Pancreatic Cancer and Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Transformation and Chemoresistance
Abstract
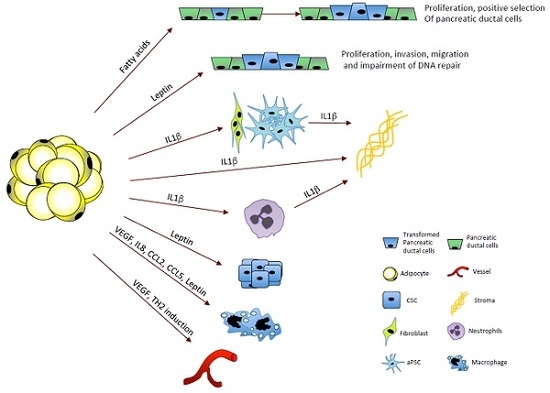
:1. Introduction
1.1. Obesity and Pancreatic Cancer
1.2. Cancerogens in Food: How Dietary Habits Are Related to PDAC
2. Obesity and Inflammation
3. Microbiota, Obesity, and Cancer
4. Hormones
5. Obesity and Chemoresistance
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collaborators, G.B.D.O.; Afshin, A.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Reitsma, M.B.; Sur, P.; Estep, K.; Lee, A.; Marczak, L.; Mokdad, A.H.; Moradi-Lakeh, M.; et al. Health effects of overweight and obesity in 195 countries over 25 years. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 13–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2018. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melisi, D.; Budillon, A. Pancreatic cancer: Between bench and bedside. Curr. Drug Targets 2012, 13, 729–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Midha, S.; Chawla, S.; Garg, P.K. Modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors for pancreatic cancer: A review. Cancer Lett. 2016, 381, 269–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, C.; Bao, Y.; Wu, C.; Kraft, P.; Ogino, S.; Ng, K.; Qian, Z.R.; Rubinson, D.A.; Stampfer, M.J.; Giovannucci, E.L.; et al. Prediagnostic body mass index and pancreatic cancer survival. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 4229–4234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, A.A.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Kooperberg, C.; Shu, X.O.; Steplowski, E.; Bueno-de-Mesquita, H.B.; Fuchs, C.S.; Gross, M.D.; Jacobs, E.J.; Lacroix, A.Z.; et al. Anthropometric measures, body mass index, and pancreatic cancer: A pooled analysis from the pancreatic cancer cohort consortium (panscan). Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 791–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genkinger, J.M.; Kitahara, C.M.; Bernstein, L.; Berrington de Gonzalez, A.; Brotzman, M.; Elena, J.W.; Giles, G.G.; Hartge, P.; Singh, P.N.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; et al. Central adiposity, obesity during early adulthood, and pancreatic cancer mortality in a pooled analysis of cohort studies. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2015, 26, 2257–2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, B.; Chung, M.J.; Park, S.W.; Park, J.Y.; Bang, S.; Park, S.W.; Song, S.Y.; Chung, J.B. Visceral obesity is associated with poor prognosis in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Nutr. Cancer 2016, 68, 201–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schauer, D.P.; Feigelson, H.S.; Koebnick, C.; Caan, B.; Weinmann, S.; Leonard, A.C.; Powers, J.D.; Yenumula, P.R.; Arterburn, D.E. Bariatric surgery and the risk of cancer in a large multisite cohort. Ann. Surg. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzer, K.M.; Xu, M.; Moro, A.; Dawson, D.W.; Du, L.; Li, G.; Chang, H.H.; Stark, A.P.; Jung, X.; Hines, O.J.; et al. Robust early inflammation of the peripancreatic visceral adipose tissue during diet-induced obesity in the krasg12d model of pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 2016, 45, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolpin, B.M.; Bao, Y.; Qian, Z.R.; Wu, C.; Kraft, P.; Ogino, S.; Stampfer, M.J.; Sato, K.; Ma, J.; Buring, J.E.; et al. Hyperglycemia, insulin resistance, impaired pancreatic beta-cell function, and risk of pancreatic cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1027–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shamali, A.; Shelat, V.; Jaber, B.; Wardak, A.; Ahmed, M.; Fontana, M.; Armstrong, T.; Abu Hilal, M. Impact of obesity on short and long term results following a pancreatico-duodenectomy. Int. J. Surg. 2017, 42, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, S.; Choti, M.A.; Assumpcao, L.; Cameron, J.L.; Gleisner, A.L.; Herman, J.M.; Eckhauser, F.; Edil, B.H.; Schulick, R.D.; Wolfgang, C.L.; et al. Impact of obesity on perioperative outcomes and survival following pancreaticoduodenectomy for pancreatic cancer: A large single-institution study. J. Gastroint. Surg. Off. J. Soc. Surg. Aliment. Tract 2010, 14, 1143–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, J.B.; Gonzalez, R.J.; Petzel, M.Q.; Lin, E.; Morris, J.S.; Gomez, H.; Lee, J.E.; Crane, C.H.; Pisters, P.W.; Evans, D.B. Influence of obesity on cancer-related outcomes after pancreatectomy to treat pancreatic adenocarcinoma. Arch. Surg. 2009, 144, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larsson, S.C.; Wolk, A. Red and processed meat consumption and risk of pancreatic cancer: Meta-analysis of prospective studies. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghorbani, Z.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Zinab, H.E.; Farrokhzad, S.; Rahimi, R.; Malekzadeh, R.; Pourshams, A. Dietary food groups intake and cooking methods associations with pancreatic cancer: A case-control study. Indian J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Indian Soc. Gastroenterol. 2015, 34, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinen, M.M.; Verhage, B.A.; Goldbohm, R.A.; van den Brandt, P.A. Meat and fat intake and pancreatic cancer risk in the netherlands cohort study. Int. J. Cancer 2009, 125, 1118–1126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.Z.; Cross, A.J.; Silverman, D.T.; Schairer, C.; Thompson, F.E.; Kipnis, V.; Subar, A.F.; Hollenbeck, A.; Schatzkin, A.; Sinha, R. Meat and meat-mutagen intake and pancreatic cancer risk in the nih-aarp cohort. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2007, 16, 2664–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Risch, H.A. Etiology of pancreatic cancer, with a hypothesis concerning the role of n-nitroso compounds and excess gastric acidity. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 948–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoental, R. The mechanisms of action of the carcinogenic nitroso and related compounds. Br. J. Cancer 1973, 28, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, N.; Hasegawa, R.; Sano, M.; Tamano, S.; Esumi, H.; Takayama, S.; Sugimura, T. A new colon and mammary carcinogen in cooked food, 2-amino-1-methyl-6-phenylimidazo[4,5-b]pyridine (phip). Carcinogenesis 1991, 12, 1503–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugimura, T.; Wakabayashi, K.; Nakagama, H.; Nagao, M. Heterocyclic amines: Mutagens/carcinogens produced during cooking of meat and fish. Cancer Sci. 2004, 95, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fukumura, D.; Incio, J.; Shankaraiah, R.C.; Jain, R.K. Obesity and cancer: An angiogenic and inflammatory link. Microcirculation 2016, 23, 191–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philip, B.; Roland, C.L.; Daniluk, J.; Liu, Y.; Chatterjee, D.; Gomez, S.B.; Ji, B.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Fleming, J.B.; et al. A high-fat diet activates oncogenic kras and cox2 to induce development of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Gastroenterology 2013, 145, 1449–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, H.H.; Moro, A.; Takakura, K.; Su, H.Y.; Mo, A.; Nakanishi, M.; Waldron, R.T.; French, S.W.; Dawson, D.W.; Hines, O.J.; et al. Incidence of pancreatic cancer is dramatically increased by a high fat, high calorie diet in krasg12d mice. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0184455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.P.; Chang, H.H.; Jung, X.; Moro, A.; Hertzer, K.; Xu, M.; Schmidt, A.; Hines, O.J.; Eibl, G. E-cadherin expression in obesity-associated, kras-initiated pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma in mice. Surgery 2015, 158, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishikawa, T.; Otsuka, M.; Suzuki, T.; Seimiya, T.; Sekiba, K.; Ishibashi, R.; Tanaka, E.; Ohno, M.; Yamagami, M.; Koike, K. Satellite rna increases DNA damage and accelerates tumor formation in mouse models of pancreatic cancer. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2018, 16, 1255–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Choi, M.R.; Park, H.; Kim, M.; Hong, J.E.; Lee, J.Y.; Chun, H.S.; Lee, K.W.; Yoon Park, J.H. Dietary fat increases solid tumor growth and metastasis of 4t1 murine mammary carcinoma cells and mortality in obesity-resistant balb/c mice. Breast Cancer Res. BCR 2011, 13, R78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soto-Pantoja, D.R.; Sipes, J.M.; Martin-Manso, G.; Westwood, B.; Morris, N.L.; Ghosh, A.; Emenaker, N.J.; Roberts, D.D. Dietary fat overcomes the protective activity of thrombospondin-1 signaling in the apc(min/+) model of colon cancer. Oncogenesis 2016, 5, e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, S.; Ishibashi, K.; Katoh, H.; Kitamoto, S.; Shirai, T.; Tanaka, S.; Kajita, M.; Ishikawa, S.; Yamauchi, H.; Yako, Y.; et al. Cell competition with normal epithelial cells promotes apical extrusion of transformed cells through metabolic changes. Nat. Cell Biol. 2017, 19, 530–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kajita, M.; Sugimura, K.; Ohoka, A.; Burden, J.; Suganuma, H.; Ikegawa, M.; Shimada, T.; Kitamura, T.; Shindoh, M.; Ishikawa, S.; et al. Filamin acts as a key regulator in epithelial defence against transformed cells. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sasaki, A.; Nagatake, T.; Egami, R.; Gu, G.; Takigawa, I.; Ikeda, W.; Nakatani, T.; Kunisawa, J.; Fujita, Y. Obesity suppresses cell-competition-mediated apical elimination of rasv12-transformed cells from epithelial tissues. Cell Rep. 2018, 23, 974–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whatcott, C.J.; Diep, C.H.; Jiang, P.; Watanabe, A.; LoBello, J.; Sima, C.; Hostetter, G.; Shepard, H.M.; Von Hoff, D.D.; Han, H. Desmoplasia in primary tumors and metastatic lesions of pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3561–3568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olive, K.P.; Jacobetz, M.A.; Davidson, C.J.; Gopinathan, A.; McIntyre, D.; Honess, D.; Madhu, B.; Goldgraben, M.A.; Caldwell, M.E.; Allard, D.; et al. Inhibition of hedgehog signaling enhances delivery of chemotherapy in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Science 2009, 324, 1457–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Maitra, A.; Wang, H. Obesity, intrapancreatic fatty infiltration, and pancreatic cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 3369–3371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hori, M.; Takahashi, M.; Hiraoka, N.; Yamaji, T.; Mutoh, M.; Ishigamori, R.; Furuta, K.; Okusaka, T.; Shimada, K.; Kosuge, T.; et al. Association of pancreatic fatty infiltration with pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2014, 5, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singhi, A.D.; Pai, R.K.; Kant, J.A.; Bartholow, T.L.; Zeh, H.J.; Lee, K.K.; Wijkstrom, M.; Yadav, D.; Bottino, R.; Brand, R.E.; et al. The histopathology of prss1 hereditary pancreatitis. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2014, 38, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, M.; Oliveira, T.; Fernandes, R. Biochemistry of adipose tissue: An endocrine organ. Arch. Med. Sci. 2013, 9, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajala, M.W.; Scherer, P.E. Minireview: The adipocyte--at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology 2003, 144, 3765–3773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incio, J.; Liu, H.; Suboj, P.; Chin, S.M.; Chen, I.X.; Pinter, M.; Ng, M.R.; Nia, H.T.; Grahovac, J.; Kao, S.; et al. Obesity-induced inflammation and desmoplasia promote pancreatic cancer progression and resistance to chemotherapy. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 852–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, C.; Piro, G.; Fassan, M.; Tamburrino, A.; Mina, M.M.; Zanotto, M.; Chiao, P.J.; Bassi, C.; Scarpa, A.; Tortora, G.; et al. An angiopoietin-like protein 2 autocrine signaling promotes emt during pancreatic ductal carcinogenesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 13822–13834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ouchi, N.; Parker, J.L.; Lugus, J.J.; Walsh, K. Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2011, 11, 85–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gilbert, C.A.; Slingerland, J.M. Cytokines, obesity, and cancer: New insights on mechanisms linking obesity to cancer risk and progression. Annu. Rev. Med. 2013, 64, 45–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vona-Davis, L.; Rose, D.P. Angiogenesis, adipokines and breast cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naugler, W.E.; Karin, M. The wolf in sheep’s clothing: The role of interleukin-6 in immunity, inflammation and cancer. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomez-Chou, S.B.; Swidnicka-Siergiejko, A.K.; Badi, N.; Chavez-Tomar, M.; Lesinski, G.B.; Bekaii-Saab, T.; Farren, M.R.; Mace, T.A.; Schmidt, C.; Liu, Y.; et al. Lipocalin-2 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by regulating inflammation in the tumor microenvironment. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2647–2660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berg, A.H.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, 939–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simons, P.J.; van den Pangaart, P.S.; van Roomen, C.P.; Aerts, J.M.; Boon, L. Cytokine-mediated modulation of leptin and adiponectin secretion during in vitro adipogenesis: Evidence that tumor necrosis factor-alpha- and interleukin-1beta-treated human preadipocytes are potent leptin producers. Cytokine 2005, 32, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poulain-Godefroy, O.; Froguel, P. Preadipocyte response and impairment of differentiation in an inflammatory environment. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 356, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Gan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yao, M.; Gu, J.; Tu, H. Leptin signaling enhances cell invasion and promotes the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via increasing mmp-13 production. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16120–16134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbuzariu, A.; Oprea-Ilies, G.M.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. The role of notch signaling and leptin-notch crosstalk in pancreatic cancer. Medicines 2018, 5, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radtke, F.; Raj, K. The role of notch in tumorigenesis: Oncogene or tumour suppressor? Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 756–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, M. Networking of wnt, fgf, notch, bmp, and hedgehog signaling pathways during carcinogenesis. Stem Cell Rev. 2007, 3, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaianigo, N.; Melisi, D.; Carbone, C. Emt and treatment resistance in pancreatic cancer. Cancers 2017, 9, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, C.; Melisi, D. Nf-κb as a target for pancreatic cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2012, 16 (Suppl. 2), S1–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melisi, D.; Chiao, P.J. Nf-κb as a target for cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2007, 11, 133–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.; Tordjman, J.; Clement, K.; Scherer, P.E. Fibrosis and adipose tissue dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2013, 18, 470–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosogai, N.; Fukuhara, A.; Oshima, K.; Miyata, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Segawa, K.; Furukawa, S.; Tochino, Y.; Komuro, R.; Matsuda, M.; et al. Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 2007, 56, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azushima, K.; Ohki, K.; Wakui, H.; Uneda, K.; Haku, S.; Kobayashi, R.; Haruhara, K.; Kinguchi, S.; Matsuda, M.; Maeda, A.; et al. Adipocyte-specific enhancement of angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein ameliorates diet-induced visceral obesity and insulin resistance. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2017, 6, e004488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lunardi, S.; Muschel, R.J.; Brunner, T.B. The stromal compartments in pancreatic cancer: Are there any therapeutic targets? Cancer Lett. 2014, 343, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nov, O.; Shapiro, H.; Ovadia, H.; Tarnovscki, T.; Dvir, I.; Shemesh, E.; Kovsan, J.; Shelef, I.; Carmi, Y.; Voronov, E.; et al. Interleukin-1beta regulates fat-liver crosstalk in obesity by auto-paracrine modulation of adipose tissue inflammation and expandability. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e53626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Auguet, T.; Quintero, Y.; Terra, X.; Martinez, S.; Lucas, A.; Pellitero, S.; Aguilar, C.; Hernandez, M.; del Castillo, D.; Richart, C. Upregulation of lipocalin 2 in adipose tissues of severely obese women: Positive relationship with proinflammatory cytokines. Obesity 2011, 19, 2295–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Ramirez, B.; Silva, C.; Rotellar, F.; Gil, M.J.; Cienfuegos, J.A.; Salvador, J.; Fruhbeck, G. Increased adipose tissue expression of lipocalin-2 in obesity is related to inflammation and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and metalloproteinase-9 activities in humans. J. Mol. Med. 2009, 87, 803–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drew, B.G.; Hamidi, H.; Zhou, Z.; Villanueva, C.J.; Krum, S.A.; Calkin, A.C.; Parks, B.W.; Ribas, V.; Kalajian, N.Y.; Phun, J.; et al. Estrogen receptor (er)alpha-regulated lipocalin 2 expression in adipose tissue links obesity with breast cancer progression. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 5566–5581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Catalan, V.; Gomez-Ambrosi, J.; Rodriguez, A.; Perez-Hernandez, A.I.; Gurbindo, J.; Ramirez, B.; Mendez-Gimenez, L.; Rotellar, F.; Valenti, V.; Moncada, R.; et al. Activation of noncanonical wnt signaling through wnt5a in visceral adipose tissue of obese subjects is related to inflammation. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1407–E1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirat, B.; Bochet, L.; Dabek, M.; Daviaud, D.; Dauvillier, S.; Majed, B.; Wang, Y.Y.; Meulle, A.; Salles, B.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Cancer-associated adipocytes exhibit an activated phenotype and contribute to breast cancer invasion. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochet, L.; Lehuede, C.; Dauvillier, S.; Wang, Y.Y.; Dirat, B.; Laurent, V.; Dray, C.; Guiet, R.; Maridonneau-Parini, I.; Le Gonidec, S.; et al. Adipocyte-derived fibroblasts promote tumor progression and contribute to the desmoplastic reaction in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 5657–5668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoico, E.; Darra, E.; Rizzatti, V.; Budui, S.; Franceschetti, G.; Mazzali, G.; Rossi, A.P.; Fantin, F.; Menegazzi, M.; Cinti, S.; et al. Adipocytes wnt5a mediated dedifferentiation: A possible target in pancreatic cancer microenvironment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20223–20235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carbone, C.; Piro, G.; Gaianigo, N.; Ligorio, F.; Santoro, R.; Merz, V.; Simionato, F.; Zecchetto, C.; Falco, G.; Conti, G.; et al. Adipocytes sustain pancreatic cancer progression through a non-canonical wnt paracrine network inducing ror2 nuclear shuttling. Int. J. Obes. 2018, 42, 334–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Fan, X.; Wang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, Z. High ror2 expression in tumor cells and stroma is correlated with poor prognosis in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 12991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Round, J.L.; Mazmanian, S.K. The gut microbiota shapes intestinal immune responses during health and disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2009, 9, 313–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gill, S.R.; Pop, M.; Deboy, R.T.; Eckburg, P.B.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Samuel, B.S.; Gordon, J.I.; Relman, D.A.; Fraser-Liggett, C.M.; Nelson, K.E. Metagenomic analysis of the human distal gut microbiome. Science 2006, 312, 1355–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graf, D.; Di Cagno, R.; Fak, F.; Flint, H.J.; Nyman, M.; Saarela, M.; Watzl, B. Contribution of diet to the composition of the human gut microbiota. Microb. Ecol. Health Dis. 2015, 26, 26164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.; Izard, J.; Walsh, E.; Batich, K.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Clarke, G.; Sela, D.A.; Muller, A.J.; Mullin, J.M.; Albert, K.; et al. The host microbiome regulates and maintains human health: A primer and perspective for non-microbiologists. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 1783–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Collins, L.B.; Wali, A.; Bigler, R.; Sun, W.; Bultman, S.J. The warburg effect dictates the mechanism of butyrate-mediated histone acetylation and cell proliferation. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 612–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donohoe, D.R.; Garge, N.; Zhang, X.; Sun, W.; O’Connell, T.M.; Bunger, M.K.; Bultman, S.J. The microbiome and butyrate regulate energy metabolism and autophagy in the mammalian colon. Cell Metab. 2011, 13, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagliari, D.; Saviano, A.; Newton, E.E.; Serricchio, M.L.; Dal Lago, A.A.; Gasbarrini, A.; Cianci, R. Gut microbiota-immune system crosstalk and pancreatic disorders. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 7946431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, L.V.; Ockhuizen, T.; Suzuki, K. Exploring the influence of the gut microbiota and probiotics on health: A symposium report. Br. J. Nutr. 2014, 112 (Suppl. 1), S1–S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ley, R.E.; Turnbaugh, P.J.; Klein, S.; Gordon, J.I. Microbial ecology: Human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006, 444, 1022–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everard, A.; Lazarevic, V.; Gaia, N.; Johansson, M.; Stahlman, M.; Backhed, F.; Delzenne, N.M.; Schrenzel, J.; Francois, P.; Cani, P.D. Microbiome of prebiotic-treated mice reveals novel targets involved in host response during obesity. ISME J. 2014, 8, 2116–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chassaing, B.; Raja, S.M.; Lewis, J.D.; Srinivasan, S.; Gewirtz, A.T. Colonic microbiota encroachment correlates with dysglycemia in humans. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 4, 205–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, Z.; Jiang, J.; Xie, H.; Li, A.; Lu, H.; Xu, S.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, H.; Cui, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Gut microbial profile analysis by miseq sequencing of pancreatic carcinoma patients in china. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 95176–95191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaud, D.S.; Izard, J. Microbiota, oral microbiome, and pancreatic cancer. Cancer J. 2014, 20, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, P.J.; Fletcher, E.M.; Gibbons, S.M.; Bouvet, M.; Doran, K.S.; Kelley, S.T. Characterization of the salivary microbiome in patients with pancreatic cancer. PeerJ 2015, 3, e1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Kolltveit, K.M.; Tronstad, L.; Olsen, I. Systemic diseases caused by oral infection. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2000, 13, 547–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dursun, E.; Akalin, F.A.; Genc, T.; Cinar, N.; Erel, O.; Yildiz, B.O. Oxidative stress and periodontal disease in obesity. Medicine 2016, 95, e3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pollak, M.N.; Schernhammer, E.S.; Hankinson, S.E. Insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 505–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giorgino, F.; Belfiore, A.; Milazzo, G.; Costantino, A.; Maddux, B.; Whittaker, J.; Goldfine, I.D.; Vigneri, R. Overexpression of insulin receptors in fibroblast and ovary cells induces a ligand-mediated transformed phenotype. Mol. Endocrinol. 1991, 5, 452–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ish-Shalom, D.; Christoffersen, C.T.; Vorwerk, P.; Sacerdoti-Sierra, N.; Shymko, R.M.; Naor, D.; De Meyts, P. Mitogenic properties of insulin and insulin analogues mediated by the insulin receptor. Diabetologia 1997, 40 (Suppl. 2), S25–S31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, N.; Jenab, M.; Gunter, M.J. Adiposity and gastrointestinal cancers: Epidemiology, mechanisms and future directions. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tape, C.J.; Ling, S.; Dimitriadi, M.; McMahon, K.M.; Worboys, J.D.; Leong, H.S.; Norrie, I.C.; Miller, C.J.; Poulogiannis, G.; Lauffenburger, D.A.; et al. Oncogenic kras regulates tumor cell signaling via stromal reciprocation. Cell 2016, 165, 1818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scales, S.J.; de Sauvage, F.J. Mechanisms of hedgehog pathway activation in cancer and implications for therapy. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2009, 30, 303–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirakawa, T.; Yashiro, M.; Doi, Y.; Kinoshita, H.; Morisaki, T.; Fukuoka, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Kimura, K.; Amano, R.; Hirakawa, K. Pancreatic fibroblasts stimulate the motility of pancreatic cancer cells through igf1/igf1r signaling under hypoxia. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0159912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bronte, V.; Tortora, G. Adipocytes and neutrophils give a helping hand to pancreatic cancers. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 821–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makinoshima, H.; Dezawa, M. Pancreatic cancer cells activate ccl5 expression in mesenchymal stromal cells through the insulin-like growth factor-I pathway. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 3697–3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Endogenous, H.; Breast Cancer Collaborative, G.; Key, T.J.; Appleby, P.N.; Reeves, G.K.; Roddam, A.W.; Helzlsouer, K.J.; Alberg, A.J.; Rollison, D.E.; Dorgan, J.F.; et al. Circulating sex hormones and breast cancer risk factors in postmenopausal women: Reanalysis of 13 studies. Br. J. Cancer 2011, 105, 709–722. [Google Scholar]
- Wallace, I.R.; McKinley, M.C.; Bell, P.M.; Hunter, S.J. Sex hormone binding globulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Endocrinol. 2013, 78, 321–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Konduri, S.; Schwarz, R.E. Estrogen receptor beta/alpha ratio predicts response of pancreatic cancer cells to estrogens and phytoestrogens. J. Surg. Res. 2007, 140, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabat, G.C.; Kamensky, V.; Rohan, T.E. Reproductive factors, exogenous hormone use, and risk of pancreatic cancer in postmenopausal women. Cancer Epidemiol. 2017, 49, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansari, D.; Carvajo, M.; Bauden, M.; Andersson, R. Pancreatic cancer stroma: Controversies and current insights. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 641–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsey, C.C.; Harbuzariu, A.; Daley-Brown, D.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Oncogenic role of leptin and notch interleukin-1 leptin crosstalk outcome in cancer. World J. Methodol. 2016, 6, 43–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbuzariu, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Leptin-notch axis impairs 5-fluorouracil effects on pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18239–18253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Perez, R.R.; Xu, Y.; Guo, S.; Watters, A.; Zhou, W.; Leibovich, S.J. Leptin upregulates vegf in breast cancer via canonic and non-canonical signalling pathways and NFκb/HIF-1α activation. Cell. Signal. 2010, 22, 1350–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Li, Y.; Kong, D.; Banerjee, S.; Ahmad, A.; Azmi, A.S.; Ali, S.; Abbruzzese, J.L.; Gallick, G.E.; Sarkar, F.H. Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells is linked with activation of the notch signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 2400–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ford, N.A.; Nunez, N.P.; Holcomb, V.B.; Hursting, S.D. Igf1 dependence of dietary energy balance effects on murine met1 mammary tumor progression, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and chemokine expression. Endoc. Relat. Cancer 2013, 20, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, S.M.; Chiao, L.J.; Nogueira, L.; Usary, J.; Perou, C.M.; Varticovski, L.; Hursting, S.D. Dietary energy balance modulates epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor progression in murine claudin-low and basal-like mammary tumor models. Cancer Prev. Res. 2012, 5, 930–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Guo, F.; Yu, Y.; Sun, T.; Ma, D.; Han, J.; Qian, Y.; Kryczek, I.; Sun, D.; Nagarsheth, N.; et al. Fusobacterium nucleatum promotes chemoresistance to colorectal cancer by modulating autophagy. Cell 2017, 170, 