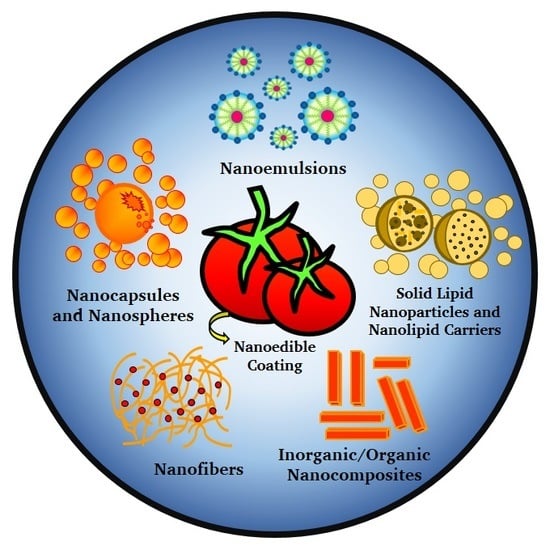
Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Nanosystems as Components of Edible Coatings
2.1. Nanoemulsion
2.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles
2.3. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles
2.4. Lipid Nanocarriers
2.5. Inorganic/Organic Nanocomposites in Edible Films
2.6. Nanotubes and Nanofibers
3. Nanosystems in Edible Coatings
3.1. Nanoemulsions in Edible Coatings
3.2. Polymeric Nanoparticles in Edible Coatings
3.3. Solid Lipid Nanoparticles (SLNs)
3.4. Incorporation of NLC Coatings
3.5. Inorganic Nanocomposites in Edible Coatings
3.6. Nanotubes and Nanofibers
4. Conclusions and Future Trends
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yousuf, B.; Qadri, O.S.; Srivastava, A.K. Recent developments in shelf-life extension of fresh-cut fruits and vegetables by application of different edible coatings: A review. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 89, 198–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maizura, M.; Fazilah, A.; Norziah, M.H.; Karim, A.A. Antibacterial Activity and Mechanical Properties of Partially Hydrolyzed Sago Starch? Alginate Edible Film Containing Lemongrass Oil. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, C324–C330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Luo, Y.; Wang, Q. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of essential oils encapsulated in zein nanoparticles prepared by liquid–liquid dispersion method. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 48, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhall, R.K. Advances in Edible Coatings for Fresh Fruits and Vegetables: A Review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2013, 53, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, E.; Plotto, A.; Narciso, J.; Bai, J. Effect of 1-methylcyclopropene on tomato flavour components, shelf life and decay as influenced by harvest maturity and storage temperature. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 969–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, A.; Tyagi, S.; Gupta, R.K.; Tyagi, Y.K. Natural gums of plant origin as edible coatings for food industry applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2017, 37, 959–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mora-Huertas, C.E.; Fessi, H.; Elaissari, A. Polymer-based nanocapsules for drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 385, 113–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dan, N. Compound release from nanostructured lipid carriers (NLCs). J. Food Eng. 2016, 171, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Del Real, A.; Piñon-Segundo, E.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, J.F. The release kinetics of β-carotene nanocapsules/xanthan gum coating and quality changes in fresh-cut melon (cantaloupe). Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 157, 1874–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial electrospun zein nanofibrous web encapsulating thymol/cyclodextrin-inclusion complex for food packaging. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, X.; Cao, X.; Ke, L.; Ma, Y.; An, J.; Wang, F. Combination of cellulose nanofibers and chain-end-functionalized polyethylene and their applications in nanocomposites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 134, 45387–45393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjan, S.; Dasgupta, N.; Chakraborty, A.R.; Melvin Samuel, S.; Ramalingam, C.; Shanker, R.; Kumar, A. Nanoscience and nanotechnologies in food industries: Opportunities and research trends. J. Nanoparticle Res. 2014, 16, 2464–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallocchio, F.; Belluco, S.; Ricci, A. Nanotechnology and Food: Brief Overview of the Current Scenario. Procedia Food Sci. 2015, 5, 85–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Sadaty, M.A. Thiamine hydrochloride (vitamin B1 ) as modifier agent for TiO2 nanoparticles and the optical, mechanical, and thermal properties of poly(vinyl chloride) composite films. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 92596–92604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Liu, D.; Liu, Y.; Song, Y.; Wu, T.; Zhang, M. Using soy protein SiOx nanocomposite film coating to extend the shelf life of apple fruit. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 52, 2018–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, E. Bioavailability of nanoparticles in nutrient and nutraceutical delivery. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 14, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, B. Nanoemulsions for food fortification with lipophilic vitamins: Production challenges, stability, and bioavailability. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2017, 119, 1500539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oca-Ávalos, J.M.M.; Candal, R.J.; Herrera, M.L. Nanoemulsions: Stability and physical properties. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 16, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, H.D.; Cerqueira, M.Â.; Vicente, A.A. Nanoemulsions for Food Applications: Development and Characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2012, 5, 854–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A.; Weiss, J. Emulsion-Based Delivery Systems for Lipophilic Bioactive Components. J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, R109–R124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClements, D.J. Food Emulsions : Principles, Practices, and Techniques; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; McClements, D.J.; Martín-Belloso, O. Edible Nanoemulsions as Carriers of Active Ingredients: A Review. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 8, 439–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; De La, M.