Melatonin May Increase Anticancer Potential of Pleiotropic Drugs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Source of Data
2. MEL—A Versatile Molecule
3. Sources of MEL
3.1. MEL in Animal Foods
3.2. MEL in Edible and Medicinal Plants
3.3. MEL Supplements and Bioavailability
4. MEL and Cancer and Vice Versa
4.1. Mechanism of Antitumor Activity of MEL
4.1.1. Antioxidant Effects
4.1.2. Apoptosis, Cell Cycle and Differentiation
4.1.3. Angiogenesis and Invasiveness
4.1.4. Antiestrogenic Activity
4.1.5. Immunomodulatory Effects
4.2. Preclinical Studies
4.2.1. MEL and Cancer: In Vitro
4.2.2. MEL and Cancer: In Vivo
4.2.3. MEL and Cancer: Clinical Results
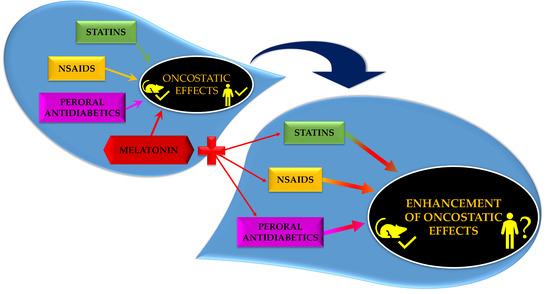
5. Pleiotropic Drugs and MEL in Cancer Prevention/Treatment
5.1. NSAIDs
NSAIDs and MEL
5.2. Statins
Statins and MEL
5.3. Peroral Antidiabetics
5.3.1. Metformin
Metformin and MEL
5.3.2. Glitazones (Thiazolidinediones)
Glitazones and MEL
5.4. Retinoids and MEL
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hirschey, M.D.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Diehl, A.M.; Drew, J.E.; Frezza, C.; Green, M.F.; Jones, L.W.; Ko, Y.H.; Le, A.; Lea, M.A.; et al. Dysregulated metabolism contributes to oncogenesis. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2015, 35, S129–S150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Srinivasan, V.; Maestroni, G.J.; Cardinali, D.P.; Poeggeler, B.; Hardeland, R. Melatonin: Nature’s most versatile biological signal? FEBS J. 2006, 273, 2813–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Fuentes-Broto, L. Melatonin: a multitasking molecule. Prog. Brain Res. 2010, 181, 127–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Bella, G.; Mascia, F.; Gualano, L.; Di Bella, L. Melatonin anticancer effects: Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 2410–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Rosales-Corral, S.A.; Tan, D.-X.; Acuna-Castroviejo, D.; Qin, L.; Yang, S.-F.; Xu, K. Melatonin, a full service anti-cancer agent: Inhibition of initiation, progression and metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, E843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seely, D.; Wu, P.; Fritz, H.; Kennedy, D.A.; Tsui, T.; Seely, A.J.; Mills, E. Melatonin as Adjuvant Cancer Care With and Without Chemotherapy. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 293–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Meng, X.; Zhang, J.-J.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Melatonin for the prevention and treatment of cancer. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 39896–39921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Posadzki, P.P.; Bajpai, R.; Kyaw, B.M.; Roberts, N.J.; Brzezinski, A.; Christopoulos, G.I.; Divakar, U.; Bajpai, S.; Soljak, M.; Dunleavy, G.; et al. Melatonin and health: an umbrella review of health outcomes and biological mechanisms of action. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Lopez-Burillo, S. Melatonin: reducing the toxicity and increasing the efficacy of drugs. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2002, 54, 1299–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.-M.; Jin, B.-Z.; Ai, F.; Duan, C.-H.; Lu, Y.-Z.; Dong, T.-F.; Fu, Q.-L. The efficacy and safety of melatonin in concurrent chemotherapy or radiotherapy for solid tumors: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2012, 69, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghari, M.H.; Ghobadi, E.; Moloudizargari, M.; Fallah, M.; Abdollahi, M. Does the use of melatonin overcome drug resistance in cancer chemotherapy? Life Sci. 2018, 196, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andersen, L.P.; Gögenur, I.; Rosenberg, J.; Reiter, R.J. The Safety of Melatonin in Humans. Clin. Drug Investig. 2016, 36, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lerner, A.B.; Case, J.D.; Takahashi, Y.; Lee, T.H.; Mori, W. Isolation of melatonin, the pineal gland factor that lightens melanocytes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1958, 80, 2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ralph, C.L. Melatonin Production by Extra-pineal Tissues. In Melatonin Current Status and Perspectives, Proceedings of an International Symposium on Melatonin, Bremen, Germany, 28–30 September, 1980; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1981; pp. 35–46. [Google Scholar]
- Vivien-Roels, B.; Pevet, P.; Beck, O.; Fevre-Montange, M. Identification of melatonin in the compound eyes of an insect, the locust (Locusta migratoria), by radioimmunoassay and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Neurosci. Lett. 1984, 49, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardeland, R.; Poeggeler, B. Non-vertebrate melatonin. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 34, 233–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Acuña-Castroviejo, D.; Escames, G.; Venegas, C.; Díaz-Casado, M.E.; Lima-Cabello, E.; López, L.C.; Rosales-Corral, S.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Extrapineal melatonin: sources, regulation, and potential functions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2997–3025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubbels, R.; Reiter, R.J.; Klenke, E.; Goebel, A.; Schnakenberg, E.; Ehlers, C.; Schiwara, H.W.; Schloot, W. Melatonin in edible plants identified by radioimmunoassay and by high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J. Pineal Res. 1995, 18, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Functions of melatonin in plants: a review. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 133–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reiter, R.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Zhou, Z.; Cruz, M.; Fuentes-Broto, L.; Galano, A. Phytomelatonin: Assisting Plants to Survive and Thrive. Molecules 2015, 20, 7396–7437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, J.; Xie, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Chen, L. Melatonin: A Multifunctional Factor in Plants. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolář, J.; Macháčková, I.; Eder, J.; Prinsen, E.; van Dongen, W.; van Onckelen, H.; Illnerová, H. Melatonin: Occurrence and daily rhythm in Chenopodium rubrum. Phytochemistry 1997, 44, 1407–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchester, L.C.; Coto-Montes, A.; Boga, J.A.; Andersen, L.P.; Zhou, Z.; Galano, A.; Vriend, J.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: an ancient molecule that makes oxygen metabolically tolerable. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 403–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, H.-M.; Zhang, Y. Melatonin: a well-documented antioxidant with conditional pro-oxidant actions. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 131–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mediavilla, M.D.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.J.; Tan, D.-X.; Manchester, L.; Reiter, R.J. Basic mechanisms involved in the anti-cancer effects of melatonin. Curr. Med. Chem. 2010, 17, 4462–4481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Singh, K.M.; Gupta, B.B. Melatonin synthesis and clock gene regulation in the pineal organ of teleost fish compared to mammals: Similarities and differences. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.B.; Spessert, R.; Vollrath, L. Molecular components and mechanism of adrenergic signal transduction in mammalian pineal gland: regulation of melatonin synthesis. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2005, 43, 115–149. [Google Scholar]
- Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: That Ubiquitously Acting Pineal Hormone. Physiology 1991, 6, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechmann, A.F.; Hollyfield, J.G. HIOMT-like immunoreactivity in the vertebrate retina: A species comparison. Exp. Eye Res. 1989, 49, 1079–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konturek, S.J.; Konturek, P.C.; Brzozowski, T.; Bubenik, G.A. Role of melatonin in upper gastrointestinal tract. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2007, 58 (Suppl. 6), 23–52. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, D.-X.; Zanghi, B.M.; Manchester, L.C.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin identified in meats and other food stuffs: potentially nutritional impact. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 57, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sae-Teaw, M.; Johns, J.; Johns, N.P.; Subongkot, S. Serum melatonin levels and antioxidant capacities after consumption of pineapple, orange, or banana by healthy male volunteers. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Phytomelatonin, natural melatonin from plants as a novel dietary supplement: Sources, activities and world market. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 48, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeMuro, R.L.; Nafziger, A.N.; Blask, D.E.; Menhinick, A.M.; Bertino, J.S. The absolute bioavailability of oral melatonin. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2000, 40, 781–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, W.-L.; Kadva, A.; Johnston, A.; Silman, R. Variable Bioavailability of Oral Melatonin. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 336, 1028–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Proietti, S.; Carlomagno, G.; Dinicola, S.; Bizzarri, M. Soft gel capsules improve melatonin’s bioavailability in humans. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2014, 10, 1193–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yan, Y.; Chen, J.-M.; Lu, T.-B. Thermodynamics and preliminary pharmaceutical characterization of a melatonin–pimelic acid cocrystal prepared by a melt crystallization method. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Lillard, J.W. Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2009, 86, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wu, W.; Deng, Y.; Zu, C.; Liu, Y. Melatonin-loaded silica coated with hydroxypropyl methylcellulose phthalate for enhanced oral bioavailability: Preparation, and in vitro-in vivo evaluation. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 112, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Zhou, Y.; Gan, R.-Y.; Xu, D.-P.; Li, H.-B. Dietary sources and bioactivities of melatonin. Nutrients 2017, 9, E367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jouan, P.-N.; Pouliot, Y.; Gauthier, S.F.; Laforest, J.-P. Hormones in bovine milk and milk products: A survey. Int. Dairy J. 2006, 16, 1408–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karunanithi, D.; Radhakrishna, A.; Sivaraman, K.P.; Biju, V.M. Quantitative determination of melatonin in milk by LC-MS/MS. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 805–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen Engler, A.; Hadash, A.; Shehadeh, N.; Pillar, G. Breastfeeding may improve nocturnal sleep and reduce infantile colic: Potential role of breast milk melatonin. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonomini, F.; Borsani, E.; Favero, G.; Rodella, L.; Rezzani, R. Dietary Melatonin Supplementation Could Be a Promising Preventing/Therapeutic Approach for a Variety of Liver Diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setyaningsih, W.; Saputro, I.E.; Barbero, G.F.; Palma, M.; García Barroso, C. Determination of Melatonin in Rice (Oryza sativa) Grains by Pressurized Liquid Extraction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, R.J.; Manchester, L.C.; Tan, D.