Liddle Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Description of a New Case
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Liddle Syndrome
2.1. Historical Description
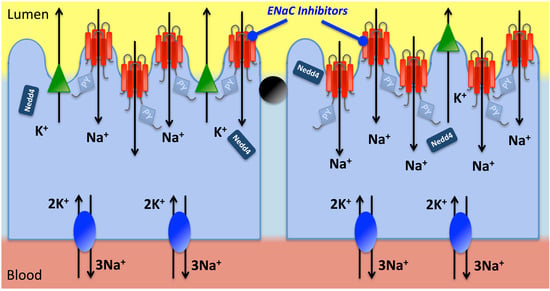
2.2. Pathophysiology and Genetics
2.3. Diagnosis Prevalence and Phenotypes
3. Description of a New Case of Liddle Syndrome
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Olsen, M.H.; Angell, S.Y.; Asma, S.; Boutouyrie, P.; Burger, D.; Chirinos, J.A.; Damasceno, A.; Delles, C.; Gimenez-Roqueplo, A.P.; Hering, D.; et al. A call to action and a lifecourse strategy to address the global burden of raised blood pressure on current and future generations: The Lancet Commission on hypertension. Lancet 2016, 388, 2665–2712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrello, J.; Monticone, S.; Buffolo, F.; Tetti, M.; Veglio, F.; Williams, T.A.; Mulatero, P. Is there a role for genomics in the management of hypertension? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, E1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zennaro, M.C.; Boulkroun, S.; Fernandes-Rosa, F. Inherited forms of mineralocorticoid hypertension. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 29, 633–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liddle, G.W.; Bledsoe, T.; Coppage, W.S.J. A familial renal disorder simulating primary aldosteronism but with negligible aldosterone secretion. Trans. Assoc. Am. Phys. 1963, 76, 199–213. [Google Scholar]
- Palmer, B.F.; Alpern, R.J. Liddle’s syndrome. Am. J. Med. 1998, 104, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botero-Velez, M.; Curtis, J.J.; Warnock, D.G. Brief report: Liddle’s syndrome revisited—A disorder of sodium reabsorption in the distal tubule. N. Engl. J. Med. 1994, 330, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimkets, R.A.; Warnock, D.G.; Bositis, C.M.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Hansson, J.H.; Schambelan, M.; Gill, J.R.; Ulick, S.; Milora, R.V.; Findling, J.W.; et al. Liddle’s syndrome: Heritable human hypertension caused by mutations in the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Cell 1994, 79, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canessa, C.M.; Schild, L.; Buell, G.; Thorens, B.; Gautschi, I.; Horisberger, J.D.; Rossier, B.C. Amiloride-sensitive epithelial Na+ channel is made of three homologous subunits. Nature 1994, 367, 463–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanukoglu, I.; Hanukoglu, A. Epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) family: Phylogeny, structure-function, tissue distribution, and associated inherited diseases. Gene 2016, 579, 95–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotin, D.; Schild, L. ENaC and its regulatory proteins as drug targets for blood pressure control. Curr. Drug Targets 2008, 9, 709–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staruschenko, A.; Medina, J.L.; Patel, P.; Shapiro, M.S.; Booth, R.E.; Stockand, J.D. Fluorescence resonance energy transfer analysis of subunit stoichiometry of the epithelial Na+ channel. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 27729–27734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jasti, J.; Furukawa, H.; Gonzales, E.B.; Gouaux, E. Structure of acid-sensing ion channel 1 at 1.9 A resolution and low pH. Nature 2007, 449, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashlan, O.B.; Adelman, J.L.; Okumura, S.; Blobner, B.M.; Zuzek, Z.; Hughey, R.P.; Kleyman, T.R.; Grabe, M. Constraint-based, homology model of the extracellular domain of the epithelial Na+ channel α subunit reveals a mechanism of channel activation by proteases. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schild, L.; Lu, Y.; Gautschi, I.; Schneeberger, E.; Lifton, R.P.; Rossier, B.C. Identification of a PY motif in the epithelial Na channel subunits as a target sequence for mutations causing channel activation found in Liddle syndrome. EMBO J. 1996, 15, 2381–2387. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rotin, D.; Staub, O. Role of the ubiquitin system in regulating ion transport. Pflugers Arch. 2011, 461, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butterworth, M.B. Regulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) by membrane trafficking. Biohim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1802, 1166–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warnock, D.G. Liddle syndrome: An autosomal dominant form of human hypertension. Kidney Int. 1998, 53, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, J.H.