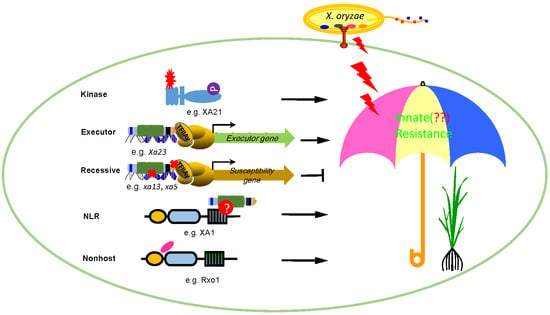
Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Broad-Spectrum Resistance Mediated by Kinases
3. Broad-Spectrum Resistance Mediated by the Xa1 Family Genes
4. Race-Specific Resistance Mediated by Recessive R Genes
5. Race-Specific Resistance Mediated by Executor R Genes
6. Durable and Broad-Spectrum Resistance Mediated by Nonhost R Genes
7. Conclusions and Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boch, J.; Bonas, U. Xanthomonas AvrBs3 family-type III effectors: Discovery and function. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 2010, 48, 419–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttner, D.; Bonas, U. Regulation and secretion of Xanthomonas virulence factors. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2010, 34, 107–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nino-Liu, D.O.; Ronald, P.C.; Bogdanove, A.J. Xanthomonas oryzae pathovars: Model pathogens of a model crop. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2006, 7, 303–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, F.F.; Yang, B. Host and pathogen factors controlling the rice-Xanthomonas oryzae interaction. Plant Physiol. 2009, 150, 1677–1686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moscou, M.J.; Bogdanove, A.J. A simple cipher governs DNA recognition by TAL effectors. Science 2009, 326, 1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, D.; Yan, C.; Pan, X.; Mahfouz, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, J.K.; Shi, Y.; Yan, N. Structural basis for sequence-specific recognition of DNA by TAL effectors. Science 2012, 335, 720–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boch, J.; Scholze, H.; Schornack, S.; Landgraf, A.; Hahn, S.; Kay, S.; Lahaye, T.; Nickstadt, A.; Bonas, U. Breaking the code of DNA binding specificity of TAL-type III effectors. Science 2009, 326, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boch, J.; Bonas, U.; Lahaye, T. TAL effectors—Pathogen strategies and plant resistance engineering. New Phytol. 2014, 204, 823–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cox, K.L.; Meng, F.; Wilkins, K.E.; Li, F.; Wang, P.; Booher, N.J.; Carpenter, S.C.D.; Chen, L.Q.; Zheng, H.; Gao, X.; et al. TAL effector driven induction of a SWEET gene confers susceptibility to bacterial blight of cotton. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Ji, C.; Liu, B.; Zou, L.; Chen, G.; Yang, B. Interfering TAL effectors of Xanthomonas oryzae neutralize R-gene-mediated plant disease resistance. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jia, H.; Sosso, D.; Li, T.; Frommer, W.B.; Yang, B.; White, F.F.; Wang, N.; Jones, J.B. Lateral organ boundaries 1 is a disease susceptibility gene for citrus bacterial canker disease. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E521–E529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, S.; Hahn, S.; Marois, E.; Hause, G.; Bonas, U. A bacterial effector acts as a plant transcription factor and induces a cell size regulator. Science 2007, 318, 648–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Sugio, A.; White, F.F. Os8N3 is a host disease-susceptibility gene for bacterial blight of rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10503–10508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antony, G.; Zhou, J.H.; Huang, S.; Li, T.; Liu, B.; White, F.; Yang, B. Rice xa13 recessive resistance to bacterial blight is defeated by induction of the disease susceptibility gene Os-11N3. Plant Cell 2010, 22, 3864–3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Wang, S. Rice MtN3/saliva/SWEET family genes and their homologs in cellular organisms. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 665–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Z.; Ma, W.; Zakria, M.; Zou, L.; Cheng, Z.; Chen, G. A transcription activator-like effector Tal7 of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola activates rice gene Os09g29100 to suppress rice immunity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 5089. [Google Scholar]
