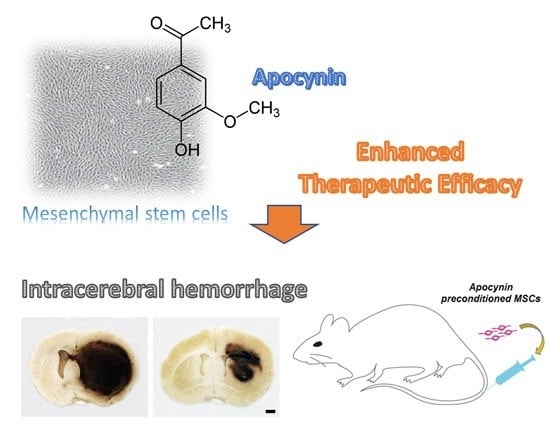
Effect of Pretreatment with the NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Apocynin on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects on Hematoma Volume and Hemispheric Enlargement
2.2. Effects on Peri-Hematoma Neuronal Death
2.3. Effects on the Expression of Tight Junction Proteins
2.4. Effects on the Amount of Exosome Production
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. MSC Preparation and Apocynin Preconditioning
4.3. ICH Model
4.4. Tissue Preparation
4.5. Measurement of the Hematoma Volume and Hemispheric Enlargement
4.6. Detection of Neuronal Death
4.7. Western Blotting
4.8. Exosome Isolation and Quantification
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Connor, B. Concise review: The use of stem cells for understanding and treating huntington’s disease. Stem Cells 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.; Gospodarev, V.; Reis, H.; Wilkinson, M.; Gaio, J.; Araujo, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.H. Traumatic brain injury and stem cell: Pathophysiology and update on recent treatment modalities. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 6392592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, C.; Wilkinson, M.; Reis, H.; Akyol, O.; Gospodarev, V.; Araujo, C.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.H. A look into stem cell therapy: Exploring the options for treatment of ischemic stroke. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 3267352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scolding, N.J.; Pasquini, M.; Reingold, S.C.; Cohen, J.A. International Conference on Cell-Based Therapies for Multiple Sclerosis. Cell-based therapeutic strategies for multiple sclerosis. Brain 2017, 140, 2776–2796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.N.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, B.Y.; Chung, S.P.; Kwon, S.W.; Suh, S.W. Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia through prevention of blood-brain barrier disruption and endothelial damage. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, T.N.; Kim, J.H.; Choi, B.Y.; Jeong, J.Y.; Chung, S.P.; Kwon, S.W.; Suh, S.W. Effect of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell administration and mild hypothermia induction on delayed neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 45, e508–e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leong, K.H.; Zhou, L.L.; Lin, Q.M.; Wang, P.; Yao, L.; Huang, Z.T. Therapeutic effects of various methods of msc transplantation on cerebral resuscitation following cardiac arrest in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3043–3051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Lin, Q.; Wang, P.; Yao, L.; Leong, K.; Tan, Z.; Huang, Z. Enhanced neuroprotective efficacy of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells co-overexpressing bdnf and vegf in a rat model of cardiac arrest-induced global cerebral ischemia. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordeiro, M.F.; Horn, A.P. Stem cell therapy in intracerebral hemorrhage rat model. World J. Stem Cells 2015, 7, 618–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Liu, N.; Zhang, P.; Pan, C.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Deng, H.; Aimaiti, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, H.; et al. Preclinical studies of stem cell transplantation in intracerebral hemorrhage: A systemic review and meta-analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 53, 5269–5277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broderick, J.; Connolly, S.; Feldmann, E.; Hanley, D.; Kase, C.; Krieger, D.; Mayberg, M.; Morgenstern, L.; Ogilvy, C.S.; Vespa, P.; et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: A guideline from the american heart association/american stroke association stroke council, high blood pressure research council, and the quality of care and outcomes in research interdisciplinary working group. Circulation 2007, 116, e391–413. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davis, S.M.; Broderick, J.; Hennerici, M.; Brun, N.C.; Diringer, M.N.; Mayer, S.A.; Begtrup, K.; Steiner, T. Hematoma growth is a determinant of mortality and poor outcome after intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurology 2006, 66, 1175–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hua, Y.; Keep, R.F.; Hoff, J.T.; Xi, G. Brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage: The role of thrombin and iron. Stroke 2007, 38, 759–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, A.I.; Mendelow, A.D.; Hanley, D.F. Intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet 2009, 373, 1632–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zia, E.; Engstrom, G.; Svensson, P.J.; Norrving, B.; Pessah-Rasmussen, H. Three-year survival and stroke recurrence rates in patients with primary intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2009, 40, 3567–3573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Simonetta, I.; Miceli, S.; Arnao, V.; Licata, G.; Pinto, A. Neurological complications of anderson-fabry disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 6014–6030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuttolomondo, A.; Pecoraro, R.; Simonetta, I.; Miceli, S.; Pinto, A.; Licata, G. Anderson-fabry disease: A. multiorgan disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19, 5974–5996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balami, J.S.; Buchan, A.M. Complications of intracerebral haemorrhage. Lancet Neurol. 2012, 11, 101–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, J.C., 3rd; Greenberg, S.M.; Anderson, C.S.; Becker, K.; Bendok, B.R.; Cushman, M.; Fung, G.L.; Goldstein, J.N.; Macdonald, R.L.; Mitchell, P.H.; et al. Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage: A guideline for healthcare professionals from the american heart association/american stroke association. Stroke 2015, 46, 2032–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.Y.; Kim, O.J.; Min, S.H.; Jeong, J.H.; Suh, S.W.; Chung, T.N. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce mortality and hematoma size in a rat intracerebral hemorrhage model in an acute phase. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1658195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saparov, A.; Ogay, V.; Nurgozhin, T.; Jumabay, M.; Chen, W.C. Preconditioning of human mesenchymal stem cells to enhance their regulation of the immune response. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 3924858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schafer, R.; Spohn, G.; Baer, P.C. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cells in regenerative medicine: Can preconditioning strategies improve therapeutic efficacy? Transfus. Med. Hemother. 2016, 43, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Li, L. Preconditioning influences mesenchymal stem cell properties in vitro and in vivo. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 1428–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, J.; Ming, L.; Shang, F.; Shen, L.; Chen, J.; Jin, Y. Apocynin suppression of nadph oxidase reverses the aging process in mesenchymal stem cells to promote osteogenesis and increase bone mass. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 18572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathore, R.; Zheng, Y.M.; Niu, C.F.; Liu, Q.H.; Korde, A.; Ho, Y.S.; Wang, Y.X. Hypoxia activates nadph oxidase to increase [ros]i and [ca2+]i through the mitochondrial ros-pkcepsilon signaling axis in pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2008, 45, 1223–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delcourt, C.; Huang, Y.; Arima, H.; Chalmers, J.; Davis, S.M.; Heeley, E.L.; Wang, J.; Parsons, M.W.; Liu, G.; Anderson, C.S.; et al. Hematoma growth and outcomes in intracerebral hemorrhage: The interact1 study. Neurology 2012, 79, 314–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poungvarin, N.; Bhoopat, W.; Viriyavejakul, A.; Rodprasert, P.; Buranasiri, P.; Sukondhabhant, S.; Hensley, M.J.; Strom, B.L. Effects of dexamethasone in primary supratentorial intracerebral hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 1987, 316, 1229–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santambrogio, S.; Martinotti, R.; Sardella, F.; Porro, F.; Randazzo, A. Is there a real treatment for stroke? Clinical and statistical comparison of different treatments in 300 patients. Stroke 1978, 9, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.L.; Kumana, C.R.; Lauder, I.J.; Cheung, Y.K.; Chan, F.L.; Kou, M.; Chang, C.M.; Cheung, R.T.; Fong, K.Y. Treatment of acute cerebral hemorrhage with intravenous glycerol. A. double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized trial. Stroke 1992, 23, 967–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.A.; Brun, N.C.; Begtrup, K.; Broderick, J.; Davis, S.; Diringer, M.N.; Skolnick, B.E.; Steiner, T. For the FAST Trial Investigators. Efficacy and safety of recombinant activated factor vii for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 358, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.A.; Brun, N.C.; Begtrup, K.; Broderick, J.; Davis, S.; Diringer, M.N.; Skolnick, B.E.; Steiner, T. For the Recombinant Activated Factor VII Intracerebral Hemorrhage Trial Investigators. Recombinant activated factor vii for acute intracerebral hemorrhage. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, W.; Zhong, J.; Yu, J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, L.; Yang, S.; Liu, P.; Xu, J.; Wang, J.; et al. Therapeutic benefit of human umbilical cord derived mesenchymal stromal cells in intracerebral hemorrhage rat: Implications of anti-inflammation and angiogenesis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2009, 24, 307–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otero, L.; Zurita, M.; Bonilla, C.; Aguayo, C.; Vela, A.; Rico, M.A.; Vaquero, J. Late transplantation of allogeneic bone marrow stromal cells improves neurologic deficits subsequent to intracerebral hemorrhage. Cytotherapy 2011, 13, 562–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.P.; Wang, Z.H.; Peng, D.Y.; Li, S.M.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.H. Therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cells in rats with intracerebral hemorrhage: Reduced apoptosis and enhanced neuroprotection. Mol. Med. Rep. 2012, 6, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayer, S.A. Ultra-early hemostatic therapy for intracerebral hemorrhage. Stroke 2003, 34, 224–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapoor, M.; Sharma, N.; Sandhir, R.; Nehru, B. Effect of the nadph oxidase inhibitor apocynin on ischemia-reperfusion hippocampus injury in rat brain. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 97, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Jang, B.G.; Choi, B.Y.; Kim, H.S.; Sohn, M.; Chung, T.N.; Choi, H.C.; Song, H.K.; Suh, S.W. Post-treatment of an nadph oxidase inhibitor prevents seizure-induced neuronal death. Brain Res. 2013, 1499, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phinney, D.G.; Pittenger, M.F. Concise review: Msc-derived exosomes for cell-free therapy. Stem Cells 2017, 35, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kho, A.R.; Kim, O.J.; Jeong, J.H.; Yu, J.M.; Kim, H.S.; Choi, B.Y.; Suh, S.W.; Chung, T.N. Administration of placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells counteracts a delayed anergic state following a transient induction of endogenous neurogenesis activity after global cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 2018, 1689, 63–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Bigio, M.R.; Yan, H.J.; Buist, R.; Peeling, J. Experimental intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Magnetic resonance imaging and histopathological correlates. Stroke 1996, 27, 2312–2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. Nih image to imagej: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiechelman, K.J.; Braun, R.D.; Fitzpatrick, J.D. Investigation of the bicinchoninic acid protein assay: Identification of the groups responsible for color formation. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 175, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faul, F.; Erdfelder, E.; Lang, A.G.; Buchner, A. G*power 3: A flexible statistical power analysis program for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences. Behav. Res. Methods 2007, 39, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Min, S.; Kim, O.J.; Bae, J.; Chung, T.N. Effect of Pretreatment with the NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Apocynin on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113679
Min S, Kim OJ, Bae J, Chung TN. Effect of Pretreatment with the NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Apocynin on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(11):3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113679
Chicago/Turabian StyleMin, Saehong, Ok Joon Kim, Jinkun Bae, and Tae Nyoung Chung. 2018. "Effect of Pretreatment with the NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Apocynin on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Intracerebral Hemorrhage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 11: 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113679
APA StyleMin, S., Kim, O. J., Bae, J., & Chung, T. N. (2018). Effect of Pretreatment with the NADPH Oxidase Inhibitor Apocynin on the Therapeutic Efficacy of Human Placenta-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Intracerebral Hemorrhage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(11), 3679. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19113679