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, L.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N. Impact of the Emulsification-Diffusion Method on the Development of Pharmaceutical Nanoparticles. Recent Pat. Drug Deliv. Formul. 2012, 6, 184–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinesh Kumar, V.; Verma, P.R.P.; Singh, S.K. Development and evaluation of biodegradable polymeric nanoparticles for the effective delivery of quercetin using a quality by design approach. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 61, 330–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcuzzo, E.; Sensidoni, A.; Debeaufort, F.; Voilley, A. Encapsulation of aroma compounds in biopolymeric emulsion based edible films to control flavour release. Carbohydr. Polym. 2010, 9, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, S.; Liu, L.; Yue, X.; Zhang, W.; Yang, Q.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J. Inhibition of the double-edged effect of curcumin on Maillard reaction in a milk model system by a nanocapsule strategy. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 83, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Jiang, Y.; Du, B.; Chai, Z.; Jiao, T.; Zhang, C.; Ren, F.; Leng, X. Design and characterization of controlled-release edible packaging films prepared with synergistic whey-protein polysaccharide complexes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 5824–5833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Yang, F.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Abbas, S. Formation of heat-resistant nanocapsules of jasmine essential oil via gelatin/gum arabic based complex coacervation. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 35, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coradini, K.; Lima, F.O.; Oliveira, C.M.; Chaves, P.S.; Athayde, M.L.; Carvalho, L.M.; Beck, R.C.R. Co-encapsulation of resveratrol and curcumin in lipid-core nanocapsules improves their in vitro antioxidant effects. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Yan, H.; Wang, X.; Zhou, Y.; Gao, X.; Puligundla, P.; Wan, X. Encapsulation of epigallocatechin gallate in zein/chitosan nanoparticles for controlled applications in food systems. Food Chem. 2017, 231, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Pakade, Y.B.; Kumar, V.; Singh, B.; Chaudhary, A.; Yadav, S.C. Nanoencapsulation and characterization of Albizia chinensis isolated antioxidant quercitrin on PLA nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2011, 82, 224–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, A.; Yadav, S.K.; Pakade, Y.B.; Singh, B.; Yadav, S.C. Development of biodegradable nanoparticles for delivery of quercetin. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 108, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, J.; Guo, B.; Yu, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, D.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y. Encapsulation of the flavonoid quercetin with chitosan-coated nano-liposomes. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 85, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granata, G.; Consoli, G.M.L.; Lo Nigro, R.; Geraci, C. Hydroxycinnamic acids loaded in lipid-core nanocapsules. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assis, R.Q.; Lopes, S.M.; Costa, T.M.H.; Flôres, S.H.; de Oliveira Rios, A. Active biodegradable cassava starch films incorporated lycopene nanocapsules. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayempour, S.; Montazer, M.; Mahmoudi Rad, M. Tragacanth gum as a natural polymeric wall for producing antimicrobial nanocapsules loaded with plant extract. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 81, 514–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brum, A.A.S.; dos Santos, P.P.; da Silva, M.M.; Paese, K.; Guterres, S.S.; Costa, T.M.H.; Pohlmann, A.R.; Jablonski, A.; Flôres, S.H.; de OliveiraRios, A. Lutein-loaded lipid-core nanocapsules: Physicochemical characterization and stability evaluation. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 522, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galindo-Pérez, M.J.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Mercado-Silva, E.; Real-Sandoval, S.A.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L. The Effects of Tocopherol Nanocapsules/Xanthan Gum Coatings on the Preservation of Fresh-Cut Apples: Evaluation of Phenol Metabolism. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2015, 8, 1791–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabliov, C.; Chen, H.; Yada, R. Nanotechnology and Functional Foods : Effective Delivery of Bioactive Ingredients; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Geszke-Moritz, M.; Moritz, M. Solid lipid nanoparticles as attractive drug vehicles: Composition, properties and therapeutic strategies. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 982–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramteke, K.H.; Joshi, S.A.; Dhole, S.N. Solid lipid nanoparticle: A review. IOSR J. Pharm. 2012, 2, 34–44. [Google Scholar]