-X. Melatonin in walnuts: influence on levels of melatonin and total antioxidant capacity of blood. Nutrition 2005, 21, 920–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zohar, R.; Izhaki, I.; Koplovich, A.; Ben-Shlomo, R. Phytomelatonin in the leaves and fruits of wild perennial plants. Phytochem. Lett. 2011, 4, 222–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stege, P.W.; Sombra, L.L.; Messina, G.; Martinez, L.D.; Silva, M.F. Determination of melatonin in wine and plant extracts by capillary electrochromatography with immobilized carboxylic multi-walled carbon nanotubes as stationary phase. Electrophoresis 2010, 31, 2242–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.; Huo, Y.; Tan, D.-X.; Liang, Z.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y. Melatonin in Chinese medicinal herbs. Life Sci. 2003, 73, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arnao, M.B.; Hernández-Ruiz, J. Chemical stress by different agents affects the melatonin content of barley roots. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 295–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byeon, Y.; Back, K. Melatonin synthesis in rice seedlings in vivo is enhanced at high temperatures and under dark conditions due to increased serotonin N -acetyltransferase and N -acetylserotonin methyltransferase activities. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afreen, F.; Zobayed, S.M.; Kozai, T. Melatonin in Glycyrrhiza uralensis: response of plant roots to spectral quality of light and UV-B radiation. J. Pineal Res. 2006, 41, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erland, L.A.; Saxena, P.K. Melatonin Natural Health Products and Supplements: Presence of Serotonin and Significant Variability of Melatonin Content. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2017, 13, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Srinivasan, V.; Spence, D.W.; Pandi-Perumal, S.R.; Trakht, I.; Cardinali, D.P. Therapeutic actions of melatonin in cancer: possible mechanisms. Integr. Cancer Ther. 2008, 7, 189–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, R.G.; Blask, D.E.; Brainard, G.C.; Hansen, J.; Lockley, S.W.; Provencio, I.; Rea, M.S.; Reinlib, L. Meeting Report: The Role of Environmental Lighting and Circadian Disruption in Cancer and Other Diseases. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kothari, L.S.; Shah, P.N.; Mhatre, M.C. Effect of continuous light on the incidence of 9,10-dimethyl-1,2-benzanthracene induced mammary tumors in female Holtzman rats. Cancer Lett. 1982, 16, 313–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.N.; Mhatre, M.C.; Kothari, L.S. Effect of melatonin on mammary carcinogenesis in intact and pinealectomized rats in varying photoperiods. Cancer Res. 1984, 44, 3403–3407. [Google Scholar]
- Megdal, S.P.; Kroenke, C.H.; Laden, F.; Pukkala, E.; Schernhammer, E.S. Night work and breast cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 2023–2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Lu, Y.; Wu, K.; Lin, Q.; Shen, W.; Zhu, M.; Huang, S.; Chen, J. Does night work increase the risk of breast cancer? A systematic review and meta-analysis of epidemiological studies. Cancer Epidemiol. 2013, 37, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schernhammer, E.S.; Laden, F.; Speizer, F.E.; Willet, W.C.; Hunter, D.J.; Kawachi, I.; Fuchs, C.S.; Colditz, G.A. Night-shift work and risk of colorectal cancer in the Nurses’ Health Study. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 825–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papantoniou, K.; Castaño-Vinyals, G.; Espinosa, A.; Aragonés, N.; Pérez-Gómez, B.; Burgos, J.; Gómez-Acebo, I.; Llorca, J.; Peiró, R.; Jimenez-Moleón, J.J. Night shift work, chronotype and prostate cancer risk in the MCC-Spain case-control study. Int. J. Cancer 2015, 137, 1147–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mancio, J.; Leal, C.; Ferreira, M.; Norton, P.; Lunet, N. Does the association of prostate cancer with night-shift work differ according to rotating vs. fixed schedule? A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2018, 21, 337–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.-S.; Armstrong, M.E.; Cairns, B.J.; Key, T.J.; Travis, R.C. Shift work and chronic disease: The epidemiological evidence. Occup. Med. (Chic. Ill). 2011, 61, 78–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, H.-B.; Bin, K.-Y.; Liu, W.-H.; Yang, F.-S. Shift work, night work, and the risk of prostate cancer. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017, 96, e8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, J. Night Shift Work and Risk of Breast Cancer. Curr. Environ. Heal. Reports 2017, 4, 325–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, S.M.; Belancio, V.P.; Dauchy, R.T.; Xiang, S.; Brimer, S.; Mao, L.; Hauch, A.; Lundberg, P.W.; Summers, W.; Yuan, L.; et al. Melatonin: an inhibitor of breast cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2015, 22, R183–R204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Savvidis, C.; Koutsilieris, M. Circadian rhythm disruption in cancer biology. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 1249–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maiese, K. Moving to the Rhythm with Clock (Circadian) Genes, Autophagy, mTOR, and SIRT1 in Degenerative Disease and Cancer. Curr. Neurovasc. Res. 2017, 14, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shostak, A. Circadian Clock, Cell Division, and Cancer: From Molecules to Organism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatka, P.; Žúbor, P.; Busselberg, D.; Kwon, T.K.; Adámek, M.; Petrovič, D.; Opatrilová, R.; Gazdíková, K.; Caprnda, M.; Rodrigo, L.; Danko, J.; Kružliak, P. Melatonin and breast cancer: Evidences from preclinical and human studies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2018, 122, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galano, A.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin and its metabolites vs oxidative stress: From individual actions to collective protection. J. Pineal Res. 2018, 65, e12514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, H.; Ertekin, T.; Atay, E.; Nisari, M.; Susar Güler, H.; Al, Ö.; Payas, A.; Yılmaz, S. Antioxidant role of melatonin against nicotine’s teratogenic effects on embryonic bone development. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2018, 21, 787–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galano, A.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin: A Versatile Protector against Oxidative DNA Damage. Molecules 2018, 23, 530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Ma, S.-J.; Luo, J.-H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, R.-X.; Liu, H.; Li, L.; Zhang, Z.-G.; Zhou, R.-X. Melatonin induces the apoptosis and inhibits the proliferation of human gastric cancer cells via blockade of the AKT/MDM2 pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1975–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.; Chen, X.; Li, S.; Sun, B.; Hang, C. Melatonin Treatment Regulates SIRT3 Expression in Early Brain Injury (EBI) Due to Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) in a Mouse Model of Subarachnoid Hemorrhage (SAH). Med. Sci. Monit. 2018, 24, 3804–3814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Hidalgo, M.; Guerrero, J.M.; Villegas, I.; Packham, G.; de la Lastra, C.A. Melatonin, A Natural Programmed Cell Death Inducer in Cancer. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 3805–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winczyk, K.; Pawlikowski, M.; Karasek, M. Melatonin and RZR/ROR receptor ligand CGP 52608 induce apoptosis in the murine colonic cancer. J. Pineal Res. 2001, 31, 179–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.-Y.; Li, W.-M.; Zhou, L.-L.; Lu, Q.-N.; He, W. Melatonin induces apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells through HDAC4 nuclear import mediated by CaMKII inactivation. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 58, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koçak, N.; Dönmez, H.; Yildirim, İ.H. Effects of melatonin on apoptosis and cell differentiation in MCF-7 derived cancer stem cells. Cell. Mol. Biol. (Noisy-le-grand). 2018, 64, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eck-Enriquez, K.; Kiefer, T.L.; Spriggs, L.L.; Hill, S.M. Pathways through which a regimen of melatonin and retinoic acid induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2000, 61, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.-L. Melatonin and Doxorubicin synergistically induce cell apoptosis in human hepatoma cell lines. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.-M.; Woo, S. H.; Oh, S.T.; Hong, S.-E.; Choe, T.-B.; Ye, S.-K.; Kim, E.-K.; Seong, M.K.; Kim, H.-A.; Noh, W.C.; et al. Melatonin enhances arsenic trioxide-induced cell death via sustained upregulation of Redd1 expression in breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 422, 64–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; González-González, A.; González, A.; Cos, S.; Martínez-Campa, C. Melatonin enhances the apoptotic effects and modulates the changes in gene expression induced by docetaxel in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plaimee, P.; Weerapreeyakul, N.; Barusrux, S.; Johns, N.P. Melatonin potentiates cisplatin-induced apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human lung adenocarcinoma cells. Cell Prolif. 2015, 48, 67–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, C.-J.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, Y.-T.; Lai, C.-S.; Hsu, Y.-C. Melatonin Suppresses the Growth of Ovarian Cancer Cell Lines (OVCAR-429 and PA-1) and Potentiates the Effect of G1 Arrest by Targeting CDKs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-K.; Tsao, C.-H.; Hsieh, C.-C.; Lin, G.-J.; Ma, K.-H.; Shieh, Y.-S.; Sytwu, H.-K.; Chen, Y.-W. Melatonin exerts anti-oral cancer effect via suppressing LSD1 in patient-derived tumor xenograft models. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33756–33769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Barceló, E.J.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Alonso-González, C.; Rueda, N. Breast cancer therapy based on melatonin. Recent Patents Endocrine, Metab. Immune Drug Discov. 2012, 6, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sainz, R.M.; Mayo, J.C.; Tan, D.-X.; León, J.; Manchester, L.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin reduces prostate cancer cell growth leading to neuroendocrine differentiation via a receptor and PKA independent mechanism. Prostate 2005, 63, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; Alvarez-García, V.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Alonso-González, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin promotes differentiation of 3T3-L1 fibroblasts. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 52, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Zuo, L.; Gui, S.; Zhou, Q.; Wei, W.; Wang, Y. Induction of cell differentiation and promotion of endocan gene expression in stomach cancer by melatonin. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2012, 39, 2843–2849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goradel, N.H.; Asghari, M.H.; Moloudizargari, M.; Negahdari, B.; Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Abdollahi, M. Melatonin as an angiogenesis inhibitor to combat cancer: Mechanistic evidence. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2017, 335, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zonta, Y.R.; Martinez, M.; Camargo, I.C.; Domeniconi, R.F.; Lupi Júnior, L.A.; Pinheiro, P.F.; Reiter, R.J.; Martinez, F.E.; Chuffa, L.G. Melatonin Reduces Angiogenesis in Serous Papillary Ovarian Carcinoma of Ethanol-Preferring Rats. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, A.; González-González, A.; Alonso-González, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin inhibits angiogenesis in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells by downregulation of VEGF. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 2433–2440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jardim-Perassi, B.V.; Arbab, A.S.; Ferreira, L.C.; Borin, T.F.; Varma, N.R.; Iskander, A.S.; Shankar, A.; Ali, M.M.; de Campos Zuccari, D.A. Effect of Melatonin on Tumor Growth and Angiogenesis in Xenograft Model of Breast Cancer. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e85311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Barceló, E.J.; Cos, S.; Mediavilla, D.; Martínez-Campa, C.; González, A.; Alonso-González, C. Melatonin-estrogen interactions in breast cancer. J. Pineal Res. 2005, 38, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-García, V.; González, A.; Martínez-Campa, C.; Alonso-González, C.; Cos, S. Melatonin modulates aromatase activity and expression in endothelial cells. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 2058–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Cos, S.; Martinez-Campa, C.; Alonso-Gonzalez, C.; Sanchez-Mateos, S.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Sánchez-Barceló, E.J. Selective estrogen enzyme modulator actions of melatonin in human breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2008, 45, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Barceló, E.J.; Mediavilla, M.D.; Alonso-González, C.; Reiter, R.J. Melatonin uses in oncology: breast cancer prevention and reduction of the side effects of chemotherapy and radiation. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2012, 21, 819–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrillo-Vico, A.; Lardone, P.; Álvarez-Sánchez, N.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Guerrero, J. Melatonin: Buffering the Immune System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8638–8683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moore, C.B.; Siopes, T.D. Melatonin enhances cellular and humoral immune responses in the Japanese quail (Coturnix coturnix japonica) via an opiatergic mechanism. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2003, 131, 258–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baghban Rahimi, S.; Mohebbi, A.; Vakilzadeh, G.; Biglari, P.; Razeghi Jahromi, S.; Mohebi, S.R.; Shirian, S.; Gorji, A.; Ghaemi, A. Enhancement of therapeutic DNA vaccine potency by melatonin through inhibiting VEGF expression and induction of antitumor immunity mediated by CD8+ T cells. Arch. Virol. 2018, 163, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glenister, R.; McDaniel, K.; Francis, H.; Venter, J.; Jensen, K.; Dusio, G.; Gaudio, E.; Glaser, S.; Meng, F.; Alpini, G. Therapeutic actions of melatonin on gastrointestinal cancer development and progression. Transl. Gastrointest. Cancer 2013, 2, 11–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongsena, W.; Charoensuk, L.; Dangtakot, R.; Pinlaor, P.; Intuyod, K.; Pinlaor, S. Melatonin suppresses eosinophils and Th17 cells in hamsters treated with a combination of human liver fluke infection and a chemical carcinogen. Pharmacol. Reports 2018, 70, 98–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gatti, G.; Lucini, V.; Dugnani, S.; Calastretti, A.; Spadoni, G.; Bedini, A.; Rivara, S.; Mor, M.; Canti, G.; Scaglione, F.; et al. Antiproliferative and pro-apoptotic activity of melatonin analogues on melanoma and breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68338–68353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calastretti, A.; Gatti, G.; Lucini, V.; Dugnani, S.; Canti, G.; Scaglione, F.; Bevilacqua, A. Melatonin Analogue Antiproliferative and Cytotoxic Effects on Human Prostate Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kast, R.E. Agomelatine or ramelteon as treatment adjuncts in glioblastoma and other M1- or M2-expressing cancers. Contemp. Oncol. (Poznan, Poland) 2015, 19, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaworek, J.; Leja-Szpak, A.; Nawrot-Porąbka, K.; Szklarczyk, J.; Kot, M.; Pierzchalski, P.; Góralska, M.; Ceranowicz, P.; Warzecha, Z.; Dembinski, A.; et al. Effects of Melatonin and Its Analogues on Pancreatic Inflammation, Enzyme Secretion, and Tumorigenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girgert, R.; Hanf, V.; Emons, G.; Gründker, C. Membrane-bound melatonin receptor MT1 down-regulates estrogen responsive genes in breast cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 47, 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, C.; Yuan, L.; Dai, J.; Lai, L.; Mao, L.; Xiang, S.; Rowan, B.; Hill, S.M. Melatonin inhibits mitogenic cross-talk between retinoic acid-related orphan receptor alpha (RORα) and ERα in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Steroids 2010, 75, 944–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, L.; Yuan, L.; Slakey, L.M.; Jones, F.E.; Burow, M.E.; Hill, S.M. Inhibition of breast cancer cell invasion by melatonin is mediated through regulation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Breast Cancer Res. 2010, 12, R107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, C.-M.; Lin, C.-W.; Yang, J.-S.; Yang, W.-E.; Su, S.-C.; Yang, S.-F. Melatonin inhibits TPA-induced oral cancer cell migration by suppressing matrix metalloproteinase-9 activation through the histone acetylation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 21952–21967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maschio-Signorini, L.B.; Gelaleti, G.B.; Moschetta, M.G.; Borin, T.F.; Jardim-Perassi, B.V; Lopes, J.R.; Lacerda, J.Z.; Roela, R.A.; Bordin, N.A.; Corrêa, L.A.; et al. Melatonin Regulates Angiogenic and Inflammatory Proteins in MDA-MB-231 Cell Line and in Co-culture with Cancer-associated Fibroblasts. Anticancer. Agents Med. Chem. 2016, 16, 1474–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuffa, L.G.; Reiter, R.J.; Lupi, L.A. Melatonin as a promising agent to treat ovarian cancer: Molecular mechanisms. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 945–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ataei, N.; Aghaei, M.; Panjehpour, M. The protective role of melatonin in cadmium-induced proliferation of ovarian cancer cells. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 13, 159–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Nabat, E.; Movassaghpour, A.A.; Shanehbandi, D.; Faramarzian Azimi Maragheh, B.; Matluobi, D.; Barazvan, B.; Kazemi, M.; Samadi, N.; et al. The impact of different extracellular matrices on melatonin effect in proliferation and stemness properties of ovarian cancer cells. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 87, 288–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbarzadeh, M.; Movassaghpour, A.A.; Ghanbari, H.; Kheirandish, M.; Fathi Maroufi, N.; Rahbarghazi, R.; Nouri, M.; Samadi, N. The potential therapeutic effect of melatonin on human ovarian cancer by inhibition of invasion and migration of cancer stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 17062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, V.W.; Yau, W.L.; Tam, C.W.; Yao, K.-M.; Shiu, S.Y. Melatonin Inhibits Androgen Receptor Splice Variant-7 (AR-V7)-Induced Nuclear Factor-Kappa B (NF-κB) Activation and NF-κB Activator-Induced AR-V7 Expression in Prostate Cancer Cells: Potential Implications for the Use of Melatonin in Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC) Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo, J.C.; Hevia, D.; Quiros-Gonzalez, I.; Rodriguez-Garcia, A.; Gonzalez-Menendez, P.; Cepas, V.; Gonzalez-Pola, I.; Sainz, R.M. IGFBP3 and MAPK/ERK signaling mediates melatonin-induced antitumor activity in prostate cancer. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, E.J.; Won, G.; Lee, J.; Lee, S.; Kim, S.-H. Upregulation of miRNA3195 and miRNA374b Mediates the Anti-Angiogenic Properties of Melatonin in Hypoxic PC-3 Prostate Cancer Cells. J. Cancer 2015, 6, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rodriguez-Garcia, A.; Mayo, J.C.; Hevia, D.; Quiros-Gonzalez, I.; Navarro, M.; Sainz, R.M. Phenotypic changes caused by melatonin increased sensitivity of prostate cancer cells to cytokine-induced apoptosis. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 33–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung-Hynes, B.; Schmit, T.L.; Reagan-Shaw, S.R.; Siddiqui, I.A.; Mukhtar, H.; Ahmad, N. Melatonin, a novel Sirt1 inhibitor, imparts antiproliferative effects against prostate cancer in vitro in culture and in vivo in TRAMP model. J. Pineal Res. 2011, 50, 140–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Fan, M.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Song, C.; Yan, Y.; Jin, Y.; Huang, Z.; Lin, C.; Wu, J. Melatonin induces cell apoptosis in AGS cells through the activation of JNK and P38 MAPK and the suppression of nuclear Factor-Kappa B: A novel therapeutic implication for gastric cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 37, 2323–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, C.; Huang, Q.; Zhu, H. Melatonin Inhibits the Proliferation of Gastric Cancer Cells Through Regulating the miR-16-5p-Smad3 Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2018, 37, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.-X.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, R.-X. Involvement of nuclear receptor RZR/RORγ in melatonin-induced HIF-1α inactivation in SGC-7901 human gastric cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2541–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudra, D.S.; Pal, U.; Maiti, N.C.; Reiter, R.J.; Swarnakar, S. Melatonin inhibits matrix metalloproteinase-9 activity by binding to its active site. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 54, 398–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, J.; Casado, J.; Jiménez Ruiz, S.M.; Zurita, M.S.; González-Puga, C.; Rejón, J.D.; Gila, A.; Muñoz de Rueda, P.; Pavón, E.J.; Reiter, R.J.; et al. Melatonin reduces endothelin-1 expression and secretion in colon cancer cells through the inactivation of FoxO-1 and NF-κβ. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, C.W.; Kim, S.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.H. Melatonin Promotes Apoptosis of Colorectal Cancer Cells via Superoxide-mediated ER Stress by Inhibiting Cellular Prion Protein Expression. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 3951–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Yoon, Y.M.; Han, Y.-S.; Yun, C.W.; Lee, S.H. Melatonin Promotes Apoptosis of Oxaliplatin-resistant Colorectal Cancer Cells Through Inhibition of Cellular Prion Protein. Anticancer Res. 2018, 38, 1993–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, J.; Li, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Zheng, C.; Lin, L.; Tan, B.; Huang, M.; Fan, M. Melatonin induces cell apoptosis in Mia PaCa-2 cells via the suppression of nuclear factor-κB and activation of ERK and JNK: A novel therapeutic implication for pancreatic cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 2861–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, H.-Q.; Li, H.; Tian, T.; Lu, Y.-X.; Bai, L.; Chen, L.-Z.; Sheng, H.; Mo, H.-Y.; Zeng, J.-B.; Deng, W.; et al. Melatonin overcomes gemcitabine resistance in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by abrogating nuclear factor-κB activation. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 27–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Jung, K.H.; Yan, H.H.; Kim, S.