Hepatoprotective Effect of Loquat Leaf Flavonoids in PM2.5-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Regulation of IRs-1/Akt and CYP2E1/JNK Pathways
Abstract
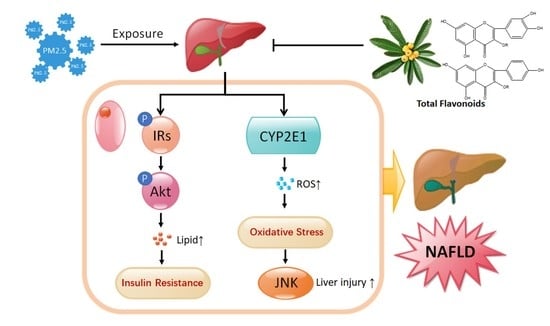
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Analysis of Chemical Constituents of TF by HPLC-QTOF/MS
2.2. Effect of TF on the Body and Liver Weight in Mice Exposed to PM2.5
2.3. Histopathological Examinations
2.4. Improvement of TF on Lipid Metabolism
2.5. Reduced Oxidative Stress and Liver Injury in PM2.5-Induced NAFLD Mice
2.6. TF Changes Pathways Involved in Insulin Resistance and Oxidative Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Reagents, and Antibodies
4.2. Preparation and Analysis of TF from Loquat Leaf
4.3. Animals
4.4. Exposure Protocol
4.5. Blood and Tissue Collection
4.6. Biochemical Parameters Analysis
4.7. Liver Histology Assessment
4.8. Western Blotting
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PM2.5 | Ambient fine particulate matter (aerodynamic diameter < 2.5 μm) |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| TF | Total flavonoids |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| SOD | Superoxide dismutase |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| IRs-1 | Insulin receptor substrate-1 |
| Akt | Protein kinase B |
| CYP2E1 | Cytochrome P450 2E1 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| NASH | Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis |
| IR | Insulin resistance |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| COPD | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
| TC | Total cholesterol |
| TG | Triglycerides |
| HDL | High-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| LDL | Low-density lipoprotein cholesterol |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer solution |
| H&E | Hematoxylin & eosin |
| SDS-PAGE | SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| TBS | Tris-buffered saline |
| SE | Standard error |
References
- Sun, L.; Liu, C.; Xu, X.; Ying, Z.; Maiseyeu, A.; Wang, A.; Allen, K.; Lewandowski, R.P.; Bramble, L.A.; Morishita, M.; et al. Ambient fine particulate matter and ozone exposures induce inflammation in epicardial and perirenal adipose tissues in rats fed a high fructose diet. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2013, 10, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Dandekar, A.; Kim, H.; Qiu, Y.; Xu, X.; Cui, Y.; Wang, A.; Chen, L.C.; et al. Exposure to fine airborne particulate matters induces hepatic fibrosis in murine models. J. Hepatol. 2015, 63, 1397–1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zheng, Z.; Xu, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, A.; Zhang, C.; Huttemann, M.; Grossman, L.I.; Chen, L.C.; Rajagopalan, S.; Sun, Q.; et al. Exposure to ambient particulate matter induces a NASH-like phenotype and impairs hepatic glucose metabolism in an animal model. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qiu, H.; Schooling, C.M.; Sun, S.; Tsang, H.; Yang, Y.; Lee, R.S.; Wong, C.M.; Tian, L. Long-term exposure to fine particulate matter air pollution and type 2 diabetes mellitus in elderly: A cohort study in Hong Kong. Environ. Int. 2018, 113, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadros, C.V.; Crawford, J.; Treble, P.C.; Baker, A.; Cohen, D.D.; Atanacio, A.J.; Hankin, S.; Roach, R. Chemical characterisation and source identification of atmospheric aerosols in the Snowy Mountains, south-eastern Australia. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 630, 432–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alfaro-Moreno, E.; Martinez, L.; Garcia-Cuellar, C.; Bonner, J.C.; Murray, J.C.; Rosas, I.; Rosales, S.P.; Osornio-Vargas, A.R. Biologic effects induced in vitro by PM10 from three different zones of Mexico City. Environ. Health Perspect. 2002, 110, 715–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soukup, J.M.; Becker, S. Human alveolar macrophage responses to air pollution particulates are associated with insoluble components of coarse material, including particulate endotoxin. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2001, 171, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nemmar, A.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Hoet, P.H.; Dinsdale, D.; Smith, T.; Xu, H.; Vermylen, J.; Nemery, B. Ultrafine particles affect experimental thrombosis in an in vivo hamster model. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2002, 166, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanyal, A.J. NASH: A global health problem. Hepatol. Res. 2011, 41, 670–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, L.A.; Shackel, N.A.; McLennan, S.V. Extracellular Vesicles: A New Frontier in Biomarker Discovery for Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarantino, G.; Capone, D.; Finelli, C. Exposure to ambient air particulate matter and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 3951–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Y.; Zheng, Z.; Kim, H.; Yang, Z.; Zhang, G.; Shi, X.; Sun, F.; Peng, C.; Ding, Y.; Wang, A.; et al. Inhalation Exposure to PM2.5 Counteracts Hepatic Steatosis in Mice Fed High-fat Diet by Stimulating Hepatic Autophagy. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16286–16296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Zhang, W.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Ding, W. Airborne PM2.5-Induced Hepatic Insulin Resistance by Nrf2/JNK-Mediated Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2017, 14, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, C.P.; James, O.F. Steatohepatitis: A tale of two “hits”? Gastroenterology 1998, 114, 842–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.H.; Oh, K.J.; Kim, H.R.; Han, H.S.; Lee, H.Y.; Park, K.G.; Nam, K.H.; Koo, S.H.; Chae, H.J. Effect of BI-1 on insulin resistance through regulation of CYP2E1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32229–32244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, D.; Cui, H.; Zhang, Y. Lack of ClC-2 Alleviates High Fat Diet-Induced Insulin Resistance and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 2187–2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, T.; Zhang, C.L.; Zhao, N.; Guan, M.J.; Xiao, M.; Yang, R.; Zhao, X.L.; Yu, L.H.; Zhu, Z.P.; Xie, K.Q. Impairment of Akt activity by CYP2E1 mediated oxidative stress is involved in chronic ethanol-induced fatty liver. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 295–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Sun, Y.; Shan, A. Effects of phoxim-induced hepatotoxicity on SD rats and the protection of vitamin E. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2017, 24, 24916–24927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jian, T.; Ao, X.; Wu, Y.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Zhao, L.; Tong, B.; Ren, B.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Total sesquiterpene glycosides from Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica) leaf alleviate high-fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease through cytochrome P450 2E1 inhibition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 91, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matalka, K.Z.; Abdulridha, N.A.; Badr, M.M.; Mansoor, K.; Qinna, N.A.; Qadan, F. Eriobotrya japonica Water Extract Characterization: An Inducer of Interferon-Gamma Production Mainly by the JAK-STAT Pathway. Molecules 2016, 21, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shih, C.C.; Ciou, J.L.; Lin, C.H.; Wu, J.B.; Ho, H.Y. Cell suspension culture of Eriobotrya japonica regulates the diabetic and hyperlipidemic signs of high-fat-fed mice. Molecules 2013, 18, 2726–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, B.R.; Oh, J.; Kim, H.A.; Kim, Y.J.; Jeong, K.S.; Rhyu, D.Y. Anti-Obesity Effects of the Mixture of Eriobotrya japonica and Nelumbo nucifera in Adipocytes and High-Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2015, 43, 681–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xu, C.; Li, X. Biological Activities of Extracts from Loquat (Eriobotrya japonica Lindl.): A Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, H.; Chen, J.; Li, W.L.; Ren, B.R.; Wu, J.L.; Zhang, H.Q. Hypoglycemic effect of the total flavonoid fraction from folium Eriobotryae. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 967–971. [Google Scholar]
- Kong, F.; Su, Z.; Guo, X.; Zeng, F.; Bi, Y. Antidiabetic and Lipid-Lowering Effects of the Polyphenol Extracts from the Leaves of Clausena lansium (Lour.) Skeels on Streptozotocin-Induced Type 2 Diabetic Rats. J. Food Sci. 2018, 83, 212–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.; Pan, R.; Ding, L.; Zhang, F.; Hu, L.; Ding, B.; Zhu, L.; Xia, Y.; Dou, X. Rutin exhibits hepatoprotective effects in a mouse model of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by reducing hepatic lipid levels and mitigating lipid-induced oxidative injuries. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2017, 49, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coogan, P.F.; White, L.F.; Yu, J.; Burnett, R.T.; Seto, E.; Brook, R.D.; Palmer, J.R.; Rosenberg, L.; Jerrett, M. PM2.5 and Diabetes and Hypertension Incidence in the Black Women’s Health Study. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 202–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Younossi, Z.M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A manifestation of the metabolic syndrome. Cleve. Clin. J. Med. 2008, 75, 721–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Qiu, X.; Xu, F.; Lin, Y.; Fang, Y.; Zhu, T. Macrophage-Mediated Effects of Airborne Fine Particulate Matter (PM2.5) on Hepatocyte Insulin Resistance in Vitro. ACS Omega 2016, 1, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Jian, T.; Lv, H.; Ding, X.; Zuo, Y.; Ren, B.; Chen, J.; Li, W. Antitussive and expectorant properties of growing and fallen leaves of loquat (Eriobotrya japonica). Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 2018, 28, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Hu, Z.; Li, G.; Huo, S.; Ma, F.; Cui, A.; Xue, Y.; Han, Y.; Gong, Q.; Gao, J.; et al. Hepatic CREBZF couples insulin to lipogenesis by inhibiting insig activity and contributes to hepatic steatosis in diet-induced insulin-resistant mice. Hepatology 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honma, M.; Sawada, S.; Ueno, Y.; Murakami, K.; Yamada, T.; Gao, J.; Kodama, S.; Izumi, T.; Takahashi, K.; Tsukita, S.; et al. Selective insulin resistance with differential expressions of IRS-1 and IRS-2 in human NAFLD livers. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Koh, A.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Lee, J.O.; Lee, M.N.; Jo, K.J.; Tran, H.N.K.; Kim, E.; Min, B.S.; et al. Inhibition of C1-Ten PTPase activity reduces insulin resistance through IRS-1 and AMPK pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17777–17789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.J.; Liu, J. Actein ameliorates hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in high fat diet-induced NAFLD by regulation of insulin and leptin resistant. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1386–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.L.; Zhang, J.L.; Zhang, P.; Wang, J.Q.; Li, Z.H. Alpinetin improved high fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) through improving oxidative stress, inflammatory response and lipid metabolism. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1397–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Kim, H.B.; Kim, M.C.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Park, W.Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, J.B.; et al. Hippo-mediated suppression of IRS2/AKT signaling prevents hepatic steatosis and liver cancer. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1010–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Surapaneni, K.M.; Priya, V.V.; Mallika, J. Pioglitazone, quercetin and hydroxy citric acid effect on cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) enzyme levels in experimentally induced non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH). Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 2736–2741. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aljomah, G.; Baker, S.S.; Liu, W.; Kozielski, R.; Oluwole, J.; Lupu, B.; Baker, R.D.; Zhu, L. Induction of CYP2E1 in non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 99, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leung, T.M.; Nieto, N. CYP2E1 and oxidant stress in alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2013, 58, 395–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abdelmegeed, M.A.; Banerjee, A.; Yoo, S.H.; Jang, S.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Song, B.J. Critical role of cytochrome P450 2E1 (CYP2E1) in the development of high fat-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 860–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jian, T.; Wu, Y.; Ding, X.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Zuo, Y.; Ren, B.; Zhao, L.; Tong, B.; Chen, J.; et al. A novel sesquiterpene glycoside from Loquat leaf alleviates oleic acid-induced steatosis and oxidative stress in HepG2 cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 1125–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schattenberg, J.M.; Czaja, M.J. Regulation of the effects of CYP2E1-induced oxidative stress by JNK signaling. Redox. Biol. 2014, 3, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.; Liao, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, C.; Li, X.; Wang, G. Elevated expression of miR-146, miR-139 and miR-340 involved in regulating Th1/Th2 balance with acute exposure of fine particulate matter in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2018, 54, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ren, X.; Tang, Y.; Sun, J.; Feng, J.; Chen, L.; Chen, H.; Zeng, S.; Chen, C.; Li, X.; Zhu, H.; et al. Flavone protects HBE cells from DNA double-strand breaks caused by PM2.5. Hum. Cell 2018, 31, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grasselli, E.; Voci, A.; Canesi, L.; De Matteis, R.; Goglia, F.; Cioffi, F.; Fugassa, E.; Gallo, G.; Vergani, L. Direct effects of iodothyronines on excess fat storage in rat hepatocytes. J. Hepatol. 2011, 54, 1230–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jian, T.; Ding, X.; Wu, Y.; Ren, B.; Li, W.; Lv, H.; Chen, J. Hepatoprotective Effect of Loquat Leaf Flavonoids in PM2.5-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Regulation of IRs-1/Akt and CYP2E1/JNK Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103005
Jian T, Ding X, Wu Y, Ren B, Li W, Lv H, Chen J. Hepatoprotective Effect of Loquat Leaf Flavonoids in PM2.5-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Regulation of IRs-1/Akt and CYP2E1/JNK Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103005
Chicago/Turabian StyleJian, Tunyu, Xiaoqin Ding, Yuexian Wu, Bingru Ren, Weilin Li, Han Lv, and Jian Chen. 2018. "Hepatoprotective Effect of Loquat Leaf Flavonoids in PM2.5-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Regulation of IRs-1/Akt and CYP2E1/JNK Pathways" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103005
APA StyleJian, T., Ding, X., Wu, Y., Ren, B., Li, W., Lv, H., & Chen, J. (2018). Hepatoprotective Effect of Loquat Leaf Flavonoids in PM2.5-Induced Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease via Regulation of IRs-1/Akt and CYP2E1/JNK Pathways. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3005. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103005