- Rostami, E.; Kashanian, S.; Azandaryani, A.H.; Faramarzi, H.; Dolatabadi, J.E.N.; Omidfar, K. Drug targeting using solid lipid nanoparticles. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2014, 18, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.M.; Rajasekaran, D.; Ludford-Menting, M.; Eldridge, D.S.; Palombo, E.A.; Harding, I.H. Transport of stearic acid-based solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) into human epithelial cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 140, 204–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gastaldi, L.; Battaglia, L.; Peira, E.; Chirio, D.; Muntoni, E.; Solazzi, I.; Gallarate, M.; Dosio, F. Solid lipid nanoparticles as vehicles of drugs to the brain: Current state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katouzian, I.; Faridi Esfanjani, A.; Jafari, S.M.; Akhavan, S. Formulation and application of a new generation of lipid nano-carriers for the food bioactive ingredients. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 62, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; Del Real, A.; González-Reza, R.M.; Galindo-Pérez, M.J.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Fresh-cut Red Delicious apples coating using tocopherol/mucilage nanoemulsion: Effect of coating on polyphenol oxidase and pectin methylesterase activities. Food Res. Int. 2016, 62, 974–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santalices, I.; Gonella, A.; Torres, D. Advances on the formulation of proteins using nanotechnologies. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 42, 155–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadab, M.; Haque, S.; Madheswaran, T.; Zeeshan, F.; Meka, V.S.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Kesharwani, P. Lipid based nanocarriers system for topical delivery of photosensitizers. Drug Discov. Today 2017, 221, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sala, M.; Diab, R.; Elaissari, A.; Fessi, H. Lipid nanocarriers as skin drug delivery systems: Properties, mechanisms of skin interactions and medical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Göke, K.; Bunjes, H. Drug solubility in lipid nanocarriers: Influence of lipid matrix and available interfacial area. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 529, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacatusu, I.; Badea, G.; Popescu, M.; Bordei, N.; Istrati, D.; Moldovan, L.; Seciuc, A.M.; Pantelid, M.I.; Rasitd, I.; Badea, N. Marigold extract, azelaic acid and black caraway oil into lipid nanocarriers provides a strong anti-inflammatory effect in vivo. Ind. Crops Prod. 2017, 109, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamjidi, F.; Shahedi, M.; Varshosaz, J.; Nasirpour, A. Nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC): A potential delivery system for bioactive food molecules. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 19, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Formulation of food grade nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) for potential applications in medicinal-functional foods. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 39, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagherpour, S.; Alizadeh, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, S.; Mohammadi, M.; Hamishehkar, H. Preparation and characterization of Betasitosterol-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for butter enrichment. Food Biosci. 2017, 20, 51–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, P.; Rahi, P.; Pandey, V.; Asati, S.; Soni, V. Nanostructure lipid carriers: A modish contrivance to overcome the ultraviolet effects. Egypt. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2017, 4, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keivani Nahr, F.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H.; Samadi Kafil, H. Food grade nanostructured lipid carrier for cardamom essential oil: Preparation, characterization and antimicrobial activity. J. Funct. Foods 2018, 40, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babazadeh, A.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Novel nanostructured lipid carriers as a promising food grade delivery system for rutin. J. Funct. Foods 2016, 26, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soleimanian, Y.; Goli, S.A.H.; Varshosaz, J.; Sahafi, S.M. Formulation and characterization of novel nanostructured lipid carriers made from beeswax, propolis wax and pomegranate seed oil. Food Chem. 2018, 24, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Wang, Q.; Li, T.; Xia, N.; Xia, Q. Nanostructured lipid carrier (NLC) as a strategy for encapsulation of quercetin and linseed oil: Preparation and in vitro characterization studies. J. Food Eng. 2017, 215, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, A.; Padua, G.W. Review: Nanocomposites in food packaging. J. Food Sci. 2010, 75, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, C.; Wu, Y.; Fang, D.; Pei, F.; Mariga, A.M.; Yang, W.; Hu, Q. Effect of nanocomposite packaging on postharvest senescence of Flammulina velutipes. Food Chem. 2018, 246, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushesh Saba, M.; Amini, R. Nano-ZnO/carboxymethyl cellulose-based active coating impact on ready-to-use pomegranate during cold storage. Food Chem. 2017, 232, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Yang, D.; Zhong, R.; Li, Y.; Zhou, H.; Qiu, X. Preparation of lignin-based silica composite submicron particles from alkali lignin and sodium silicate in aqueous solution using a direct precipitation method. Ind. Crops Prod. 2015, 74, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peters, B.L.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; Pike, D.Q.; Müller, M.; de Pablo, J.J. Nonequilibrium Simulations of Lamellae Forming Block Copolymers under Steady Shear: A Comparison of Dissipative Particle Dynamics and Brownian Dynamics. Macromolecules 2012, 458, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klangmuang, P.; Sothornvit, R. Combination of beeswax and nanoclay on barriers, sorption isotherm and mechanical properties of hydroxypropyl methylcellulose-based composite films. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 222–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, O.L.; Pereira, R.N.; Martins, A.; Rodrigues, R.; Fuciños, C.; Teixeira, J.A.; Pastrana, L.; Malcata, F.X.; Vicente, A.A. Design of whey protein nanostructures for incorporation and release of nutraceutical compounds in food. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1377–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahami, A.; Fathi, M. Fabrication and characterization of novel nanofibers from cress seed mucilage for food applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45811–45816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otoni, C.G.; de Moura, M.R.; Aouada, F.A.; Camilloto, G.P.; Cruz, R.S.; Lorevice, M.V.; Soares, N.D.F.; Mattoso, L.H. Antimicrobial and physical-mechanical properties of pectin/papaya puree/cinnamaldehyde nanoemulsion edible composite films. Food Hydrocoll. 2014, 41, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arfat, Y.A.; Ahmed, J.; Hiremath, N.; Auras, R.; Joseph, A. Thermo-mechanical, rheological, structural and antimicrobial properties of bionanocomposite films based on fish skin gelatin and silver-copper nanoparticles. Food Hydrocoll. 2017, 62, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, X.; Zhou, Y.; Bai, L.; Liu, F.; Zhang, R.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, B.; Deng, Y.; McClements, D.J. Production of highly concentrated oil-in-water emulsions using dual-channel microfluidization: Use of individual and mixed natural emulsifiers (saponin and lecithin). Food Res. Int. 2017, 96, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otoni, C.G.; Pontes, S.F.O.; Medeiros, E.A.A.; Soares, N.D.F. Edible Films from Methylcellulose and Nanoemulsions of Clove Bud (Syzygium aromaticum) and Oregano (Origanum vulgare) Essential Oils as Shelf Life Extenders for Sliced Bread. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 5214–5219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-García, M.; Bosquez-Molina, E.; Hernández-Romano, J.; Zavala-Padilla, G.; Terrés-Rojas, E.; Alia-Tejacal, I.; Barrera-Nechaa, L.; Hernández-Lópeza, M.; Bautista-Baños, S. Use of chitosan-based edible coatings in combination with other natural compounds, to control Rhizopus stolonifer and Escherichia coli DH5α in fresh tomatoes. Crop Prot. 2012, 38, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sow, L.C.; Tirtawinata, F.; Yang, H.; Shao, Q.; Wang, S. Carvacrol nanoemulsion combined with acid electrolysed water to inactivate bacteria, yeast in vitro and native microflora on shredded cabbages. Food Control 2017, 76, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taştan, Ö.; Pataro, G.; Donsì, F.; Ferrari, G.; Baysal, T. Decontamination of fresh-cut cucumber slices by a combination of a modified chitosan coating containing carvacrol nanoemulsions and pulsed light. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 260, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Córdoba, L.J.; Sobral, P.J.A. Physical and antioxidant properties of films based on gelatin, gelatin-chitosan or gelatin-sodium caseinate blends loaded with nanoemulsified active compounds. J. Food Eng. 2017, 21, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salvia-Trujillo, L.; Rojas-Graü, M.A.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martín-Belloso, O. Use of antimicrobial nanoemulsions as edible coatings: Impact on safety and quality attributes of fresh-cut Fuji apples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2015, 105, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, Y.A.; Oh, Y.J.; Song, A.Y.; Won, J.S.; Song, K.B.; Min, S.C. Comparison of effectiveness of edible coatings using emulsions containing lemongrass oil of different size droplets on grape berry safety and preservation. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 75, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Severino, R.; Vu, K.D.; Donsì, F.; Salmieri, S.; Ferrari, G.; Lacroix, M. Antibacterial and physical effects of modified chitosan based-coating containing nanoemulsion of mandarin essential oil and three non-thermal treatments against Listeria innocua in green beans. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 191, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Artiga-Artigas, M.; Acevedo-Fani, A.; Martín-Belloso, O. Improving the shelf life of low-fat cut cheese using nanoemulsion-based edible coatings containing oregano essential oil and mandarin fiber. Food Control 2017, 76, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shadman, S.; Hosseini, S.E.; Langroudi, H.E.; Shabani, S. Evaluation of the effect of a sunflower oil-based nanoemulsion with Zataria multiflora Boiss. Essential oil on the physicochemical properties of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fillets during cold storage. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 795, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natrajan, D.; Srinivasan, S.; Sundar, K.; Ravindran, A. Formulation of essential oil-loaded chitosan–alginate nanocapsules. J. Food Drug Anal. 2015, 23, 560–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakos, I.L.; D’autilia, F.; Garzoni, A.; Bonferoni, C.; Scarpellini, A.; Brunetti, V.; Carzino, R.; Bianchini, P.; Pompa, P.P.; Athanassiou, A. All natural cellulose acetate—Lemongrass essential oil antimicrobial nanocapsules. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 510, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Hashemi, M.; Hosseini, S.M. Postharvest treatment of nanochitosan-based coating loaded with Zataria multiflora essential oil improves antioxidant activity and extends shelf-life of cucumber. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2016, 33, 580–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghaouth, A.; Arul, J.; Asselin, A.; Benhamou, N. Antifungal activity of chitosan on post-harvest pathogens: Induction of morphological and cytological alterations in Rhizopus stolonifer. Mycol. Res. 1992, 96, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vargas, M.; Albors, A.; Chiralt, A.; González-Martínez, C. Quality of cold-stored strawberries as affected by chitosan–oleic acid edible coatings. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2006, 41, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petriccione, M.; Mastrobuoni, F.; Pasquariello, M.; Zampella, L.; Nobis, E.; Capriolo, G.; Scortichini, M. Effect of Chitosan Coating on the Postharvest Quality and Antioxidant Enzyme System Response of Strawberry Fruit during Cold Storage. Foods 2015, 4, 501–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Wu, R.; Strik, B.C.; Zhao, Y. Effect of edible coatings on the quality of fresh blueberries (Duke and Elliott) under commercial storage conditions. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2011, 59, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, M.A.; Ali, A.; Manickam, S. Application of a Chitosan Based Nanoparticle Formulation as an Edible Coating for Tomatoes (Solanum lycoperiscum L.). Acta Hortic. 2013, 1012, 445–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilon, L.; Spricigo, P.C.; Miranda, M.; de Moura, M.R.; Assis, O.B.G.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Ferreira, M.D. Chitosan nanoparticle coatings reduce microbial growth on fresh-cut apples while not affecting quality attributes. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 50, 440–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eshghi, S.; Hashemi, M.; Mohammadi, A.; Badii, F.; Mohammadhoseini, Z.; Ahmadi, K. Effect of Nanochitosan-Based Coating with and without Copper Loaded on Physicochemical and Bioactive Components of Fresh Strawberry Fruit (Fragaria x ananassa Duchesne) During Storage. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 72, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Hernández, G.B.; Amodio, M.L.; Colelli, G. Carvacrol-loaded chitosan nanoparticles maintain quality of fresh-cut carrots. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017, 41, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.P.; Espinosa, Y.G.; Norton, I.T. Encapsulation systems for the delivery of hydrophilic nutraceuticals: Food application. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017, 35, 450–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.; Mercado-Silva, E.; Ramirez-Zamorano, P.; Cornejo-Villegas, M.A.; Gutiérrez-Cortez, E.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Use of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLNs) in edible coatings to increase guava (Psidium guajava L.) shelf-life. Food Res. Int. 2013, 51, 946–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Betanzos, C.I.; Hernández-Sánchez, H.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Alicia Del Real, L.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, M. The Evaluation of Mechanical, Thermal, Optical and Microstructural Properties of Edible Films with Solid Lipid Nanoparticles-Xanthan Gum Stored at Different Temperatures and Relative Humidities. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1756–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Betanzos, C.I.; Hernández-Sánchez, H.; Bernal-Couoh, T.F.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D.; Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.D.L.L. Physicochemical, total phenols and pectin methylesterase changes on quality maintenance on guava fruit (Psidium guajava L.) coated with candeuba wax solid lipid nanoparticles-xanthan gum. Food Res. Int. 2017, 101, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milsmann, J.; Oehlke, K.; Schrader, K.; Greiner, R.; Steffen-Heins, A. Fate of edible solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) in surfactant stabilized o/w emulsions. Part 1: Interplay of SLN and oil droplets. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Righeschi, C.; Bergonzi, M.C.; Isacchi, B.; Bazzicalupi, C.; Gratteri, P.; Bilia, A.R. Enhanced curcumin permeability by SLN formulation: The PAMPA approach. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 66, 475–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aditya, N.P.; Macedo, A.S.; Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Kim, S.; Chang, P.-S.; Ko, S. Development and evaluation of lipid nanocarriers for quercetin delivery: A comparative study of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN), nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC), and lipid nanoemulsions (LNE). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Couto, R.; Alvarez, V.; Temelli, F. Encapsulation of Vitamin B2 in solid lipid nanoparticles using supercritical CO2. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2017, 120, 432–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, C.; Decker, E.A.; Xiao, H.; McClements, D.J. Impact of lipid nanoparticle physical state on particle aggregation and β-carotene degradation: Potential limitations of solid lipid nanoparticles. Food Res. Int. 2013, 52, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Carvalho, S.M.; Noronha, C.M.; Floriani, C.L.; Lino, R.C.; Rocha, G.; Bellettini, I.C.; Ogliari, P.J.; Barreto, P.L.M. Optimization of α-tocopherol loaded solid lipid nanoparticles by central composite design. Ind. Crops Prod. 2013, 49, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandita, D.; Kumar, S.; Poonia, N.; Lather, V. Solid lipid nanoparticles enhance oral bioavailability of resveratrol, a natural polyphenol. Food Res. Int. 2014, 62, 1165–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathakoti, K.; Manubolu, M.; Hwang, H.-M. Nanostructures: Current uses and future applications in food science. J. Food Drug Anal. 2017, 25, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Livney, Y.D. Nanostructured delivery systems in food: Latest developments and potential future directions. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2015, 3, 125–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Zhuang, P.; Luan, L.; Sun, Q.; Cao, F. Preparation and characterization of novel nanocarriers containing krill oil for food application. J. Funct. Foods 2015, 19, 902–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, L.G.; Castro, G.R. Novel technologies for the encapsulation of bioactive food compounds. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2016, 7, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo-Fani, A.; Soliva-Fortuny, R.; Martín-Belloso, O. Nanoemulsions as edible coatings. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2017, 15, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, D.R.B.; Michelon, M.; de Figueiredo Furtado, G.; Sinigaglia-Coimbra, R.; Cunha, R.L. β-Carotene-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers produced by solvent displacement method. Food Res. Int. 2016, 90, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.; Park, K.S.; Kim, J.; Jeong, S.G.; Lee, C.S. Microfluidic synthesis of monodisperse pectin hydrogel microspheres based on in situ gelation and settling collection. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2017, 92, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zardini, A.; Mohebbi, M.; Farhoosh, R.; Bolurian, S. Production and characterization of nanostructured lipid carriers and solid lipid nanoparticles containing lycopene for food fortification. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 55, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortez-Vega, W.R.; Pizato, S.; de Souza, J.T.A.; Prentice, C. Using edible coatings from Whitemouth croaker (Micropogonias furnieri) protein isolate and organo-clay nanocomposite for improve the conservation properties of fresh-cut “Formosa” papaya. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2014, 22, 197–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junqueira-Gonçalves, M.P.; Salinas, G.E.; Bruna, J.E.; Niranjan, K. An assessment of lactobiopolymer-montmorillonite composites for dip coating applications on fresh strawberries. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2017, 97, 1846–1853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sani, A.M.; Ehsani, A.; Hashemi, M. Whey protein isolate/cellulose nanofibre/TiO2 nanoparticle/rosemary essential oil nanocomposite film: Its effect on microbial and sensory quality of lamb meat and growth of common foodborne pathogenic bacteria during refrigeration. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2017, 251, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.W.; Aisar, M.; Jahangir, M.; Abbasi, K.S.; Khan, S.U.; Ali, N.; Liaquat, M. Influence of CMC- and guar gum-based silver nanoparticle coatings combined with low temperature on major aroma volatile components and the sensory quality of kinnow (Citrus reticulata). Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 512, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.; Jung, J.; Simonsen, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, Y. Cellulose Nanocrystal Reinforced Chitosan Coatings for Improving the Storability of Postharvest Pears Under Both Ambient and Cold Storages. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 453–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guimarães, I.C.; dos Reis, K.C.; Menezes, E.G.T.; Rodrigues, A.C.; da Silva, T.F.; de Oliveira, I.R.N.; Boas, E.V.D. Cellulose microfibrillated suspension of carrots obtained by mechanical defibrillation and their application in edible starch films. Ind. Crops Prod. 2016, 89, 285–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Liu, Y.; Jia, H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, Z.; Ni, Y. Effects of Cellulose Nanofibers Filling and Palmitic Acid Emulsions Coating on the Physical Properties of Fish Gelatin Films. Food Biophys. 2017, 12, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Bioactive Substance | Functionality | Biopolymer Matrix | Food/Product | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carvacrol | Antimicrobial | - | Cabbage | The antimicrobial activity of a carvacrol nanoemulsion was proven from the results of inhibition of E. coli and P. pastoris growth in nutrient broth [73]. |
| Carvacrol | Antimicrobial | Chitosan | Cucumber | The combination of pulsed light (12 J/cm2) with the edible coating (0.08% carvacrol) resulted in a strong synergistic effect, with E. coli reduction reaching >5 log cycles [ 74]. |
| Cinnamaldehyde | Antimicrobial | Pectin (low and high methyl ester) | Edible films (in vitro) | The antimicrobial activity provided by cinnamaldehyde against food pathogens was remarkably improved by droplet size reduction due to increased surface area [ 68]. |
| Cinnamaldehyde, garlic essential oil and α-tocopherol | Antioxidant | Gelatin Chitosan Sodium caseinate | Edible films (in vitro) | The best antioxidant activity and physical properties were evaluated for the film based on gelatin-sodium caseinate, indicating its potential use as an active edible coating and biodegradable packaging materia [ 75]. |
| Clove bud and oregano essential oils | Antimicrobial and Shelf Life Extender | Methylcellulose | Sliced Bread | The films developed showed positive effects on yeast and mold counts compared to the commercial antifungal agent used [ 71]. |
| Lemongrass essential oil | Antimicrobial | Sodium alginate | Fresh-cut apple | Nanoemulsion-based edible coatings presented higher E. coli inactivation and slower psychrophilic bacteria growth compared to conventional emulsions at the same concentration [76]. |
| Lemongrass oil | Antimicrobial Antioxidant | Chitosan | Grape berry | The use of the nanoemulsion effectively reduced the initial growth of S. typhimurium, total aerobic mesophiles, yeasts and molds, and showed retention of antioxidant capacity [77]. |