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Suzuki, H.; Schild, L.; Shimkets, R.; Lu, Y.; Canessa, C.; Iwasaki, T.; Rossier, B.C.; Lifton, R.P. Hypertension caused by a truncated epithelial sodium channel γ subunit: Genetic heterogeneity of Liddle syndrome. Nat. Genet. 1995, 11, 76–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.Q.; Xiao, Y.; Tian, T.; Gao, L.G.; Zhou, X.L. Molecular genetics of Liddle’s syndrome. Clin. Chim. Acta 2014, 436, 202–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rotin, D. Role of the UPS in Liddle syndrome. BMC Biochem. 2008, 9, S5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schild, L.; Canessa, C.M.; Shimkets, R.A.; Gautschi, I.; Lifton, R.P.; Rossier, B.C. A mutation in the epithelial sodiumm channel causing Liddle disease increases channel activity in the Xenopus laevis oocyte expression system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 5699–5703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Firsov, D.; Schild, L.; Gautschi, I.; Mérillat, A.M.; Schneeberger, E.; Rossier, B.C. Cell surface expression of the epithelial Na channel and a mutant causing Liddle syndrome: A quantitative approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 15370–15375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anantharam, A.; Tian, Y.; Palmer, L.G. Open probability of the epithelial sodium channel is regulated by intracellular sodium. J. Physiol. 2006, 574, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knight, K.K.; Olson, D.R.; Zhou, R.; Snyder, P.M. Liddle’s syndrome mutations increase Na+ transport through dual effects on epithelial Na+ channel surface expression and proteolytic cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2805–2808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kellenberger, S.; Gautschi, I.; Rossier, B.C.; Schild, L. Mutations causing Liddle syndrome reduce sodium-dependent downregulation of the epithelial sodium channel in the Xenopus oocyte expression system. J. Clin. Investig. 1998, 101, 2741–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, M.; Gautschi, I.; van Bemmelen, M.X.; di Benedetto, M.; Brooks, A.S.; Lugtenberg, D.; Schild, L.; Hoorn, E.J. A missense mutation in the extracellular domain of αENaC causes Liddle syndrome. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 3291–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Qin, F.; Sun, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Wu, Y.; Ma, W.; Wang, W.; Wu, X.; Qin, Y.; et al. Analysis of the genes involved in Mendelian forms of low-renin hypertension in Chinese early-onset hypertensive patients. J. Hypertens. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melander, O.; Orho, M.; Fagerudd, J.; Bengtsson, K.; Groop, P.H.; Mattiasson, I.; Groop, L.; Hulthén, U.L. Mutations and variants of the epithelial sodium channel gene in Liddle’s syndrome and primary hypertension. Hypertension 1998, 31, 1118–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kyuma, M.; Ura, N.; Torii, T.; Takeuchi, H.; Takizawa, H.; Kitamura, K.; Tomita, K.; Sasaki, S.; Shimamoto, K. A family with liddle’s syndrome caused by a mutation in the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2001, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.Y.; Chen, X.; Ren, Y.; Long, Y.; Tian, H.M. Liddle’s syndrome caused by a novel mutation of the γ-subunit of epithelial sodium channel gene SCNN1G in Chinese. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2010, 27, 132–135. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Chen, J.; Shao, L.; Song, W.; Hui, R.; Wang, Y. Phenotype-genotype analysis in two Chinese families with Liddle syndrome. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2014, 41, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.P.; Yang, K.Q.; Jiang, X.J.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhang, H.M.; Zou, Y.B.; Song, L.; Bian, J.; Hui, R.T.; Liu, Y.X.; et al. Prevalence of Liddle syndrome among young hypertension patients of undetermined cause in a Chinese population. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2015, 17, 902–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polfus, L.M.; Boerwinkle, E.; Gibbs, R.A.; Metcalf, G.; Muzny, D.; Veeraraghavan, N.; Grove, M.; Shete, S.; Wallace, S.; Milewicz, D.; et al. Whole-exome sequencing reveals an inherited R566X mutation of the epithelial sodium channel β-subunit in a case of early-onset phenotype of Liddle syndrome. Cold Spring Harb. Mol. Case Stud. 2016, 2, a001255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Tong, A.; Jiang, J.; Wang, F.; Li, C. Liddle syndrome: Clinical and genetic profiles. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2017, 19, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freercks, R.; Meldau, S.; Jones, E.; Ensor, J.; Weimers-Willard, C.; Rayner, B. Liddle’s syndrome in an African male due to a novel frameshift mutation in the β-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel gene. Cardiovasc. J. Afr. 2017, 28, E4–E6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phoojaroenchanachai, M.; Buranakitjaroen, P.; Limwongse, C. Liddle’s syndrome: A case report. J. Med. Assoc. Thail. 2015, 98, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeunemaitre, X.; Bassilana, F.; Persu, A.; Dumont, C.; Champigny, G.; Lazdunski, M.; Corvol, P.; Barbry, P. Genotype-phenotype analysis of a newly discovered family with Liddle’s syndrome. J. Hypertens. 1997, 15, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Findling, J.W.; Raff, H.; Hansson, J.H.; Lifton, R.P. Liddle’s syndrome: Prospective genetic screening and suppressed aldosterone secretion in an extended kindred. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1997, 82, 1071–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, T.; Okauchi, Y.; Matsuzaki, Y.; Kuwajima, K.; Kondo, H.; Horiuchi, N.; Nakao, K.; Iwata, M.; Yokogoshi, Y.; Shintani, Y.; et al. Identification of a single cytosine base insertion mutation at Arg-597 of the β subunit of the human epithelial sodium channel in a family with Liddle’s disease. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 1998, 138, 691–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson, S.N.J.; Williams, B.; Houtman, P.; Trembath, R.C. The diagnosis of Liddle Syndrome by identification of a mutation in the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. J. Med. Genet. 1998, 35, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Ishida, T.; Ozono, R.; Matsuura, H.; Yamamoto, Y.; Kambe, M.; Chayama, K.; Oshima, T. A frameshift mutation of β subunit of epithelial sodium channel in a case of isolated Liddle syndrome. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 2379–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awadalla, M.; Patwardhan, M.; Alsamsam, A.; Imran, N. Management of Liddle syndrome in pregnancy: A case report and literature review. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2017, 2017, 6279460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Tian, Y.; Gao, Y.; Guo, X. A study of mutation(s) of the epithelial sodium channel gene in a Liddle’s syndrome family. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi 2001, 40, 390–393. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hiltunen, T.P.; Hannila-Handelberg, T.; Petäjäniemi, N.; Kantola, I.; Tikkanen, I.; Virtamo, J.; Gautschi, I.; Schild, L.; Kontula, K. Liddle’s syndrome associated with a point mutation in the extracellular domain of the epithelial sodium channel γ subunit. J. Hypertens. 2002, 20, 2383–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, L.; Wang, L.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Hui, R.; Hu, A. A family with Liddle syndrome caused by a novel missense mutation in the PY motif of the β-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. J. Pediatr. 2013, 162, 166–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, Z.M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Liu, J.H.; Zeng, R.; Zhou, Q.; Yu, Z.Q.; Jiang, L. The importance of genetic counseling and genetic screening: A case report of a 16-year-old boy with resistant hypertension and severe hypokalemia. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2017, 11, 136–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawathiparnich, P.; Sumboonnanonda, A.; Weerakulwattana, P.; Limwongse, C. A novel mutation in the β-subunit of the epithelial sodium channel gene (SCNN1B) in a Thai family with Liddle’s syndrome. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 22, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.; Farnetti, E.; Debonneville, A.; Nicoli, D.; Grasselli, C.; Regolisti, G.; Negro, A.; Perazzoli, F.; Casali, B.; Mantero, F.; et al. Liddle’s syndrome caused by a novel missense mutation (P617L) of the epithelial sodium channel β subunit. J. Hypertens. 