Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Turmeric Extract Incorporated Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion
Abstract
:1. Introduction
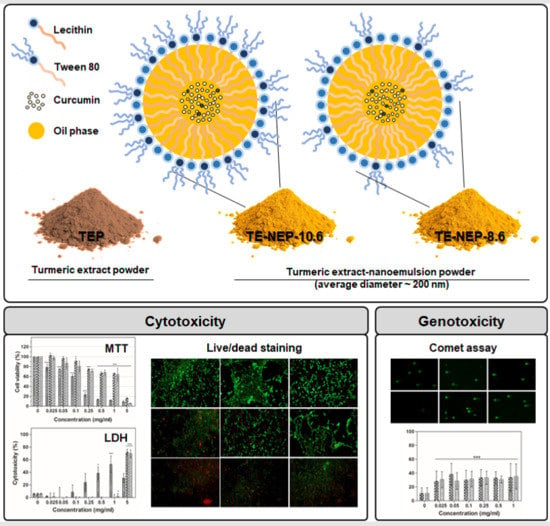
2. Results
Cytotoxicity of Turmeric Extract-Loaded Nanoemulsion
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Preparation
4.2. Cell Culture
4.2.1. Cell Lines
4.2.2. Primary Cells
4.3. Cytotoxicity Assay
4.3.1. MTT Assay
4.3.2. Live/Dead Assay
4.3.3. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Assay
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, Y.; Meher, J.G.; Raval, K.; Khan, F.A.; Chaurasia, M.; Jain, N.K.; Chourasia, M.K. Nanoemulsion: Concepts, development and applications in drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2017, 252, 28–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bush, L.; Stevenson, L.; Lane, K.E. The oxidative stability of omega-3 oil-in-water nanoemulsion systems suitable for functional food enrichment: A systematic review of the literature. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, H.D.; Cerqueira, M.Â.; Vicente, A.A. Nanoemulsions for food applications: Development and characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, P.; Zeng, Q.; Tai, K.; He, X.; Yao, Y.; Hong, X.; Yuan, F. Preparation of curcumin-loaded emulsion using high pressure homogenization: Impact of oil phase and concentration on physicochemical stability. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 84, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laokuldilok, N.; Thakeow, P.; Kopermsub, P.; Utama-ang, N. Optimisation of microencapsulation of turmeric extract for masking flavour. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 695–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaraj, S.D.; Neelakantan, P. Curcumin-pharmacological actions and its role in dentistry. Asian J. Pharm. Res. Health Care 2014, 6, 19–22. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari, E.; Benassi, R.; Saladini, M.; Orteca, G.; Gazova, Z.; Siposova, K. In vitro study on potential pharmacological activity of curcumin analogues and their copper complexes. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2017, 89, 411–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiwidjaja, J.; McLachlan, A.J.; Boddy, A.V. Curcumin as a clinically-promising anti-cancer agent: Pharmacokinetics and drug interactions. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 953–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, R.M.; Pereira, S.V.; Siqueira, S.; Salomão, W.F.; Freitas, L.A.P. Curcuminoid content and antioxidant activity in spray dried microparticles containing turmeric extract. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Nguyen, M.-H.; Cheow, W.S.; Hadinoto, K. A new bioavailability enhancement strategy of curcumin via self-assembly nano-complexation of curcumin and bovine serum albumin. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartono, S.B.; Hadisoewignyo, L.; Yang, Y.; Meka, A.K.; Yu, C. Amine functionalized cubic mesoporous silica nanoparticles as an oral delivery system for curcumin bioavailability enhancement. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 505605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashidi, L.; Khosravi-Darani, K. The applications of nanotechnology in food industry. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 723–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushen, M.; Kerry, J.; Morris, M.; Cruz-Romero, M.; Cummins, E. Nanotechnologies in the food industry–Recent developments, risks and regulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 24, 30–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulizzi, F. Nanotechnology and food: What people think. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission, E. Commission Recommendation of 18 October 2011 on the definition of nanomaterial (2011/696/EU). Official Journal of the European Union, 2011. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/research/industrial_technologies/pdf/policy/commission-recommendation-on-the-definition-of-nanomater-18102011_en.pdf (accessed on 20 October 2011).
- Committee, E.S. Guidance on the risk assessment of the application of nanoscience and nanotechnologies in the food and feed chain. EFSA J. 2011, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OFFICE, G.P. An Act to Authorize Appropriations for Nanoscience, Nanoengineering, and Nanotechnology Research, and for Other Purposes; U.S. Government Publishing Office: Washington, DC, USA, 2003; Volume 149, pp. 1923–1932.
- Health, U.D.O.; Services, H. Guidance for Industry: Considering Whether an FDA-Regulated Product Involves the Application of Nanotechnology; FDA Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER): Silver Spring, MD, USA, 2014; pp. 1–14.
