, 68, 337–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyden, G.S.; Donoghue, M.J.; Howarth, D.G. Duplications and expression of radialis-like genes in dipsacales. Int. J. Plant Sci. 2012, 173, 971–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howarth, D.G.; Donoghue, M.J. Duplications and expression of divaricata-like genes in dipsacales. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2009, 26, 1245–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Särkinen, T.; Bohs, L.; Olmstead, R.G.; Knapp, S. A phylogenetic framework for evolutionary study of the nightshades (solanaceae): A dated 1000-tip tree. BMC Evol. Biol. 2013, 13, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.H.; Yang, X.Y.; He, K.; Liu, M.H.; Li, J.G.; Gao, Z.F.; Lin, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.F.; Wang, X.X.; Qiu, X.M.; et al. The MYB transcription factor superfamily of arabidopsis: Expression analysis and phylogenetic comparison with the rice myb family. Plant Mol. Biol. 2006, 60, 107–124. [Google Scholar]
- Rosinski, J.A.; Atchley, W.R. Molecular evolution of the MYB family of transcription factors: Evidence for polyphyletic origin. J. Mol. Evol. 1998, 46, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, H.D.; Denekamp, M.; Greco, R.; Jin, H.; Leyva, A.; Meissner, R.C.; Petroni, K.; Urzainqui, A.; Bevan, M.; Martin, C.; et al. Towards functional characterisation of the members of the R2R3-MYB gene family from arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 1998, 16, 263–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kranz, H.; Scholz, K.; Weisshaar, B. C-MYB Oncogene-like genes encoding three MYB repeats occur in all major plant lineages. Plant J. 2000, 21, 231–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.L.; Martin, C. Multifunctionality and diversity within the plant MYB-gene family. Plant Mol. Biol. 1999, 41, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stracke, R.; Werber, M.; Weisshaar, B. The R2R3-MYB gene family in arabidopsis thaliana. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2001, 4, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riechmann, J.L.; Ratcliffe, O.J. A genomic perspective on plant transcription factors. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2000, 3, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, A.; Meier, I.; Wienand, U. The tomato i-box binding factor lemybi is a member of a novel class of MYB-like proteins. Plant J. 1999, 20, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevenson, C.E.M.; Burton, N.; Costa, M.M.R.; Nath, U.; Dixon, R.A.; Coen, E.S.; Lawson, D.M. Crystal structure of the MYB domain of the rad transcription factor from Antirrhinum majus. Protein Struct. Funct. Biol. 2006, 65, 1041–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huelsenbeck, J.P.; Ronquist, F. Mrbayes: Bayesian inference of phylogenetic trees. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 754–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A. RAxML-VI-HPC: Maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2688–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, A.; Hoover, P.; Rougemont, J. A rapid bootstrap algorithm for the RAxML web servers. Syst. Biol. 2008, 57, 758–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, M.A.; Pfeiffer, W.; Schwartz, T. Creating the cipres science gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees. In Proceedings of the Gateway Computing Environments Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA, USA, 14 November 2010; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Darriba, D.; Taboada, G.L.; Doallo, R.; Posada, D. Jmodeltest 2: More models, new heuristics and parallel computing. Nat. Meth. 2012, 9, 772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guindon, S.; Gascuel, O. A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst. Biol. 2003, 52, 696–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akaike, H. Information theory and an extension of the maximum likelihood principle. In Proceedings of the Second International Symposium in Information Theory, Tsahkadsor, Armenia, 2–8 September 1971; Petrov, B.N., Csaki, F., Eds.; Akademiai Kiado: Budapest, Hungary, 1973; pp. 267–281. [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt, H.A.; Strimmer, K.; Vingron, M.; von Haeseler, A. Tree-puzzle: Maximum likelihood phylogenetic analysis using quartets and parallel computing. Bioinformatics 2002, 18, 502–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, M.; Kishino, H.; Yano, T.A. Dating of the human ape splitting by a molecular clock of mitochondrial-DNA. J. Mol. Evol. 1985, 22, 160–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. Consel: For assessing the confidence of phylogenetic tree selection. Bioinformatics 2001, 17, 1246–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishino, H.; Hasegawa, M. Evaluation of the maximum-likelihood estimate of the evolutionary tree topologies from DNA-sequence data, and the branching order in hominoidea. J. Mol. Evol. 1989, 29, 170–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimodaira, H.; Hasegawa, M. Multiple comparisons of log-likelihoods with applications to phylogenetic inference. Mol. Biol. Evol. 1999, 16, 1114–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimodaira, H. An approximately unbiased test of phylogenetic tree selection. Syst. Biol. 2002, 51, 492–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Susko, E.; Leigh, J.; Doolittle, W.F.; Bapteste, E. Visualizing and assessing phylogenetic congruence of core gene sets: A case study of the gamma-proteobacteria. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2006, 23, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maddison, W.; Maddison, D. Mesquite: A Modular System for Evolutionary Analysis. Version 3.2. Available online: http://mesquiteproject.org (accessed on 11 January 2017).