- Salzberg, S.L.; Sommer, D.D.; Schatz, M.C.; Phillippy, A.M.; Rabinowicz, P.D.; Tsuge, S.; Furutani, A.; Ochiai, H.; Delcher, A.L.; Kelley, D.; et al. Genome sequence and rapid evolution of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae PXO99A. BMC Genom. 2008, 9, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogdanove, A.J.; Koebnik, R.; Lu, H.; Furutani, A.; Angiuoli, S.V.; Patil, P.B.; Van Sluys, M.A.; Ryan, R.P.; Meyer, D.F.; Han, S.W.; et al. Two new complete genome sequences offer insight into host and tissue specificity of plant pathogenic Xanthomonas spp. J. Bacteriol. 2011, 193, 5450–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, K.E.; Booher, N.J.; Wang, L.; Bogdanove, A.J. TAL effectors and activation of predicted host targets distinguish Asian from African strains of the rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola while strict conservation suggests universal importance of five TAL effectors. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Yamada, K.; Ishikawa, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Hayashi, N.; Uchihashi, K.; Ishihama, N.; Kishi-Kaboshi, M.; Takahashi, A.; Tsuge, S.; et al. A receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase targeted by a plant pathogen effector is directly phosphorylated by the chitin receptor and mediates rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishikawa, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Sakamoto, K.; Yoshimura, S.; Inoue, K.; Tsuge, S.; Kojima, C.; Kawasaki, T. Bacterial effector modulation of host E3 ligase activity suppresses PAMP-triggered immunity in rice. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cheong, H.; Kim, C.Y.; Jeon, J.S.; Lee, B.M.; Sun Moon, J.; Hwang, I. Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae type III effector XopN targets OsVOZ2 and a putative thiamine synthase as a virulence factor in rice. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, C.; Yang, B. Mutagenesis of 18 type III effectors reveals virulence function of XopZPXO99 in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2010, 23, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, K.K.; Verma, G.; Manju; Junaid, A.; Mani, C. Rice pathogen Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae employs inducible hrp-dependent XopF type III effector protein for its growth, pathogenicity and for suppression of PTI response to induce blight disease. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2016, 144, 311–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akimoto-Tomiyama, C.; Furutani, A.; Tsuge, S.; Washington, E.J.; Nishizawa, Y.; Minami, E.; Ochiai, H. XopR, a type III effector secreted by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae, suppresses microbe-associated molecular pattern-triggered immunity in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2012, 25, 505–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, M.K.; Nathawat, R.; Sinha, D.; Haque, A.S.; Sankaranarayanan, R.; Sonti, R.V. Mutations in the predicted active site of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae XopQ differentially affect virulence, suppression of host innate immunity, and induction of the HR in a nonhost plant. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, D.; Gupta, M.K.; Patel, H.K.; Ranjan, A.; Sonti, R.V. Cell wall degrading enzyme induced rice innate immune responses are suppressed by the type 3 secretion system effectors XopN, XopQ, XopX and XopZ of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S.; Fang, A.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Zhang, K.; Mao, Y.; Sun, W. The Type III effector AvrBs2 in Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola suppresses rice immunity and promotes disease development. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2015, 28, 869–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kourelis, J.; van der Hoorn, R.A.L. Defended to the nines: 25 years of resistance gene cloning identifies nine mechanisms for R protein function. Plant Cell 2018, 30, 285–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Yin, Z.; White, F. TAL effectors and the executor R genes. Front. Plant Sci. 2015, 6, 641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Triplett, L.R.; Cohen, S.P.; Heffelfinger, C.; Schmidt, C.L.; Huerta, A.I.; Tekete, C.; Verdier, V.