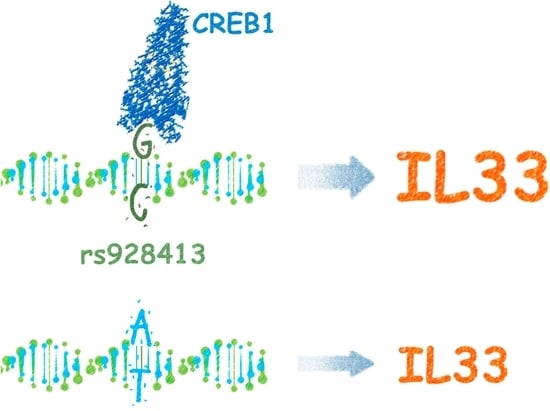
The Risk G Allele of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs928413 Creates a CREB1-Binding Site That Activates IL33 Promoter in Lung Epithelial Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Presence of “G” Allele of rs928413 Is Associated with Increased IL33 Promoter Activity
2.2. Risk Allele of rs928413 in IL33 Promoter Creates CREB1-Binding Site
2.3. CREB1 Activation Is Associated with Elevated IL33 Promoter Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines
4.2. Ethical Approval
4.3. Luciferase Reporter Constructss
4.4. NCIH-196 Transfection and Luciferase Reporter Assay
4.5. Pull-Down Assay
4.6. CREB1 Knockdown Using siRNA
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmitz, J.; Owyang, A.; Oldham, E.; Song, Y.; Murphy, E.; McClanahan, T.K.; Zurawski, G.; Moshrefi, M.; Qin, J.; Li, X.; et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity 2005, 23, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pichery, M.; Mirey, E.; Mercier, P.; Lefrancais, E.; Dujardin, A.; Ortega, N.; Girard, J.P. Endogenous IL-33 is highly expressed in mouse epithelial barrier tissues, lymphoid organs, brain, embryos, and inflamed tissues: in situ analysis using a novel Il-33-LacZ gene trap reporter strain. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 3488–3495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cayrol, C.; Girard, J. IL-33: An alarmin cytokine with crucial roles in innate immunity, inflammation and allergy. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2014, 31, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lott, J.M.; Sumpter, T.L.; Turnquist, H.R. New dog and new tricks: Evolving roles for IL-33 in type 2 immunity. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2015, 97, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.E. IL-33: A tissue derived cytokine pathway involved in allergic inflammation and asthma. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2009, 40, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, F.Y.; Pitman, N.I.; McInnes, I.B. Disease-associated functions of IL-33: The new kid in the IL-1 family. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neill, D.R.; Wong, S.H.; Bellosi, A.; Flynn, R.J.; Daly, M.; Langford, T.K.A.; Bucks, C.; Kane, C.M.; Fallon, P.G.; Pannell, R.; et al. Nuocytes represent a new innate effector leukocyte that mediates type-2 immunity. Nature 2010, 464, 1367–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Préfontaine, D.; Lajoie-Kadoch, S.; Foley, S.; Audusseau, S.; Olivenstein, R.; Halayko, A.J.; Lemière, C.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q. Increased expression of IL-33 in severe asthma: evidence of expression by airway smooth muscle cells. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 5094–5103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Stolarski, B.; Kewin, P.; Murphy, G.; Corrigan, C.J.; Ying, S.; Pitman, N.; Mirchandani, A.; Rana, B.; van Rooijen, N.; et al. IL-33 amplifies the polarization of alternatively activated macrophages that contribute to airway inflammation. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 6469–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Préfontaine, D.; Nadigel, J.; Chouiali, F.; Audusseau, S.; Semlali, A.; Chakir, J.; Martin, J.G.; Hamid, Q. Increased IL-33 expression by epithelial cells in bronchial asthma. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 125, 752–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raeiszadeh Jahromi, S.; Mahesh, P.A.; Jayaraj, B.S.; Madhunapantula, S.R.V.; Holla, A.D.; Vishweswaraiah, S.; Ramachandra, N.B. Serum levels of IL-10, IL-17F and IL-33 in patients with asthma: A case-control study. J. Asthma 2014, 51, 1004–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christianson, C.A.; Goplen, N.P.; Zafar, I.; Irvin, C.; Good, J.T.; Rollins, D.R.; Gorentla, B.; Liu, W.; Gorska, M.M.; Chu, H.W.; et al. Persistence of asthma requires multiple feedback circuits involving type 2 innate lymphoid cells and IL-33. