Characterization of a Novel Porin-Like Protein, ExtI, from Geobacter sulfurreducens and Its Implication in the Reduction of Selenite and Tellurite
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Conservation of ExtI Homologs in Other Geobacteraceae
2.2. Membrane Localization of ExtI
2.3. ExtI Production Does Not Respond to Changes in Osmolality or Phosphate Concentration
2.4. Construction of the ExtI-Deficient Strain
2.5. ExtI Appears Unimportant for Fumarate Respiration, Permeation of β-Lactam Antibiotics and Fe(III) Reduction
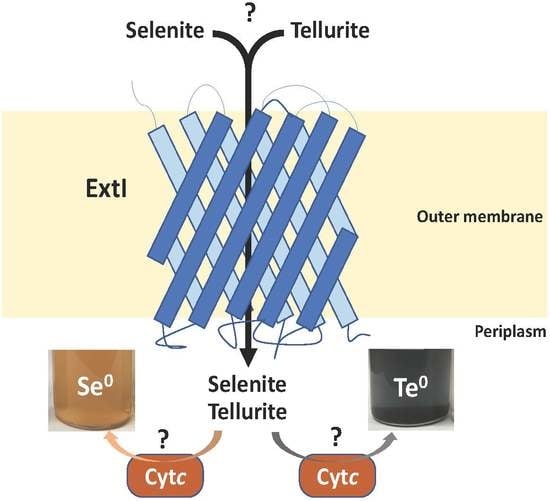
2.6. ExtI Deficiency Affects the Conversion of Selenite/Tellurite to Se0/Te0
2.7. ExtI Is Important for the Localization or Stabilization of Certain Heme-Containing Proteins
3. Discussion
3.1. Can a Similar Mechanism Be Employed between Phosphate Channels and Selenite/Tellurite Channels?
3.2. The Association of ExtI with Other Uncharacterized Genes Is Highly Conserved in Geobacteraceae
3.3. Possible Role of ExtI
3.4. The Association between Selenite Reduction and Iron Reduction
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals, Bacterial Strains and Growth Conditions
4.2. Subcellular Fractionation
4.3. Protein Quantification
4.4. SDS-PAGE and Western Blotting
4.5. In Situ Proteinase K Treatment
4.6. Susceptibility Assays with Antibiotic and Chalcogen Oxyanions
4.7. Gene Disruption
4.8. RT-PCR Analysis
4.9. Heme-Staining
4.10. Determination of Se0, Te0 and Fe(II)
4.11. Bioinformatic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Cytc | Cytochrome c |
| Pcc | Porin-cytochrome |
| HG-AFS | hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry |
References
- Nancharaiah, Y.V.; Lens, P.N. Ecology and biotechnology of selenium-respiring bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2015, 79, 61–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, R.J.; Borghese, R.; Zannoni, D. Microbial processing of tellurium as a tool in biotechnology. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debieux, C.M.; Dridge, E.J.; Mueller, C.M.; Splatt, P.; Paszkiewicz, K.; Knight, I.; Florance, H.; Love, J.; Titball, R.W.; Lewis, R.J.; et al. A bacterial process for selenium nanosphere assembly. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 13480–13485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eswayah, A.S.; Smith, T.J.; Gardiner, P.H.E. Microbial transformations of selenium species of relevance to bioremediation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 4848–4859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMoll-Decker, H.; Macy, J.M. The periplasmic nitrite reductase of Thauera selenatis may catalyze the reduction of selenite to elemental selenium. Arch. Microbiol. 1993, 160, 241–247. [Google Scholar]
- Harrison, G.; Curle, C.; Laishley, E.J. Purification and characterization of an inducible dissimilatory type sulfite reductase from Clostridium pasteurianum. Arch. Microbiol. 1984, 138, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanke, L.J.; Bryant, R.D.; Laishley, E.J. Hydrogenase I of Clostridium pasteurianum functions as a novel selenite reductase. Anaerobe 1995, 1, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.B.; Cheng, Y.Y.; Wu, C.; Li, W.W.; Li, N.; Yang, Z.C.; Tong, Z.H.; Yu, H.Q. Selenite reduction by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1 is mediated by fumarate reductase in periplasm. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afkar, E.; Lisak, J.; Saltikov, C.; Basu, P.; Oremland, R.S.; Stolz, J.F. The respiratory arsenate reductase from Bacillus selenitireducens strain MLS10. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2003, 226, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garbisu, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Yang, W.H.; Yee, B.C.; Carlson, D.L.; Yee, A.; Smith, N.R.; Otero, R.; Buchanan, B.B.; Leighton, T. Physiological mechanisms regulating the conversion of selenite to elemental selenium by Bacillus subtilis. Biofactors 1995, 5, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hunter, W.J.; Manter, D.K. Reduction of selenite to elemental red selenium by Pseudomonas sp. Strain CA5. Curr. Microbiol. 