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Leach, J.E. A resistance locus in the American heirloom rice variety Carolina Gold Select is triggered by TAL effectors with diverse predicted targets and is effective against African strains of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Plant J. 2016, 87, 472–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hutin, M.; Sabot, F.; Ghesquiere, A.; Koebnik, R.; Szurek, B. A knowledge-based molecular screen uncovers a broad-spectrum OsSWEET14 resistance allele to bacterial blight from wild rice. Plant J. 2015, 84, 694–703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Cao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Q. Xa26, a gene conferring resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae in rice, encodes an LRR receptor kinase-like protein. Plant J. 2004, 37, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, K.; Cao, J.; Zhang, J.; Xia, F.; Ke, Y.; Zhang, H.; Xie, W.; Liu, H.; Cui, Y.; Cao, Y.; et al. Improvement of multiple agronomic traits by a disease resistance gene via cell wall reinforcement. Nat. Plants 2017, 3, 17009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, W.Y.; Wang, G.L.; Chen, L.L.; Kim, H.S.; Pi, L.Y.; Holsten, T.; Gardner, J.; Wang, B.; Zhai, W.X.; Zhu, L.H.; et al. A receptor kinase-like protein encoded by the rice disease resistance gene, Xa21. Science 1995, 270, 1804–1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, J.D.; Dangl, J.L. The plant immune system. Nature 2006, 444, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Akamatsu, A.; Wong, H.L.; Fujiwara, M.; Okuda, J.; Nishide, K.; Uno, K.; Imai, K.; Umemura, K.; Kawasaki, T.; Kawano, Y.; et al. An OsCEBiP/OsCERK1-OsRacGEF1-OsRac1 module is an essential early component of chitin-induced rice immunity. Cell Host Microbe 2013, 13, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, D.Z.; Wang, G.X.; Zhou, J.M. Receptor kinases in plant-pathogen interactions: More than pattern recognition. Plant Cell 2017, 29, 618–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.L.; Xue, H.W. Global analysis of expression profiles of rice receptor-like kinase genes. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.J.; Han, S.W.; Chen, X.; Ronald, P.C. Elucidation of XA21-mediated innate immunity. Cell Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1017–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Schwessinger, B.; Joe, A.; Thomas, N.; Liu, F.; Albert, M.; Robinson, M.R.; Chan, L.J.; Luu, D.D.; Chen, H.; et al. The rice immune receptor XA21 recognizes a tyrosine-sulfated protein from a Gram-negative bacterium. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pruitt, R.N.; Joe, A.; Zhang, W.G.; Feng, W.; Stewart, V.; Schwessinger, B.; Dinneny, J.R.; Ronald, P.C. A microbially derived tyrosine-sulfated peptide mimics a plant peptide hormone. New Phytol. 2017, 215, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.; Ding, X.; Cai, M.; Zhao, J.; Lin, Y.; Li, X.; Xu, C.; Wang, S. The expression pattern of a rice disease resistance gene Xa3/Xa26 is differentially regulated by the genetic backgrounds and developmental stages that influence its function. Genetics 2007, 177, 523–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.J.; Li, X.H.; Xiao, J.H.; Wing, R.A.; Wang, S.P. Ortholog alleles at Xa3/Xa26 locus confer conserved race-specific resistance against Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Mol. Plant 2012, 5, 281–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, Y.; Cao, Y.L.; Xu, C.G.; Li, X.H.; Wang, S.P. Xa3, conferring resistance for rice bacterial blight and encoding a receptor kinase-like protein, is the same as Xa26. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2006, 113, 1347–1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deng, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Wang, S. Exploring the mechanism and efficient use of a durable gene-mediated resistance to bacterial blight disease in rice. Mol. Breed. 2018, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, S.; Yamanouchi, U.; Katayose, Y.; Toki, S.; Wang, Z.X.; Kono, I.; Kurata, N.; Yano, M.; Iwata, N.; Sasaki, T. Expression of Xa1, a bacterial blight-resistance gene in rice, is induced by bacterial inoculation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 1663–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Read, A.C.; Rinaldi, F.C.; Hutin, M.; He, Y.