-J.; Rumman, M.; Park, J.H.; Han, B.; Lee, J.E.; Kang, Y.W.; Lim, J. H.; et al. Melatonin Synergizes with Sorafenib to Suppress Pancreatic Cancer via Melatonin Receptor and PDGFR-β/STAT3 Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1751–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Li, Z.; Zhang, C.; Yu, W.; Tang, Z.; Li, Y.; Feng, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, Q.; Huang, W.; et al. Targeting NF-κB/AP-2β signaling to enhance antitumor activity of cisplatin by melatonin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.; Hoffmann, K.; Gao, C.; Petrulionis, M.; Herr, I.; Schemmer, P. Melatonin promotes sorafenib-induced apoptosis through synergistic activation of JNK/c-jun pathway in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 62, e12398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto-Domínguez, N.; Ordóñez, R.; Fernández, A.; Méndez-Blanco, C.; Baulies, A.; Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C.; Mauriz, J.L.; González-Gallego, J. Melatonin-induced increase in sensitivity of human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to sorafenib is associated with reactive oxygen species production and mitophagy. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 396–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-W.; Lee, L.-M.; Lee, W.-J.; Chu, C.-Y.; Tan, P.; Yang, Y.-C.; Chen, W.-Y.; Yang, S.-F.; Hsiao, M.; Chien, M.-H. Melatonin inhibits MMP-9 transactivation and renal cell carcinoma metastasis by suppressing Akt-MAPKs pathway and NF-κB DNA-binding activity. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, E.J.; Woo, S.M.; Min, K.-J.; Kwon, T.K. Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of Bim controls apoptosis in melatonin-treated human renal cancer Caki cells. J. Pineal Res. 2014, 56, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, K.-J.; Kim, H.S.; Park, E.J.; Kwon, T.K. Melatonin enhances thapsigargin-induced apoptosis through reactive oxygen species-mediated upregulation of CCAATenhancer-binding protein homologous protein in human renal cancer cells. J. Pineal Res. 2012, 53, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.-J.; Fu, L.; Tang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Qin, L.; Wang, J.; Yu, Z.; Shi, D.; Xiao, X.; Xie, F.; et al. Melatonin inhibits AP-2β/hTERT, NF-κB/COX-2 and Akt/ERK and activates caspase/Cyto C signaling to enhance the antitumor activity of berberine in lung cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 2985–3001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Pan, Y.; Yang, Y.; Di, S.; Jiang, S.; Ma, Z.; Li, T.; Zhang, Z.; Li, W.; Li, X.; et al. HDAC1 inhibition by melatonin leads to suppression of lung adenocarcinoma cells via induction of oxidative stress and activation of apoptotic pathways. J. Pineal Res. 2015, 59, 321–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, S.; Wang, X.; Geng, P.; Tang, X.; Xiang, L.; Lu, X.; Li, J.; Ruan, Z.; Chen, J.; Xie, G.; et al. Melatonin regulates PARP1 to control the senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP) in human fetal lung fibroblast cells. J. Pineal Res. 2017, 63, e12405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; Gao, J. Melatonin increases human cervical cancer HeLa cells apoptosis induced by cisplatin via inhibition of JNK/Parkin/mitophagy axis. In Vitro Cell. Dev. Biol. Anim. 2018, 54, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pariente, R.; Pariente, J.A.; Rodríguez, A.B.; Espino, J. Melatonin sensitizes human cervical cancer HeLa cells to cisplatin-induced cytotoxicity and apoptosis: Effects on oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation. J. Pineal Res. 2016, 60, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.S.; Kim, T.-J.; Yoo, Y.-M. Melatonin combined with endoplasmic reticulum stress induces cell death via the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in B16F10 melanoma cells. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e92627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonmati-Carrion, M.A.; Alvarez-Sánchez, N.; Hardeland, R.; Madrid, J.A.; Rol, M. A Comparison of B16 Melanoma Cells and 3T3 Fibroblasts Concerning Cell Viability and ROS Production in the Presence of Melatonin, Tested Over a Wide Range of Concentrations. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 3901–3920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, L.; Xu, Y.; Reiter, R.J.; Pan, Y.; Chen, D.; Liu, Y.; Pu, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, Z. Inhibition of ERK1/2 Signaling Pathway is Involved in Melatonin’s Antiproliferative Effect on Human MG-63 Osteosarcoma Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 39, 2297–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yang, Z. Effects of melatonin combined with Cis-platinum or methotrexate on the proliferation of osteosarcoma cell line SaOS-2. Acta Acad. Med. Sin. 2015, 37, 215–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, D.G.; Moretti, I.F.; Marie, S.K. Mitochondria Transcription Factor A: A Putative Target for the Effect of Melatonin on U87MG Malignant Glioma Cell Line. Molecules 2018, 23, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Pang, B.; Gu, G.; Gao, T.; Zhang, R.; Pang, Q.; Liu, Q. Melatonin Inhibits Glioblastoma Stem-like cells through Suppression of EZH2-NOTCH1 Signaling Axis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 13, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhelev, Z.; Ivanova, D.; Bakalova, R.; Aoki, I.; Higashi, T. Synergistic cytotoxicity of melatonin and new-generation anticancer drugs against leukemia lymphocytes but not normal lymphocytes. Anticancer Res. 2017, 37, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamanishi, M.; Narazaki, H.; Asano, T. Melatonin overcomes resistance to clofarabine in two leukemic cell lines by increased expression of deoxycytidine kinase. Exp. Hematol. 2015, 43, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdomo, J.; Cabrera, J.; Estévez, F.; Loro, J.; Reiter, R.J.; Quintana, J. Melatonin induces apoptosis through a caspase-dependent but reactive oxygen species-independent mechanism in human leukemia Molt-3 cells. J. Pineal Res. 2013, 55, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wurtman, R.J.; Altschule, M.D.; Holmgren, U. Effects of pinealectomy and of a bovine pineal extract in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Content 1959, 197, 108–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodin, A.E. The Growth and Spread of Walker 256 Carcinoma in Pinealectomized Rats. Cancer Res. 1963, 23, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Morozov, V.G.; Khavinson, V.K.; Dilman, V.M. A comparison of the antitumor activity of extracts from the epiphysis and hypothalamus, melatonin and sigetin (derivative of diphenylhexane) in mice with transplantable cancer of the mammary gland (Russian). Vopr. Onkol. 1973, 19, 99–101. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- El-Domeiri, A.A.; Das Gupta, T.K. Reversal by melatonin of the effect of pinealectomy on tumor growth. Cancer Res. 1973, 33, 2830–2833. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vijayalaxmi; Thomas, C.R.; Reiter, R.J.; Herman, T.S. Melatonin: From Basic Research to Cancer Treatment Clinics. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 2575–2601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Popovich, I.G.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Anisimov, S.V.; Vesnushkin, G.M.; Vinogradova, I.A. Melatonin as antioxidant, geroprotector and anticarcinogen. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1757, 573–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Campa, C.; Menéndez-Menéndez, J.; Alonso-González, C.; González, A.; Álvarez-García, V.; Cos, S. What is known about melatonin, chemotherapy and altered gene expression in breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 13, 2003–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Asghari, M.H.; Farhood, B.; Rahimifard, M.; Hashemi Goradel, N.; Abdollahi, M. The role of melatonin on chemotherapy-induced reproductive toxicity. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 70, 291–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghi-Aminjan, H.; Farhood, B.; Rahimifard, M.; Didari, T.; Baeeri, M.; Hassani, S.; Hosseini, R.; Abdollahi, M. The protective role of melatonin in chemotherapy-induced nephrotoxicity: a systematic review of non-clinical studies. Expert Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2018, 14, 937–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.-W.; Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Chen, P.; Peng, X.; Ma, C.; Zhang, W.-J.; Li, P.-D. Melatonin suppresses thyroid cancer growth and overcomes radioresistance via inhibition of p65 phosphorylation and induction of ROS. Redox Biol. 2018, 16, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Barni, S.; Mandalà, M.; Ardizzoia, A.; Paolorossi, F.; Vaghi, M.; Longarini, R.; Malugani, F.; Tancini, G. Decreased toxicity and increased efficacy of cancer chemotherapy using the pineal hormone melatonin in metastatic solid tumour patients with poor clinical status. Eur. J. Cancer 1999, 35, 1688–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Ardizzoia, A.; Barni, S.; Paolorossi, F.; Tancini, G.; Meregalli, S.; Esposti, D.; Zubelewicz, B.; Braczowski, R. A randomized study of tamoxifen alone versus tamoxifen plus melatonin in estrogen receptor-negative heavily pretreated metastatic breast-cancer patients. Oncol. Rep. 1995, 2, 871–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P.; Chilelli, M.; Villa, S.; Cerizza, L.; Tancini, G. Five years survival in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer patients treated with chemotherapy alone or chemotherapy and melatonin: a randomized trial. J. Pineal Res. 2003, 35, 12–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lissoni, P. Biochemotherapy with standard chemotherapies plus the pineal hormone melatonin in the treatment of advanced solid neoplasms. Pathol. Biol. 2007, 55, 201–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.-J.; Shen, F.; Wang, K.; Wu, M.-C. Patients with advanced primary hepatocellular carcinoma treated by melatonin and transcatheter arterial chemoembolization: A prospective study. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2002, 1, 183–186. [Google Scholar]
- Lissoni, P.; Brivio, O.; Brivio, F.; Barni, S.; Tancini, G.; Crippa, D.; Meregalli, S. Adjuvant therapy with the pineal hormone melatonin in patients with lymph node relapse due to malignant melanoma. J. Pineal Res. 1996, 21, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Meregalli, S.; Nosetto, L.; Barni, S.; Tancini, G.; Fossati, V.; Maestroni, G. Increased survival time in brain glioblastomas by a radioneuroendocrine strategy with radiotherapy plus melatonin compared to radiotherapy alone. Oncology 1996, 53, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lissoni, P.; Barni, S.; Tancini, G.; Ardizzoia, A.; Ricci, G.; Aldeghi, R.; Brivio, F.; Tisi, E.; Rovelli, F.; Rescaldani, R.; et al. A randomised study with subcutaneous low-dose interleukin 2 alone vs interleukin 2 plus the pineal neurohormone melatonin in advanced solid neoplasms other than renal cancer and melanoma. Br. J. Cancer 1994, 69, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lissoni, P.; Brivio, F.; Fumagalli, L.; Messina, G.; Vigoré, L.; Parolini, D.; Colciago, M.; Rovelli, F. Neuroimmunomodulation in medical oncology: Application of psychoneuroimmunology with subcutaneous low-dose IL-2 and the pineal hormone melatonin in patients with untreatable metastatic solid tumors. Anticancer Res. 2008, 28, 1377–1381. [Google Scholar]
- Cerea, G.; Vaghi, M.; Ardizzoia, A.; Villa, S.; Bucovec, R.; Mengo, S.; Gardani, G.; Tancini, G.; Lissoni, P. Biomodulation of cancer chemotherapy for metastatic colorectal cancer: a randomized study of weekly low-dose irinotecan alone versus irinotecan plus the oncostatic pineal hormone melatonin in metastatic colorectal cancer patients progressing on 5-fluorouracil-containing combinations. Anticancer Res. 2003, 23, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar]
