Ixeris dentata Extract Increases Salivary Secretion through the Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in a Diabetes-Induced Xerostomia Rat Model
Abstract
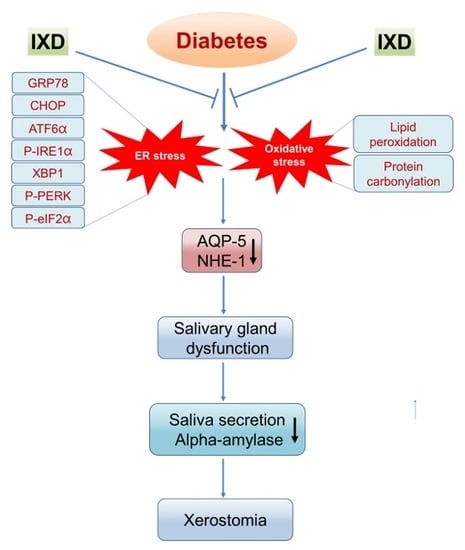
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Efficacy of Active Compound from IXD Extracts and Effect on Amylase Expression
2.2. IXD Extracts Increase Amylase Synthesis and Secretion in High Concentration Glucose Treated Human Salivary Gland Cells
2.3. The Effects of the IXD Extract on Salivary Parameters
2.4. The Effects of the IXD Extract on Salivary Amylase Expression
2.5. The IXD Extract Increases Fluid Secretion through the Activation of AQP5 and NHE1 in the Submandibular Gland
2.6. The IXD Extract Regulates ER Stress-Induced Hyposalivation in Diabetic Rats
2.7. The IXD Extract Improves Protein Folding and Reduces Oxidative Stress Induced by Diabetes
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and Preparation
4.2. Quantitation of Pure Compound Using HPLC-DAD
4.3. Chemicals and Reagents
4.4. Cell Culture and Treatment
4.5. Animals
4.6. Experimental Design
4.7. Induction and Assessment of Blood and Saliva Glucose Level
4.8. Collection of Total Saliva
4.9. Salivary Protein Concentration Measurement
4.10. Amylase Assay
4.11. Immunoblotting
4.12. Immunoprecipitation
4.13. Haematoxylin and Eosin Stain
4.14. Immunohistochemistry
4.15. Double Labelled Immunofluorescence
4.16. TBARS Assay
4.17. Salivary Carbonyl Assay
4.18. Statistical Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| STZ | Streptozotocin |
| DM | Diabetes mellitus |
| IXD | Ixeris dentata |
| AQP5 | Aquaporin-5 |
| ER | Endoplasmic reticulum |
| GCT | Granular convoluted tubule |
| NHE1 | Sodium/Hydrogen exchanger-1 |
| GRP78/BiP | Glucose regulated protein-78 kDA/Binding immunoglobulin protein |
| GADD153/CHOP | Growth arrest- and DNA damage-inducible gene 153/CCAAT enhancer binding protein homologous protein |
| p-eIF2α | Phosphorylated eukaryotic translational initial factor 2 alpha |
| p-PERK | Phosphorylated protein kinase R like endoplasmic reticulum kinase |
| ATF6α | Activating transcription factor 6 alpha |
| p-IRE1α | Phosphorylated inositol-requiring enzyme 1 alpha |
| sXBP1 | Spliced X box binding protein 1 |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| PDI | Protein disulphide isomerase |
| ERO1α | Endoplasmic reticulum oxidoreductin 1 alpha |
| CBB | Coomassie Brilliant Blue |
| NaCl | Sodium Chloride |
| ERAD | Endoplasmic reticulum associated protein degradation |
| EDEM | Endoplasmic reticulum degradation enhancing alpha mannosidase like protein |
| SERCA | Sarco/endoplasmic-reticulum Ca2+-ATPase |
| HSP | Heat shock protein |
| GSH | Glutathione |
| IP | Intraperitoneal |
| SDS-PAGE | Sodium dodecyl sulphate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis |
| PVDF | Polyvinylidene fluoride |
| FITC | Fluorescein isothiocyanate |
| TRITC | Tetramethylrhodamine isothiocyanate |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde |
| TBARS | Thiobarbituric acid reactive substances |
| SEM | Standard error mean |
| ANOVA | Analysis of variance |
References
- Bhattarai, K.R.; Junjappa, R.; Handigund, M.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. The imprint of salivary secretion in autoimmune disorders and related pathological conditions. Autoimmun. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanci, A. Ten Cate’s Oral Histology: Development, Structure, and Function; Elsevier Health Sciences; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Jeon, Y.D.; Kee, J.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Han, Y.H.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, S.J.; Um, J.Y.; Hong, S.H. Effects of Ixeris dentata water extract and caffeic acid on allergic inflammation in vivo and in vitro. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 15, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhattarai, K.R.; Lee, S.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Ixeris dentata extract regulates salivary secretion through the activation of aquaporin-5 and prevents diabetes-induced xerostomia. J. Exp. Pharmacol. 2017, 9, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, S.H.; Park, K.; Chae, H.J.; Kim, H.R. Ixeris dentata-induced regulation of amylase synthesis and secretion in glucose-treated human salivary gland cells. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2013, 62, 739–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mekahli, D.; Bultynck, G.; Parys, J.B.; De Smedt, H.; Missiaen, L. Endoplasmic-reticulum calcium depletion and disease. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedirko, N.V.; Kruglikov, I.A.; Kopach, O.V.; Vats, J.A.; Kostyuk, P.G.; Voitenko, N.V. Changes in functioning of rat submandibular salivary gland under streptozotocin-induced diabetes are associated with alterations of Ca2+ signaling and Ca2+ transporting pumps. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1762, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ambudkar, I.S. Polarization of calcium signaling and fluid secretion in salivary gland cells. Curr. Med. Chem. 2012, 19, 5774–5781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arhakis, A.; Karagiannis, V.; Kalfas, S. Salivary alpha-amylase activity and salivary flow rate in young adults. Open Dent. J. 2013, 7, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchbhai, A.S.; Degwekar, S.S.; Bhowte, R.R. Estimation of salivary glucose, salivary amylase, salivary total protein and salivary flow rate in diabetics in India. J. Oral Sci. 2010, 52, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.K.; Cuzzort, L.M.; McKean, R.K.; Allen, E.D. Effects of diabetes and insulin on alpha-amylase messenger RNA levels in rat parotid glands. J. Dent. Res. 1990, 69, 1500–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoh, K.; Narita, T.; Matsuki-Fukushima, M.; Okabayashi, K.; Ito, T.; Senpuku, H.; Sugiya, H. E2f1-deficient NOD/SCID mice have dry mouth due to a change of acinar/duct structure and the down-regulation of AQP5 in the salivary gland. Pflugers Arch. 2013, 465, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.; Yuan, Z.; Inoue, N.; Cho, G.; Shono, M.; Ishikawa, Y. Abnormal subcellular localization of AQP5 and downregulated AQP5 protein in parotid glands of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1810, 543–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, S.; Maruyama, J.; Watanabe, T.; Ito, Y.; Arioka, M.; Kitamoto, K. In vivo imaging of endoplasmic reticulum and distribution of mutant alpha-amylase in Aspergillus Oryzae. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2010, 47, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaufman, R.J. Orchestrating the unfolded protein response in health and disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2002, 110, 1389–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Huang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zheng, P.; Chen, Z. Expression of autophagy and ER stress-related proteins in primary salivary adenoid cystic carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2012, 208, 635–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhotra, J.D.; Kaufman, R.J. The endoplasmic reticulum and the unfolded protein response. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2007, 18, 716–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnamoorthy, T.; Pavitt, G.D.; Zhang, F.; Dever, T.E.; Hinnebusch, A.G. Tight binding of the phosphorylated alpha subunit of initiation factor 2 (eIF2alpha) to the regulatory subunits of guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B is required for inhibition of translation initiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 5018–5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walter, P.; Ron, D. The unfolded protein response: From stress pathway to homeostatic regulation. Science 2011, 334, 1081–1086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baban, B.; Liu, J.Y.; Abdelsayed, R.; Mozaffari, M.S. Reciprocal relation between GADD153 and Del-1 in regulation of salivary gland inflammation in Sjogren syndrome. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 95, 288–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baban, B.; Liu, J.Y.; Mozaffari, M.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress response and inflammatory cytokines in type 2 diabetic nephropathy: Role of indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase and programmed death-1. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2013, 94, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katsiougiannis, S.; Tenta, R.; Skopouli, F.N. Endoplasmic reticulum stress causes autophagy and apoptosis leading to cellular redistribution of the autoantigens Ro/Sjogren’s syndrome-related antigen A (SSA) and La/SSB in salivary gland epithelial cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 244–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Cardozo, A.K.; Cnop, M. The role for endoplasmic reticulum stress in diabetes mellitus. Endocr. Rev. 2008, 29, 42–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrera, M.J.; Aguilera, S.; Castro, I.; Cortes, J.; Bahamondes, V.; Quest, A.F.G.; Molina, C.; Gonzalez, S.; Hermoso, M.; Urzua, U.; et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines enhance ERAD and ATF6alpha pathway activity in salivary glands of Sjogren’s syndrome patients. J. Autoimmun. 