-Q.; Triplett, L.R.; Bogdanove, A.J. Suppression of Xo1-mediated disease resistance in rice by a truncated, non-DNA-binding TAL effector of Xanthomonas oryzae. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Z.; Zhu, L.; Song, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Xia, Y.; Qiu, M.; Lin, Y.; Li, H.; Kong, L.; et al. A paralogous decoy protects Phytophthora sojae apoplastic effector PsXEG1 from a host inhibitor. Science 2017, 355, 710–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schornack, S.; Ballvora, A.; Gürlebeck, D.; Peart, J.; Ganal, M.; Baker, B.; Bonas, U.; Lahaye, T. The tomato resistance protein Bs4 is a predicted non-nuclear TIR-NB-LRR protein that mediates defense responses to severely truncated derivatives of AvrBs4 and overexpressed AvrBs3. Plant J. 2004, 37, 46–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Peng, Z.; Long, J.; Sosso, D.; Liu, B.; Eom, J.S.; Huang, S.; Liu, S.; Vera Cruz, C.; Frommer, W.B.; et al. Gene targeting by the TAL effector PthXo2 reveals cryptic resistance gene for bacterial blight of rice. Plant J. 2015, 82, 632–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cernadas, R.A.; Doyle, E.L.; Nino-Liu, D.O.; Wilkins, K.E.; Bancroft, T.; Wang, L.; Schmidt, C.L.; Caldo, R.; Yang, B.; White, F.F.; et al. Code-assisted discovery of TAL effector targets in bacterial leaf streak of rice reveals contrast with bacterial blight and a novel susceptibility gene. PLoS Pathog. 2014, 10, e1003972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; Streubel, J.; Balzergue, S.; Champion, A.; Boch, J.; Koebnik, R.; Feng, J.; Verdier, V.; Szurek, B. Colonization of rice leaf blades by an African strain of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae depends on a new TAL effector that induces the rice nodulin-3 Os11N3 gene. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2011, 24, 1102–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Streubel, J.; Pesce, C.; Hutin, M.; Koebnik, R.; Boch, J.; Szurek, B. Five phylogenetically close rice SWEET genes confer TAL effector-mediated susceptibility to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. New Phytol. 2013, 200, 808–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Lalonde, S.; Takanaga, H.; Hartung, M.L.; Qu, X.Q.; Guo, W.J.; Kim, J.G.; Underwood, W.; Chaudhuri, B.; et al. Sugar transporters for intercellular exchange and nutrition of pathogens. Nature 2010, 468, 527–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chong, J.; Piron, M.C.; Meyer, S.; Merdinoglu, D.; Bertsch, C.; Mestre, P. The SWEET family of sugar transporters in grapevine: VvSWEET4 is involved in the interaction with Botrytis cinerea. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6589–6601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asai, Y.; Kobayashi, Y. Increased expression of the tomato SISWEET15 gene during grey mold infection and the possible involvement of the sugar efflux to apoplasm in the disease susceptibility. J. Plant Pathol. Microbiol. 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.Q.; Qu, X.Q.; Hou, B.H.; Sosso, D.; Osorio, S.; Fernie, A.R.; Frommer, W.B. Sucrose efflux mediated by SWEET proteins as a key step for phloem transport. Science 2012, 335, 207–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdier, V.; Triplett, L.R.; Hummel, A.W.; Corral, R.; Cernadas, R.A.; Schmidt, C.L.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Leach, J.E. Transcription activator-like (TAL) effectors targeting OsSWEET genes enhance virulence on diverse rice (Oryza sativa) varieties when expressed individually in a TAL effector-deficient strain of Xanthomonas oryzae. New Phytol. 2012, 196, 1197–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Z.; Yuan, M.; Yao, J.; Ge, X.; Yuan, B.; Xu, C.; Li, X.; Fu, B.; Li, Z.; Bennetzen, J.L.; et al. Promoter mutations of an essential gene for pollen development result in disease resistance in rice. Genes Dev. 2006, 20, 1250–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q.; Yuan, M.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Xiao, J.; Wang, S. A paralog of the MtN3/saliva family recessively confers race-specific resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae in rice. Plant Cell Environ. 