- Berk, L.; Berkey, B.; Rich, T.; Hrushesky, W.; Blask, D.; Gallagher, M.; Kudrimoti, M.; McGarry, R.C.; Suh, J.; Mehta, M. Randomized Phase II Trial of High-Dose Melatonin and Radiation Therapy for RPA Class 2 Patients With Brain Metastases (RTOG 0119). Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 68, 852–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookprasert, A.; Johns, N.P.; Pnunmanee, A.; Pongthai, P.; Cheawchanwattana, A.; Johns, J.; Konsil, J.; Plaimee, P.; Porasuphatana, S.; Jitpimolmard, S. Melatonin in patients with cancer receiving chemotherapy: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 7327–7337. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, G.; Colori, B. The Di Bella Method (DBM) improved survival, objective response and performance status in a retrospective observational clinical study on 23 tumours of the head and neck. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2012, 33, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, G.; Mascia, F.; Ricchi, A.; Colori, B. Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of the first-line treatment with somatostatin combined with melatonin, retinoids, vitamin D3, and low doses of cyclophosphamide in 20 cases of breast cancer: a preliminary report. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2013, 34, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, G.; Mascia, F.; Colori, B. The Di Bella Method (DBM) in the treatment of prostate cancer: A preliminary retrospective study of 16 patients and a review of the literature. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2013, 34, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Di Bella, G.; Colori, B.; Toscano, R. Complete objective response, stable for 5 years, with the Di Bella Method, of multiple-metastatic carcinoma of the breast. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2017, 38, 401–407. [Google Scholar]
- Todisco, M. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia: long-lasting remission with combination of cyclophosphamide, somatostatin, bromocriptine, retinoids, melatonin, and ACTH. Cancer Biother. Radiopharm. 2009, 24, 353–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, L.P.; Werner, M.U.; Rosenkilde, M.M.; Harpsøe, N.G.; Fuglsang, H.; Rosenberg, J.; Gögenur, I. Pharmacokinetics of oral and intravenous melatonin in healthy volunteers. BMC Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.-Y.; Xiao, D.; Wang, L.; Dong, L.-H.; Yan, Z.-X.; Shen, Z.-X.; Chen, S.-J.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, W.-L. Therapeutic metformin/AMPK activation blocked lymphoma cell growth via inhibition of mTOR pathway and induction of autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onseng, K.; Johns, N.P.; Khuayjarernpanishk, T.; Subongkot, S.; Priprem, A.; Hurst, C.; Johns, J. Beneficial Effects of Adjuvant Melatonin in Minimizing Oral Mucositis Complications in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Receiving Concurrent Chemoradiation. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 2017, 23, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-David, M.A.; Elkayam, R.; Gelernter, I.; Pfeffer, R.M. Melatonin for Prevention of Breast Radiation Dermatitis: A Phase II, Prospective, Double-Blind Randomized Trial. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2016, 18, 188–192. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rao, P.; Knaus, E.E. Evolution of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs): cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibition and beyond. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 11, 81s–110s. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiao, Y.; Yang, T.; Gan, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, C.; Gong, Y.; Lu, Z. Associations between aspirin use and the risk of cancers: a meta-analysis of observational studies. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elwood, P.C.; Morgan, G.; Pickering, J.E.; Galante, J.; Weightman, A.L.; Morris, D.; Kelson, M.; Dolwani, S. Aspirin in the Treatment of Cancer: Reductions in Metastatic Spread and in Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of Published Studies. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0152402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothwell, P.M.; Wilson, M.; Price, J.F.; Belch, J.F.; Meade, T.W.; Mehta, Z. Effect of daily aspirin on risk of cancer metastasis: a study of incident cancers during randomised controlled trials. Lancet (London, England) 2012, 379, 1591–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Xu, Z.; Li, H. NSAIDs Use and Reduced Metastasis in Cancer Patients: results from a meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruder, E.H.; Laiyemo, A.O.; Graubard, B.I.; Hollenbeck, A.R.; Schatzkin, A.; Cross, A.J. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and colorectal cancer risk in a large, prospective cohort. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2011, 106, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paleari, L.; Puntoni, M.; Clavarezza, M.; DeCensi, M.; Cuzick, J.; DeCensi, A. PIK3CA Mutation, Aspirin Use after Diagnosis and Survival of Colorectal Cancer. A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Epidemiological Studies. Clin. Oncol. (R. Coll. Radiol). 2016, 28, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Gao, P.; Sun, J.; Song, Y.; Tsai, C.; Liu, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, P.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z. Aspirin and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs after but not before diagnosis are associated with improved breast cancer survival: A meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control 2015, 26, 589–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin-Fenton, D.P.; Heide-Jørgensen, U.; Ahern, T.P.; Lash, T.L.; Christiansen, P.; Ejlertsen, B.; Sørensen, H.T. Low-dose Aspirin, Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs, Selective COX-2 Inhibitors and Breast Cancer Recurrence. Epidemiology 2016, 27, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nagle, C.M.; Ibiebele, T.I.; DeFazio, A.; Protani, M.M.; Webb, P.M. Australian Ovarian Cancer Study Group Aspirin, nonaspirin nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, acetaminophen and ovarian cancer survival. Cancer Epidemiol. 2015, 39, 196–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.-Y.; Chuah, K.L.; Eng, P.; Leong, S.S.; Lim, E.; Lim, T.K.; Ng, A.; Poh, W.T.; Tee, A.; Teh, M.; et al. Aspirin and non-aspirin non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and risk of lung cancer. Lung Cancer 2012, 77, 246–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doat, S.; Cénée, S.; Trétarre, B.; Rebillard, X.; Lamy, P.-J.; Bringer, J.-P.; Iborra, F.; Murez, T.; Sanchez, M.; Menegaux, F. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and prostate cancer risk: results from the EPICAP study. Cancer Med. 2017, 6, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Ding, X.-W.; Yang, R.-K.; Huang, S.-L.; Kastelein, F.; Bruno, M.; Yu, X.-J.; Zhou, D.; Zou, X.-P. Cyclooxygenase inhibitors use is associated with reduced risk of esophageal adenocarcinoma in patients with Barrett’s esophagus: a meta-analysis. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 110, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huang, X.-Z.; Chen, Y.; Wu, J.; Zhang, X.; Wu, C.-C.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Sun, S.-S.; Chen, W.-J. Aspirin and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs use reduce gastric cancer risk: A dose-response meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 4781–4795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verdoodt, F.; Friis, S.; Dehlendorff, C.; Albieri, V.; Kjaer, S.K. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and risk of endometrial cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Gynecol. Oncol. 2016, 140, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, X.-J.; He, Q.; Zhang, J.-M.; Fan, H.-J.; Wen, Z.-F.; Qin, Y.-R. High-dose aspirin consumption contributes to decreased risk for pancreatic cancer in a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pancreas 2014, 43, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, A.; Yarla, N.S.; Madka, V.; Rao, C. V Clinically Relevant Anti-Inflammatory Agents for Chemoprevention of Colorectal Cancer: New Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, S.M.; Hawk, E.T.; Lubet, R.A. Coxibs and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in animal models of cancer chemoprevention. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2011, 4, 1728–1735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurpinar, E.; Grizzle, W.E.; Piazza, G.A. COX-Independent Mechanisms of Cancer Chemoprevention by Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricciotti, E.; Fitzgerald, G.A. Prostaglandins and Inflammation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 986–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, B.; Qu, L.; Yan, S. Cyclooxygenase-2 promotes tumor growth and suppresses tumor immunity. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Keeton, A.B.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Piazza, G.A. Inhibition of PDE5 by Sulindac Sulfide Selectively Induces Apoptosis and Attenuates Oncogenic Wnt/ -Catenin-Mediated Transcription in Human Breast Tumor Cells. Cancer Prev. Res. 2011, 4, 1275–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Steinert, G.; Oancea, C.; Roos, J.; Hagemeyer, H.; Maier, T.; Ruthardt, M.; Puccetti, E. Sulindac sulfide reverses aberrant self-renewal of progenitor cells induced by the AML-associated fusion proteins PML/RARα and PLZF/RARα. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e22540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, N.; Xi, Y.; Tinsley, H.N.; Gurpinar, E.; Gary, B.D.; Zhu, B.; Li, Y.; Chen, X.; Keeton, A.B.; Abadi, A.H.; et al. Sulindac selectively inhibits colon tumor cell growth by activating the cGMP/PKG pathway to suppress Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2013, 12, 1848–1859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tinsley, H.N.; Gary, B.D.; Thaiparambil, J.; Li, N.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Maxuitenko, Y.Y.; Keeton, A.B.; Piazza, G.A. Colon tumor cell growth-inhibitory activity of sulindac sulfide and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs is associated with phosphodiesterase 5 inhibition. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2010, 3, 1303–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Môciková-Kalická, K.; Bojková, B.; Adámeková, E.; Mníchová-Chamilová, M.; Kubatka, P.; Ahlersová, E.; Ahlers, I. Preventive effect of Indomethacin and melatonin on 7,12-dimethylbenz/a/anthracene-induced mammary carcinogenesis in female Sprague-Dawley rats. A preliminary report. Folia Biol. (Praha). 2001, 47, 75–79. [Google Scholar]
- Kubatka, P.; Kalická, K.; Bojková, B.; Ahlers, I.; Ahlersová, E.; Péč, M. Neoplastic effect of indomethacin in N-methyl-N-nitrosourea induced mammary carcinogenesis in female rats | Neoplastické účinky indometacínu v N-metyl-N-nitrozoureou indukovanej mamárnej karcinogenéze u samíc potkanov. Klin. Onkol. 2012, 25, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubatka, P.; Kalická, K.; Chamilová, M.; Ahlersová, E.; Ahlers, I.; Bojková, B.; Adámeková, E. Nimesulide and melatonin in mammary carcinogenesis prevention in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Neoplasma 2002, 49, 255–259. [Google Scholar]