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Unsupervised learning of multiple motifs in biopolymers using expectation maximization. Mach. Learn. 1995, 21, 51–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Elkan, C. Fitting a mixture model by expectation maximization to discover motifs in biopolymers. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1994, 2, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]








| Species | Family | Location | Voucher | Sequence Names | Clades | # of Clones Sequenced |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Petunia sp. | Solanaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_23 (VCU) | Petunia sp RAD1 | RAD2A | 12 |
| Petunia sp RAD2 | RAD2A | 20 | ||||
| Petunia sp RAD3 | RAD2B | 8 | ||||
| Lycium ruthenicum Murray. | Solanaceae | Taxkorgan Tajik Autonomous County, Xinjiang, China | CPG13183 (PE) | Lycium ruthenicum Murr RAD | RAD2A | 20 |
| Atropa belladonna L. | Solanaceae | Hotel Elites, Nathia Gali, Northwest Frontier Province, Pakistan | CPG13594 (PE) | Atropa belladonna Linn RAD | RAD2B | 20 |
| Schizanthus pinnatus Ruiz & Pav. | Solanaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_20 (VCU) | Schizanthus pinnatus RAD1 | RAD2B | 21 |
| Schizanthus pinnatus RAD2 | RAD2A | 22 | ||||
| Schizanthus grahamii Gillies | Solanaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_19 (VCU) | Schizanthus grahamii RAD1 | RAD2A | 21 |
| Schizanthus grahamii RAD2 | RAD2B | 19 | ||||
| Nicotiana obtusifolia M.Martens & Galeotti. | Solanaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_11 (VCU) | Nicotiana obtusifolia RAD1 | RAD2A | 14 |
| Nicotiana obtusifolia RAD2 | RAD2A | 16 | ||||
| Solanum lycopersicum L. | Solanaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_21 (VCU) | Solanum lycopersicum microtom RAD1 | RAD2A | 17 |
| Solanum lycopersicum microtom RAD2 | RAD2B | 13 | ||||
| Evolvulus sp. | Convolvulaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_18 (VCU) | Evulupus sp RAD1 | RAD2B | 20 |
| Evulupus sp RAD2 | RAD2A | 17 | ||||
| Ipomoea tricolor Cav. | Convolvulaceae | VCU Greenhouse | Zhang_Lab_22 (VCU) | Ipomoea tricolor RAD1 | RAD2A | 20 |
| Tree Topology | l | δ | p Values | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KH | SH | AU | |||
| 1: [A-B-C] [D-E-F] | −34754.03 | 0.00 | 0.794 | 0.997 | 0.872 |
| 2: [B-C] [A-D-E-F] | −34775.47 | 21.45 | 0.037 * | 0.284 | 0.048 * |
| 3: [A-C] [B-D-E-F] | −34801.25 | 47.22 | <0.001 * | 0.029 | <0.001 * |
| 4: [A-B] [C-D-E-F] | −34808.97 | 54.95 | <0.001 * | 0.014 | <0.001 * |
| 5: [A] [B-C-D-E-F] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
| 6: [B] [A-C-D-E-F] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
| 7: [C] [A-B-D-E-F] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
| 8: [A-B-C-D-E-F] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
| 9: [A-B-C-D] [E-F] | −34774.05 | 20.02 | 0.206 | 0.343 | 0.213 |
| 10: [A-B-C-E] [D-F] | −34818.22 | 64.19 | <0.001 * | 0.004 | <0.001 * |
| 11: [A-B-C-F] [D-E] | −34818.03 | 64.00 | <0.001 * | 0.007 | <0.001 * |
| 12: [A-B-C-D-E] [F] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
| 13: [A-B-C-D-F] [E] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
| 14: [A-B-C-E-F] [D] | −34820.49 | 66.46 | <0.001 * | 0.003 | <0.001 * |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, A.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W. Evolution of RAD- and DIV-Like Genes in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091961
Gao A, Zhang J, Zhang W. Evolution of RAD- and DIV-Like Genes in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2017; 18(9):1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091961
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Ao, Jingbo Zhang, and Wenheng Zhang. 2017. "Evolution of RAD- and DIV-Like Genes in Plants" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 18, no. 9: 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091961
APA StyleGao, A., Zhang, J., & Zhang, W. (2017). Evolution of RAD- and DIV-Like Genes in Plants. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 18(9), 1961. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18091961