2008, 26, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossi, E.; Farnetti, E.; Nicoli, D.; Sazzini, M.; Perazzoli, F.; Regolisti, G.; Grasselli, C.; Santi, R.; Negro, A.; Mazzeo, V.; et al. A clinical phenotype mimicking essential hypertension in a newly discovered family with Liddle’s syndrome. Am. J. Hypertens. 2011, 24, 930–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caretto, A.; Primerano, L.; Novara, F.; Zuffardi, O.; Genovese, S.; Rondinelli, M. A therapeutic challenge: Liddle’s syndrome managed with amiloride during pregnancy. Case Rep. Obstet. Gynecol. 2014, 2014, 156250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inoue, J.; Iwaoka, T.; Tokunaga, H.; Takamune, K.; Naomi, S.; Araki, M.; Takahama, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Tomita, K. A family with Liddle’s syndrome caused by a new missense mutation in the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1998, 83, 2210–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freundlich, M.; Ludwig, M. A novel epithelial sodium channel β-subunit mutation associated with hypertensive Liddle syndrome. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2005, 20, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Zhou, W.; Jiang, L.; Cui, B.; Ye, L.; Su, T.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ning, G. Mutation analysis of SCNN1B in a family with Liddle’s syndrome. Endocrine 2006, 29, 385–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, K.Q.; Lu, C.X.; Fan, P.; Zhang, Y.; Meng, X.; Dong, X.Q.; Luo, F.; Liu, Y.X.; Zhang, H.M.; Wu, H.Y.; et al. Genetic screening of SCNN1B and SCNN1G genes in early-onset hypertensive patients helps to identify Liddle syndrome. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2018, 40, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansson, J.H.; Schild, L.; Lu, Y.; Wilson, T.A.; Gautschi, I.; Shimkets, R.; Nelson-Williams, C.; Rossier, B.C.; Lifton, R.P. A de novo missense mutation of the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel causes hypertension and Liddle syndrome, identifying a proline-rich segment critical for regulation of channel activity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1995, 92, 11495–11499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uehara, Y.; Sasaguri, M.; Kinoshita, A.; Tsuji, E.; Kiyose, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Noda, K.; Ideishi, M.; Inoue, J.; Tomita, K.; et al. Genetic analysis of the epithelial sodium channel in Liddle’s syndrome. J. Hypertens. 1998, 16, 1131–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeda, I.; Horii, M.; Yamano, S.; Kawamoto, A.; Shiiki, H.; Fujimoto, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Doi, K. Case of nonfamilial idiopathic Liddle syndrome. Nihon Naika Gakkai Zasshi 1999, 88, 339–341. (In Japanese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.J.; Zhang, K.X.; Zhu, D.L.; He, X.; Han, Z.Y.; Zhan, Y.M.; Yang, L.W. Diagnosis of Liddle syndrome by genetic analysis of β and γ subunits of epithelial sodium channel—A report of five affected family members. J. Hypertens. 2001, 19, 885–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashita, Y.; Koga, M.; Takeda, Y.; Enomoto, N.; Uchida, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Yamano, S.; Dohi, K.; Marumo, F.; Sasaki, S. Two sporadic cases of Liddle’s syndrome caused by de novo ENaC mutations. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2001, 37, 499–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büyükkaragöz, B.; Yilmaz, A.C.; Karcaaltincaba, D.; Ozdemir, O.; Ludwig, M. Liddle syndrome in a Turkish family with heterogeneous phenotypes. Pediatr. Int. 2016, 58, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciechanowicz, A.; Dolezel, Z.; Placha, G.; Starha, J.; Góra, J.; Gaciong, Z.; Brodkiewicz, A.; Adler, G. Liddle syndrome caused by P616R mutation of the epithelial sodium channel β subunit. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2005, 20, 837–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furuhashi, M.; Kitamura, K.; Adachi, M.; Miyoshi, T.; Wakida, N.; Ura, N.; Shikano, Y.; Shinshi, Y.; Sakamoto, K.; Hayashi, M.; et al. Liddle’s syndrome caused by a novel mutation in the proline-rich PY motif of the epithelial sodium channel β-subunit. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 90, 340–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogdanović, R.; Kuburović, V.; Stajić, N.; Mughal, S.S.; Hilger, A.; Ninić, S.; Prijić, S.; Ludwig, M. Liddle syndrome in a Serbian family and literature review of underlying mutations. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2012, 171, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.P.; Gao, L.G.; Zhou, X.L.; Wu, H.Y.; Zhang, L.; Wen, D.; Li, Y.H.; Liu, Y.X.; Tian, T.; Fan, X.H.; et al. Genetic diagnosis of Liddle’s syndrome by mutation analysis of SCNN1B and SCNN1G in a Chinese family. Chin. Med. J. 2012, 125, 1401–1404. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yang, K.Q.; Lu, C.X.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Jiang, X.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, X.L. A novel frameshift mutation of epithelial sodium channel β-subunit leads to Liddle syndrome in an isolated case. Clin. Endocrinol. 2015, 82, 611–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamura, H.; Schild, L.; Enomoto, N.; Matsui, N.; Marumo, F.; Rossier, B.C. Liddle disease caused by a missense mutation of β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel gene. J. Clin. Investig. 1996, 97, 1780–1784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Kong, L.Q.; Huang, D.J. Liddle syndrome complicating with nonfunctional adrenal cortical adenoma: A case report. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi 2017, 45, 331–332. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Zheng, D.; Hui, R. A novel epithelial sodium channel γ-subunit de novo frameshift mutation leads to Liddle syndrome. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 801–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterov, V.; Krueger, B.; Bertog, M.; Dahlmann, A.; Palmisano, R.; Korbmacher, C. In Liddle Syndrome, Epithelial sodium channel is hyperactive mainly in the early part of the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron. Hypertension 2016, 67, 1256–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nesterov, V.; Dahlmann, A.; Krueger, B.; Bertog, M.; Loffing, J.; Korbmacher, C. Aldosterone-dependent and -independent regulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in mouse distal nephron. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2012, 303, F1289–F1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.S.; Wang, H.W.; Reza, E.; Whitman, S.C.; Tuana, B.S.; Leenen, F.H. Distribution of epithelial sodium channels and mineralocorticoid receptors in cardiovascular regulatory centers in rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 289, R1787–R1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huysse, J.W.; Amin, M.S.; Yang, B.; Leenen, F.H. Salt-induced hypertension in a mouse model of Liddle syndrome is mediated by epithelial sodium channels in the brain. Hypertension 2012, 60, 691–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Hua, Q.; Chen, Y.; Cai, Y.; Liu, R. Association of epithelial sodium channel β-subunit common polymorphism with essential hypertension families in a Chinese population. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 2014, 70, 1277–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, H.S.; Hong, K.W.; Lim, J.E.; Hwang, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Shin, C.; Park, H.K.; Oh, B. Genetic variations in the sodium balance-regulating genes ENaC, NEDD4L, NDFIP2 and USP2 influence blood pressure and hypertension. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2010, 33, 15–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persu, A.; Barbry, P.; Bassilana, F.; Houot, A.M.; Mengual, R.; Lazdunski, M.; Corvol, P.; Jeunemaitre, X. Genetic analysis of the β subunit of the epithelial Na+ channel in essential hypertension. Hypertension 1998, 32, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, E.H.; Dong, Y.B.; Sagnella, G.A.; Rothwell, M.; Onipinla, A.K.; Markandu, N.D.; Cappuccio, F.P.; Cook, D.G.; Persu, A.; Corvol, P.; et al. Association of hypertension with T594M mutation in β subunit of epithelial sodium channels in black people resident in London. Lancet 1998, 351, 1388–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.B.; Zhu, H.D.; Baker, E.H.; Sagnella, G.A.; MacGregor, G.A.; Carter, N.D.; Wicks, P.D.; Cook, D.G.; Cappuccio, F.P. T594M and G442V polymorphisms of the sodium channel β subunit and hypertension in a black population. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2001, 15, 425–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rayner, B.L.; Owen, E.P.; King, J.A.; Soule, S.G.; Vreede, H.; Marais, D.; Davidson, J.S. A new mutation, R563Q, of the β subunit of the epithelial sodium channel associated with low-renin. Low-aldosterone hypertension. J. Hypertens. 