Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by β-Synuclein
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Cell-Free Coexpression of αS and βS Allows for Investigation of Their Inter-Regulatory Effect
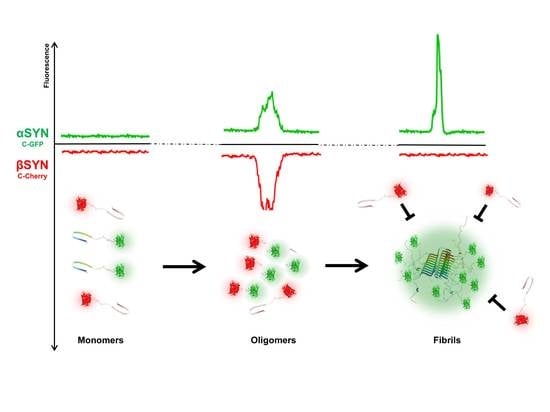
2.2. β-Synuclein Is a Selective Inhibitor of Different Aggregation Pathways of α-Synuclein
2.3. Preferential Binding to Smaller Oligomers Determines a More Efficient Inhibition of Aggregation
2.4. β-Synuclein Does Not Bind to the Aggregates of α-Synuclein Mutants
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of LTE
4.2. Gateway Cloning System for Cell-Free Protein Expression
4.3. Cell-Free Coexpression and Fluorescence Spectroscopy of α- and β-Synucleins
4.4. Brightness Analysis
4.5. Two-Color Coincidence Measurements
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| αS | α-Synuclein |
| αSYN | α-Synuclein |
| βS | β-Synuclein |
| βSYN | β-Synuclein |
| PD | Parkinson’s Disease |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| DLB | Dementia with Lewy Bodies |
| IDP | Intrinsically Disordered Protein |
| BP | Brightness parameter |
| GFP | Green Fluorescent Protein |
| sGFP | “superfolder” Green Fluorescent Protein |
| mCherry | Monomeric Cherry |
| LTE | Leishmania Tarentolae Extract |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SE | Standard Error |
| WT | Wild-type |
| LTE | Leishmania tarentolae extract |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazineethanesulfonic acid |
References
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. α-Synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goedert, M.; Spillantini, M.G.; Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. 100 years of Lewy pathology. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2013, 9, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burré, J. The synaptic function of α-synuclein. J. Park. Dis. 2015, 5, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burré, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Südhof, T.C. α-Synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alderson, T.R.; Markley, J.L. Biophysical characterization of α-synuclein and its controversial structure. Intrinsically Disord. Proteins 2013, 1, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winner, B.; Jappelli, R.; Maji, S.K.; Desplats, P.A.; Boyer, L.; Aigner, S.; Hetzer, C.; Loher, T.; Vilar, M.; Campioni, S. In vivo demonstration that α-synuclein oligomers are toxic. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 4194–4199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremades, N.; Cohen, S.I.; Deas, E.; Abramov, A.Y.; Chen, A.Y.; Orte, A.; Sandal, M.; Clarke, R.W.; Dunne, P.; Aprile, F.A. Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of α-synuclein. Cell 2012, 149, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoyer, W.; Cherny, D.; Subramaniam, V.; Jovin, T.M. Impact of the acidic C-terminal region comprising amino acids 109–140 on α-synuclein aggregation in vitro. Biochemistry 2004, 43, 16233–16242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallea, J.I.; Celej, M.S. Structural insights into amyloid oligomers of the Parkinson Disease-related protein α-Synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 26733–26742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danzer, K.M.; Krebs, S.K.; Wolff, M.; Birk, G.; Hengerer, B. Seeding induced by α-synuclein oligomers provides evidence for spreading of α-synuclein pathology. J. Neurochem. 2009, 111, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.-J.; Suk, J.-E.; Patrick, C.; Bae, E.-J.; Cho, J.-H.; Rho, S.; Hwang, D.; Masliah, E.; Lee, S.-J. Direct transfer of α-synuclein from neuron to astroglia causes inflammatory responses in synucleinopathies. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 9262–9272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iljina, M.; Garcia, G.A.; Horrocks, M.H.; Tosatto, L.; Choi, M.L.; Ganzinger, K.A.; Abramov, A.Y.; Gandhi, S.; Wood, N.W.; Cremades, N. Kinetic model of the aggregation of α-synuclein provides insights into prion-like spreading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1206–E1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narkiewicz, J.; Giachin, G.; Legname, G. In vitro aggregation assays for the characterization of α-synuclein prion-like properties. Prion 2014, 8, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Uversky, V.N.; Fink, A.L. Effect of familial Parkinson’s disease point mutations A30P and A53T on the structural properties, aggregation, and fibrillation of human α-synuclein. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 11604–11613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Agnaf, O.; Jakes, R.; Curran, M.D.; Wallace, A. Effects of the mutations Ala30 to Pro and Ala53 to Thr on the physical and morphological properties of α-synuclein protein implicated in Parkinson’s disease. FEBS Lett. 1998, 440, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coskuner, O.; Wise-Scira, O. Structures and free energy landscapes of the A53T mutant-type α-synuclein protein and impact of A53T mutation on the structures of the wild-type α-synuclein protein with dynamics. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2013, 4, 1101–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahay, S.; Ghosh, D.; Dwivedi, S.; Anoop, A.; Mohite, G.M.; Kombrabail, M.; Krishnamoorthy, G.; Maji, S.K. Familial Parkinson disease-associated mutations alter the site-specific microenvironment and dynamics of α-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 7804–7822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tosatto, L.; Horrocks, M.H.; Dear, A.J.; Knowles, T.P.; Dalla Serra, M.; Cremades, N.; Dobson, C.M.; Klenerman, D. Single-molecule FRET studies on α-synuclein oligomerization of Parkinson’s disease genetically related mutants. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.W.; Drakulic, S.; Deas, E.; Ouberai, M.; Aprile, F.A.; Arranz, R.; Ness, S.; Roodveldt, C.; Guilliams, T.; De-Genst, E.J. Structural characterization of toxic oligomers that are kinetically trapped during α-synuclein fibril formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1994–E2003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanovic, A.N.; Lindhoud, S.; Semerdzhiev, S.A.; Claessens, M.M.; Subramaniam, V. Oligomers of Parkinson’s disease-related α-Synuclein mutants have similar structures but distinctive membrane permeabilization properties. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 3142–3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreon, A.C.M.; Gambin, Y.; Lemke, E.A.; Deniz, A.A. Interplay of α-synuclein binding and conformational switching probed by single-molecule fluorescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5645–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sierecki, E.; Giles, N.; Bowden, Q.; Polinkovsky, M.E.; Steinbeck, J.; Arrioti, N.; Rahman, D.; Bhumkar, A.; Nicovich, P.R.; Ross, I. Nanomolar oligomerization and selective co-aggregation of α-synuclein pathogenic mutants revealed by single-molecule fluorescence. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 37630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Souillac, P.; Millett, I.S.; Doniach, S.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M.; Fink, A.L. Biophysical properties of the synucleins and their propensities to fibrillate inhibition of α-synuclein assembly by β-and γ-synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11970–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowska, M.K.; Wu, K.-P.; Baum, J. Unveiling transient protein-protein interactions that modulate inhibition of α-synuclein aggregation by β-synuclein, a pre-synaptic protein that co-localizes with α-synuclein. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. β-Synuclein inhibits α-synuclein aggregation: A possible role as an anti-parkinsonian factor. Neuron 2001, 32, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.-Y.; Lansbury, P.T. β-Synuclein inhibits formation of α-synuclein protofibrils: A possible therapeutic strategy against Parkinson’s Disease. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 3696–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, J.A.; McHugh, P.C.; Pan, S.; Cunningham, A.; Brown, D.R. Counter-regulation of α-and β-synuclein expression at the transcriptional level. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 2013, 57, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Windisch, M.; Hutter-Paier, B.; Rockenstein, E.; Hashimoto, M.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. Development of a new treatment for Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease using anti-aggregatory β-synuclein-derived peptides. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2002, 19, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaltiel-Karyo, R.; Frenkel-Pinter, M.; Egoz-Matia, N.; Frydman-Marom, A.; Shalev, D.E.; Segal, D.; Gazit, E. Inhibiting α-synuclein oligomerization by stable cell-penetrating β-synuclein fragments recovers phenotype of Parkinson’s disease model flies. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Crews, L.; Bar-On, P.; Gage, F.; Marr, R.; Masliah, E. An antiaggregation gene therapy strategy for Lewy body disease utilizing β-synuclein lentivirus in a transgenic model. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1713–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigelny, I.F.; Bar-On, P.; Sharikov, Y.; Crews, L.; Hashimoto, M.; Miller, M.A.; Keller, S.H.; Platoshyn, O.; Yuan, J.X.J.; Masliah, E. Dynamics of α-synuclein aggregation and inhibition of pore-like oligomer development by β-synuclein. FEBS J. 2007, 274, 1862–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.W.; Buell, A.K.; Michaels, T.C.; Meisl, G.; Carozza, J.; Flagmeier, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Knowles, T.P.; Dobson, C.M.; Galvagnion, C. β-Synuclein suppresses both the initiation and amplification steps of α-synuclein aggregation via competitive binding to surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, Y.; Limprasert, P.; Murray, I.V.; Smith, A.C.; Lee, V.M.