- Department, I.A. Management System of Nanotechnology Applied Food; National Food Safety Information Service: Seoul, Korea, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- McClements, D.J.; Rao, J. Food-grade nanoemulsions: Formulation, fabrication, properties, performance, biological fate, and potential toxicity. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 285–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Edible lipid nanoparticles: Digestion, absorption, and potential toxicity. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 409–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitzner, S.R.; Stange, J.; Klammt, S.; Peszynski, P.; Schmidt, R.; NÖLDGE-SCHOMBURG, G. Extracorporeal detoxification using the molecular adsorbent recirculating system for critically ill patients with liver failure. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2001, 12, S75–S82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lakatta, E.G. Cardiovascular System. In Comprehensive Physiology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekwall, B.; Silano, V.; Paganuzzi-Stammati, A.; Zucco, F. Toxicity Tests with Mammalian Cell Cultures; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1990; pp. 75–99. [Google Scholar]
- Bhushani, J.A.; Karthik, P.; Anandharamakrishnan, C. Nanoemulsion-based delivery system for improved bioaccessibility and Caco-2 cell monolayer permeability of green tea catechins. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 372–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, A.; Nikmaram, N.; Roohinejad, S.; Estevinho, B.N.; Rocha, F.; Greiner, R.; McClements, D.J. Production, properties, and applications of solid self-emulsifying delivery systems (S-SEDS) in the food and pharmaceutical industries. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 538, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joung, H.J.; Choi, M.J.; Kim, J.T.; Park, S.H.; Park, H.J.; Shin, G.H. Development of Food-Grade Curcumin Nanoemulsion and its Potential Application to Food Beverage System: Antioxidant Property and In Vitro Digestion. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Chi, M.-H.; Shen, C.-M.; Chen, H.-W.; Yang, W.-J.; Lee, M.-H. Preparation of curcumin microemulsions with food-grade soybean oil/lecithin and their cytotoxicity on the HepG2 cell line. Food Chem. 2014, 154, 282–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prabhakar, K.; Afzal, S.M.; Surender, G.; Kishan, V. Tween 80 containing lipid nanoemulsions for delivery of indinavir to brain. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2013, 3, 345–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z.; Thu, H.E.; Amjad, M.W.; Ahmed, T.A.; Khan, S. Exploring recent developments to improve antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antimicrobial efficacy of curcumin: A review of new trends and future perspectives. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 77, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, P.; Singh, M. Study of curcumin antioxidant activities in robust oil–water nanoemulsions. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 12506–12519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Estaca, J.; Balaguer, M.; López-Carballo, G.; Gavara, R.; Hernández-Muñoz, P. Improving antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of curcumin by means of encapsulation in gelatin through electrohydrodynamic atomization. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 70, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, R.L.; Luis, P.B.; Varuzza, P.V.; Joseph, A.I.; Presley, S.H.; Chaturvedi, R.; Schneider, C. The anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin is mediated by its oxidative metabolites. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 21243–21252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Du, Z.; Wang, W.; Sanidad, K.; Zhang, G. Structure and activity relationship of curucmin: Role of methoxy group in anti-inflammatory and anti-colitis effects of curcumin. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 972.24. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.-P.; Wang, Q.-X.; Lin, H.-P.; Chang, N. Anti-tumor bioactivities of curcumin on mice loaded with gastric carcinoma. Food Funct. 2017, 8, 3319–3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirohi, V.K.; Popli, P.; Sankhwar, P.; Kaushal, J.B.; Gupta, K.; Manohar, M.; Dwivedi, A. Curcumin exhibits anti-tumor effect and attenuates cellular migration via Slit-2 mediated down-regulation of SDF-1 and CXCR4 in endometrial adenocarcinoma cells. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 44, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mock, C.D.; Jordan, B.C.; Selvam, C. Recent advances of curcumin and its analogues in breast cancer prevention and treatment. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 75575–75588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EFSA. Scientific Opinion on the reevaluation of curcumin (E 100) as a food additive. EFSA J. 2010, 8, 46. [Google Scholar]