2003, 21, 921–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, Q.; Menon, A.G.; Stockand, J.D. Functional polymorphisms in the α-subunit of the human epithelial Na+ channel increase activity. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2006, 290, F821–F827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, Z.Y.; Stebbing, M.; Ellis, J.A.; Lamantia, A.; Harrap, S.B. Genetic linkage of β and γ subunits of epithelial sodium channel to systolic blood pressure. Lancet 1999, 353, 1222–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lange, M.; Spector, T.D.; Andrew, T. Genome-wide scan for blood pressure suggests linkage to chromosome 11, and replication of loci on 16, 17, and 22. Hypertension 2004, 44, 872–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büsst, C.J.; Scurrah, K.J.; Ellis, J.A.; Harrap, S.B. Selective genotyping reveals association between the epithelial sodium channel γ-subunit and systolic blood pressure. Hypertension 2007, 50, 672–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Büsst, C.J.; Bloomer, L.D.; Scurrah, K.J.; Ellis, J.A.; Barnes, T.A.; Charchar, F.J.; Braund, P.; Hopkins, P.N.; Samani, N.J.; Hunt, S.C.; et al. The epithelial sodium channel γ-subunit gene and blood pressure: Family based association, renal gene expression, and physiological analyses. Hypertension 2011, 58, 1073–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pagani, L.; Diekmann, Y.; Sazzini, M.; De Fanti, S.; Rondinelli, M.; Farnetti, E.; Casali, B.; Caretto, A.; Novara, F.; Zuffardi, O.; et al. Three reportedly unrelated families with liddle syndrome inherited from a common ancestor. Hypertension 2018, 71, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bubien, J.K. Epithelial Na+ channel (ENaC), hormones, and hypertension. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 23527–23531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unwin, R.J.; Luft, F.C.; Shirley, D.G. Pathophysiology and management of hypokalemia: A clinical perspective. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amlal, H.; Krane, C.M.; Chen, Q.; Soleimani, M. Early polyuria and urinary concentrating defect in potassium deprivation. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2000, 279, F655–F663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepersack, T.; Allegre, S.; Jeunemaître, X.; Leeman, M.; Praet, J.P. Liddle syndrome phenotype in an octogenarian. J. Clin. Hypertens. 2015, 17, 59–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monticone, S.; Buffolo, F.; Tetti, M.; Veglio, F.; Pasini, B.; Mulatero, P. Genetics in endocrinology: The expanding genetic horizon of primary aldosteronism. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 178, R101–R111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulatero, P.; di Cella, S.M.; Williams, T.A.; Milan, A.; Mengozzi, G.; Chiandussi, L.; Gomez-Sanchez, C.E.; Veglio, F. Glucocorticoid remediable aldosteronism: Low morbidity and mortality in a four-generation italian pedigree. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 87, 3187–3191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulatero, P.; Verhovez, A.; Morello, F.; Veglio, F. Diagnosis and treatment of low-renin hypertension. Clin. Endocrinol. 2007, 67, 324–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lurbe, E.; Agabiti-Rosei, E.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dominiczak, A.; Erdine, S.; Hirth, A.; Invitti, C.; Litwin, M.; Mancia, G.; Pall, D.; et al. 2016 European Society of Hypertension guidelines for the management of high blood pressure in children and adolescents. J. Hypertens. 2016, 34, 1887–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Study | Country | Families (n) | Patients (Genetic/Clinical Diagnosis) | Sex (M/F, not Available) | Hypertension (n/tot Available) | Spontaneous Hypokalemia (n/tot Available) | Low Aldosterone (n/tot Available) | Reported Symptoms/TOD/CV Events/Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCNN1A mutations (NM_001038.5→NP_001029.1 isoform 1) | ||||||||
| p.Cys479Arg | ||||||||
| Salih M. (2017) [26] | The Netherlads | 1 | 2/0 | 1/1 | 1/2 | 1/1 | 2/2 | None |
| SCNN1B mutations (NM_000336.2→NP_000327.2) | ||||||||
| p.Gln564* | ||||||||
| Liu K. (2017) [27] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | Stroke |
| p.Arg566* | ||||||||
| Shimkets R.A. (1994) [7] * | USA | 2 | 19/4 | 10/8, 1 | 19/19 | 3/3 | 3/3 | Renal failure, history of juvenile CV accidents |