2009, 58, 493–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro, M.E.; Molina, R.; Diaz, W.; Pichuantes, S.E.; Vasquez, C.C. The dihydrolipoamide dehydrogenase of Aeromonas caviae ST exhibits NADH-dependent tellurite reductase activity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2008, 375, 91–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diaz-Vasquez, W.A.; Abarca-Lagunas, M.J.; Arenas, F.A.; Pinto, C.A.; Cornejo, F.A.; Wansapura, P.T.; Appuhamillage, G.A.; Chasteen, T.G.; Vasquez, C.C. Tellurite reduction by Escherichia coli NDH-II dehydrogenase results in superoxide production in membranes of toxicant-exposed cells. Biometals 2014, 27, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avazeri, C.; Turner, R.J.; Pommier, J.; Weiner, J.H.; Giordano, G.; Vermeglio, A. Tellurite reductase activity of nitrate reductase is responsible for the basal resistance of Escherichia coli to tellurite. Microbiology 1997, 143, 1181–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugin, B.; Cornejo, F.A.; Munoz-Diaz, P.; Munoz-Villagran, C.M.; Vargas-Perez, J.I.; Arenas, F.A.; Vasquez, C.C. Glutathione reductase-mediated synthesis of tellurium-containing nanostructures exhibiting antibacterial properties. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 7061–7070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderon, I.L.; Arenas, F.A.; Perez, J.M.; Fuentes, D.E.; Araya, M.A.; Saavedra, C.P.; Tantalean, J.C.; Pichuantes, S.E.; Youderian, P.A.; Vasquez, C.C. Catalases are NAD(P)H-dependent tellurite reductases. PLoS ONE 2006, 1, e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, M.D.; Kaplan, S. Identification of intrinsic high-level resistance to rare-earth-oxides and oxyanions in members of the class proteobacteria—Characterization of tellurite, selenite, and rhodium sesquioxide reduction in Rhodobacter sphaeroides. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 1505–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiong, M.; Gonzalez, E.; Barra, R.; Vasquez, C. Purification and biochemical characterization of tellurite-reducing activities from Thermus thermophilus HB8. J. Bacteriol. 1988, 170, 3269–3273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kessi, J.; Hanselmann, K.W. Similarities between the abiotic reduction of selenite with glutathione and the dissimilatory reaction mediated by Rhodospirillum rubrum and Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 50662–50669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Painter, E.P. The chemistry and toxicity of selenium compounds, with special reference to the selenium problem. Chem. Rev. 1941, 28, 179–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltman, C.; Donald, L.J.; Yurkov, V. Two distinct periplasmic enzymes are responsible for tellurite/tellurate and selenite reduction by strain ER-Te-48 associated with the deep sea hydrothermal vent tube worms at the Juan de Fuca Ridge black smokers. Arch. Microbiol. 2017, 199, 1113–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trutko, S.M.; Akimenko, V.K.; Suzina, N.E.; Anisimova, L.A.; Shlyapnikov, M.G.; Baskunov, B.P.; Duda, V.I.; Boronin, A.M. Involvement of the respiratory chain of gram-negative bacteria in the reduction of tellurite. Arch. Microbiol. 2000, 173, 178–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovley, D.R.; Holmes, D.E.; Nevin, K.P. Dissimilatory Fe(III) and Mn(IV) reduction. Adv. Microb. Physiol. 2004, 49, 219–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levar, C.E.; Hoffman, C.L.; Dunshee, A.J.; Toner, B.M.; Bond, D.R. Redox potential as a master variable controlling pathways of metal reduction by Geobacter sulfurreducens. ISME J. 2017, 11, 741–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgado, L.; Bruix, M.; Pessanha, M.; Londer, Y.Y.; Salgueiro, C.A. Thermodynamic characterization of a triheme cytochrome family from Geobacter sulfurreducens reveals mechanistic and functional diversity. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Zachara, J.M.; Shi, L. Direct involvement of ombB, omaB, and omcB genes in extracellular reduction of Fe(III) by Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, J.; Levar, C.; Edwards, M.J.; Babauta, J.T.; Kennedy, D.W.; Shi, Z.; Beyenal, H.; Bond, D.R.; et al. A trans-outer membrane porin-cytochrome protein complex for extracellular electron transfer by Geobacter sulfurreducens PCA. Environ. Microbiol. Rep. 2014, 6, 776–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Dong, H.; Reguera, G.; Beyenal, H.; Lu, A.; Liu, J.; Yu, H.Q.; Fredrickson, J.K. Extracellular electron transfer mechanisms between microorganisms and minerals. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2016, 14, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, L.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Zachara, J.M. Genomic analyses of bacterial porin-cytochrome gene clusters. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, C.H.; Levar, C.E.; Jimenez-Otero, F.; Bond, D.R. Genome scale mutational analysis of Geobacter sulfurreducens reveals distinct molecular mechanisms for respiration and sensing of poised electrodes vs. Fe(III) oxides. J. Bacteriol. 