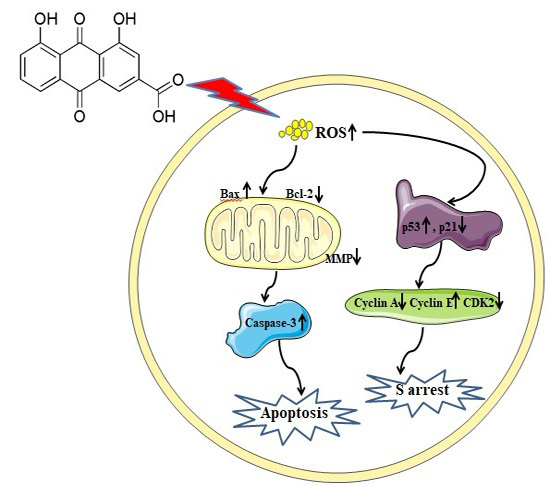
Rhein Induces Cell Death in HepaRG Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Rhein Induces Cytotoxicity in HepaRG Cells
2.2. Rhein Induces Apoptosis in HepaRG Cells
2.3. Effects of Rhein on Intracellular ROS and GSH Levels
2.4. Rhein Decreases MMP in HepaRG Cells
2.5. Rhein Elicits DNA Fragmentation and S Phase Cell Cycle Arrest in HepaRG Cells
2.6. Effects of Rhein on Levels of Apoptosis-Regulated Proteins in HepaRG Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Cultures and Treatment
4.3. Cell Viability Assay
4.4. Morphological Apoptosis
4.5. Apoptosis Analysis
4.6. Measurement of Intracellular ROS and GSH
4.7. Measurement of Mitochondrial Membrane Potential
4.8. Cell Cycle Analysis
4.9. Western Blot Analysis
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, M.; Li, Y.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, H. Metabolic Activation of Rhein: Insights into the Potential Toxicity Induced by Rhein-Containing Herbs. J. Agric. Food. Chem. 2016, 28, 5742–5750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Fujii, M.; Hou, D.X. Rhein induces apoptosis in HL-60 cells via reactive oxygen species-independent mitochondrial death pathway. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2003, 418, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, P.; Huang, Z.; Chen, G. Rhein induces apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7402 cells. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2008, 36, 805–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, S.J.; Huang, S.H.; Lin, Y.J.; Tsou, Y.Y.; Lin, C.W. Antiviral activity of Rheum palmatum methanol extract and chrysophanol against Japanese encephalitis virus. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2014, 37, 1117–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, X.; Fang, L.; Liu, F.; Cai, R.; Peng, C.; Qi, Y. Rhein exerts pro- and anti-inflammatory actions by targeting IKKβ inhibition in LPS-activated macrophages. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 72, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smolarz, H.D.; Swatko-Ossor, M.; Ginalska, G.; Medyńska, E. Antimycobacterial effect of extract and its components from Rheum rhaponticum. J. AOAC Int. 2013, 96, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.Y.; Chiang, S.Y.; Lin, J.G.; Yang, J.S.; Ma, Y.S.; Liao, C.L.; Lai, T.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Chung, J.G. Emodin, aloe-emodin and rhein induced DNA damage and inhibited DNA repair gene expression in SCC-4 human tongue cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.L.; Chung, J.G.; Lu, Y.C.; Yang, C.Y.; Chen, S.S. Rhein inhibits invasion and migration of human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells in vitro by down-regulation of matrix metalloproteinases-9 and vascular endothelial growth factor. Oral Oncol. 2009, 45, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsia, T.C.; Yang, J.S.; Chen, G.W.; Chiu, T.H.; Lu, H.F.; Yang, M.D.; Yu, F.S.; Liu, K.C.; Lai, K.C.; Lin, C.C.; et al. The roles of endoplasmic reticulum stress and Ca2+ on rhein-induced apoptosis in A-549 human lung cancer cells. Anticancer Res. 2009, 29, 309–318. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xu, Y.; Lei, B.; Wang, W.; Ge, X.; Li, J. Rhein induces apoptosis of human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cells via an intrinsic mitochondrial pathway. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2012, 45, 1052–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.L.; Chen, S.S.; Lu, Y.C.; Liang, R.Y.; Ho, Y.T.; Yang, C.Y.; Chung, J.G. Rhein induces apoptosis through induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress and Ca2+-dependent mitochondrial death pathway in human nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 3313–3322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Xie, L.; Chen, M.; Chen, L. Effects of an astragalus polysaccharide and rhein combination on apoptosis in rats with chronic renal failure. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 271862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Li, J.; Zhu, S.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Wan, M.; Tang, W. Rhein Induces a Necrosis-Apoptosis Switch in Pancreatic Acinar Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 2014, 404853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- KoraMagazi, A.; Wang, D.; Yousef, B.; Guerram, M.; Yu, F. Rhein triggers apoptosis via induction of endoplasmic reticulum stress, caspase-4 and intracellular calcium in primary human hepatic HL-7702 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 473, 230–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.L.; Hsu, Y.L.; Ng, L.T.; Lin, C.C. Rhein inhibits the growth and induces the apoptosis of Hep G2 cells. Planta Med. 2004, 70, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Ch, R.; Mudiam, M.K.; Vashishtha, V.M.; Raisuddin, S.; Das, M. Activity-Guided Chemo Toxic Profiling of Cassia occidentalis (CO) Seeds: Detection of Toxic Compounds in Body Fluids of CO-Exposed Patients and Experimental Rats. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1120–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Yadav, A.; Srivastava, A.; Tripathi, A.; Raisuddin, S.; Das, M. Mechanism of Rhein-Induced Apoptosis in Rat Primary Hepatocytes: Beneficial Effect of Cyclosporine A. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2015, 28, 1133–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, Z.; Lei, Q.; Yang, R.; Zhu, S.; Ke, X.X.; Yang, L.; Cui, H.; Yi, L. Inhibition of neurotensin receptor 1 induces intrinsic apoptosis via let-7a-3p/Bcl-w axis in glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 116, 1572–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AnvariFar, H.; Amirkolaie, A.K.; Miandare, H.K.; Ouraji, H.; Jalali, M.A.; Üçüncü, S.İ. Apoptosis in fish: Environmental factors and programmed cell death. Cell Tissue Res. 2016, 368, 425–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.; Wang, H.; Xue, F.; Wang, X.; Fei, C.; Wang, M.; Zhang, T.; Yao, X.; He, P. Effects of diclazuril on apoptosis and mitochondrial transmembrane potential in second-generation merozoites of Eimeria tenella. Vet. Parasitol. 2010, 168, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Julien, O.; Wells, J.A. Caspases and their substrates. Cell Death Differ. 2017, 24, 1380–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Lu, P.; Song, G.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, D.; Liu, X. Involvement of PI3K/Akt, ERK and p38 signaling pathways in emodin-mediated extrinsic and intrinsic human hepatoblastoma cell apoptosis. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2016, 92, 26–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.C.; Lai, K.C.; Yang, J.S.; Liao, C.L.; Hsia, T.C.; Chen, G.W.; Lin, J.J.; Lin, H.J.; Chiu, T.H.; Tang, Y.J. Involvement of reactive oxygen species and caspase-dependent pathway in berberine-induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in C6 rat glioma cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jian, K.L.; Zhang, C.; Shang, Z.C.; Yang, L.; Kong, L.Y. Eucalrobusone C suppresses cell proliferation and induces ROS-dependent mitochondrial apoptosis via the p38 MAPK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Phytomedicine 2017, 25, 71–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabsi, A.M.; Lim, K.L.; Paterson, I.C.; Ali-Saeed, R.; Muharram, B.A. Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Induction via Modulation of Mitochondrial Integrity by Bcl-2 Family Members and Caspase Dependence in Dracaena cinnabari-Treated H400 Human Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Biomed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 4904016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, M.C.; Hymery, N.; Troadec, S.; Pawtowski, A.; Coton, E.; Madec, S. Hepatotoxicity of fusariotoxins, alone and in combination, towards the HepaRG human hepatocyte cell line. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 109, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Geng, X.C.; Wang, J.F.; Miao, Y.F.; Lu, Y.L.; Li, B. The HepaRG cell line, a superior in vitro model to L-02, HepG2 and hiHeps cell lines for assessing drug-induced liver injury. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2016, 32, 37–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleury, C.; Mignotte, B.; Vayssière, J.L. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species in cell death signaling. Biochimie 2002, 84, 131–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, H.; Wartenberg, M.; Hescheler, J. Reactive Oxygen Species as Intracellular Messengers during Cell Growth and Differentiation. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2001, 11, 173–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Ruiz, C.; Fernández-Checa, J.C. Redox regulation of hepatocyte apoptosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 22, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Shamoto-Nagai, M.; Maruyama, W.; Osawa, T.; Naoi, M. Phytochemicals prevent mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and protect SH-SY5Y cells against apoptosis induced by PK11195, a ligand for outer membrane translocator protein. J. Neural Transm. 2017, 124, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.L.; Ma, Y.G.; Xue, Y.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xie, H.; Qiu, G.R. Curcumin induces small cell lung cancer NCI-H446 cell apoptosis via the reactive oxygen species-mediated mitochondrial pathway and not the cell death receptor pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2012, 31, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.B.; Ma, Y.G.; Xue, Y.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Xie, H.; Qiu, G.R. Effect of processing on the chemical contents and hepatic and renal toxicity of rhubarb studied by canonical correlation analysis. Yao Xue Xue Bao 2009, 44, 885–890. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Boonstra, J.; Post, J.A. Molecular events associated with reactive oxygen species and cell cycle progression in mammalian cells. Gene 2004, 337, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, N.; Shi, X.; Ding, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Wang, Z. Non-esterified fatty acids activate the ROS-p38-p53/Nrf2 signaling pathway to induce bovine hepatocyte apoptosis in vitro. Apoptosis 2014, 19, 984–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, K.; Jain, S.K. Oxidative stress and apoptosis. Pathophysiology 2000, 7, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, Y.M.; Bae, Y.S.; Lee, S.Y. Molecular ordering of ROS production, mitochondrial changes, and caspase activation during sodium salicylate-induced apoptosis. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2003, 34, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, M.R. Reactive oxygen species and death: Oxidative DNA damage in atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vousden, K.H.; Lu, X. Live or let die: The cell’s response to p53. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2002, 2, 594–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fridman, J.S.; Lowe, S.W. Control of apoptosis by p53. Oncogene 2003, 22, 9030–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, W.W.; Yang, J.S.; Lai, K.C.; Kuo, C.L.; Hsu, C.K.; Wang, C.K.; Chang, C.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Tang, N.Y.; Chen, P.Y.; et al. Rhein induced apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress, caspase- and mitochondria-dependent pathways in SCC-4 human tongue squamous cancer cells. In Vivo 2009, 23, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cullen, S.P.; Brunet, M.; Martin, S.J. Granzymes in cancer and immunity. Cell Death Differ. 2010, 17, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schleich, K.; Lavrik, I.N. Mathematical modeling of apoptosis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2013, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ip, S.W.; Weng, Y.S.; Lin, S.Y.; Mei, D.Y.; Tang, N.Y.; Su, C.C.; Chung, J.G. The role of Ca+2 on rhein-induced apoptosis in human cervical cancer Ca Ski cells. Anticancer Res. 2007, 27, 379–389. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heo, S.K.; Yun, H.J.; Park, W.H.; Park, S.D. Rhein Inhibits TNF-α-Induced Human Aortic Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation via Mitochondrial-Dependent Apoptosis. J. Vasc. Res. 2009, 46, 375–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, X.; Lin, Z.Q.; Liu, B.; Wei, Y.Q. Caspase-mediated programmed cell death pathways as potential therapeutic targets in cancer. Cell Prolif. 2012, 45, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, H.M.; Tsai, H.C.; Lin, Y.L.; Yang, J.S.; Huang, A.C.; Yang, M.D.; Hsu, S.C.; Chung, M.C.; Gibson, W.W.; Chung, J.G. Mitochondrial-dependent caspase activation pathway is involved in baicalein-induced apoptosis in human hepatoma J5 cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 35, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chan, S.F.; Chen, Y.Y.; Lin, J.J.; Liao, C.L.; Ko, Y.C.; Tang, N.Y.; Kuo, C.L.; Liu, K.C.; Chung, J.G. Triptolide induced cell death through apoptosis and autophagy in murine leukemia WEHI-3 cells in vitro and promoting immune responses in WEHI-3 generated leukemia mice in vivo. Environ. Toxicol. 2017, 32, 550–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, X.; Shi, Z.; Peng, Z.; Zhao, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, X.; Liu, G.; Li, X. Acetoacetate Induces Hepatocytes Apoptosis by the ROS-Mediated MAPKs Pathway in Ketotic Cows. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 3296–3308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afri, M.; Frimer, A.A.; Cohen, Y. Active oxygen chemistry within the liposomal bilayer. Part IV: Locating 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (DCF), 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein (DCFH) and 2′,7′-dichlorodihydrofluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) in the lipid bilayer. Chem. Phys. Lipids 2004, 131, 122–133. [Google Scholar]
- He, Z.; Pu, L.; Yuan, C.; Jia, M.; Wang, J. Nutrition deficiency promotes apoptosis of cartilage endplate stem cells in a caspase-independent manner partially through upregulating BNIP3. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2017, 49, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, X.L.; Zhang, Y.J.; Wang, X.F.; Zhang, W.J.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, Y.J.; Lu, J.H.; Mei, J.W.; Hu, Y.P. Casticin induces apoptosis and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in gallbladder cancer cells. Cancer Cell Int. 2017, 17, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robles-Escajeda, E.; Lerma, D.; Nyakeriga, A.M.; Ross, J.A.; Kirken, R.A.; Aguilera, R.J.; Varela-Ramirez, A. Searching in mother nature for anti-cancer activity: Anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effect elicited by green barley on leukemia/lymphoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e0073508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, S.H.; Jiang, G.B.; Yao, J.H.; Li, W.; Han, B.J.; Zhang, C.; Zeng, C.C.; Liu, Y.J. Cytotoxic activity, DNA damage, cellular uptake, apoptosis and western blot analysis of ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complex against human lung decarcinoma A549 cell. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 152, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
You, L.; Dong, X.; Yin, X.; Yang, C.; Leng, X.; Wang, W.; Ni, J. Rhein Induces Cell Death in HepaRG Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041060
You L, Dong X, Yin X, Yang C, Leng X, Wang W, Ni J. Rhein Induces Cell Death in HepaRG Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041060
Chicago/Turabian StyleYou, Longtai, Xiaoxv Dong, Xingbin Yin, Chunjing Yang, Xin Leng, Wenping Wang, and Jian Ni. 2018. "Rhein Induces Cell Death in HepaRG Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Pathway" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041060
APA StyleYou, L., Dong, X., Yin, X., Yang, C., Leng, X., Wang, W., & Ni, J. (2018). Rhein Induces Cell Death in HepaRG Cells through Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptotic Pathway. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1060. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041060