- Karakoti, A.; Hench, L.; Seal, S. The potential toxicity of nanomaterials—The role of surfaces. JOM J. Miner. Met. Mater. Soc. 2006, 58, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberdörster, G.; Oberdörster, E.; Oberdörster, J. Nanotoxicology: An emerging discipline evolving from studies of ultrafine particles. Environ. Health Perspect. 2005, 113, 823–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borm, P.J.; Robbins, D.; Haubold, S.; Kuhlbusch, T.; Fissan, H.; Donaldson, K.; Schins, R.; Stone, V.; Kreyling, W.; Lademann, J. The potential risks of nanomaterials: A review carried out for ECETOC. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2006, 3, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nel, A.; Xia, T.; Mädler, L.; Li, N. Toxic potential of materials at the nanolevel. Science 2006, 311, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beliciu, C.; Moraru, C. Effect of solvent and temperature on the size distribution of casein micelles measured by dynamic light scattering. J. Dairy Sci. 2009, 92, 1829–1839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teng, T.-P.; Hung, Y.-H.; Teng, T.-C.; Chen, J.-H. Performance evaluation on an air-cooled heat exchanger for alumina nanofluid under laminar flow. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2011, 6, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogawa, S.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Influence of environmental conditions on the stability of oil in water emulsions containing droplets stabilized by lecithin−chitosan membranes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 5522–5527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klang, V.; Matsko, N.B.; Valenta, C.; Hofer, F. Electron microscopy of nanoemulsions: An essential tool for characterisation and stability assessment. Micron 2012, 43, 85–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, W.P.; Thomas, A.D.; Kaina, B. DNA damage and the balance between survival and death in cancer biology. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2016, 16, 20–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohnishi, S.; Ma, N.; Thanan, R.; Pinlaor, S.; Hammam, O.; Murata, M.; Kawanishi, S. DNA damage in inflammation-related carcinogenesis and cancer stem cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2013, 2013, 387014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Dhawan, A. Genotoxic and carcinogenic potential of engineered nanoparticles: An update. Arch. Toxicol. 2013, 87, 1883–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landsiedel, R.; Kapp, M.D.; Schulz, M.; Wiench, K.; Oesch, F. Genotoxicity investigations on nanomaterials: Methods, preparation and characterization of test material, potential artifacts and limitations—Many questions, some answers. Mutat. Res. 2009, 681, 241–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, J.; Jiang, L.-P.; Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Yao, X.-F.; Zhong, L.-F. Curcumin-induced genotoxicity and antigenotoxicity in HepG2 cells. Toxicon 2007, 49, 1219–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zorn-Kruppa, M.; Tykhonova, S.; Belge, G.; Diehl, H.A.; Engelke, M. Comparison of human corneal cell cultures in cytotoxicity testing. Altex 2004, 21, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kong, B.; Seog, J.H.; Graham, L.M.; Lee, S.B. Experimental considerations on the cytotoxicity of nanoparticles. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 929–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.-Y.; Joachim, E.; Choi, H.; Kim, K. Toxicity of silica nanoparticles depends on size, dose, and cell type. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 1407–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, G.K.; Chan, P.P.; Teo, A.; Loo, J.S.C.; Anderson, J.M.; Tan, T.T.Y. In vitro cytotoxicity evaluation of biomedical nanoparticles and their extracts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93, 337–346. [Google Scholar]
- Sambale, F.; Wagner, S.; Stahl, F.; Khaydarov, R.; Scheper, T.; Bahnemann, D. Investigations of the toxic effect of silver nanoparticles on mammalian cell lines. J. Nanomater. 2015, 16, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Sample | HLB Value | MCT Oil (g) | Surfactant (g) | DW (mL) | TEP (g) | Dextrin (g) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lecithin | Tween 80 | ||||||
| TE-NEP-8.6 | 8.6 | 500 | 400 | 100 | 9000 | 107.41 | 1107.41 |
| TE-NEP-10.6 | 10.6 | 750 | 412.5 | 337.5 | 8500 | 161.11 | 1661.11 |
| Sample | AVE (μg/mL) | STD |
|---|---|---|
| TE-NEP-8.6 | 1.64 | 0.01 |
| TE-NEP-10.6 | 1.83 | 0.02 |
| TEP | 32.48 | 0.46 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yoon, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Kang, M.G.; Kim, G.J.; Shin, S.Y.; Baek, S.H.; Lee, B.N.; Hong, S.J.; Kim, J.T.; Hong, K.; et al. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Turmeric Extract Incorporated Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010280
Yoon HJ, Zhang X, Kang MG, Kim GJ, Shin SY, Baek SH, Lee BN, Hong SJ, Kim JT, Hong K, et al. Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Turmeric Extract Incorporated Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(1):280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010280
Chicago/Turabian StyleYoon, Hee Jeong, Xiaowei Zhang, Min Gyeong Kang, Gyeong Jin Kim, Sun Young Shin, Sang Hong Baek, Bom Nae Lee, Su Jung Hong, Jun Tae Kim, Kwonho Hong, and et al. 2018. "Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Turmeric Extract Incorporated Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 1: 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010280
APA StyleYoon, H. J., Zhang, X., Kang, M. G., Kim, G. J., Shin, S. Y., Baek, S. H., Lee, B. N., Hong, S. J., Kim, J. T., Hong, K., & Bae, H. (2018). Cytotoxicity Evaluation of Turmeric Extract Incorporated Oil-in-Water Nanoemulsion. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(1), 280. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010280