| Mandarin essential oil | Antimicrobial | Chitosan | Green beans | The combination of the bioactive coating and UV-C treatment reduced the L. innocua population and maintained the microbial load at a constant level during storage [78]. |
| Oregano essential oil | Antimicrobial | Mandarin fiber | Low-fat cut cheese | High effectiveness on the inactivation of pathogens such as Staphylococcus aureus, and preserved the outward appearance of the cheese during the study period [79]. |
| Zataria multiflora Boiss. essential oil | Inhibition of lipid oxidation | - | Rainbow trout fillets | The use of the nanoemulsion showed good-quality, protective features against lipid oxidation, including the peroxide value, free fatty acids and total volatile basic nitrogen during refrigerated storage [ 80]. |
| α-tocopherol | Enzymatic activities and shelf life extender | Nopal mucilage | Fresh-cut apples | The coatings formed with the nanoemulsion had a significant inhibitory effect on PME and PPO activity, in contrast to conventional emulsions [ 46]. |
| Bioactive Compound | Matrix Lipid | Surfactant/Stabilizer(s) | Food Product | Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | Candeuba®S wax (carnauba wax and candelilla wax) | Poloxamer 407 | Guava (Psidium guajava L.) | The potential use of SLNs in edible coatings could be applied easily to minimize the senescence of several products [ 93]. |
| - | Candeuba®S wax (carnauba wax and candelilla wax) | Poloxamer 407 | Edible Films (in vitro) | These findings suggest that SLN films have potential uses in preservation as nano-coatings for whole fruits and vegetables [ 94]. |
| - | Candeuba®S wax (carnauba wax and candelilla wax) | Poloxamer 407 | Guava (Psidium guajava L.) | The application of candeuba wax (SLN) helps to conservate the natural maturation process, but at a slower rate [ 95]. |
| - | Glyceryl tristearate | Polyoxymethylene 20, sorbitan monolaurate, sucrose stearate and soy bean lecithin | Emulsion o/w | The presence of SLNs in emulsions led to increased emulsion stability as reflected by droplet size measurements and accelerated creaming experiments [ 96]. |
| Curcumin | Glyceryl behenate | Poloxamer 188, soy lecithin and Polysorbate 80 | In vitro | Increased the extremely low oral bioavailability of curcumin [ 97]. |
| Quercetin | Glyceryl monostearate | Polysorbate 80, sorbitan monolaurate and lecithin | In vitro | Bioaccessibility increased significantly when incorporated into the SLN compared to free quercetin in its native form [ 98]. |
| Vitamin B2 | Fully hydrogenated canola oil | Polyethylene glycol (PEG) and sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS) | In vitro | It is possible to generate nano-scale solid lipid particles with a high content of a hydrophilic bioactive; however, further fine-tuning is needed [ 99]. |
| β-carotene | Cocoa butter and/or hydrogenated palm oil | Polysorbate 80 | In vitro | SLN may not be better than liquid lipid nanoparticles for encapsulating bioactive food ingredients [ 100]. |
| α-tocopherol | Glyceryl behenate/soy lecithin | Soya lecithin, Poloxamer 188 | In vitro | The stability of the SLN formulation was improved as well as the retention of α-tocopherol [ 101]. |
| Resveratrol | Stearic acid | Poloxamer 188 | In vitro | The lipid formulation produced a significant improvement in the oral bioavailability of resveratrol as compared to the intact suspension [ 102]. |
| Active Compound/Functionality | Solid Lipid | Liquid Lipid (Oil) | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cardamom oil/Antimicrobial | Cocoa butter | Olive oil | NLCs had high entrapment efficiency (>90%), few changes were detected in the turbidity of systems after storage time with no significant aggregation and encapsulation was able to protect the antimicrobial activity of cardamom oil so in can be used as food supplements [ 56]. |
| β-carotene/Pigment | Tristearin | Sunflower oil | β-carotene incorporation reduced the particles polydispersity and NLCs exhibited an improvement of β-carotene loading capacity compared with SLN. NLCs exhibited advantages over the SLN such as enhanced loading capacity and prevention of active expulsion [ 108]. |
| Vitamin D/Antioxidant, calcium absorption | Glycerol monostearate | Oleic acid | In vitro digestion in simulated gastrointestinal fluids demonstrated their capability for controlled release because the NLCs were able to remain stable and protect the VD3 in simulated stomach fluid [ 109]. |
| Pomegranate seed oil/Antioxidant | Beeswax, propolis wax | Glyceryl behenate | Lecithin, Tween 80Formulation variables had significant effects on physical properties of NLCs and presented excellent physical stability. The optimum formulations contained 10% oil and 6% surfactant [ 58]. |
| Rutin/Nutraceutical, antimicrobial | Cacao butter | Oleic acid | NLCs with a rutin to lipid ratio of 10% were selected as an optimum formulation obtaining round shaped NLCs to fortify food samples as a method for designing new functional foods [ 57]. |
| Betasitosterol/Anti-inflammatory, cholesterol reduction | Precirol | Miglyol | NLCs showed a high encapsulation efficiency (99.96%) and showed a good stability during three months’ storage period when incorporated in butter increasing acid and peroxide values as well as antioxidant properties [ 54]. |
| Quercetin/Antioxidant | Glyceryl monostearate | Linseed oil | The addition of linseed oil improved the in vitro antioxidant activities of quercetin loaded NLCs exhibiting a sustained pattern. Lower lipid oxidation was found in quercetin and linseed oil co-loaded NLC compared with conventional linseed oil emulsion NLCs were stable for more than 3 months at 25 °C [ 59]. |