2016, 75, 68–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sepúlveda, D.; Aguilera, S.; Barrera, M.-J.; Bahamondes, V.; Castro, I.; Molina, C.; Cortés, J.; González, S.; Leyton, C.; González, M.-J. SAT0380 Impaired Ire1Alpha/XBP-1 Pathway is Associated with Glandular Dysfunction in SjÖgren’s Syndrome. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74 (Suppl. 2), 796–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.; Talwar, P.; Parimisetty, A.; Lefebvre d’Hellencourt, C.; Ravanan, P. A molecular web: Endoplasmic reticulum stress, inflammation, and oxidative stress. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Korennykh, A.V.; Behrman, S.L.; Walter, P. Mammalian endoplasmic reticulum stress sensor IRE1 signals by dynamic clustering. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 16113–16118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, J.H.; Li, H.; Yasumura, D.; Cohen, H.R.; Zhang, C.; Panning, B.; Shokat, K.M.; Lavail, M.M.; Walter, P. IRE1 signaling affects cell fate during the unfolded protein response. Science 2007, 318, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.R.; Lee, H.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Kim, H.K.; Kim, N.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Ixeris dentata decreases ER stress and hepatic lipid accumulation through regulation of ApoB secretion. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2014, 42, 639–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karjalainen, K.M.; Knuuttila, M.L.; Kaar, M.L. Salivary factors in children and adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Pediatr. Dent. 1996, 18, 306–311. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sreebny, L.M.; Yu, A.; Green, A.; Valdini, A. Xerostomia in diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 1992, 15, 900–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vreugdenhil, A.P.; Nieuw Amerongen, A.V.; de Lange, G.L.; Roukema, P.A. Localization of amylase and mucins in the major salivary glands of the mouse. Histochem. J. 1982, 14, 767–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delporte, C. Aquaporins in salivary glands and pancreas. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2014, 1840, 1524–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, K.; Evans, R.L.; Watson, G.E.; Nehrke, K.; Richardson, L.; Bell, S.M.; Schultheis, P.J.; Hand, A.R.; Shull, G.E.; Melvin, J.E. Defective fluid secretion and NaCl absorption in the parotid glands of Na+/H+ exchanger-deficient mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 27042–27050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.L.; Bell, S.M.; Schultheis, P.J.; Shull, G.E.; Melvin, J.E. Targeted disruption of the Nhe1 gene prevents muscarinic agonist-induced up-regulation of Na(+)/H(+) exchange in mouse parotid acinar cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 29025–29030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gilbert, H.F. Protein disulfide isomerase and assisted protein folding. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 29399–293402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevier, C.S.; Kaiser, C.A. Ero1 and redox homeostasis in the endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, D.; Ship, J.A. The effect of dehydration on parotid salivary gland function. Spec. Care Dentist. 1997, 17, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walsh, N.P.; Montague, J.C.; Callow, N.; Rowlands, A.V. Saliva flow rate, total protein concentration and osmolality as potential markers of whole body hydration status during progressive acute dehydration in humans. Arch. Oral Biol. 2004, 49, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, M.E.; Colloca, M.E.; Paez, R.G.; Schallmach, J.N.; Koss, M.A.; Chervonagura, A. Salivary characteristics of diabetic children. Braz. Dent. J. 2003, 14, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandel, A.L.; Breslin, P.A. High endogenous salivary amylase activity is associated with improved glycemic homeostasis following starch ingestion in adults. J. Nutr. 2012, 142, 853–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Young, H.S.; Kim, B.W. Hypoglycemic and hypolipemic effects of Ixeris dentata in diabetic rats. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 1990, 13, 269–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leborgne-Castel, N.; Jelitto-Van Dooren, E.P.; Crofts, A.J.; Denecke, J. Overexpression of BiP in tobacco alleviates endoplasmic reticulum stress. Plant Cell 1999, 11, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Delporte, C.; Steinfeld, S. Distribution and roles of aquaporins in salivary glands. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1758, 1061–1070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oehlke, O.; Sprysch, P.; Rickmann, M.; Roussa, E. Na+/H+ exchanger isoforms are differentially regulated in rat submandibular gland during acid/base disturbances in vivo. Cell Tissue Res. 2006, 323, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelling, J.R.; Abu Jawdeh, B.G. Regulation of cell survival by Na+/H+ exchanger-1. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F625–F632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Liu, K.J.; Xiang, B. Effect of Phenylephrine Pretreatment on the Expressions of Aquaporin 5 and c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase in Irradiated Submandibular Gland. Radiat. Res. 2015, 183, 693–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sundar Rajan, S.; Srinivasan, V.; Balasubramanyam, M.; Tatu, U. Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress & diabetes. Indian J. Med. Res. 2007, 125, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schroder, M.; Kaufman, R.J. ER stress and the unfolded protein response. Mutat. Res. 2005, 569, 29–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanjore, H.; Lawson, W.E.; Blackwell, T.S. Endoplasmic reticulum stress as a pro-fibrotic stimulus. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1832, 940–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giusti, L.; Baldini, C.; Ciregia, F.; Giannaccini, G.; Giacomelli, C.; De Feo, F.; Delle Sedie, A.; Riente, L.; Lucacchini, A.; Bazzichi, L.; et al. Is GRP78/BiP a potential salivary biomarker in patients with rheumatoid arthritis? Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2010, 4, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, S.A.; You, S.; Yoon, H.J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.S.; Lee, K.; Ahn, J.H.; Hwang, D.; Lee, A.S.; Kim, K.J.; et al. A novel pathogenic role of the ER chaperone GRP78/BiP in rheumatoid arthritis. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 871–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagler, R.; Marmary, Y.; Fox, P.C.; Baum, B.J.; Har-El, R.; Chevion, M. Irradiation-induced damage to the salivary glands: The role of redox-active iron and copper. Radiat. Res. 1997, 147, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okabayashi, K.; Narita, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Sugiya, H. Effect of Oxidative Stress on Secretory Function in Salivary Gland Cells. In Oxidative Stress-Environmental Induction and Dietary Antioxidants; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, S.H.; Sung, T.H.; Kim, M.R. Ixeris dentata extract maintains glutathione concentrations in mouse brain tissue under oxidative stress induced by kainic acid. J. Med. Food 2003, 6, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.G.; Ohana, E.; Park, H.W.; Yang, D.; Muallem, S. Molecular mechanism of pancreatic and salivary gland fluid and HCO3 secretion. Physiol. Rev. 2012, 92, 39–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, H.Y.; Lee, G.H.; Bhattarai, K.R.; Park, B.H.; Koo, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Chae, H.J. Bax Inhibitor-1 regulates hepatic lipid accumulation via ApoB secretion. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bhattarai, K.R.; Lee, H.-Y.; Kim, S.-H.; Kim, H.-R.; Chae, H.-J. Ixeris dentata Extract Increases Salivary Secretion through the Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in a Diabetes-Induced Xerostomia Rat Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041059
Bhattarai KR, Lee H-Y, Kim S-H, Kim H-R, Chae H-J. Ixeris dentata Extract Increases Salivary Secretion through the Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in a Diabetes-Induced Xerostomia Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041059
Chicago/Turabian StyleBhattarai, Kashi Raj, Hwa-Young Lee, Seung-Hyun Kim, Hyung-Ryong Kim, and Han-Jung Chae. 2018. "Ixeris dentata Extract Increases Salivary Secretion through the Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in a Diabetes-Induced Xerostomia Rat Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041059
APA StyleBhattarai, K. R., Lee, H. -Y., Kim, S. -H., Kim, H. -R., & Chae, H. -J. (2018). Ixeris dentata Extract Increases Salivary Secretion through the Regulation of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in a Diabetes-Induced Xerostomia Rat Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1059. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041059