548–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.; Alekseyenko, A.V.; Wu, J.; Peters, B.A.; Jacobs, E.J.; Gapstur, S.M.; Purdue, M.P.; Abnet, C.C.; Stolzenberg-Solomon, R.; Miller, G.; et al. Human oral microbiome and prospective risk for pancreatic cancer: A population-based nested case-control study. Gut 2018, 67, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitsuhashi, K.; Nosho, K.; Sukawa, Y.; Matsunaga, Y.; Ito, M.; Kurihara, H.; Kanno, S.; Igarashi, H.; Naito, T.; Adachi, Y.; et al. Association of fusobacterium species in pancreatic cancer tissues with molecular features and prognosis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 7209–7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karpinska, A.; Safranow, K.; Kladny, J.; Sulzyc-Bielicka, V. The influence of obesity on results of at (doxorubicin plus docetaxel) neoadjuvant chemotherapy in locally advanced breast cancer patients. Polski Przeglad Chirurgiczny 2015, 87, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guiu, B.; Petit, J.M.; Bonnetain, F.; Ladoire, S.; Guiu, S.; Cercueil, J.P.; Krause, D.; Hillon, P.; Borg, C.; Chauffert, B.; et al. Visceral fat area is an independent predictive biomarker of outcome after first-line bevacizumab-based treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer. Gut 2010, 59, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.W.; Han, S.W.; Cha, Y.; Lee, K.H.; Kim, T.Y.; Oh, D.Y.; Im, S.A.; Bang, Y.J.; Park, J.W.; Ryoo, S.B.; et al. Prognostic influence of body mass index and body weight gain during adjuvant folfox chemotherapy in korean colorectal cancer patients. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrache, F.; Vullierme, M.P.; Roy, C.; El Assoued, Y.; Couvelard, A.; O’Toole, D.; Mitry, E.; Hentic, O.; Hammel, P.; Levy, P.; et al. Arterial phase enhancement and body mass index are predictors of response to chemoembolisation for liver metastases of endocrine tumours. Br. J. Cancer 2007, 96, 49–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griggs, J.J.; Mangu, P.B.; Anderson, H.; Balaban, E.P.; Dignam, J.J.; Hryniuk, W.M.; Morrison, V.A.; Pini, T.M.; Runowicz, C.D.; Rosner, G.L.; et al. Appropriate chemotherapy dosing for obese adult patients with cancer: American society of clinical oncology clinical practice guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. Off. J. Am. Soc. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanley, M.J.; Abernethy, D.R.; Greenblatt, D.J. Effect of obesity on the pharmacokinetics of drugs in humans. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2010, 49, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blouin, R.A.; Warren, G.W. Pharmacokinetic considerations in obesity. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 88, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candelaria, P.V.; Rampoldi, A.; Harbuzariu, A.; Gonzalez-Perez, R.R. Leptin signaling and cancer chemoresistance: Perspectives. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2017, 8, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cascetta, P.; Cavaliere, A.; Piro, G.; Torroni, L.; Santoro, R.; Tortora, G.; Melisi, D.; Carbone, C. Pancreatic Cancer and Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Transformation and Chemoresistance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113331
Cascetta P, Cavaliere A, Piro G, Torroni L, Santoro R, Tortora G, Melisi D, Carbone C. Pancreatic Cancer and Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Transformation and Chemoresistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113331
Chicago/Turabian StyleCascetta, Priscilla, Alessandro Cavaliere, Geny Piro, Lorena Torroni, Raffaela Santoro, Giampaolo Tortora, Davide Melisi, and Carmine Carbone. 2018. "Pancreatic Cancer and Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Transformation and Chemoresistance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113331
APA StyleCascetta, P., Cavaliere, A., Piro, G., Torroni, L., Santoro, R., Tortora, G., Melisi, D., & Carbone, C. (2018). Pancreatic Cancer and Obesity: Molecular Mechanisms of Cell Transformation and Chemoresistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3331. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113331