Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt
Abstract
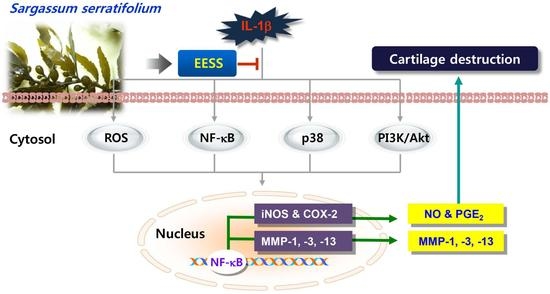
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of EESS on SW1353 and Rat Articular Chondrocyte Cytotoxicity
2.2. EESS Suppresses the IL-1β-Mediated Generation of ROS
2.3. EESS Reduces IL-1β-Induced NO and PGE2 Production
2.4. EESS Inhibits IL-1β-Induced iNOS and COX-2 Expression
2.5. EESS Decreases IL-1β-Mediated Increase of MMP-1, -3, and -13 Production
2.6. EESS Attenuates IL-1β-Induced Expression of MMP-1, -3, and -13
2.7. EESS Alleviates IL-1β-Induced Nuclear Accumulation of NF-κB p65
2.8. Effects of EESS on IL-1β-Induced Activation of MAPKs and PI3K/Akt Signaling Pathways
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Preparation of EESS
4.3. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.4. Detection of the Intracellular ROS Levels
4.5. NO Measurement and ELISA Assay
4.6. RNA Isolation and RT-PCR
4.7. Western Blot Analysis
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| COX-2 | Cyclooxygenase-2 |
| DCF-DA | 5,6-carboxy-2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin diacetate |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium |
| DMSO | Dimethylsulfoxide |
| ECL | Enhanced chemiluminescence |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EESS | Ethanol extract of S. serratifolium |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| FBS | Fetal bovine serum |
| GAPDH | Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase |
| HRP | Horseradish-peroxidase |
| IL-1β | Interleukin-1β |
| iNOS | Inducible NO synthase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| NAC | N-acetyl-l-cysteine |
| NF-κB | Nuclear factor-kappa B |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| OA | Osteoarthritis |
| PBS | Phosphate buffered saline |
| PGE2 | Prostaglandin E2 |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction |
References
- Brittberg, M.; Gomoll, A.H.; Canseco, J.A.; Far, J.; Lind, M.; Hui, J. Cartilage repair in the degenerative ageing knee. Acta Orthop. 2016, 87, 26–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andriacchi, T.P.; Favre, J.; Erhart-Hledik, J.C.; Chu, C.R. A systems view of risk factors for knee osteoarthritis reveals insights into the pathogenesis of the disease. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 43, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, Y.O.; Chun, J.S. Estrogen-related receptor γ is a novel catabolic regulator of osteoarthritis pathogenesis. BMB Rep. 2018, 51, 165–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochberg, M.; Chevalier, X.; Henrotin, Y.; Hunter, D.J.; Uebelhart, D. Symptom and structure modification in osteoarthritis with pharmaceutical-grade chondroitin sulfate: What’s the evidence? Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 2013, 29, 259–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martel-Pelletier, J.; Boileau, C.; Pelletier, J.P.; Roughley, P.J. Cartilage in normal and osteoarthritis conditions. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2008, 22, 351–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blasioli, D.J.; Kaplan, D.L. The roles of catabolic factors in the development of osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2014, 20, 355–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jotanovic, Z.; Mihelic, R.; Sestan, B.; Dembic, Z. Role of interleukin-1 inhibitors in osteoarthritis: An evidence-based review. Drugs Aging 2012, 29, 343–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.F.; Sandell, L.J. Inflammatory mediators: Tracing links between obesity and osteoarthritis. Crit. Rev. Eukaryot. Gene Expr. 2011, 21, 131–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panina, S.B.; Krolevets, I.V.; Milyutina, N.P.; Sagakyants, A.B.; Kornienko, I.V.; Ananyan, A.A.; Zabrodin, M.A.; Plotnikov, A.A.; Vnukov, V.V. Circulating levels of proinflammatory mediators as potential biomarkers of post-traumatic knee osteoarthritis development. J. Orthop. Traumatol. 2017, 18, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ramonda, R.; Lorenzin, M.; Modesti, V.; Campana, C.; Ortolan, A.; Frallonardo, P.; Punzi, L. Serological markers of erosive hand osteoarthritis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2013, 24, 11–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Q.H.; Cheng, Y.; Chen, W.P.; Zhong, H.M.; Wang, X.H. Celastrol, an inhibitor of heat shock protein 90β potently suppresses the expression of matrix metalloproteinases, inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase-2 in primary human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2013, 708, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldring, M.B.; Otero, M. Inflammation in osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2011, 23, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roman-Blas, J.A.; Jimenez, S.A. NF-kappaB as a potential therapeutic target in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 2006, 14, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinge, S.A.; Sawyer, G.A. Effectiveness and safety of topical versus oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: A comprehensive review. Phys. Sportsmed. 2013, 41, 64–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herndon, C.M. Topical delivery of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis. J. Pain Palliat. Care Pharmacother. 