Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Splicing Correction in Individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis due to Compound Heterozygosity for the c.2991+1655A>G Mutation in CEP290
Abstract
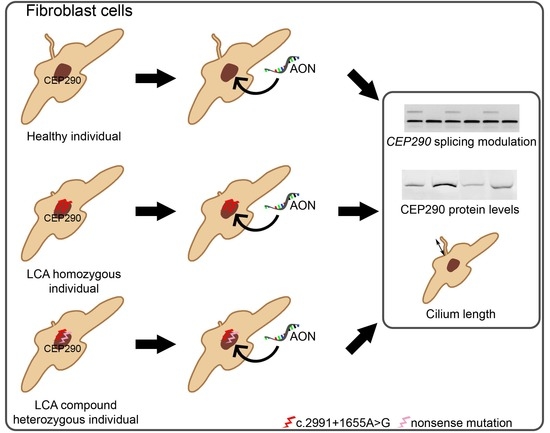
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Information of the LCA-Affected Individuals
2.2. AON Efficacy at RNA Level
2.3. AON Efficacy at Protein Level
2.4. AON Efficacy at Ciliation Level
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Patient-Derived Fibroblast Cells
4.3. Cell Culture and AON Transfections
4.4. RNA Analysis
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. Immunocytochemistry Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AON | Antisense oligonucleotide |
| CEP290 | Centrosomal protein of 290 kDa |
| IRD | Inherited retinal dystrophy |
| LCA | Leber congenital amaurosis |
| PBS | Phosphate Buffered Saline buffer |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcription PCR |
| RT | Room temperature |
References
- Den Hollander, A.I.; Roepman, R.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Cremers, F.P. Leber congenital amaurosis: Genes, proteins and disease mechanisms. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- RetNet. Available online: https://sph.uth.edu/RETNET (accessed on 24 January 2018).
- Koenekoop, R.K. An overview of Leber congenital amaurosis: A model to understand human retinal development. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2004, 49, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stone, E.M. Leber congenital amaurosis—A model for efficient genetic testing of heterogeneous disorders: LXIV Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 144, 791–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craige, B.; Tsao, C.C.; Diener, D.R.; Hou, Y.; Lechtreck, K.F.; Rosenbaum, J.L.; Witman, G.B. CEP290 tethers flagellar transition zone microtubules to the membrane and regulates flagellar protein content. J. Cell Biol. 2010, 190, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garanto, A.; van Beersum, S.E.; Peters, T.A.; Roepman, R.; Cremers, F.P.; Collin, R.W. Unexpected CEP290 mRNA splicing in a humanized knock-in mouse model for Leber congenital amaurosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e79369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garcia-Gonzalo, F.R.; Corbit, K.C.; Sirerol-Piquer, M.S.; Ramaswami, G.; Otto, E.A.; Noriega, T.R.; Seol, A.D.; Robinson, J.F.; Bennett, C.L.; Josifova, D.J.; et al. A transition zone complex regulates mammalian ciliogenesis and ciliary membrane composition. Nat. Genet. 2011, 43, 776–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valente, E.M.; Silhavy, J.L.; Brancati, F.; Barrano, G.; Krishnaswami, S.R.; Castori, M.; Lancaster, M.A.; Boltshauser, E.; Boccone, L.; Al-Gazali, L.; et al. Mutations in CEP290, which encodes a centrosomal protein, cause pleiotropic forms of Joubert syndrome. Nat. Genet. 2006, 38, 623–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppieters, F.; Lefever, S.; Leroy, B.P.; De Baere, E. CEP290, a gene with many faces: Mutation overview and presentation of CEP290base. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, 1097–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drivas, T.G.; Wojno, A.P.; Tucker, B.A.; Stone, E.M.; Bennett, J. Basal exon skipping and genetic pleiotropy: A predictive model of disease pathogenesis. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perrault, I.; Delphin, N.; Hanein, S.; Gerber, S.; Dufier, J.L.; Roche, O.; Defoort-Dhellemmes, S.; Dollfus, H.; Fazzi, E.; Munnich, A.; et al. Spectrum of NPHP6/CEP290 mutations in Leber congenital amaurosis and delineation of the associated phenotype. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallespin, E.; Lopez-Martinez, M.A.; Cantalapiedra, D.; Riveiro-Alvarez, R.; Aguirre-Lamban, J.; Avila-Fernandez, A.; Villaverde, C.; Trujillo-Tiebas, M.J.; Ayuso, C. Frequency of CEP290 c.2991_1655A>G mutation in 175 Spanish families affected with Leber congenital amaurosis and early-onset retinitis pigmentosa. Mol. Vis. 2007, 13, 2160–2162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Den Hollander, A.I.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Yzer, S.; Lopez, I.; Arends, M.L.; Voesenek, K.E.; Zonneveld, M.N.; Strom, T.M.; Meitinger, T.; Brunner, H.G.; et al. Mutations in the CEP290 (NPHP6) gene are a frequent cause of Leber congenital amaurosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collin, R.W.; den Hollander, A.I.; van der Velde-Visser, S.D.; Bennicelli, J.; Bennett, J.; Cremers, F.P. Antisense Oligonucleotide (AON)-based Therapy for Leber Congenital Amaurosis Caused by a Frequent Mutation in CEP290. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gerard, X.; Perrault, I.; Hanein, S.; Silva, E.; Bigot, K.; Defoort-Delhemmes, S.; Rio, M.; Munnich, A.; Scherman, D.; Kaplan, J.; et al. AON-mediated Exon Skipping Restores Ciliation in Fibroblasts Harboring the Common Leber Congenital Amaurosis CEP290 Mutation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2012, 1, e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parfitt, D.A.; Lane, A.; Ramsden, C.M.; Carr, A.J.; Munro, P.M.; Jovanovic, K.; Schwarz, N.; Kanuga, N.; Muthiah, M.N.; Hull, S.; et al. Identification and Correction of Mechanisms Underlying Inherited Blindness in Human iPSC-Derived Optic Cups. Cell Stem Cell 2016, 18, 769–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garanto, A.; Chung, D.C.; Duijkers, L.; Corral-Serrano, J.C.; Messchaert, M.; Xiao, R.; Bennett, J.; Vandenberghe, L.H.; Collin, R.W. In vitro and in vivo rescue of aberrant splicing in CEP290-associated LCA by antisense oligonucleotide delivery. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2016, 25, 2552–2563. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bonifert, T.; Gonzalez Menendez, I.; Battke, F.; Theurer, Y.; Synofzik, M.; Schols, L.; Wissinger, B. Antisense Oligonucleotide Mediated Splice Correction of a Deep Intronic Mutation in OPA1. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slijkerman, R.W.; Vache, C.; Dona, M.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Claustres, M.; Hetterschijt, L.; Peters, T.A.; Hartel, B.P.; Pennings, R.J.; Millan, J.M.; et al. Antisense Oligonucleotide-based Splice Correction for USH2A-associated Retinal Degeneration Caused by a Frequent Deep-intronic Mutation. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, S.F.; Jazayeri, A.; Matthes, M.T.; Yasumura, D.; Yang, H.; Peralta, R.; Watt, A.; Freier, S.; Hung, G.; Adamson, P.S.; et al. Allele-Specific Inhibition of Rhodopsin with an Antisense Oligonucleotide Slows Photoreceptor Cell Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 6362–6375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammond, S.M.; Wood, M.J. Genetic therapies for RNA mis-splicing diseases. Trends Genet. 2011, 27, 196–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, H.; Lu, Q.; Insinna-Kettenhofen, C.; Nagashima, K.; English, M.A.; Semler, E.M.; Mahgerefteh, J.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Li, T.; Brooks, B.P.; et al. In Vitro Modeling Using Ciliopathy-Patient-Derived Cells Reveals Distinct Cilia Dysfunctions Caused by CEP290 Mutations. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ClinicalTrials.gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ (accessed on 24 January 2018).