| Resveratrol/Antioxidant | Lauric acid, stearic acid, cacao butter | Glycerol, oleic acid, miglyol, corn oil | The stability of different formulations was evaluated over 60 days of storage finding that the optimum formulation was reached by oil to solid lipid ratio of 15%, surfactant to emulsion ratio of 6% and storage at 20 °C for 30 min with sonication treatment [ 53]. |
| Lycopene/Red color, antioxidant | Glycerol distearate, glycerol monostearate | Caprylic/capric triglyceride | Encapsulation efficiency of NLCs was significantly higher than SLNs. Glycerol monostearate containing nanoparticles showed phase separation after 30 days in 6 and 25 °C when incorporated in a beverage product. A sensory analysis indicated that nanoencapsulation could avoid the poor solubility and taste of lycopene [ 110]. |
| Nano-Inorganic Component | Functionality | Biopolymer Matrix | Food/Product | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nano-SiOx | Quality preservation, Shelf life extender | Soy protein isolate (SPI) | Apples | The preparation of edible a coating by ultrasonic processing and incorporation into an SPI matrix results in a decreased respiration rate, maintenance of firmness, and extension of shelf life [ 15]. |
| Montmorillo-nite (MMT) | Antimicrobial psychotropic microorganism, (fungi and yeasts) Shelf life extender | Whitemouth croaker/ore-gano essential oil | Fresh-cut papaya, pear | Adding 15 g/L of montmorillonite at 80°C and essential oil of oregano decreased weight loss and maintained the quality of papaya; moreover, the edible coating helped slow microbial grow [ 111]. |
| Montmorillo-nite (MMT) | Antifungal effect Increase storage time | Whey protein isolate (WPI)/calcium caseinate | Strawbe-rries | This edible coating contained 70% WPI, 0.5% potassium sorbate, 3.75% calcium caseinate and 0.375% MMT. It was effective in limiting mold growth during at least 12 days, and maintained the quality of the fresh coated strawberries [ 112]. |
| TiO2 | E.coli., L. monocytogenes, S. aureus | Cellulose nanofibers, WPI and rosemary essential oil | Lamb meat | The film coating with nano-TiO2 and rosemary reduced the growth of microorganisms more effectively and increased shelf life by 12–15 days [ 113]. |
| Nano-ZnO2 | Carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) | Ready-to-eat pomegranate | Edible coatings with 0.2% ZnO2 were the most effective, decreasing yeast and mold growth at 6 and 12 days of storage, though the bacterial load increased after 12 days of storage. The combination of CMC with nano-ZnO2 helped maintain bioactive compounds in the pomegranate [ 62]. | |
| Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) | E. coli, S. aureus, Penicillium italicum | Fantasia japônica leaf extract | Citrus fruit | AgNPs caused cell deformation, cytoplasmic leakage and cell death of P. italicum. AgNPs also showed significant activity on E. coli and S. aureus with beneficial effects for Citrus fruit preservation [15]. |
| Silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) | Retention of volatile compounds | CMC/guar gum | Kinnow (Citrus reticulata) | Coating emulsion base and silver nanoparticles were mixed with CMC or guar gum at 1:1. The final concentration of Ag was 0.03 mg/L. The coating was applied to the fruit surface, finding that the ZnO2 coating helped maintain the volatile compounds of the products [ 114]. |
| Nanotube/Nanofiber | Function | Biopolymer Matrix | Food | Conditions | Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microfibrilla-ted Carrot (MC) | Improve mechani-cal properties | Starch | Carrot | Carrot MFC supensions were obtained after 20–40 pas-sages through the defibrillator | Reinforce mechanical properties of the edible coating and diminished permeability to water vapor, with which these possess good functionality and compatibility [116]. |
| Avicel® Cellulose NanoFibers (CNF) | Mechani-cal, glass transition (Tg) | Chitosan | Foods | 0–20% CNF 0–30% glycerol | Finding that optimal concentrations to obtain a decrease in vitreous transition temperature were 15% of nanocellulose fibers and 18% of glycerol as plasticizer [115]. |
| Cellulose NanoFibers (CNF) | Gas barrier and mechani-cal resistance | Fish Gelatin (FG) Palmitic acid | Foods | 2% CFN and 6% FG | It was found that the use of CFN as reinforcement for edible coatings contributed to improving the properties of the water- vapor barrier and mechanical strength [117]. |
| Zein nanofibers | Encap-sulated curcu-min, anti-microbial agent | curcumin | Apples | Electrospun zein (2.5–5%) | The surface was inoculated with Botrytis cinereal and Penicillium expasum; then, apples were coated by electro-spinning with zein nanotubes and storage for 15 days, revealing the inhibi-tion of microbial growth increase in the shelf life of apples [10]. |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zambrano-Zaragoza, M.L.; González-Reza, R.; Mendoza-Muñoz, N.; Miranda-Linares, V.; Bernal-Couoh, T.F.; Mendoza-Elvira, S.; Quintanar-Guerrero, D. Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030705
Zambrano-Zaragoza ML, González-Reza R, Mendoza-Muñoz N, Miranda-Linares V, Bernal-Couoh TF, Mendoza-Elvira S, Quintanar-Guerrero D. Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030705
Chicago/Turabian StyleZambrano-Zaragoza, María L., Ricardo González-Reza, Néstor Mendoza-Muñoz, Verónica Miranda-Linares, Tania F. Bernal-Couoh, Susana Mendoza-Elvira, and David Quintanar-Guerrero. 2018. "Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030705
APA StyleZambrano-Zaragoza, M. L., González-Reza, R., Mendoza-Muñoz, N., Miranda-Linares, V., Bernal-Couoh, T. F., Mendoza-Elvira, S., & Quintanar-Guerrero, D. (2018). Nanosystems in Edible Coatings: A Novel Strategy for Food Preservation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030705