- Orendáš, P.; Kassayová, M.; Kajo, K.; Ahlers, I.; Kubatka, P.; Bojková, B.; Péč, M.; Ahlersová, E. Celecoxib and melatonin in prevention of female rat mammary carcinogenesis. Neoplasma 2009, 56, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padillo, F.J.; Ruiz-Rabelo, J.F.; Cruz, A.; Perea, M.D.; Tasset, I.; Montilla, P.; Túnez, I.; Muntané, J. Melatonin and celecoxib improve the outcomes in hamsters with experimental pancreatic cancer. J. Pineal Res. 2010, 49, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soran, H.; Adam, S.; Durrington, P.N. Optimising treatment of hyperlipidaemia: Quantitative evaluation of UK, USA and European guidelines taking account of both LDL cholesterol levels and cardiovascular disease risk. Atherosclerosis 2018, 278, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlson, B.W.; Nicholls, S.J.; Lundman, P.; Barter, P.J.; Palmer, M.K. Modeling Statin-Induced Reductions of Cardiovascular Events in Primary Prevention: A VOYAGER Meta-Analysis. Cardiology 2018, 140, 30–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmadi, Y.; Ghorbanihaghjo, A.; Argani, H. The balance between induction and inhibition of mevalonate pathway regulates cancer suppression by statins: A review of molecular mechanisms. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 273, 273–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.-T.; Ho, H.J.; Lin, J.-T.; Shieh, J.-J.; Wu, C.-Y. Simvastatin-induced cell cycle arrest through inhibition of STAT3/SKP2 axis and activation of AMPK to promote p27 and p21 accumulation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lin, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jiang, X.; Kou, X.; Bao, Y.; Liu, H.; Sun, F.; Ling, S.; Qin, N.; Jiang, L.; et al. Mevastatin blockade of autolysosome maturation stimulates LBH589-induced cell death in triple-negative breast cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17833–17848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kany, S.; Woschek, M.; Kneip, N.; Sturm, R.; Kalbitz, M.; Hanschen, M.; Relja, B. Simvastatin exerts anticancer effects in osteosarcoma cell lines via geranylgeranylation and c-Jun activation. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1285–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Pan, Y.; Ma, H.; Li, W. Simvastatin Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Human Lung Cancer Cells. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2013, 20, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castellanos-Esparza, Y.C.; Wu, S.; Huang, L.; Buquet, C.; Shen, R.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, B.; García Latorre, E.A.; Boyer, O.; Varin, R.; Jiménez-Zamudio, L.A.; et al. Synergistic promoting effects of pentoxifylline and simvastatin on the apoptosis of triple-negative MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 52, 1246–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatka, P.; Žihlavniková, K.; Solár, P.; Kajo, K.; Valentová, V.; Péč, M.; Bojková, B.; Kassayová, M.; Stollárová, N.; Ahlers, I. Antitumor effects of atorvastatin in the chemoprevention of rat mammary carcinogenesis. Biologia (Bratisl). 2011, 66, 727–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kubatka, P.; Žihlavniková, K.; Kajo, K.; Péč, M.; Stollárová, N.; Bojková, B.; Kassayová, M.; Orendáš, P. Antineoplastic effects of simvastatin in experimental breast cancer. Klin. Onkol. 2011, 24, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jones, H.M.; Fang, Z.; Sun, W.; Clark, L.H.; Stine, J.E.; Tran, A.-Q.; Sullivan, S.A.; Gilliam, T.P.; Zhou, C.; Bae-Jump, V.L. Atorvastatin exhibits anti-tumorigenic and anti-metastatic effects in ovarian cancer in vitro. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 2478–2490. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubatka, P.; Stollárová, N.; Škarda, J.; Žihlavníková, K.; Kajo, K.; Kapinová, A.; Adamicová, K.; Péč, M.; Dobrota, D.; Bojková, B.; et al. Preventive effects of fluvastatin in rat mammary carcinogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2013, 22, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rentala, S.; Chintala, R.; Guda, M.; Chintala, M.; Komarraju, A.L.; Mangamoori, L.N. Atorvastatin inhibited Rho-associated kinase 1 (ROCK1) and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) mediated adhesion and differentiation of CD133+CD44+ prostate cancer stem cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 586–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, S.; Liberona, M.F.; Cerda-Infante, J.; Sánchez, M.; Henríquez, J.; Bizama, C.; Bravo, M.L.; Gonzalez, P.; Gejman, R.; Brañes, J.; et al. Simvastatin interferes with cancer ‘stem-cell’ plasticity reducing metastasis in ovarian cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2018, 25, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.P.; Singh, S. Statins are associated with reduced risk of gastric cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Oncol. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Med. Oncol. 2013, 24, 1721–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, H.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z.; Luo, Z.; Zhou, X. Relationship Between the Use of Statins and Patient Survival in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0126944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, T.; Loke, Y.; Beales, I.L. Systematic Review and Meta-analysis: Use of Statins Is Associated with a Reduced Incidence of Oesophageal Adenocarcinoma. J. Gastrointest. Cancer 2018, 49, 442–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zhu, Q.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Xie, W.; Hu, L. Statin use and endometrial cancer risk: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62425–62434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, N.; Du, H.; Zhou, B.; Ye, Y. Statins on hepatocellular carcinoma risk in hepatitis B or C patients protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018, 97, e11950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.-B.; Hu, E.-D.; Fu, R.-Q. Statin Use and Cancer Incidence in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Network Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2018, 2018, 8620682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubatka, P.; Kružliak, P.; Rotrekl, V.; Jelínkova, Š.; Mladosievičová, B. Statins in oncological research: from experimental studies to clinical practice. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 92, 296–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henslee, A.B.; Steele, T.A. Combination statin and chemotherapy inhibits proliferation and cytotoxicity of an aggressive natural killer cell leukemia. Biomark. Res. 2018, 6, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orendáš, P.; Kubatka, P.; Bojková, B.; Kassayová, M.; Kajo, K.; Výbohová, D.; Kružliak, P.; Péč, M.; Adamkov, M.; Kapinová, A.; et al. Melatonin potentiates the anti-tumour effect of pravastatin in rat mammary gland carcinoma model. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 95, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubatka, P.; Bojková, B.; Kassayová, M.; Orendáš, P.; Kajo, K.; Výbohová, D.; Kružliak, P.; Adamicová, K.; Péč, M.; Stollárová, N.; et al. Combination of Pitavastatin and melatonin shows partial antineoplastic effects in a rat breast carcinoma model. Acta Histochem. 2014, 116, 1454–1461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vigneri, P.; Frasca, F.; Sciacca, L.; Pandini, G.; Vigneri, R. Diabetes and cancer. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2009, 16, 1103–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Harding, J.L.; Shaw, J.E.; Peeters, A.; Cartensen, B.; Magliano, D.J. Cancer risk among people with type 1 and type 2 diabetes: disentangling true associations, detection bias, and reverse causation. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 264–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cignarelli, A.; Genchi, V.A.; Caruso, I.; Natalicchio, A.; Perrini, S.; Laviola, L.; Giorgino, F. Diabetes and cancer: Pathophysiological fundamentals of a ‘dangerous affair. ’ Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 143, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nattrass, M.; Alberti, K.G. Biguanides. Diabetologia 1978, 14, 71–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilman, V.M. Age-Associated Elevation of Hypothalamic Treshold to Feedback Control, and Its Role in Development, Ageing, and Disease. Lancet 1971, 297, 1211–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.N. Biological Interactions of Aging and Carcinogenesis. In Biological Basis of Geriatric Oncology; Balducci, L., Extermann, M., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2005; pp. 17–50. ISBN 978-0-387-23961-3. [Google Scholar]
- Evans, J.M.; Donnelly, L.A.; Emslie-Smith, A.M.; Alessi, D.R.; Morris, A.D. Metformin and reduced risk of cancer in diabetic patients. BMJ 2005, 330, 1304–1305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quinn, B.J.; Kitagawa, H.; Memmott, R.M.; Gills, J.J.; Dennis, P.A. Repositioning metformin for cancer prevention and treatment. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 24, 469–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulten, H.-J. Pleiotropic Effects of Metformin on Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimova, I.N.; Liu, B.; Fan, Z.; Edgerton, S.M.; Dillon, T.; Lind, S.E.; Thor, A.D. Metformin inhibits breast cancer cell growth, colony formation and induces cell cycle arrest in vitro. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, H.-P.; Shieh, J.-J.; Chang, C.-C.; Chen, T.-T.; Lin, J.-T.; Wu, M.-S.; Lin, J.-H.; Wu, C.-Y. Metformin decreases hepatocellular carcinoma risk in a dose-dependent manner: population-based and in vitro studies. Gut 2013, 62, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gotlieb, W.H.; Saumet, J.; Beauchamp, M.-C.; Gu, J.; Lau, S.; Pollak, M.N.; Bruchim, I. In vitro metformin anti-neoplastic activity in epithelial ovarian cancer. Gynecol. Oncol. 2008, 110, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Gong, J.; Iwama, H.; Kitanaka, A.; Tani, J.; Miyoshi, H.; Nomura, K.; Mimura, S.; Kobayashi, M.; Aritomo, Y.; et al. The antidiabetic drug metformin inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2012, 11, 549–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, A.; Sunayama, J.; Okada, M.; Watanabe, E.; Seino, S.; Shibuya, K.; Suzuki, K.; Narita, Y.; Shibui, S.; Kayama, T.; et al. Glioma-initiating cell elimination by metformin activation of FOXO3 via AMPK. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2012, 1, 811–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnevi, E.; Said, K.; Andersson, R.; Rosendahl, A.H. Metformin-mediated growth inhibition involves suppression of the IGF-I receptor signalling pathway in human pancreatic cancer cells. BMC Cancer 2013, 13, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzzai, M.; Jones, R.G.; Amaravadi, R.K.; Lum, J.J.; DeBerardinis, R.J.; Zhao, F.; Viollet, B.; Thompson, C.B. Systemic treatment with the antidiabetic drug metformin selectively impairs p53-deficient tumor cell growth. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6745–6752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anisimov, V.N. Metformin for cancer and aging prevention: Is it a time to make the long story short? Oncotarget 2015, 6, 39398–39407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, M.D.; Grubbs, C.J.; Bode, A.M.; Reid, J.M.; McGovern, R.; Bernard, P.S.; Stijleman, I.J.; Green, J.E.; Bennett, C.; Juliana, M.; et al. Lack of Effect of Metformin on Mammary Carcinogenesis in Nondiabetic Rat and Mouse Models. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2015, 8, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhu, Z.; Jiang, W.; Thompson, M.D.; McGinley, J.N.; Thompson, H.J. Metformin as an energy restriction mimetic agent for breast cancer prevention. J. Carcinog. 