2017, 199, e00340-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, J.E.; Glaven, R.H.; Esteve-Nunez, A.; Nunez, C.; Shelobolina, E.S.; Bond, D.R.; Lovley, D.R. Genetic characterization of a single bifunctional enzyme for fumarate reduction and succinate oxidation in Geobacter sulfurreducens and engineering of fumarate reduction in Geobacter metallireducens. J. Bacteriol. 2006, 188, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cologgi, D.L.; Lampa-Pastirk, S.; Speers, A.M.; Kelly, S.D.; Reguera, G. Extracellular reduction of uranium via Geobacter conductive pili as a protective cellular mechanism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 15248–15252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, C.I.; Pattrick, R.A.; Law, N.; Charnock, J.M.; Coker, V.S.; Fellowes, J.W.; Oremland, R.S.; Lloyd, J.R. Investigating different mechanisms for biogenic selenite transformations: Geobacter sulfurreducens, Shewanella oneidensis and Veillonella atypica. Environ. Technol. 2009, 30, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonowska, A.; Heulin, T.; Vermeglio, A. Selenite and tellurite reduction by Shewanella oneidensis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2005, 71, 5607–5609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikaido, H. Molecular basis of bacterial outer membrane permeability revisited. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2003, 67, 593–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeth, K.; Thein, M. Porins in prokaryotes and eukaryotes: Common themes and variations. Biochem. J. 2010, 431, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairman, J.W.; Noinaj, N.; Buchanan, S.K. The structural biology of β-barrel membrane proteins: A summary of recent reports. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2011, 21, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koebnik, R.; Locher, K.P.; Van Gelder, P. Structure and function of bacterial outer membrane proteins: Barrels in a nutshell. Mol. Microbiol. 2000, 37, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, R.; Schmid, A.; Van der Ley, P.; Tommassen, J. Molecular basis of porin selectivity: Membrane experiments with OmpC-PhoE and OmpF-PhoE hybrid proteins of Escherichia coli K-12. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1989, 981, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hancock, R.E.; Egli, C.; Benz, R.; Siehnel, R.J. Overexpression in Escherichia coli and functional analysis of a novel PPi-selective porin, oprO, from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 471–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, K.; Struyve, M.; Bosch, D.; Benz, R.; Tommassen, J. One single lysine residue is responsible for the special interaction between polyphosphate and the outer membrane porin PhoE of Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 1989, 264, 16393–16398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pages, J.M.; James, C.E.; Winterhalter, M. The porin and the permeating antibiotic: A selective diffusion barrier in Gram-negative bacteria. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2008, 6, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, T.M.; Myers, C.R. The outer membrane protein Omp35 affects the reduction of Fe(III), nitrate, and fumarate by Shewanella oneidensis MR-1. BMC Microbiol. 2004, 4, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Afkar, E.; Reguera, G.; Schiffer, M.; Lovley, D.R. A novel Geobacteraceae-specific outer membrane protein J (OmpJ) is essential for electron transport to Fe(III) and Mn(IV) oxides in Geobacter sulfurreducens. BMC Microbiol. 2005, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duperthuy, M.; Schmitt, P.; Garzon, E.; Caro, A.; Rosa, R.D.; Le Roux, F.; Lautredou-Audouy, N.; Got, P.; Romestand, B.; de Lorgeril, J.; et al. Use of OmpU porins for attachment and invasion of Crassostrea gigas immune cells by the oyster pathogen Vibrio splendidus. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2993–2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, T.; Ju, L.; Yin, J.; Gao, H. Positive regulation of the Shewanella oneidensis OmpS38, a major porin facilitating anaerobic respiration, by Crp and Fur. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartshorne, R.S.; Reardon, C.L.; Ross, D.; Nuester, J.; Clarke, T.A.; Gates, A.J.; Mills, P.C.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Zachara, J.M.; Shi, L.; et al. Characterization of an electron conduit between bacteria and the extracellular environment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 22169–22174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Methe, B.A.; Nelson, K.E.; Eisen, J.A.; Paulsen, I.T.; Nelson, W.; Heidelberg, J.F.; Wu, D.; Wu, M.; Ward, N.; Beanan, M.J.; et al. Genome of Geobacter sulfurreducens: Metal reduction in subsurface environments. Science 2003, 302, 1967–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.H.; Hixson, K.K.; Aklujkar, M.A.; Lipton, M.S.; Smith, R.D.; Lovley, D.R.; Mester, T. Proteome of Geobacter sulfurreducens grown with Fe(III) oxide or Fe(III) citrate as the electron acceptor. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1784, 1935–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.H.; Hixson, K.K.; Giometti, C.S.; Stanley, A.; Esteve-Nunez, A.; Khare, T.; Tollaksen, S.L.; Zhu, W.; Adkins, J.N.; Lipton, M.S.; et al. The proteome of dissimilatory metal-reducing microorganism Geobacter sulfurreducens under various growth conditions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1764, 1198–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, K.; Qian, X.; Morgado, L.; Kim, B.C.; Mester, T.; Izallalen, M.; Salgueiro, C.A.; Lovley, D.R. Purification and characterization of OmcZ, an outer-surface, octaheme c-type cytochrome essential for optimal current production by Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3999–4007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, M.; Mihara, H.; Goto, S.; Esaki, N.; Kanehisa, M. Mining prokaryotic genomes for unknown amino acids: A stop-codon-based approach. BMC Bioinform. 2007, 8, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Butler, J.E.; Young, N.D.; Lovley, D.R. Evolution of electron transfer out of the cell: Comparative genomics of six Geobacter genomes. BMC Genom. 2010, 11, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siehnel, R.J.; Egli, C.; Hancock, R.E. Polyphosphate-selective porin OprO of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Expression, purification and sequence. Mol. Microbiol. 1992, 6, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aklujkar, M.; Coppi, M.V.; Leang, C.; Kim, B.C.; Chavan, M.A.; Perpetua, L.A.; Giloteaux, L.; Liu, A.; Holmes, D.E. Proteins involved in electron transfer to Fe(III) and Mn(IV) oxides by Geobacter sulfurreducens and Geobacter uraniireducens. Microbiology 2013, 159, 515–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauschenbach, I.; Narasingarao, P.; Haggblom, M.M. Desulfurispirillum indicum sp. nov., a selenate- and selenite-respiring bacterium isolated from an estuarine canal. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2011, 61, 654–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mills, J.; Wyborn, N.R.; Greenwood, J.A.; Williams, S.G.; Jones, C.W. An outer-membrane porin inducible by short-chain amides and urea in the methylotrophic bacterium Methylophilus methylotrophus. Microbiology 1997, 143, 2373–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, P.Y.; Fasman, G.D. Conformational parameters for amino acids in helical, β-sheet, and random coil regions calculated from proteins. Biochemistry 1974, 13, 211–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savojardo, C.; Fariselli, P.; Casadio, R. BETAWARE: A machine-learning tool to detect and predict transmembrane β-barrel proteins in prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 504–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petersen, T.N.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 4.0: Discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions. Nat. Methods 2011, 8, 785–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonnhammer, E.L.; von Heijne, G.; Krogh, A. A hidden Markov model for predicting transmembrane helices in protein sequences. Proc. Int. Conf. Intell. Syst. Mol. Biol. 1998, 6, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Krogh, A.; Larsson, B.; von Heijne, G.; Sonnhammer, E.L. Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: Application to complete genomes. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 305, 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nielsen, H.; Engelbrecht, J.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G. Identification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic signal peptides and prediction of their cleavage sites. Protein Eng. 1997, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, N.Y.; Wagner, J.R.; Laird, M.R.; Melli, G.; Rey, S.; Lo, R.; Dao, P.; Sahinalp, S.C.; Ester, M.; Foster, L.J.; et al. PSORTb 3.0: Improved protein subcellular localization prediction with refined localization subcategories and predictive capabilities for all prokaryotes. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1608–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, H.; Sandie, R.; Wang, Y.; Andrade-Navarro, M.A.; Niederweis, M. Identification of outer membrane proteins of Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis 2008, 88, 526–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilkins, M.R.; Gasteiger, E.; Bairoch, A.; Sanchez, J.C.; Williams, K.L.; Appel, R.D.; Hochstrasser, D.F. Protein identification and analysis tools in the ExPASy server. Methods Mol. Biol. 1999, 112, 531–552. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pratt, L.A.; Hsing, W.; Gibson, K.E.; Silhavy, T.J. From acids to osmZ: Multiple factors influence synthesis of the OmpF and OmpC porins in Escherichia coli. Mol. Microbiol. 1996, 20, 911–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finn, R.D.; Coggill, P.; Eberhardt, R.Y.; Eddy, S.R.; Mistry, J.; Mitchell, A.L.; Potter, S.C.; Punta, M.; Qureshi, M.; Sangrador-Vegas, A.; et al. The Pfam protein families database: Towards a more sustainable future. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016, 44, D279–D285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poole, K.; Parr, T.R., Jr.; Hancock, R.E. Phosphate-selective porins from the outer membranes of fluorescent Pseudomonas sp. Can. J. Microbiol. 1987, 33, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tommassen, J.; Overduin, P.; Lugtenberg, B.; Bergmans, H. Cloning of phoE, the structural gene for the Escherichia coli phosphate limitation-inducible outer membrane pore protein. J. Bacteriol. 1982, 149, 668–672. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Forst, S.A.; Roberts, D.L. Signal transduction by the EnvZ-OmpR phosphotransfer system in bacteria. Res. Microbiol. 1994, 145, 363–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikenaka, K.; Ramakrishnan, G.; Inouye, M.; Tsung, K.; Inouye, M. Regulation of the ompC gene of Escherichia coli. Involvement of three tandem promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 1986, 261, 9316–9320. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kojima, S.; Nikaido, H. Permeation rates of penicillins indicate that Escherichia coli porins function principally as nonspecific channels. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E2629–E2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benz, R.; Egli, C.; Hancock, R.E. Anion transport through the phosphate-specific OprP-channel of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane: Effects of phosphate, di- and tribasic anions and of negatively-charged lipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1993, 1149, 224–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moraes, T.F.; Bains, M.; Hancock, R.E.; Strynadka, N.C. An arginine ladder in OprP mediates phosphate-specific transfer across the outer membrane. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2007, 14, 85–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Guessan, A.L.; Elifantz, H.; Nevin, K.P.; Mouser, P.J.; Methe, B.; Woodard, T.L.; Manley, K.; Williams, K.H.; Wilkins, M.J.; Larsen, J.T.; et al. Molecular analysis of phosphate limitation in Geobacteraceae during the bioremediation of a uranium-contaminated aquifer. ISME J. 2010, 4, 253–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elias, A.; Diaz-Vasquez, W.; Abarca-Lagunas, M.J.; Chasteen, T.G.; Arenas, F.; Vasquez, C.C. The ActP acetate transporter acts prior to the PitA phosphate carrier in tellurite uptake by Escherichia coli. Microbiol. Res. 2015, 177, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Sampietro, M.; Serra-Cardona, A.; Canadell, D.; Casas, C.; Arino, J.; Herrero, E. The yeast Aft2 transcription factor determines selenite toxicity by controlling the low affinity phosphate transport system. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 32836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Hu, B.; Li, W.; Che, R.; Deng, K.; Li, H.; Yu, F.; Ling, H.; Li, Y.; Chu, C. OsPT2, a phosphate transporter, is involved in the active uptake of selenite in rice. New Phytol. 2014, 201, 1183–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McDermott, J.R.; Rosen, B.P.; Liu, Z. Jen1p: A high affinity selenite transporter in yeast. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 3934–3941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berry, E.A.; Guergova-Kuras, M.; Huang, L.S.; Crofts, A.R. Structure and function of cytochrome bc complexes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2000, 69, 1005–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobias, J.; Suvorova, E.I.; Bernier-Latmani, R. Role of proteins in controlling selenium nanoparticle size. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 195605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzalez-Gil, G.; Lens, P.N.; Saikaly, P.E. Selenite reduction by anaerobic microbial aggregates: Microbial community structure, and proteins associated to the produced selenium spheres. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 571–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, C.S.; Debieux, C.M.; Dridge, E.J.; Splatt, P.; Wright, M. Biomineralization of selenium by the selenate-respiring bacterium Thauera selenatis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustus, A.M.; Celaya, T.; Husain, F.; Humbard, M.; Misra, R. Antibiotic-sensitive TolC mutants and their suppressors. J. Bacteriol. 2004, 186, 1851–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beketskaia, M.S.; Bay, D.C.; Turner, R.J. Outer membrane protein OmpW participates with small multidrug resistance protein member EmrE in quaternary cationic compound efflux. J. Bacteriol. 2014, 196, 1908–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lacourciere, G.M.; Levine, R.L.; Stadtman, T.C. Direct detection of potential selenium delivery proteins by using an Escherichia coli strain unable to incorporate selenium from selenite into proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 9150–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogasawara, Y.; Lacourciere, G.; Stadtman, T.C. Formation of a selenium-substituted rhodanese by reaction with selenite and glutathione: Possible role of a protein perselenide in a selenium delivery system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 9494–9498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihara, H.; Kurihara, T.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshimura, T.; Esaki, N. cDNA cloning, purification, and characterization of mouse liver selenocysteine lyase. Candidate for selenium delivery protein in selenoprotein synthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 6195–6200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Gladyshev, V.N. An algorithm for identification of bacterial selenocysteine insertion sequence elements and selenoprotein genes. Bioinformatics 2005, 21, 2580–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, H.; Ma, Z.Z.; Chen, X.L.; Zhang, H.Y.; Bao, Z.Y.; Wei, C.H.; Xie, S.Y.; Wu, S.T. Geochemical characteristics of selenium and its correlation to other elements and minerals in selenium-enriched rocks in Ziyang County, Shaanxi Province, China. J. Earth Sci. 2016, 27, 763–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, E.; Taillefert, M. The role of soluble Fe(III) in the cycling of iron and sulfur in coastal marine sediments. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2005, 50, 1129–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppi, M.V.; Leang, C.; Sandler, S.J.; Lovley, D.R. Development of a genetic system for Geobacter sulfurreducens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2001, 67, 3180–3187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Hage, N.; Babb, K.; Carroll, J.A.; Lindstrom, N.; Fischer, E.R.; Miller, J.C.; Gilmore, R.D., Jr.; Mbow, M.L.; Stevenson, B. Surface exposure and protease insensitivity of Borrelia burgdorferi Erp (OspEF-related) lipoproteins. Microbiology 2001, 147, 821–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francis, R.T., Jr.; Becker, R.R. Specific indication of hemoproteins in polyacrylamide gels using a double-staining process. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 136, 509–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Rodas, D.; Mellano, F.; Morales, E.; Giraldez, I. A simplified method for inorganic selenium and selenoaminoacids speciation based on HPLC-TR-HG-AFS. Talanta 2013, 106, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lovley, D.R.; Phillips, E.J. Organic matter mineralization with reduction of ferric iron in anaerobic sediments. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1986, 51, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jahan, M.I.; Tobe, R.; Mihara, H. Characterization of a Novel Porin-Like Protein, ExtI, from Geobacter sulfurreducens and Its Implication in the Reduction of Selenite and Tellurite. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030809
Jahan MI, Tobe R, Mihara H. Characterization of a Novel Porin-Like Protein, ExtI, from Geobacter sulfurreducens and Its Implication in the Reduction of Selenite and Tellurite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030809
Chicago/Turabian StyleJahan, Mst. Ishrat, Ryuta Tobe, and Hisaaki Mihara. 2018. "Characterization of a Novel Porin-Like Protein, ExtI, from Geobacter sulfurreducens and Its Implication in the Reduction of Selenite and Tellurite" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030809
APA StyleJahan, M. I., Tobe, R., & Mihara, H. (2018). Characterization of a Novel Porin-Like Protein, ExtI, from Geobacter sulfurreducens and Its Implication in the Reduction of Selenite and Tellurite. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 809. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030809