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudbjartsson, D.F.; Bjornsdottir, U.S.; Halapi, E.; Helgadottir, A.; Sulem, P.; Jonsdottir, G.M.; Thorleifsson, G.; Helgadottir, H.; Steinthorsdottir, V.; Stefansson, H.; et al. Sequence variants affecting eosinophil numbers associate with asthma and myocardial infarction. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 342–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moffatt, M.; Gut, I.; Demenais, F.; Strachan, D.; Bouzigon, E.; Heath, S. A Large-Scale, Consortium-Based Genomewide Association Study of Asthma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, D.G.; Ampleford, E.J.; Chiu, G.Y.; Gauderman, W.J.; Gignoux, C.R.; Graves, P.E.; Himes, B.E.; Levin, A.M.; Mathias, R.A.; Hancock, D.B.; et al. Meta-analysis of genome-wide association studies of asthma in ethnically diverse North American populations. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bonnelykke, K.; Sleiman, P.; Nielsen, K.; Kreiner-møller, E.; Mercader, J.M.; Belgrave, D.; Dekker, H.T.; Den Husby, A.; Sevelsted, A.; Faura-tellez, G.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies CDHR3 as a susceptibility locus for early childhood asthma with severe exacerbations. Nat. Genet. 2013, 46, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhang, J.; Hu, H.; Jin, Y.; Xue, M. Polymorphisms of RAD50, IL33 and IL1RL1 are associated with atopic asthma in Chinese population. Tissue Antigens 2015, 86, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schroder, P.; Casaca, V.; Illi, S.; Schieck, M.; Michel, S.; Bock, A.; Roduit, C.; Frei, R.; Lluis, A.; Shaub, B. IL-33 polymorphisms are associated with increased risk of hay fever and reduced Regulatory T cells in a birth cohort. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 687–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tominaga, S.; Hayakawa, M.; Tsuda, H.; Ohta, S.; Yanagisawa, K. Presence of a novel exon 2E encoding a putative transmembrane protein in human IL-33 gene. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuda, H.; Komine, M.; Tominaga, S.; Ohtsuki, M. Identification of the promoter region of human IL-33 responsive to induction by IFNγ. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2017, 85, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barretina, J.; Caponigro, G.; Stransky, N.; Venkatesan, K.; Margolin, A.A.; Kim, S.; Kryukov, G.V.; Sonkin, D.; Reddy, A.; Liu, M.; et al. The Cancer Cell Line Encyclopedia enables predictive modelling of anticancer drug sensitivity. Nature 2012, 463, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vorontsov, I.E.; Kulakovskiy, I.V.; Khimulya, G.; Nikolaeva, D.D.; Makeev, V.J. PERFECTOS-APE: Predicting regulatory functional effect of SNPs by approximate P-value estimation. In Proceedings of the Bioinformatics 2015 6th International Conference on Bioinformatics Models, Methods and Algorithms, Lisbon, Portugal, 12–15 January 2015; pp. 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitola, M.; Carlsson, P.; Mahlapuu, M.; Enerbäck, S.; Pelto-Huikko, M. Forkhead transcription factor FoxF2 is expressed in mesodermal tissues involved in epithelio-mesenchymal. Dev. Dyn. 2000, 218, 136–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormestad, M.; Astorga, J.; Landgren, H.; Wang, T.; Carlsson, P. Foxf1 and Foxf2 control murine gut development by limiting mesenchymal Wnt signaling and promoting extracellular matrix production. Development 2006, 133, 833–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, T.; Tamakoshi, T.; Uezato, T.; Shu, F.; Kanzaki-Kato, N.; Fu, Y.; Koseki, H.; Yoshida, N.; Sugiyama, T.; Miura, N. Forkhead transcription factor Foxf2 (LUN)-deficient mice exhibit abnormal development of secondary palate. Dev. Biol. 2003, 259, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtois, G.; Morgan, J.; Campbell, L.; Fourel, G.; Crabtree, G. Interaction of a Liver-Specific Nuclear Factor with the Fibrinogen and α1-Antitrypsin Promoters. Science 1987, 238, 688–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pedersen, K.; Chhabra, K.; Nguen, V.; Lazartigues, E. The transcription factor HNF1α induces expression of angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in pancreatic islets from evolutionarily conserved promoter motifs. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 43, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Cam, L.; Lacroix, M.; Ciemerych, M.A.; Sardet, C.; Sicinski, P. The E4F Protein Is Required for Mitotic Progression during Embryonic Cell Cycles. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 6467–6475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chagraoui, J.; Niessen, S.; Lessard, J.; Girard, S.; Coulombe, P.; Meloche, S.; Sauvageau, G. p120E4F-1: A novel candidate factor for mediating Bmi-1 function in hematopoietic stem cells. Blood 2004, 104, 307. [Google Scholar]
- Hatchi, E.; Rodier, G.; Lacroix, M.; Caramel, J.; Kirsh, O.; Jacquet, C.; Schrepfer, E.; Lagarrigue, S.; Linares, L.K.; Lledo, G.; et al. E4F1 deficiency results in oxidative stress-mediated cell death of leukemic cells. J. Exp. Med. 2011, 208, 1403–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shaywitz, A.J.; Greenberg, M.E. CREB: a stimulus-induced transcription factor activated by a diverse array of extracellular signals. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1999, 68, 821–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J.; Adcock, I.M. Transcription factors and asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 1998, 12, 221–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartel, S.; Schulz, N.; Alessandrini, F.; Schamberger, A.C.; Pagel, P.; Theis, F.J.; Milger, K.; Noessner, E.; Stick, S.M.; Kicic, A.; et al. Pulmonary microRNA profiles identify involvement of Creb1 and Sec14l3 in bronchial epithelial changes in allergic asthma. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiappara, G.; Chanez, P.; Bruno, A.; Pace, E.; Pompeo, F.; Bousquet, J.; Bonsignore, G.; Gjomarkaj, M. Variable p-CREB expression depicts different asthma phenotypes. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 62, 787–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koga, Y.; Hisada, T.; Ishizuka, T.; Utsugi, M.; Ono, A.; Yatomi, M.; Kamide, Y.; Aoki-Saito, H.; Tsurumaki, H.; Dobashi, K.; et al. CREB regulates TNF-α-induced GM-CSF secretion via p38 MAPK in human lung fibroblasts. Allergol. Int. 2016, 65, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, A.Y.; Sakamoto, K.M.; Miller, L.S. The Role of the Transcription Factor CREB in Immune Function. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6413–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, W.; Liang, Q.; Balzar, S.; Wenzel, S.; Gorska, M.; Alam, R. Cell-specific activation profile of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2, Jun N-terminal kinase, and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinases in asthmatic airways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 121, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, P.J. New therapies for asthma: Is there any progress? Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2010, 31, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabio, G.; Davis, R.J. TNF and MAP kinase signalling pathways. Semin. Immunol. 2014, 26, 237–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ying, S.; Robinson, D.S.; Varney, V.; Meng, Q.; Tsicopoulos, A.; Moqbel, R.; Durham, S.R.; Kay, A.B.; Hamid, Q. TNF alpha mRNA expression in allergic inflammation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 1991, 21, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, K.S.; Lee, W.; Chung, C.; Koo, J.S.; Yang, E.J.; Choi, Y.; Yoon, J.; Song, K.S.; Lee, W.; Chung, K.C.; et al. Mechanisms of Signal Transduction: Interleukin-1β and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α Induce MUC5AC Overexpression through a Mechanism Involving ERK/p38 Mitogen-activated Protein Kinases-MSK1-CREB Activation in Human Airway Epithelial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 23243–23250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitsett, J.A.; Alenghat, T. Respiratory epithelial cells orchestrate pulmonary innate immunity. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. The immunology of asthma. Nat. Immunol. 2015, 16, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, A.; Fujimoto, Y.; Fukase, K.; Takada, H. Various human epithelial cells express functional Toll-like receptors, NOD1 and NOD2 to produce anti-microbial peptides, but not proinflammatory cytokines. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 3100–3111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovach, M.A.; Standiford, T.J. Toll like receptors in diseases of the lung. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1399–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leiva-Juárez, M.M.; Kolls, J.K.; Evans, S.E. Lung epithelial cells: Therapeutically inducible effectors of antimicrobial defense. Mucosal Immunol. 2018, 11, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asokananthan, N.; Graham, P.T.; Fink, J.; Knight, D.A.; Bakker, A.J.; McWilliam, A.S.; Thompson, P.J.; Stewart, G.A. Activation of Protease-Activated Receptor (PAR)-1, PAR-2, and PAR-4 Stimulates IL-6, IL-8, and Prostaglandin E2 Release from Human Respiratory Epithelial Cells. J. Immunol. 2002, 168, 3577–3585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hammad, H.; Chieppa, M.; Perros, F.; Willart, M.A.; Germain, R.N.; Lambrecht, B.N. House dust mite allergen induces asthma via Toll-like receptor 4 triggering of airway structural cells. Nat. Med. 2009, 15, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, A.T.; Peterson, E.A.; Chakir, J.; Wills-Karp, M. Innate immune responses of airway epithelium to house dust mite are mediated through β-glucan-dependent pathways. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 612–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idzko, M.; Hammad, H.; Van Nimwegen, M.; Kool, M.; Willart, M.A.M.; Muskens, F.; Hoogsteden, H.C.; Luttmann, W.; Ferrari, D.; Di Virgilio, F.; et al. Extracellular ATP triggers and maintains asthmatic airway inflammation by activating dendritic cells. Nat. Med. 2007, 13, 913–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kool, M.; Willart, M.A.M.; van Nimwegen, M.; Bergen, I.; Pouliot, P.; Virchow, J.C.; Rogers, N.; Osorio, F.; Reis e Sousa, C.; Hammad, H.; et al. An Unexpected Role for Uric Acid as an Inducer of T Helper 2 Cell Immunity to Inhaled Antigens and Inflammatory Mediator of Allergic Asthma. Immunity 2011, 34, 527–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Herre, J.; Gronlund, H.; Brooks, H.; Hopkins, L.; Waggoner, L.; Murton, B.; Gangloff, M.; Opaleye, O.; Chilvers, E.R.; Fitzgerald, K.; et al. Allergens as Immunomodulatory Proteins: The Cat Dander Protein Fel d 1 Enhances TLR Activation by Lipid Ligands. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 1529–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Millien, V.O.; Lu, W.; Shaw, J.; Yuan, X.; Mak, G.; Roberts, L.; Song, L.Z.; Knight, J.M.; Creighton, C.J.; Luong, A.; et al. Cleavage of Fibrinogen by Proteinases Elicits Allergic Responses Through Toll-Like Receptor 4. Science 2013, 341, 792–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. Biology of Lung Dendritic Cells at the Origin of Asthma. Immunity 2009, 31, 412–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, E.; Petit-Bertron, A.F.; Bricard, R.; Levasseur, M.; Ramadan, A.; Girard, J.P.; Herbelin, A.; Dy, M. IL-33 Activates Unprimed Murine Basophils Directly In Vitro and Induces Their In Vivo Expansion Indirectly by Promoting Hematopoietic Growth Factor Production. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 3591–3597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaur, D.; Gomez, E.; Doe, C.; Berair, R.; Woodman, L.; Saunders, R.; Hollins, F.; Rose, F.R.; Amrani, Y.; May, R.; et al. IL-33 drives airway hyper-responsiveness through IL-13-mediated mast cell: Airway smooth muscle crosstalk. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 70, 556–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Kewin, P.; Murphy, G.; Russo, R.C.; Stolarski, B.; Garcia, C.C.; Komai-Koma, M.; Pitman, N.; Li, Y.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; et al. IL-33 Induces Antigen-Specific IL-5+ T Cells and Promotes Allergic-Induced Airway Inflammation Independent of IL-4. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 4780–4790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bartemes, K.R.; Iijima, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kephart, G.M.; McKenzie, A.N.; Kita, H. IL-33-Responsive Lineage-CD25+ CD44hi Lymphoid Cells Mediate Innate Type 2 Immunity and Allergic Inflammation in the Lungs. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 1503–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolarski, B.; Kurowska-Stolarska, M.; Kewin, P.; Xu, D.; Liew, F.Y. IL-33 Exacerbates Eosinophil-Mediated Airway Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 3472–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lunderius-Andersson, C.; Enoksson, M.; Nilsson, G. Mast cells respond to cell injury through the recognition of IL-33. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suzukawa, M.; Iikura, M.; Koketsu, R.; Nagase, H.; Tamura, C.; Komiya, A.; Nakae, S.; Matsushima, K.; Ohta, K.; Yamamoto, K.; et al. An IL-1 Cytokine Member, IL-33, Induces Human Basophil Activation via Its ST2 Receptor. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 5981–5989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Komai-Koma, M.; Brombacher, F.; Pushparaj, P.N.; Arendse, B.; McSharry, C.; Alexander, J.; Chaudhuri, R.; Thomson, N.C.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; McInnes, I.; et al. Interleukin-33 amplifies IgE synthesis and triggers mast cell degranulation via interleukin-4 in naive mice. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 67, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.H.; Yang, T.Y.; Park, C.S.; Ahn, S.H.; Son, B.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lim, D.H.; Jang, T.Y. Anti-IL-33 antibody has a therapeutic effect in a murine model of allergic rhinitis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012, 67, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Willart, M.A.M.; Deswarte, K.; Pouliot, P.; Braun, H.; Beyaert, R.; Lambrecht, B.N.; Hammad, H. Interleukin-1α controls allergic sensitization to inhaled house dust mite via the epithelial release of GM-CSF and IL-33. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yin, H.; Li, X.Y.; Liu, T.; Yuan, B.H.; Zhang, B.B.; Hu, S.L.; Gu, H.B.; Jin, X.B.; Zhu, J.Y. Adenovirus-mediated delivery of soluble ST2 attenuates ovalbumin-induced allergic asthma in mice. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 170, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Li, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Zeng, L.; Huang, T. Anti-IL-33 antibody treatment inhibits airway inflammation in a murine model of allergic asthma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 386, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, S.; Matsumoto, K.; Gon, Y.; Maruoka, S.; Kujime, K.; Hayashi, S.; Takeshita, I.; Horie, T. p38 MAP kinase regulates TNF alpha-, IL-1 alpha- and PAF-induced RANTES and GM-CSF production by human bronchial epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2000, 30, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, S.; Ghosh, P.; Kusaba, H.; Buchholz, M.; Longo, D.L. Effect of promoter methylation on the regulation of IFN-gamma gene during in vitro differentiation of human peripheral blood T cells into a Th2 population. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 2510–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chava, K.R.; Karpurapu, M.; Wang, D.; Bhanoori, M.; Kundumani-Sridharan, V.; Zhang, Q.; Ichiki, T.; Glasgow, W.C.; Rao, G.N. CREB-mediated IL-6 expression is required for 15(S)-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid-induced vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2009, 29, 809–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, R.M.; Holownia, A.; Chyczewska, E.; Drost, E.M.; Braszko, J.J.; Noparlik, J.; Donaldson, K.; Macnee, W. Cytoplasm-Nuclear Trafficking of Creb and Creb Phosphorylation at Ser133 During Therapy of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58, 437–444. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korneev, K.V.; Kondakova, A.N.; Sviriaeva, E.N.; Mitkin, N.A.; Palmigiano, A.; Kruglov, A.A.; Telegin, G.B.; Drutskaya, M.S.; Sturiale, L.; Garozzo, D.; et al. Hypoacylated LPS from Foodborne Pathogen Campylobacter jejuni Induces Moderate TLR4-Mediated Inflammatory Response in Murine Macrophages. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitkin, N.A.; Muratova, A.M.; Schwartz, A.M.; Kuprash, D.V. The A allele of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs630923 creates a Binding site for MEF2C resulting in reduced CXCR5 Promoter activity in B-cell lymphoblastic cell lines. Front. Immunol. 2016, 7, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitkin, N.A.; Muratova, A.M.; Sharonov, G.V.; Korneev, K.V.; Sviriaeva, E.N.; Mazurov, D.; Schwartz, A.M.; Kuprash, D.V. p63 and p73 repress CXCR5 chemokine receptor gene expression in p53-deficient MCF-7 breast cancer cells during genotoxic stress. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gene Regul. Mech. 2017, 1860, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitkin, N.A.; Muratova, A.M.; Korneev, K.V.; Pavshintsev, V.V.; Rumyantsev, K.A.; Vagida, M.S.; Uvarova, A.N.; Afanasyeva, M.A.; Schwartz, A.M.; Kuprash, D.V. Protective C allele of the single-nucleotide polymorphism rs1335532 is associated with strong binding of Ascl2 transcription factor and elevated CD58 expression in B-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 3211–3220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasson, S.A.; Kane, L.A.; Yamano, K.; Huang, C.H.; Sliter, D.A.; Buehler, E.; Wang, C.; Heman-Ackah, S.M.; Hessa, T.; Guha, R.; et al. High-content genome-wide RNAi screens identify regulators of parkin upstream of mitophagy. Nature 2013, 504, 291–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afanasyeva, M.A.; Britanova, L.V.; Korneev, K.V.; Mitkin, N.A.; Kuchmiy, A.A.; Kuprash, D.V. Clusterin is a potential lymphotoxin beta receptor target that is upregulated and accumulates in germinal centers of mouse spleen during immune response. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gorbacheva, A.M.; Korneev, K.V.; Kuprash, D.V.; Mitkin, N.A. The Risk G Allele of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs928413 Creates a CREB1-Binding Site That Activates IL33 Promoter in Lung Epithelial Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102911
Gorbacheva AM, Korneev KV, Kuprash DV, Mitkin NA. The Risk G Allele of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs928413 Creates a CREB1-Binding Site That Activates IL33 Promoter in Lung Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102911
Chicago/Turabian StyleGorbacheva, Alisa M., Kirill V. Korneev, Dmitry V. Kuprash, and Nikita A. Mitkin. 2018. "The Risk G Allele of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs928413 Creates a CREB1-Binding Site That Activates IL33 Promoter in Lung Epithelial Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102911
APA StyleGorbacheva, A. M., Korneev, K. V., Kuprash, D. V., & Mitkin, N. A. (2018). The Risk G Allele of the Single-Nucleotide Polymorphism rs928413 Creates a CREB1-Binding Site That Activates IL33 Promoter in Lung Epithelial Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 2911. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19102911