-Y.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Sopher, B.L.; La Spada, A.R. β-synuclein modulates α-synuclein neurotoxicity by reducing α-synuclein protein expression. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 3002–3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Sugama, S.; Sekiyama, K.; Sekigawa, A.; Tsukui, T.; Nakai, M.; Waragai, M.; Takenouchi, T.; Takamatsu, Y.; Wei, J. A β-synuclein mutation linked to dementia produces neurodegeneration when expressed in mouse brain. Nat. Commun. 2010, 1, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, J.; Fujita, M.; Nakai, M.; Waragai, M.; Watabe, K.; Akatsu, H.; Rockenstein, E.; Masliah, E.; Hashimoto, M. Enhanced lysosomal pathology caused by β-synuclein mutants linked to dementia with lewy bodies. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 28904–28914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambin, Y.; Polinkovsky, M.; Francois, B.; Giles, N.; Bhumkar, A.; Sierecki, E. Confocal spectroscopy to study dimerization, oligomerization and aggregation of proteins: A practical guide. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiely, A.P.; Ling, H.; Asi, Y.T.; Kara, E.; Proukakis, C.; Schapira, A.H.; Morris, H.R.; Roberts, H.C.; Lubbe, S.; Limousin, P. Distinct clinical and neuropathological features of G51D SNCA mutation cases compared with SNCA duplication and H50Q mutation. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lesage, S.; Anheim, M.; Letournel, F.; Bousset, L.; Honoré, A.; Rozas, N.; Pieri, L.; Madiona, K.; Dürr, A.; Melki, R. G51D α-synuclein mutation causes a novel Parkinsonian–pyramidal syndrome. Ann. Neurol. 2013, 73, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Snyder, H.; Mensah, K.; Hsu, C.; Hashimoto, M.; Surgucheva, I.G.; Festoff, B.; Surguchov, A.; Masliah, E.; Matouschek, A.; Wolozin, B. β-synuclein reduces proteasomal inhibition by α-synuclein but not γ-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 7562–7569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, K.; Domingo-Sàbat, M.; Santos, C.; Tolosa, E.; Ferrer, I.; Ariza, A. The decrease of β-synuclein in cortical brain areas defines a molecular subgroup of dementia with Lewy bodies. Brain 2010, 133, 3724–3733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mureev, S.; Kovtun, O.; Nguyen, U.T.; Alexandrov, K. Species-independent translational leaders facilitate cell-free expression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 747–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovtun, O.; Mureev, S.; Jung, W.; Kubala, M.H.; Johnston, W.; Alexandrov, K. Leishmania cell-free protein expression system. Methods 2011, 55, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, W.A.; Alexandrov, K. Production of eukaryotic cell-free lysate from Leishmania tarentolae. Methods Mol. Biol. 2014, 1118, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gagoski, D.; Mureev, S.; Giles, N.; Johnston, W.; Dahmer-Heath, M.; Škalamera, D.; Gonda, T.J.; Alexandrov, K. Gateway-compatible vectors for high-throughput protein expression in pro-and eukaryotic cell-free systems. J. Biotechnol. 2015, 195, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walhout, A.J.; Temple, G.F.; Brasch, M.A.; Hartley, J.L.; Lorson, M.A.; van den Heuvel, S.; Vidal, M. GATEWAY recombinational cloning: Application to the cloning of large numbers of open reading frames or ORFeomes. Methods Enzymol. 2000, 328, 575–592. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Leitao, A.; Bhumkar, A.; Hunter, D.J.B.; Gambin, Y.; Sierecki, E. Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by β-Synuclein. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020334
Leitao A, Bhumkar A, Hunter DJB, Gambin Y, Sierecki E. Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by β-Synuclein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(2):334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020334
Chicago/Turabian StyleLeitao, Andre, Akshay Bhumkar, Dominic J. B. Hunter, Yann Gambin, and Emma Sierecki. 2018. "Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by β-Synuclein" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 2: 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020334
APA StyleLeitao, A., Bhumkar, A., Hunter, D. J. B., Gambin, Y., & Sierecki, E. (2018). Unveiling a Selective Mechanism for the Inhibition of α-Synuclein Aggregation by β-Synuclein. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(2), 334. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19020334