2011, 10, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Y.; Chan, D.K.; Haugrud, A.B.; Miskimins, W.K. Mechanisms by which low glucose enhances the cytotoxicity of metformin to cancer cells both in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestri, A.; Palumbo, F.; Rasi, I.; Posca, D.; Pavlidou, T.; Paoluzi, S.; Castagnoli, L.; Cesareni, G. Metformin Induces Apoptosis and Downregulates Pyruvate Kinase M2 in Breast Cancer Cells Only When Grown in Nutrient-Poor Conditions. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.H.; Satkunam, M.; Pond, G.R.; Steinberg, G.R.; Blandino, G.; Schünemann, H.J.; Muti, P. Association of Metformin with Breast Cancer Incidence and Mortality in Patients with Type II Diabetes: A GRADE-Assessed Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2018, 27, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.B.; Eskin, M.; Eurich, D.T.; Majumdar, S.R.; Johnson, J.A. Metformin, Asian ethnicity and risk of prostate cancer in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, Y.; Zheng, L.; Mei, Z.; Xu, C.; Liu, C.; Chu, X.; Hao, B. The impact of metformin use on survival in prostate cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 100449–100458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.-X.; Tu, S.M.; Lee, M.-H.; Yeung, S.-C. Thiazolidinediones and metformin associated with improved survival of diabetic prostate cancer patients. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 2640–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, D.-C.; Gong, H.; Tan, C.-Q.; Luo, J.-Q. Prognostic significance of anti-diabetic medications in pancreatic cancer: A meta-analysis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 62349–62357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, K.; Wang, X. The Effect of Metformin on Mortality Among Diabetic Cancer Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2017, 1, pkx007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novik, A.V.; Protsenko, S.A.; Baldueva, I.A.; Berstein, L.M.; Anisimov, V.N.; Semenova, A.I.; Latipova, D.H.; Tkachenko, E.V.; Semiglazova, T.Y. The first results of assessment of clinical efficacy of melatonin and metformin in patients with disseminated skin melanoma receiving dacarbazine as first-fine systemic therapy. Vopr. Onkol. 2016, 62, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niraula, S.; Dowling, R.J.; Ennis, M.; Chang, M.C.; Done, S.; Hood, N.; Escallon, J.; Leong, W.L.; McCready, D.R.; Reedijk, M.; et al. Metformin in early breast cancer: a prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2012, 135, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Haggar, S.M.; El-Shitany, N.A.; Mostafa, M.F.; El-Bassiouny, N.A. Metformin may protect nondiabetic breast cancer women from metastasis. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2016, 33, 339–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Takahashi, H.; Sugiyama, M.; Sakai, E.; Uchiyama, T.; Suzuki, K.; Iida, H.; Sakamoto, Y.; Yoneda, K.; et al. Metformin suppresses colorectal aberrant crypt foci in a short-term clinical trial. Cancer Prev. Res. (Phila). 2010, 3, 1077–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuler, K.M.; Rambally, B.S.; Difurio, M.J.; Sampey, B.P.; Gehrig, P.A.; Makowski, L.; Bae-Jump, V.L. Antiproliferative and metabolic effects of metformin in a preoperative window clinical trial for endometrial cancer. Cancer Med. 2015, 4, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joshua, A.M.; Zannella, V.E.; Downes, M.R.; Bowes, B.; Hersey, K.; Koritzinsky, M.; Schwab, M.; Hofmann, U.; Evans, A.; Van Der Kwast, T.; et al. A pilot “window of opportunity” neoadjuvant study of metformin in localised prostate cancer. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 2014, 17, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dilman, V.M.; Berstein, L.M.; Yevtushenko, T.P.; Tsyrlina Ye., N.; Ostroumova, M.N.; Bobrov Yu., F.; Revskoy Yu., S.; Kovalenko, I.G.; Simonov, N.N. Preliminary evidence on metabolic rehabilitation of cancer patients. Arch. Geschwulstforsch. 1988, 58, 175–183. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Massey, S.; Story, D.; Li, L. Metformin: An Old Drug with New Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anisimov, V.N.; Egormin, P.A.; Piskunova, T.S.; Popovich, I.G.; Tyndyk, M.L.; Yurova, M.N.; Zabezhinski, M.A.; Anikin, I.V.; Karkach, A.S.; Romanyukha, A.A. Metformin extends life span of HER-2/neu transgenic mice and in combination with melatonin inhibits growth of transplantable tumors in vivo. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deriabina, O.N.; Plotnikova, N.A.; Anisimov, V.N. Melatonin and metformin inhibit skin carcinogenesis induced by benz(a)pyrene in mice. Vopr. Onkol. 2010, 56, 583–587. [Google Scholar]
- Man’cheva, T.A.; Demidov, D.V.; Plotnikova, N.A.; Kharitonova, T.V.; Pashkevich, I.V.; Anisimov, V.N. Melatonin and Metformin Inhibit Skin Carcinogenesis and Lipid Peroxidation Induced by Benz(a)pyrene in Female Mice. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2011, 151, 363–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osipov, M.A.; Semiglazova, T.Y.; Popovich, I.G.; Panchenko, A.V.; Tyndyk, M.L.; Zabezhinsky, M.A.; Klimenko, V.V.; Stukov, A.N.; Anisimov, V.N. Effect of metformin, melatonin and their combinations with paclitaxel on the growth of transplantable HER2-positive breast tumor in female FVB/N mice. Vopr. Onkol. 2017, 63, 650–654. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, R.E.; Buryanek, J.; McGuire, M.F. Metformin and Melatonin in Adrenocortical Carcinoma: Morphoproteomics and Biomedical Analytics Provide Proof of Concept in a Case Study. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2017, 47, 457–465. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bojková, B.; Kajo, K.; Kisková, T.; Kubatka, P.; Žúbor, P.; Solár, P.; Péč, M.; Adamkov, M. Metformin and melatonin inhibit DMBA-induced mammary tumorigenesis in rats fed a high-fat diet. Anticancer. Drugs 2018, 29, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojková, B.; Kajo, K.; Kubatka, P.; Solár, P.; Péč, M.; Adamkov, M. Metformin and melatonin improve histopathological outcome of NMU-induced mammary tumors in rats. Manuscript in preparation.
- Lin, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, S.; Wang, L.; Moorthy, B.; Xiong, D.; Cheng, T.; Ding, X.; Gu, J. Role of mammary epithelial and stromal P450 enzymes in the clearance and metabolic activation of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene in mice. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 212, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Sridhar, J.; Foroozesh, M. Cytochrome P450 Family 1 Inhibitors and Structure-Activity Relationships. Molecules 2013, 18, 14470–14495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gale, E.A. Lessons from the glitazones: a story of drug development. Lancet 2001, 357, 1870–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nissen, S.E.; Wolski, K. Rosiglitazone revisited: an updated meta-analysis of risk for myocardial infarction and cardiovascular mortality. Arch. Intern. Med. 2010, 170, 1191–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, D.; Bell, S.; Sund, R.; Hartikainen, S.A.; Tuomilehto, J.; Pukkala, E.; Keskimäki, I.; Badrick, E.; Renehan, A.G.; Buchan, I.E.; et al. Scottish Diabetes Research Network Epidemiology Group; Diabetes and Cancer Research Consortium Pioglitazone and bladder cancer risk: A multipopulation pooled, cumulative exposure analysis. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 493–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filipova, E.; Uzunova, K.; Kalinov, K.; Vekov, T. Pioglitazone and the Risk of Bladder Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Ther. 2017, 8, 705–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adil, M.; Khan, R.A.; Ghosh, P.; Venkata, S.K.; Kandhare, A.D.; Sharma, M. Pioglitazone and risk of bladder cancer in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: A systematic literature review and meta-analysis of observational studies using real-world data. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Heal. 2018, 6, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, F.; Xu, P.; Zhai, Y. The Opportunities and Challenges of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptors Ligands in Clinical Drug Discovery and Development. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, E2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Desvergne, B.; Wahli, W. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: nuclear control of metabolism. Endocr. Rev. 1999, 20, 649–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, J.; Moller, D.E. The mechanisms of action of PPARs. Annu. Rev. Med. 2002, 53, 409–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janani, C.; Ranjitha Kumari, B.D. PPAR gamma gene—A review. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2015, 9, 46–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Xu, J.; Yu, X.; Yang, R.; Han, Z.C. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ in malignant diseases. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2006, 58, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vella, V.; Nicolosi, M.L.; Giuliano, S.; Bellomo, M.; Belfiore, A.; Malaguarnera, R. PPAR-γ Agonists As Antineoplastic Agents in Cancers with Dysregulated IGF Axis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2017, 8, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Chu, E.S.; Zhao, G.; Man, K.; Wu, C.-W.; Cheng, J.T.; Li, G.; Nie, Y.; Lo, C.M.; Teoh, N.; et al. PPARgamma inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma metastases in vitro and in mice. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 106, 1486–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Blanquicett, C.; Roman, J.; Hart, C.M. Thiazolidinediones as anti-cancer agents. Cancer Ther. 2008, 6, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Youssef, J.; Badr, M. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors and cancer: challenges and opportunities. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 164, 68–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojková, B.; Orendáš, P.; Kubatka, P.; Péč, M.; Kassayová, M.; Kisková, T.; Kajo, K. Positive and negative effects of glitazones in carcinogenesis: Experimental models vs. clinical practice. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2014, 210, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojková, B.; Kajo, K.; Garajová, M.; Kubatka, P.; Péč, M.; Kisková, T.; Orendáš, P.; Kassayová, M.; Korpová, M.; Miklošová, M. Rosiglitazone shows partial oncostatic effect in rat mammary carcinogenesis. Neoplasma 2013, 60, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kulkarni, A.A.; Woeller, C.F.; Thatcher, T.H.; Ramon, S.; Phipps, R.P.; Sime, P.J. Emerging PPARγ-Independent Role of PPARγ Ligands in Lung Diseases. PPAR Res. 2012, 2012, 705352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mughal, A.; Kumar, D.; Vikram, A. Effects of Thiazolidinediones on metabolism and cancer: Relative influence of PPARγ and IGF-1 signaling. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2015, 768, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, E.; Wahl, R. Chemotherapy and Chemoprevention by Thiazolidinediones. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 845340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saez, E.; Rosenfeld, J.; Livolsi, A.; Olson, P.; Lombardo, E.; Nelson, M.; Banayo, E.; Cardiff, R.D.; Izpisua-Belmonte, J.C.; Evans, R.M. PPAR gamma signaling exacerbates mammary gland tumor development. Genes Dev. 2004, 18, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, I.K.