| Melander O. (1998) [28] * | Sweden | 1 | 6/0 | 2/4 | 4/6 | 2/6 | 3/5 | None |
| Kyuma M. (2001) [29] * | Japan | 1 | 3/0 | 2/1 | 3/3 | 2/3 | 0/1 | Muscular weakness, retinopathy |
| Shi J.Y. (2010) [30] * | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | History of stroke |
| Gong L. (2014) [31] | China | 1 | 3/0 | 2/1 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/1 | LVH |
| Wang L.P. (2015) [32] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | None |
| Polfus L.M. (2016) [33] | USA | 1 | 2/0 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 1/1 | 1/1 | Asthenia, palpitation, LVH, proteinuria |
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] * | China | 3 | 3/6 | ½ | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 | Dizziness, headache, history of SD and stroke |
| Liu K. (2017) [27] | China | 1 | 3/0 | 2/1 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 | LVH |
| p.Gln568* | ||||||||
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | Dizziness, headache |
| p. Ser570Tyrfs*589 | ||||||||
| Freerks R. (2017) [35] | South Africa (Black origin) | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | Headache, muscle fatigue, exertional dyspnoea, retinopathy, LVH |
| p.Pro575Argfs*591 | ||||||||
| Phoojaroenchanachai M. (2015) [36] | Thailand | 1 | 2/1 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 1/1 | Lightheadedness, proximal muscle weakness |
| p. Ala579Leufs*582 | ||||||||
| Jeunemaitre X. (1997) [37] | France | 1 | 4/0 | 3/1 | 4/4 | 4/4 | 4/4 | History of SD |
| p.Gln591* | ||||||||
| Shimkets R.A. (1994) [7] * | USA | 1 | 1/0 | 0/0, 1 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | n.a. |
| p.Thr594Hisfs*607 | ||||||||
| Shimkets R.A. (1994) [7] * | USA | 1 | 1/0 | 0/0, 1 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | n.a. |
| p.Ala595Argfs*607 | ||||||||
| Findling J.W. (1997) [38] * | USA | 1 | 8/2 | 1/7 | 5/8 | 2/7 | 7/7 | Myocardial infarction |
| p.Arg597Profs*607 | ||||||||
| Inoue T. (1998) [39] | Japan | 1 | 2/4 | 0/2 | 2/2 | 1/2 | 2/2 | None |
| Jackson S.N. (1998) [40] * | UK | 1 | 4/1 | 3/1 | 3/4 | 1/2 | 4/4 | None |
| Nakano Y. (2002) [41] * | Japan | 1 | 1/0 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | None |
| Gong L. (2014) [31] | China | 1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | Dizziness, chronic kidney disease, SD, history of stroke |
| Awadalla M. (2017) [42] | USA (Black origin) | 1 | 1/6 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | Proteinuria |
| p.Arg597Alafs*675 | ||||||||
| Shimkets R.A. (1994) [7] * | USA | 1 | 2/0 | 0/2 | 2/2 | 0/0 | 0/0 | n.a. |
| p.Thr601Aspfs*607 | ||||||||
| Ma X. (2001) [43] | China | 1 | 8/0 | 5/3 | 8/8 | 4/8 | 8/8 | Fatigue, headache, nycturia, history of cerebral hemorrhage |
| Hiltunen T.P. (2002) [44] | Finland | 1 | 4/0 | 1/3 | 3/4 | 1/1 | 0/0 | None |
| p.Pro603Alafs*607 | ||||||||
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] | China | 2 | 3/0 | 3/0 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 | Headache, dizziness, history of stroke and SD |
| p.Pro616Leu | ||||||||
| Gao L. (2013) [45] * | China | 1 | 7/3 | 5/2 | 7/7 | 7/7 | 0/7 | Tachycardia, LVH, history of stroke |
| Liu K. (2017) [27] | China | 3 | 7/0 | 2/5 | 7/7 | 5/7 | 1/7 | LVH |
| Kuang Z.M. (2017) [46] | China | 1 | 2/1 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 1/2 | 0/1 | Muscular weakness, history of cerebral hemorrhage |
| p.Pro617His | ||||||||
| Sawathiparnich P. (2009) [47] * | Thailand | 1 | 4/2 | 0/4 | 4/4 | 1/2 | 3/3 | Headache, LVH |
| p.Pro617Leu | ||||||||
| Rossi E. (2008) [48] | Italy | 1 | 1/2 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | LVH |
| Rossi E. (2011) [49] | Italy | 1 | 4/4 | 2/2 | 4/4 | 0/4 | 4/4 | LVH |
| Caretto A. (2014) [50] | Italy | 1 | 4/1 | 1/3 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 2/2 | Headache, visual scotoma, fetal growth retardation, history of stroke and cerebral hemorrhage |
| p.Pro617Ser | ||||||||
| Inoue J. (1998) [51] * | Japan | 1 | 4/2 | 4/0 | 1/4 | 3/4 | 0/0 | None |
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | Headache, dizziness |
| p.Pro617Serfs*621 | ||||||||
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 0/1 | 0/1 | Headache, dizziness |
| p.Pro618His | ||||||||
| Freundlich M. (2005) [52] | USA (Black) | 1 | 2/0 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 0/1 | 1/1 | None |
| Wang W. (2006) [53] * | China | 1 | 5/0 | 2/3 | 4/5 | 5/5 | 1/1 | Muscular weakness |
