Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson’s Disease in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Galangin Inhibited the Activation of Microglial Cells in an LPS-Induced PD Rat Model
2.2. Galangin Suppresses the Loss of DA Neurons in an LPS-Induced PD Rat Model
2.3. Galangin Attenuated LPS-Induced Motor Dysfunction in an LPS-Induced PD Rat Model
2.4. Galangin Suppresses the LPS-Induced Inflammatory Response in BV-2 Cells
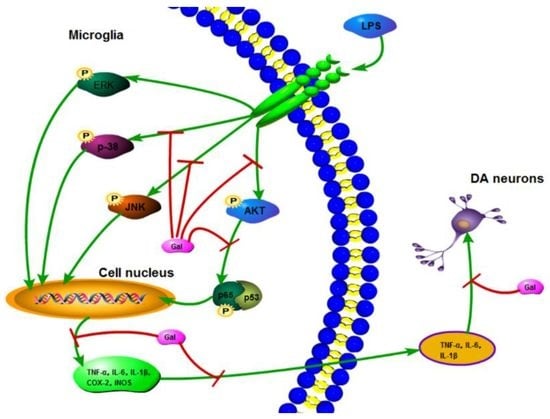
2.5. Galangin Associated with the Phosphorylation of the NF-κB p65, AKT, and MAPKs Signaling Pathways in LPS-Induced BV-2 Cells
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Reagent
4.2. Animals and Treatment
4.3. Rotational Behaviour Assay
4.4. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Cell Viability Assay
4.7. Quantitative Real-Time PCR
4.8. ELISA
4.9. Statistics
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| DA neurons | Dopaminergic neurons |
| SN | Substantia nigra |
| TH | Tyrosine hydroxylase |
| SNpc | Substantia nigra pars compacta |
References
- Cao, X.; Cao, L.; Ding, L.; Bian, J.S. A New Hope for a Devastating Disease: Hydrogen Sulfide in Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: Mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson-Lewis, V.; Blesa, J.; Przedborski, S. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2012, 18, S183–S185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipp, F.; Aktas, O. The brain as a target of inflammation: Common pathways link inflammatory and neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 518–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glass, C.K.; Saijo, K.; Winner, B.; Marchetto, M.C.; Gage, F.H. Mechanisms underlying inflammation in neurodegeneration. Cell 2010, 140, 918–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, A.I.; de Hoz, R.; Salobrar-Garcia, E.; Salazar, J.J.; Rojas, B.; Ajoy, D.; Lopez-Cuenca, I.; Rojas, P.; Trivino, A.; Ramirez, J.M. The Role of Microglia in Retinal Neurodegeneration: Alzheimer’s Disease, Parkinson, and Glaucoma. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2017, 9, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.T.; Luo, H.; Wu, J.; Lan, L.B.; Fan, D.H.; Zhu, K.D.; Chen, X.Y.; Wen, M.; Liu, H.M. Galangin induces apoptosis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells via the mitochondrial pathway. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 3377–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capasso, R.; Mascolo, N. Inhibitory effect of the plant flavonoid galangin on rat vas deferens in vitro. Life Sci. 2003, 72, 2993–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kim, K.A.; Jeong, S.; Lee, S.; Park, H.J.; Kim, N.J.; Lim, S. Anti-inflammatory, anti-nociceptive, and anti-psychiatric effects by the rhizomes of Alpinia officinarum on complete Freund’s adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2009, 126, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Luo, Q.; Bi, J.; Ding, J.; Ge, S.; Chen, F. Galangin inhibits growth of human head and neck squamous carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2014, 224, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, C.H.; Jang, S.J.; Ahn, J.; Gwon, S.Y.; Jeon, T.I.; Kim, T.W.; Ha, T.Y. Alpinia officinarum inhibits adipocyte differentiation and high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice through regulation of adipogenesis and lipogenesis. J. Med. Food 2012, 15, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sivakumar, A.S.; Anuradha, C.V. Effect of galangin supplementation on oxidative damage and inflammatory changes in fructose-fed rat liver. Chem.-Biol. Interact. 2011, 193, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.C.; Tsai, M.S.; Hsieh, P.C.; Shih, J.H.; Wang, T.S.; Wang, Y.C.; Lin, T.H.; Wang, S.H. Galangin ameliorates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by attenuating oxidative stress, inflammation and cell death in mice through inhibition of ERK and NF-kappaB signaling. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 329, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.C.; Kim, M.E.; Yoon, J.H.; Park, P.R.; Youn, H.Y.