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, J.S.; Seo, J.H. PPAR-gamma ligand promotes the growth of APC-mutated HT-29 human colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Investig. New Drugs 2008, 26, 283–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosetti, C.; Rosato, V.; Buniato, D.; Zambon, A.; La Vecchia, C.; Corrao, G. Cancer risk for patients using thiazolidinediones for type 2 diabetes: A meta-analysis. Oncologist 2013, 18, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jin, P.-P.; Sun, X.-C.; Hu, T.-T. Thiazolidinediones and risk of colorectal cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: A meta-analysis. Saudi J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monami, M.; Dicembrini, I.; Mannucci, E. Thiazolidinediones and cancer: Results of a meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Acta Diabetol. 2014, 51, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, R.; Lin, L.; Cheng, D.; Xu, Y.; Xu, M.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Bi, Y.; Li, D.; Lu, J. Thiazolidinedione therapy and breast cancer risk in diabetic women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Diabetes. Metab. Res. Rev. 2018, 34, e2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Esteva, F.J.; Ensor, J.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Lee, M.-H.; Yeung, S.-C. Metformin and thiazolidinediones are associated with improved breast cancer-specific survival of diabetic women with HER2+ breast cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2012, 23, 1771–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, H.; Yao, B.; Yan, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Tang, H.; Zhou, J.; Cao, L.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Diabetes mellitus increases the risk of bladder cancer: An updated meta-analysis of observational studies. Diabetes Technol. Ther. 2013, 15, 914–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Z.-N.; Jiang, Y.-F.; Ding, T. Risk of fracture with thiazolidinediones: An updated meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Bone 2014, 68, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizos, C.V.; Kei, A.; Elisaf, M.S. The current role of thiazolidinediones in diabetes management. Arch. Toxicol. 2016, 90, 1861–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demetri, G.D.; Fletcher, C.D.; Mueller, E.; Sarraf, P.; Naujoks, R.; Campbell, N.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Singer, S. Induction of solid tumor differentiation by the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor- ligand troglitazone in patients with liposarcoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999, 96, 3951–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Debrock, G.; Vanhentenrijk, V.; Sciot, R.; Debiec-Rychter, M.; Oyen, R.; Van Oosterom, A. A phase II trial with rosiglitazone in liposarcoma patients. Br. J. Cancer 2003, 89, 1409–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulke, M.H.; Demetri, G.D.; Sharpless, N.E.; Ryan, D.P.; Shivdasani, R.; Clark, J.S.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Kim, H.; Mayer, R.J.; Fuchs, C.S. A Phase II Study of Troglitazone, an Activator of the PPAR?? Receptor, in Patients with Chemotherapy-Resistant Metastatic Colorectal Cancer. Cancer J. 2002, 8, 395–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips, J.-C.; Petite, C.; Willi, J.-P.; Buchegger, F.; Meier, C.A. Effect of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ agonist, rosiglitazone, on dedifferentiated thyroid cancers. Nucl. Med. Commun. 2004, 25, 1183–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, M.R.; Manola, J.; Kaufman, D.S.; George, D.; Oh, W.K.; Mueller, E.; Slovin, S.; Spiegelman, B.; Small, E.; Kantoff, P.W. Rosiglitazone versus placebo for men with prostate carcinoma and a rising serum prostate-specific antigen level after radical prostatectomy and/or radiation therapy. Cancer 2004, 101, 1569–1574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yee, L.D.; Williams, N.; Wen, P.; Young, D.C.; Lester, J.; Johnson, M.V; Farrar, W.B.; Walker, M.J.; Povoski, S.P.; Suster, S.; et al. Pilot study of rosiglitazone therapy in women with breast cancer: effects of short-term therapy on tumor tissue and serum markers. Clin. Cancer Res. 2007, 13, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burstein, H.J.; Demetri, G.D.; Mueller, E.; Sarraf, P.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Winer, E.P. Use of the Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR) γ Ligand Troglitazone as Treatment for Refractory Breast Cancer: A Phase II Study. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2003, 79, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reichle, A.; Bross, K.; Vogt, T.; Bataille, F.; Wild, P.; Berand, A.; Krause, S.W.; Andreesen, R. Pioglitazone and rofecoxib combined with angiostatically scheduled trofosfamide in the treatment of far-advanced melanoma and soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2004, 101, 2247–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vogt, T.; Hafner, C.; Bross, K.; Bataille, F.; Jauch, K.-W.; Berand, A.; Landthaler, M.; Andreesen, R.; Reichle, A. Antiangiogenetic therapy with pioglitazone, rofecoxib, and metronomic trofosfamide in patients with advanced malignant vascular tumors. Cancer 2003, 98, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hau, P.; Kunz-Schughart, L.; Bogdahn, U.; Baumgart, U.; Hirschmann, B.; Weimann, E.; Muhleisen, H.; Ruemmele, P.; Steinbrecher, A.; Reichle, A. Low-dose chemotherapy in combination with COX-2 inhibitors and PPAR-gamma agonists in recurrent high-grade gliomas—A phase II study. Oncology 2007, 73, 21–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esteva, F.J.; Moulder, S.L.; Gonzalez-Angulo, A.M.; Ensor, J.; Murray, J.L.; Green, M.C.; Koenig, K.B.; Lee, M.-H.; Hortobagyi, G.N.; Yeung, S.-C. Phase I trial of exemestane in combination with metformin and rosiglitazone in nondiabetic obese postmenopausal women with hormone receptor-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2013, 71, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Read, W.L.; Baggstrom, M.Q.; Fracasso, P.M.; Govindan, R. A phase I study of bexarotene and rosiglitazone in patients with refractory cancers. Chemotherapy 2008, 54, 236–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousselot, P.; Prost, S.; Guilhot, J.; Roy, L.; Etienne, G.; Legros, L.; Charbonnier, A.; Coiteux, V.; Cony-Makhoul, P.; Huguet, F.; et al. Pioglitazone together with imatinib in chronic myeloid leukemia: A proof of concept study. Cancer 2017, 123, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkmaz, A.; Tamura, H.; Manchester, L.C.; Ogden, G.B.; Tan, D.-X.; Reiter, R.J. Combination of melatonin and a peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist induces apoptosis in a breast cancer cell line. J. Pineal Res. 2009, 46, 115–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojková, B.; Garajová, M.; Kajo, K.; Péč, M.; Kubatka, P.; Kassayová, M.; Kisková, T.; Orendáš, P.; Ahlersová, E.; Ahlers, I. Pioglitazone in chemically induced mammary carcinogenesis in rats. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2010, 19, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bojková, B.; Orendáš, P.; Kajo, K.; Kubatka, P.; Výbohová, D.; Bálentová, S.; Kružliak, P.; Zulli, A.; Demečková, V.; Péč, M.; et al. Role of high-fat diet on the effect of pioglitazone and melatonin in a rat model of breast cancer. Eur. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 25, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omenn, G.S.; Goodman, G.E.; Thornquist, M.D.; Balmes, J.; Cullen, M.R.; Glass, A.; Keogh, J.P.; Meyskens, F.L.; Valanis, B.; Williams, J.H.; et al. Effects of a Combination of Beta Carotene and Vitamin A on Lung Cancer and Cardiovascular Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1996, 334, 1150–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Masi, A.; Leboffe, L.; De Marinis, E.; Pagano, F.; Cicconi, L.; Rochette-Egly, C.; Lo-Coco, F.; Ascenzi, P.; Nervi, C. Retinoic acid receptors: From molecular mechanisms to cancer therapy. Mol. Aspects Med. 2015, 41, 1–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uray, I.P.; Dmitrovsky, E.; Brown, P.H. Retinoids and rexinoids in cancer prevention: from laboratory to clinic. Semin. Oncol. 2016, 43, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Connolly, R.M.; Nguyen, N.K.; Sukumar, S. Molecular Pathways: Current Role and Future Directions of the Retinoic Acid Pathway in Cancer Prevention and Treatment. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 1651–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theodosiou, M.; Laudet, V.; Schubert, M. From carrot to clinic: an overview of the retinoic acid signaling pathway. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2010, 67, 1423–1445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlersová, E.; Ahlers, I.; Kubatka, P.; Bojková, B.; Môciková, K.; Gajdošová, Š.; Onderková, H.M. Melatonin and retinyl acetate as chemopreventives in DMBA-induced mammary carcinogenesis in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Folia Biol. (Praha). 2000, 46, 69–72. [Google Scholar]
- Bojková, B.; Kubatka, P.; Môcikova, K.; Mníchová, M.; Ahlersová, E.; Ahlers, I. Effects of retinyl acetate and melatonin on N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced mammary carcinogenesis in rats. A preliminary report. Folia Biol. (Praha). 2000, 46, 73–76. [Google Scholar]
- Teplitzky, S.R.; Kiefer, T.L.; Cheng, Q.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Moroz, K.; Myers, L.; Anderson, M.B.; Collins, A.; Dai, J.; Yuan, L.; et al. Chemoprevention of NMU-induced rat mammary carcinoma with the combination of melatonin and 9-cis-retinoic acid. Cancer Lett. 2001, 168, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowfar, S.; Teplitzky, S.R.; Melancon, K.; Kiefer, T.L.; Cheng, Q.; Dwivedi, P.D.; Bischoff, E.D.; Moroz, K.; Anderson, M.B.; Dai, J.; et al. Tumor Prevention by 9-Cis-Retinoic Acid in the N-Nitroso-N-Methylurea Model of Mammary Carcinogenesis is Potentiated by the Pineal Hormone Melatonin. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2002, 72, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melancon, K.; Cheng, Q.; Kiefer, T.L.; Dai, J.; Lai, L.; Dong, C.; Yuan, L.; Collins, A.; Thiyagarajah, A.; Long, S.; et al. Regression of NMU-induced mammary tumors with the combination of melatonin and 9-cis-retinoic acid. Cancer Lett. 2005, 227, 39–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orendáš, P.; Kubatka, P.; Kajo, K.; Stollarová, N.; Kassayová, M.; Bojková, B.; Péč, M.; Nosáľ, V.; Kisková, T.; Žihľavniková, K.; Karšňáková, R. Melatonin enhanced bexarotene efficacy in experimental mammary carcinogenesis. Neoplasma 2012, 59, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bojková, B.; Kubatka, P.; Qaradakhi, T.; Zulli, A.; Kajo, K. Melatonin May Increase Anticancer Potential of Pleiotropic Drugs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123910
Bojková B, Kubatka P, Qaradakhi T, Zulli A, Kajo K. Melatonin May Increase Anticancer Potential of Pleiotropic Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(12):3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123910
Chicago/Turabian StyleBojková, Bianka, Peter Kubatka, Tawar Qaradakhi, Anthony Zulli, and Karol Kajo. 2018. "Melatonin May Increase Anticancer Potential of Pleiotropic Drugs" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 12: 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123910
APA StyleBojková, B., Kubatka, P., Qaradakhi, T., Zulli, A., & Kajo, K. (2018). Melatonin May Increase Anticancer Potential of Pleiotropic Drugs. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(12), 3910. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19123910