Taurine Administration Recovers Motor and Learning Deficits in an Angelman Syndrome Mouse Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
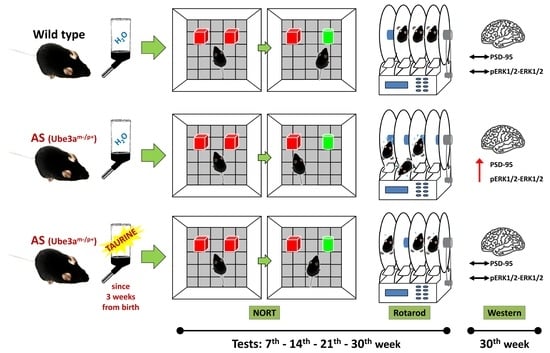
2.1. Taurine Ameliorates Motor Coordination of Ube3am−/p+ Mice
2.2. Open Field Test Reveals a Partial Improvement upon Taurine Administration
2.3. Learning and Memory Deficits Improve in Ube3am−/p+ after Taurine Administration
2.4. Effect of Taurine on Synaptic Markers
2.5. Taurine Content in Brain and Serum
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals
4.2. Tissue Collection
4.3. Taurine Administration
4.4. Test Groups
4.5. Behavioral Tests
4.5.1. Rotarod
4.5.2. Open Field (OF) and Spontaneous Locomotor Activity
4.5.3. Novel-Object Recognition Test (NORT)
4.6. Western Blotting
4.7. HPLC Method
4.7.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.7.2. Samples Preparation
4.7.3. Derivatization Procedure
4.7.4. Chromatography System
4.8. Statistical Analyses
4.8.1. Behavioral Tests
4.8.2. Neurotransmitters Dosage
4.8.3. Western-Blot
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AS | Angelman Syndrome |
| UBE3A | Ubiquitin-protein ligase E3A |
| GABA | Gamma aminobutyric acid |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| OFT | Open field test |
| NORT | Novel object recognition test |
| PSD-95 | PostSynaptic Density-95 |
| pERK1/2 | Phospho-extracellular signal-regulated Kinase |
| ERK1/2 | Total-extracellular signal-regulated Kinase |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HPLC | High performance liquid chromatography |
Appendix A

References
- Williams, C.A.; Angelman, H.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Driscoll, D.J.; Hendrickson, J.E.; Knoll, J.H.; Magenis, R.E.; Schinzel, A.; Wagstaff, J.; Whidden, E.M.; et al. Angelman syndrome: Consensus for diagnostic criteria. Angelman Syndrome Foundation. Am. J. Med. Genet. 1995, 56, 237–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, C.A.; Beaudet, A.L.; Clayton-Smith, J.; Knoll, J.H.; Kyllerman, M.; Laan, L.A.; Magenis, R.E.; Moncla, A.; Schinzel, A.A.; Summers, J.A.; et al. Angelman syndrome 2005: Updated consensus for diagnostic criteria. Am. J. Med. Genet. Part A 2006, 140, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burette, A.C.; Judson, M.C.; Burette, S.; Phend, K.D.; Philpot, B.D.; Weinberg, R.J. Subcellular organization of UBE3A in neurons. J. Comp. Neurol. 2017, 525, 233–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grier, M.D.; Carson, R.P.; Lagrange, A.H. Toward a broader view of Ube3a in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome: Expression in brain, spinal cord, sciatic nerve and glial cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dagli, A.I.; Mueller, J.; Williams, C.A. Angelman syndrome. In Genereviews((r)); Adam, M.P., Ardinger, H.H., Pagon, R.A., Wallace, S.E., Bean, L.J.H., Stephens, K., Amemiya, A., Eds.; University of Washington: Seattle, WA, USA, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Margolis, S.S.; Sell, G.L.; Zbinden, M.A.; Bird, L.M. Angelman syndrome. Neurotherapeutics 2015, 12, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roden, W.H.; Peugh, L.D.; Jansen, L.A. Altered GABA(A) receptor subunit expression and pharmacology in human Angelman syndrome cortex. Neurosci. Lett. 2010, 483, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santini, E.; Turner, K.L.; Ramaraj, A.B.; Murphy, M.P.; Klann, E.; Kaphzan, H. Mitochondrial superoxide contributes to hippocampal synaptic dysfunction and memory deficits in angelman syndrome model mice. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 16213–16220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llewellyn, K.J.; Nalbandian, A.; Gomez, A.; Wei, D.; Walker, N.; Kimonis, V.E. Administration of coq10 analogue ameliorates dysfunction of the mitochondrial respiratory chain in a mouse model of angelman syndrome. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 76, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berkowitz, B.A.; Lenning, J.; Khetarpal, N.; Tran, C.; Wu, J.Y.; Berri, A.M.; Dernay, K.; Haacke, E.M.; Shafie-Khorassani, F.; Podolsky, R.H.; et al. In vivo imaging of prodromal hippocampus ca1 subfield oxidative stress in models of alzheimer disease and angelman syndrome. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 4179–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Judson, M.C.; Wallace, M.L.; Sidorov, M.S.; Burette, A.C.; Gu, B.; van Woerden, G.M.; King, I.F.; Han, J.E.; Zylka, M.J.; Elgersma, Y.; et al. GABAergic neuron-specific loss of Ube3a causes Angelman syndrome-like EEG abnormalities and enhances seizure susceptibility. Neuron 2016, 90, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egawa, K.; Kitagawa, K.; Inoue, K.; Takayama, M.; Takayama, C.; Saitoh, S.; Kishino, T.; Kitagawa, M.; Fukuda, A. Decreased tonic inhibition in cerebellar granule cells causes motor dysfunction in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benitez-Diaz, P.; Miranda-Contreras, L.; Mendoza-Briceno, R.V.; Pena-Contreras, Z.; Palacios-Pru, E. Prenatal and postnatal contents of amino acid neurotransmitters in mouse parietal cortex. Dev. Neurosci. 