- Plotnikova, O.V.; Pugacheva, E.N.; Golemis, E.A. Primary cilia and the cell cycle. Methods Cell Biol. 2009, 94, 137–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Rajendran, V.; Sethumadhavan, R.; Purohit, R. CEP proteins: The knights of centrosome dynasty. Protoplasma 2013, 250, 965–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Park, J.E.; Jang, C.Y. DDA3 targets Cep290 into the centrosome to regulate spindle positioning. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 463, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerard, X.; Perrault, I.; Munnich, A.; Kaplan, J.; Rozet, J.M. Intravitreal Injection of Splice-switching Oligonucleotides to Manipulate Splicing in Retinal Cells. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2015, 4, e250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.Y.; Garrett, K.L.; da Cruz, L.; Constable, I.J.; Rakoczy, P.E. Dynamics of phosphorothioate oligonucleotides in normal and laser photocoagulated retina. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 83, 852–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, W.Y.; Garrett, K.L.; Wang, C.G.; Zhang, K.; Ma, Z.Z.; Constable, I.J.; Rakoczy, P.E. Preclinical evaluation of a phosphorothioate oligonucleotide in the retina of rhesus monkey. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2002, 82, 167–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anonymous. Fomivirsen approved for CMV retinitis: First antisense drug. AIDS Treat. News 1998, 7. [Google Scholar]
- Roehr, B. Fomivirsen approved for CMV retinitis. J. Int. Assoc. Phys. AIDS Care 1998, 4, 14–16. [Google Scholar]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Individual | Cell Line | Gender | Allele 1 (cDNA) | Allele 1 (Protein) | Allele 2 (cDNA) | Allele 2 (Protein) | Ocular Phenotype | Age at Onset | Extra-Ocular Features |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control 1 | CON1 | Female | + | + | + | + | Healthy | ||
| Control 2 | CON2 | Female | + | + | + | + | Healthy | ||
| Control 3 | CON3 | Male | + | + | + | + | Healthy | ||
| LCA 1 | LCA1 | Male | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | LCA | birth | none |
| LCA 2 | LCA2 | Female | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | LCA | birth | none |
| LCA 3 | LCA3 | Female | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | LCA | birth | none |
| LCA 4 | LCA4 | Female | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | c.5668G>T | p.Gly1890* | LCA/EORP | early childhood | none |
| LCA 5 | LCA5 | Male | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | c.4723A>T | p.Lys1575* | LCA | birth | none |
| LCA 6 | LCA6 | Male | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | c.5668G>T | p.Gly1890* | LCA | birth (based on anamnesis) | immotile spermatozoa |
| Unaffected mother LCA3 | HET1 | Female | c.2991+1655A>G | p.Cys998* | + | + | Healthy |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duijkers, L.; Van den Born, L.I.; Neidhardt, J.; Bax, N.M.; Pierrache, L.H.M.; Klevering, B.J.; Collin, R.W.J.; Garanto, A. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Splicing Correction in Individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis due to Compound Heterozygosity for the c.2991+1655A>G Mutation in CEP290. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030753
Duijkers L, Van den Born LI, Neidhardt J, Bax NM, Pierrache LHM, Klevering BJ, Collin RWJ, Garanto A. Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Splicing Correction in Individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis due to Compound Heterozygosity for the c.2991+1655A>G Mutation in CEP290. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030753
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuijkers, Lonneke, L. Ingeborgh Van den Born, John Neidhardt, Nathalie M. Bax, Laurence H. M. Pierrache, B. Jeroen Klevering, Rob W. J. Collin, and Alejandro Garanto. 2018. "Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Splicing Correction in Individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis due to Compound Heterozygosity for the c.2991+1655A>G Mutation in CEP290" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030753
APA StyleDuijkers, L., Van den Born, L. I., Neidhardt, J., Bax, N. M., Pierrache, L. H. M., Klevering, B. J., Collin, R. W. J., & Garanto, A. (2018). Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Splicing Correction in Individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis due to Compound Heterozygosity for the c.2991+1655A>G Mutation in CEP290. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030753