2011, 34, 1958–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, M.; Ke, Y.G.; Huang, R.Y.; Ma, L.; Yang, Z.Y.; Chu, Z.H.; Xiao, J.H.; Li, X.H.; Wang, S.P. A host basal transcription factor is a key component for infection of rice by TALE-carrying bacteria. eLife 2016, 5, e19605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Zou, L.; Ji, Z.; Xu, X.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Alfano, J.R.; Chen, G. Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae TALE proteins recruit OsTFIIAγ1 to compensate for the absence of OsTFIIAγ5 in bacterial blight in rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2018, 19, 2248–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Zhang, X.P.; Fan, Y.L.; Gao, Y.; Zhu, Q.L.; Zheng, C.K.; Qin, T.F.; Li, Y.Q.; Che, J.Y.; Zhang, M.W.; et al. XA23 is an executor R protein and confers broad-spectrum disease resistance in rice. Mol. Plant 2015, 8, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, D.; Wang, J.; Zeng, X.; Gu, K.; Qiu, C.; Yang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Goh, M.; Luo, Y.; Murata-Hori, M.; et al. The rice TAL effector-dependent resistance protein XA10 triggers cell death and calcium depletion in the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Cell 2014, 26, 497–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, K.; Yang, B.; Tian, D.; Wu, L.; Wang, D.; Sreekala, C.; Yang, F.; Chu, Z.; Wang, G.L.; White, F.F.; et al. R gene expression induced by a type-III effector triggers disease resistance in rice. Nature 2005, 435, 1122–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romer, P.; Hahn, S.; Jordan, T.; Strauβ, T.; Bonas, U.; Lahaye, T. Plant pathogen recognition mediated by promoter activation of the pepper Bs3 resistance gene. Science 2007, 318, 645–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Goh, M.L.; Sreekala, C.; Yin, Z. XA27 depends on an amino-terminal signal-anchor-like sequence to localize to the apoplast for resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv oryzae. Plant Physiol. 2008, 148, 1497–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.L.; Qin, T.F.; Yu, H.M.; Zhang, X.P.; Che, J.Y.; Gao, Y.; Zheng, C.K.; Yang, B.; Zhao, K.J. The broad bacterial blight resistance of rice line CBB23 is triggered by a novel transcription activator-like (TAL) effector of Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2014, 15, 333–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Tian, D.; Gu, K.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Yin, Z. Induction of Xa10-like Genes in Rice Cultivar Nipponbare Confers Disease Resistance to Rice Bacterial Blight. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2017, 30, 466–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makino, S.; Sugio, A.; White, F.; Bogdanove, A.J. Inhibition of resistance gene-mediated defense in rice by Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2006, 19, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niks, R.E.; Marcel, T.C. Nonhost and basal resistance: How to explain specificity? New Phytol. 2009, 182, 817–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, B.; Lin, X.; Poland, J.; Trick, H.; Leach, J.; Hulbert, S. A maize resistance gene functions against bacterial streak disease in rice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 15383–15388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Triplett, L.R.; Shidore, T.; Long, J.; Miao, J.; Wu, S.; Han, Q.; Zhou, C.; Ishihara, H.; Li, J.; Zhao, B.; et al. AvrRxo1 is a bifunctional type III secreted effector and toxin-antitoxin system component with homologs in diverse environmental contexts. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Q.; Zhou, C.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Triplett, L.; Miao, J.; Tokuhisa, J.; Deblais, L.; Robinson, H.; Leach, J.E.; et al. Crystal structure of Xanthomonas AvrRxo1-ORF1, a type III effector with a polynucleotide kinase domain, and its interactor AvrRxo1-ORF2. Structure 2015, 23, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Chang, Q.; Feng, W.; Zhang, B.; Wu, T.; Li, N.; Yao, F.; Ding, X.; Chu, Z. Domain dissection of AvrRxo1 for suppressor, avirulence and cytotoxicity functions. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e113875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shidore, T.; Broeckling, C.D.; Kirkwood, J.S.; Long, J.J.; Miao, J.; Zhao, B.; Leach, J.E.; Triplett, L.R. The effector AvrRxo1 phosphorylates NAD in planta. PLoS Pathog. 