2003, 25, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adedara, I.A.; Abolaji, A.O.; Idris, U.F.; Olabiyi, B.F.; Onibiyo, E.M.; Ojuade, T.D.; Farombi, E.O. Neuroprotective influence of taurine on fluoride-induced biochemical and behavioral deficits in rats. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2017, 261, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.Y.; Kim, H.V.; Yoon, J.H.; Kang, B.R.; Cho, S.M.; Lee, S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Cho, Y.; Woo, J.; et al. Taurine in drinking water recovers learning and memory in the adult APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 7467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezzomo, N.J.; Fontana, B.D.; Kalueff, A.V.; Barcellos, L.J.G.; Rosemberg, D.B. Understanding taurine CNS activity using alternative zebrafish models. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2017, 83, 525–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leon, R.; Wu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wei, J.; Buddhala, C.; Prentice, H.; Wu, J.Y. Protective function of taurine in glutamate-induced apoptosis in cultured neurons. J. Neurosci. Res. 2009, 87, 1185–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gebara, E.; Udry, F.; Sultan, S.; Toni, N. Taurine increases hippocampal neurogenesis in aging mice. Stem Cell Res. 2015, 14, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesnoy-Marchais, D. Persistent GABAA/C responses to gabazine, taurine and β-alanine in rat hypoglossal motoneurons. Neuroscience 2016, 330, 191–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reyes-Haro, D.; Cabrera-Ruiz, E.; Estrada-Mondragon, A.; Miledi, R.; Martinez-Torres, A. Modulation of GABA-A receptors of astrocytes and STC-1 cells by taurine structural analogs. Amino Acids 2014, 46, 2587–2593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, A.; Iio, W. Antidepressant-like effect of chronic taurine administration and its hippocampal signal transduction in rats. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 775, 29–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrill, J.R.; Pinniger, G.J.; Graves, J.A.; Grounds, M.D.; Arthur, P.G. Increasing taurine intake and taurine synthesis improves skeletal muscle function in the mdx mouse model for Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 3095–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuwirth, L.S.; Volpe, N.P.; Ng, S.; Marsillo, A.; Corwin, C.; Madan, N.; Ferraro, A.M.; El Idrissi, A. Taurine recovers mice emotional learning and memory disruptions associated with fragile X syndrome in context fear and auditory cued-conditioning. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2015, 803, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva-Santos, S.; van Woerden, G.M.; Bruinsma, C.F.; Mientjes, E.; Jolfaei, M.A.; Distel, B.; Kushner, S.A.; Elgersma, Y. Ube3a reinstatement identifies distinct developmental windows in a murine Angelman syndrome model. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 2069–2076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godavarthi, S.K.; Dey, P.; Maheshwari, M.; Jana, N.R. Defective glucocorticoid hormone receptor signaling leads to increased stress and anxiety in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2012, 21, 1824–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, C.; Rioult-Pedotti, M.S.; Migani, P.; Yu, C.J.; Tiwari, R.; Parang, K.; Spaller, M.R.; Goebel, D.J.; Marshall, J. Impairment of TrkB-PSD-95 signaling in Angelman syndrome. PLoS Biol. 2013, 11, e1001478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar-Martinez, E.; Morrisroe, C.; Sharrocks, A.D. The ubiquitin ligase UBE3A dampens ERK pathway signalling in HPV E6 transformed HeLa cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stornetta, R.L.; Zhu, J.J. Ras and Rap signaling in synaptic plasticity and mental disorders. Neuroscientist 2011, 17, 54–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sved, D.W.; Godsey, J.L.; Ledyard, S.L.; Mahoney, A.P.; Stetson, P.L.; Ho, S.; Myers, N.R.; Resnis, P.; Renwick, A.G. Absorption, tissue distribution, metabolism and elimination of taurine given orally to rats. Amino Acids 2007, 32, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, A.D.; Pearce, D.A. Location- and sex-specific differences in weight and motor coordination in two commonly used mouse strains. Sci. Rep. 2013, 3, 2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez-Benitez, R.; Ramos-Mandujano, G.; Pasantes-Morales, H. Taurine stimulates proliferation and promotes neurogenesis of mouse adult cultured neural stem/progenitor cells. Stem Cell Res. 2012, 9, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Idrissi, A. Taurine increases mitochondrial buffering of calcium: Role in neuroprotection. Amino Acids 2008, 34, 321–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prentice, H.; Pan, C.; Gharibani, P.M.; Ma, Z.; Price, A.L.; Giraldo, G.S.; Retz, H.M.; Gupta, A.; Chen, P.C.; Chiu, H.; et al. Analysis of neuroprotection by taurine and taurine combinations in primary neuronal cultures and in neuronal cell lines exposed to glutamate excitotoxicity and to hypoxia/re-oxygenation. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 975, 207–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.Y.; Wu, H.; Jin, Y.; Wei, J.; Sha, D.; Prentice, H.; Lee, H.H.; Lin, C.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Yang, L.L. Mechanism of neuroprotective function of taurine. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2009, 643, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Idrissi, A.; Neuwirth, L.S.; L’Amoreaux, W. Taurine regulation of short term synaptic plasticity in fragile X mice. J. Biomed. Sci. 2010, 17, S15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilb, W.; Kirischuk, S.; Luhmann, H.J. Role of tonic GABAergic currents during pre- and early postnatal rodent development. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 7, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Gao, Y.; Xiao, Z.; Chen, B.; Han, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Dai, J. Erk1/2 promotes proliferation and inhibits neuronal differentiation of neural stem cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 461, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrill, J.R.; Pinniger, G.J.; Nair, K.V.; Grounds, M.D.; Arthur, P.G. Beneficial effects of high dose taurine treatment in juvenile dystrophic mdx mice are offset by growth restriction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0187317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.H.; Armstrong, D.; Albrecht, U.; Atkins, C.M.; Noebels, J.L.; Eichele, G.; Sweatt, J.D.; Beaudet, A.L. Mutation of the Angelman ubiquitin ligase in mice causes increased cytoplasmic p53 and deficits of contextual learning and long-term potentiation. Neuron 1998, 21, 799–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seibenhener, M.L.; Wooten, M.C. Use of the open field maze to measure locomotor and anxiety-like behavior in mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ennaceur, A.; Delacour, J. A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: Behavioral data. Behav. Brain Res. 1988, 31, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antunes, M.; Biala, G. The novel object recognition memory: Neurobiology, test procedure, and its modifications. Cogn. Process. 2012, 13, 93–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perucho, J.; Gonzalo-Gobernado, R.; Bazan, E.; Casarejos, M.J.; Jimenez-Escrig, A.; Asensio, M.J.; Herranz, A.S. Optimal excitation and emission wavelengths to analyze amino acids and optimize neurotransmitters quantification using precolumn opa-derivatization by hplc. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 963–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanli, N.; Tague, S.E.; Lunte, C. Analysis of amino acid neurotransmitters from rat and mouse spinal cords by liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2015, 107, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeger, S.L.; Liang, K.Y.; Albert, P.S. Models for longitudinal data: A generalized estimating equation approach. Biometrics 1988, 44, 1049–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guzzetti, S.; Calzari, L.; Buccarello, L.; Cesari, V.; Toschi, I.; Cattaldo, S.; Mauro, A.; Pregnolato, F.; Mazzola, S.M.; Russo, S. Taurine Administration Recovers Motor and Learning Deficits in an Angelman Syndrome Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041088
Guzzetti S, Calzari L, Buccarello L, Cesari V, Toschi I, Cattaldo S, Mauro A, Pregnolato F, Mazzola SM, Russo S. Taurine Administration Recovers Motor and Learning Deficits in an Angelman Syndrome Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(4):1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041088
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuzzetti, Sara, Luciano Calzari, Lucia Buccarello, Valentina Cesari, Ivan Toschi, Stefania Cattaldo, Alessandro Mauro, Francesca Pregnolato, Silvia Michela Mazzola, and Silvia Russo. 2018. "Taurine Administration Recovers Motor and Learning Deficits in an Angelman Syndrome Mouse Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 4: 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041088
APA StyleGuzzetti, S., Calzari, L., Buccarello, L., Cesari, V., Toschi, I., Cattaldo, S., Mauro, A., Pregnolato, F., Mazzola, S. M., & Russo, S. (2018). Taurine Administration Recovers Motor and Learning Deficits in an Angelman Syndrome Mouse Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(4), 1088. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19041088