| Yang K.Q. (2018) [54] | China | 1 | 6/2 | 3/3 | 4/6 | 4/6 | 6/6 | Syncope, microalbuminuria, LVH, headache, history of stroke |
| p.Pro618Leu | ||||||||
| Hansson J.H. (1995) [55] * | USA (Black origin) | 1 | 3/0 | 1/2 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 2/2 | Stroke |
| Uehara Y. (1998) [56] * | Japan | 1 | 1/0 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | None |
| Takeda I. (1999) [57] * | Japan | 1 | 1/0 | 0/0, 1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/0 | n.a. |
| Gao P.J.(2001) [58] * | China | 1 | 5/2 | 4/1 | 4/5 | 1/5 | 1/5 | History of stroke and SD |
| Yamashita Y. (2001) [59] * | Japan | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | n.a. |
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] | China | 2 | 2/0 | 2/0 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 0/2 | None |
| Büyükkaragöz B. (2016) [60] | Turkey | 1 | 5/0 | 1/4 | 5/5 | 3/5 | 4/4 | Headache, dizziness, LVH, retinopathy, history of SD |
| This manuscript | Italy | 1 | 1/1 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | History of SD |
| p.Pro618Arg | ||||||||
| Ciechanowicz A. (2005) [61] * | Czech Republic | 1 | 2/0 | 2/0 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 2/2 | None |
| Furuhashi M. (2005) [62] * | Japan | 1 | 2/0 | 0/2 | 1/2 | 2/2 | 2/2 | Asthenia |
| p.Pro618Ser | ||||||||
| Uehara Y. (1998) [56] * | Japan | 1 | 2/2 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 2/2 | 1/2 | None |
| Bogdanović R. (2012) [63] | Serbia | 1 | 3/3 | 2/1 | 3/3 | 1/3 | 3/3 | LVH, history of SD |
| Wang L.P. (2012) [64] * | China | 1 | 3/0 | 0/3 | 3/3 | 3/3 | 0/3 | None |
| p. Asn619Glnfs*621 | ||||||||
| Yang K.Q. (2015) [65] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | None |
| Cui Y. (2017) [34] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | Headache, dizziness, history of stroke |
| Liu K. (2017) [27] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 0/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | Mild impairment of renal function |
| p.Tyr620His | ||||||||
| Tamura H. (1996) [66] * | Japan | 1 | 5/0 | 3/2 | 5/5 | 2/4 | 4/4 | Chronic kidney disease |
| SCNN1G mutations (NM_001039.3→NP_001030.2) | ||||||||
| p.Asn530Ser | ||||||||
| Hiltunen T.P. (2002) [44] | Finland | 1 | 2/0 | 1/1 | 2/2 | 1/2 | 0/1 | None |
| p.Gln567* | ||||||||
| Shi J.Y. (2010) [30] | China | 1 | 3/0 | 2/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | n.a. |
| Zhang P. (2017) [67] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 1/1 | Muscular weakness, polyuria, polydipsia, LVH |
| p.Glu571* | ||||||||
| Wang L.P. (2015) [32] | China | 1 | 6/1 | 2/4 | 5/6 | 6/6 | 0/6 | History of stroke |
| Liu K. (2017) [27] | China | 1 | 5/0 | 1/4 | 5/5 | 5/5 | 0/5 | Stroke, aortic stenosis |
| p.Trp573* | ||||||||
| Hansson J.H. (1995) [18] * | Japan | 1 | 6/0 | 2/4 | 6/6 | 5/6 | 4/6 | Leg numbness |
| p.Trp575* | ||||||||
| Yamashita Y. (2001) [59] * | Japan | 1 | 1/0 | 0/0, 1 | 1/1 | 0/0 | 0/0 | n.a. |
| p.Glu583Aspfs*585 | ||||||||
| Wang Y. (2007) [68] | China | 1 | 1/0 | 1/0 | 1/1 | 1/1 | 0/1 | None |
| TOTAL | ||||||||
| - | 72 | 200/51 | 97/98, 5 | 182/197 (92,4%) | 117/163 (71,8%) | 85/146 (58,2%) | - | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tetti, M.; Monticone, S.; Burrello, J.; Matarazzo, P.; Veglio, F.; Pasini, B.; Jeunemaitre, X.; Mulatero, P. Liddle Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Description of a New Case. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030812
Tetti M, Monticone S, Burrello J, Matarazzo P, Veglio F, Pasini B, Jeunemaitre X, Mulatero P. Liddle Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Description of a New Case. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(3):812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030812
Chicago/Turabian StyleTetti, Martina, Silvia Monticone, Jacopo Burrello, Patrizia Matarazzo, Franco Veglio, Barbara Pasini, Xavier Jeunemaitre, and Paolo Mulatero. 2018. "Liddle Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Description of a New Case" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 3: 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030812
APA StyleTetti, M., Monticone, S., Burrello, J., Matarazzo, P., Veglio, F., Pasini, B., Jeunemaitre, X., & Mulatero, P. (2018). Liddle Syndrome: Review of the Literature and Description of a New Case. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(3), 812. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19030812