2017, 13, e1006442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, M.R.; Zhao, M.F.; Xie, X.W.; Zhu, L.H.; Fu, B.Y.; Li, Z.K. Genome-wide gene responses in a transgenic rice line carrying the maize resistance gene Rxo1 to the rice bacterial streak pathogen, Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.D.; Wang, G.L. Plant innate immunity in rice: A defense against pathogen infection. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2016, 3, 295–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummel, A.W.; Wilkins, K.E.; Wang, L.; Cernadas, R.A.; Bogdanove, A.J. A transcription activator-like effector from Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzicola elicits dose-dependent resistance in rice. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2017, 18, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quibod, I.L.; Perez-Quintero, A.; Booher, N.J.; Dossa, G.S.; Grande, G.; Szurek, B.; Vera Cruz, C.; Bogdanove, A.J.; Oliva, R. Effector diversification contributes to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae phenotypic adaptation in a semi-isolated environment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Liu, B.; Spalding, M.H.; Weeks, D.P.; Yang, B. High-efficiency TALEN-based gene editing produces disease-resistant rice. Nat. Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 390–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanvillain-Baufume, S.; Reschke, M.; Sole, M.; Auguy, F.; Doucoure, H.; Szurek, B.; Meynard, D.; Portefaix, M.; Cunnac, S.; Guiderdoni, E.; et al. Targeted promoter editing for rice resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae reveals differential activities for SWEET14-inducing TAL effectors. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2017, 15, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Minkenberg, B.; Yang, Y. Boosting CRISPR/Cas9 multiplex editing capability with the endogenous tRNA-processing system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, 3570–3675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Wei, P.; Zhang, B.; Gou, F.; Feng, Z.; Mao, Y.; Yang, L.; Zhang, H.; Xu, N.; et al. The CRISPR/Cas9 system produces specific and homozygous targeted gene editing in rice in one generation. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2014, 12, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.J.; Wang, C.L.; Liu, P.Q.; Lei, C.L.; Hao, W.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Y.G.; Zhao, K.J. Enhanced rice blast resistance by CRISPR/Cas9-targeted mutagenesis of the ERF transcription factor gene OsERF922. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0154027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhu, Z.; Chern, M.; Yin, J.; Yang, C.; Ran, L.; Cheng, M.; He, M.; Wang, K.; Wang, J.; et al. A natural allele of a transcription factor in rice confers broad-spectrum blast resistance. Cell 2017, 170, 114–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, A.W.; Doyle, E.L.; Bogdanove, A.J. Addition of transcription activator-like effector binding sites to a pathogen strain-specific rice bacterial blight resistance gene makes it effective against additional strains and against bacterial leaf streak. New Phytol. 2012, 195, 883–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, X.; Tian, D.; Gu, K.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Luo, Y.; White, F.F.; Yin, Z. Genetic engineering of the Xa10 promoter for broad-spectrum and durable resistance to Xanthomonas oryzae pv. oryzae. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 993–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ji, Z.; Wang, C.; Zhao, K. Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103008
Ji Z, Wang C, Zhao K. Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(10):3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103008
Chicago/Turabian StyleJi, Zhiyuan, Chunlian Wang, and Kaijun Zhao. 2018. "Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 10: 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103008
APA StyleJi, Z., Wang, C., & Zhao, K. (2018). Rice Routes of Countering Xanthomonas oryzae. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(10), 3008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19103008