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, J.S. Anti-inflammatory effects of galangin on lipopolysaccharide-activated macrophages via ERK and NF-kappaB pathway regulation. Immunopharmacol. Immunotoxicol. 2014, 36, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huh, J.E.; Jung, I.T.; Choi, J.; Baek, Y.H.; Lee, J.D.; Park, D.S.; Choi, D.Y. The natural flavonoid galangin inhibits osteoclastic bone destruction and osteoclastogenesis by suppressing NF-kappaB in collagen-induced arthritis and bone marrow-derived macrophages. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 698, 57–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.H.; Bae, Y.; Kim, S.H. Galangin attenuates mast cell-mediated allergic inflammation. Food Chem. Toxicol. Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2013, 57, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.S.; Tao, W.; Miao, Q.B.; Lu, S.C.; Zhu, Y.B. Galangin dampens mice lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury. Inflammation 2014, 37, 1661–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, W.J.; Qian, Y.; Shen, Y.; Du, Q.; Chen, F.F.; Wu, Z.Z.; Li, X.; Huang, M. Galangin Abrogates Ovalbumin-Induced Airway Inflammation via Negative Regulation of NF-kappaB. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. ECAM 2013, 2013, 767689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoogland, I.C.; Houbolt, C.; van Westerloo, D.J.; van Gool, W.A.; van de Beek, D. Systemic inflammation and microglial activation: Systematic review of animal experiments. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Qu, R.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, R.; Ma, S. Rhynchophylline attenuates LPS-induced pro-inflammatory responses through down-regulation of MAPK/NF-kappaB signaling pathways in primary microglia. Phytother. Res. PTR 2012, 26, 1528–1533. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- De Oliveira, A.C.; Candelario-Jalil, E.; Bhatia, H.S.; Lieb, K.; Hull, M.; Fiebich, B.L. Regulation of prostaglandin E2 synthase expression in activated primary rat microglia: Evidence for uncoupled regulation of mPGES-1 and COX-2. Glia 2008, 56, 844–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, B.; Liu, J.; Ju, C.; Yang, D.; Chen, G.; Xu, S.; Zeng, Y.; Yan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, D.; et al. Licochalcone A Prevents the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons by Inhibiting Microglial Activation in Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-Induced Parkinson’s Disease Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Liu, D.F.; Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, D.; Xu, S.Y.; Chen, G.X.; Huang, B.X.; Ren, W.Z.; Wang, W.; Fu, S.P.; et al. Vanillin Protects Dopaminergic Neurons against Inflammation-Mediated Cell Death by Inhibiting ERK1/2, P38 and the NF-kappaB Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.P.; Wang, J.F.; Xue, W.J.; Liu, H.M.; Liu, B.R.; Zeng, Y.L.; Li, S.N.; Huang, B.X.; Lv, Q.K.; Wang, W.; et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of BHBA in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models are mediated by GPR109A-dependent mechanisms. J. Neuroinflamm. 2015, 12, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suter, M.R.; Wen, Y.R.; Decosterd, I.; Ji, R.R. Do glial cells control pain? Neuron Glia Biol. 2007, 3, 255–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagatsu, T.; Levitt, M.; Udenfriend, S. Tyrosine Hydroxylase. The Initial Step in Norepinephrine Biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 1964, 239, 2910–2917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jorge-Finnigan, A.; Kleppe, R.; Jung-Kc, K.; Ying, M.; Marie, M.; Rios-Mondragon, I.; Salvatore, M.F.; Saraste, J.; Martinez, A. Phosphorylation at serine 31 targets tyrosine hydroxylase to vesicles for transport along microtubules. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 14092–14107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerstedt, U. Postsynaptic supersensitivity after 6-hydroxy-dopamine induced degeneration of the nigro-striatal dopamine system. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1971, 367, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungerstedt, U. Striatal dopamine release after amphetamine or nerve degeneration revealed by rotational behaviour. Acta Physiol. Scand. Suppl. 1971, 367, 49–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stansley, B.; Post, J.; Hensley, K. A comparative review of cell culture systems for the study of microglial biology in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2012, 9, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henn, A.; Lund, S.; Hedtjarn, M.; Schrattenholz, A.; Porzgen, P.; Leist, M. The suitability of BV2 cells as alternative model system for primary microglia cultures or for animal experiments examining brain inflammation. Altex 2009, 26, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, J.S.; Ley, S.C. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 13, 679–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boje, K.M. Nitric oxide neurotoxicity in neurodegenerative diseases. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 2004, 9, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, W.; Ye, X.; Bao, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D. Inhibition of Src tyrosine kinase activity by squamosamide derivative FLZ attenuates neuroinflammation in both in vivo and in vitro Parkinson’s disease models. Neuropharmacology 2013, 75, 201–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Fu, S.; Feng, W.; Huang, B.; Xu, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, J. AMP010014A09 in Sus Scrofa Encodes an Analog of G Protein-Coupled Receptor 109A, Which Mediates the Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Beta-Hydroxybutyric Acid. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 42, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








| Gene | Sequence | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | (F): 5′-GCAACTGCTGCACGAAATC-3′ (R): 5′-CTGCTTGTCCTCTGCCCAC-3′ | 136 |
| IL-1β | (F): 5′-GTTCCCATTAGACAACTGCACTACAG-3′ (R): 5′-GTCGTTGCTTGGTTCTCCTTGTA-3′ | 139 |
| IL-6 | (F): 5′-CCAGAAACCGCTATGAAGTTCC-3′ (R): 5′-GTTGGGAGTGGTATCCTCTGTGA-3′ | 138 |
| iNOS | (F): 5′-GAACTGTAGCACAGCACAGGAAAT-3′ (R): 5′-CGTACCGGATGAGCTGTGAAT-3′ | 158 |
| COX-2 | (F): 5′-CAGTTTATGTTGTCTGTCCAGAGTTTC-3′ (R): 5′-CCAGCACTTCACCCATCAGTT-3′ | 127 |
| β-actin | (F): 5′-GTCAGGTCATCACTATCGGCAAT-3′ (R): 5′-AGAGGTCTTTACGGATGTCAACGT-3′ | 147 |
| Gene | Sequence | Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|
| TNF-α | (F): 5′-CCACGCTCTTCTGTCTACTG-3′ (R): 5′-GCTACGGGCTTGTCACTC-3′ | 145 |
| IL-1β | (F): 5′-TGTGATGTTCCCATTAGAC-3′ (R): 5′-AATACCACTTGTTGGCTTA-3′ | 131 |
| IL-6 | (F): 5′-AGCCACTGCCTTCCCTAC-3′ (R): 5′-TTGCCATTGCACAACTCTT-3′ | 156 |
| iNOS | (F): 5′-CACCCAGAAGAGTTACAGC-3′ (R): 5′-GGAGGGAAGGGAGAATAG-3′ | 186 |
| COX-2 | (F): 5′-AGAGTCAGTTAGTGGGTAGT-3′ (R): 5′-CTTGTAGTAGGCTTAAACATAG-3′ | 170 |
| β-actin | (F): 5′-GTCAGGTCATCACTATCGGCAAT-3′ (R): 5′-AGAGGTCTTTACGGATGTCAACGT-3′ | 147 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, G.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L.; Ran, X.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Huang, B.; Wang, W.; Fu, S. Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson’s Disease in Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010012
Chen G, Liu J, Jiang L, Ran X, He D, Li Y, Huang B, Wang W, Fu S. Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson’s Disease in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010012
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Guangxin, Juxiong Liu, Liqiang Jiang, Xin Ran, Dewei He, Yuhang Li, Bingxu Huang, Wei Wang, and Shoupeng Fu. 2018. "Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson’s Disease in Rats" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010012
APA StyleChen, G., Liu, J., Jiang, L., Ran, X., He, D., Li, Y., Huang, B., Wang, W., & Fu, S. (2018). Galangin Reduces the Loss of Dopaminergic Neurons in an LPS-Evoked Model of Parkinson’s Disease in Rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010012