2012, 26, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fitton, J.H. Therapies from fucoidan; multifunctional marine polymers. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1731–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vadalà, M.; Palmieri, B. From algae to “functional foods”. Clin. Ter. 2015, 166, e281–e300. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ali, M.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Seong, S.H.; Kim, H.R.; Jung, H.A.; Choi, J.S. α-glucosidase and protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B inhibitory activity of plastoquinones from marine brown alga Sargassum serratifolium. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, S.J.; Joung, E.J.; Kwon, M.S.; Lee, B.; Utsuki, T.; Oh, C.W.; Kim, H.R. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethanolic extract of Sargassum serratifolium in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 1023–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, C.W.; Park, M.S.; Kim, N.H.; Lee, J.H.; Oh, C.W.; Kim, H.R.; Kim, G.D. Hexane extract from Sargassum serratifolium inhibits the cell proliferation and metastatic ability of human glioblastoma U87MG cells. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 2602–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gwon, W.G.; Lee, B.; Joung, E.J.; Choi, M.W.; Yoon, N.; Shin, T.; Oh, C.W.; Kim, H.R. Sargaquinoic acid inhibits TNF-α-induced NF-κB signaling, thereby contributing to decreased monocyte adhesion to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2015, 63, 9053–9061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziskoven, C.; Jäger, M.; Zilkens, C.; Bloch, W.; Brixius, K.; Krauspe, R. Oxidative stress in secondary osteoarthritis: From cartilage destruction to clinical presentation? Orthop. Rev. 2010, 2, e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fay, J.; Varoga, D.; Wruck, C.J.; Kurz, B.; Goldring, M.B.; Pufe, T. Reactive oxygen species induce expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in chondrocytes and human articular cartilage explants. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, R189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lepetsos, P.; Papavassiliou, A.G. ROS/oxidative stress signaling in osteoarthritis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1862, 576–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Xie, G.; Wang, W. Reactive oxygen species: The 2-edged sword of osteoarthritis. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2012, 344, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigoglou, S.; Papavassiliou, A.G. The NF-κB signalling pathway in osteoarthritis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuliga, M. NF-kappaB signaling in chronic inflammatory airway disease. Biomolecules 2015, 5, 1266–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Dea, E.; Hoffmann, A. The regulatory logic of the NF-kappaB signaling system. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a000216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, J.W.; Lee, H.H.; Lee, K.W.; Kim, K.Y.; Kim, S.G.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Park, C.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.W.; et al. Mori folium inhibits interleukin-1β-induced expression of matrix metalloproteinases and inflammatory mediators by suppressing the activation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK in SW1353 human chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2016, 37, 452–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.C.; Hsiao, G.; Lin, K.H.; Hsieh, M.S.; Jayakumar, T.; Wu, T.S.; Sheu, J.R. Cinnamophilin isolated from Cinnamomum philippinense protects against collagen degradation in human chondrocytes. Phytother. Res. 2013, 27, 892–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.; Kim, H.P. Matrix metalloproteinase-13 expression in IL-1β-treated chondrocytes by activation of the p38 MAPK/c-Fos/AP-1 and JAK/STAT pathways. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2011, 34, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, Z.; Wang, S.; Wang, J. Peroxiredoxin 4 inhibits IL-1β-induced chondrocyte apoptosis via PI3K/AKT signaling. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 90, 414–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, H.L.; Yi, J.S.; Kim, T.S.; Oh, Y.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, M.; Bang, J.S.; Ko, K.; Ahn, I.Y.; Ko, K.; et al. Development of a test method for the evaluation of DNA damage in mouse spermatogonial stem cells. Toxicol. Res. 2017, 33, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, S.K.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, J.H.; Son, Y.H.; Lee, M.W.; Kim, H.J.; Noh, S.A.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, I.G.; Lee, M.J. Docosahexaenoic acid-mediated protein aggregates may reduce proteasome activity and delay myotube degradation during muscle atrophy in vitro. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanjeewa, K.K.; Fernando, I.P.; Kim, E.A.; Ahn, G.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory activity of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated from an enzymatic digest of brown seaweed Sargassum horneri in RAW 264.7 cells. Nutr. Res. Pract. 2017, 11, 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.; Jeong, J.-W.; Lee, D.-S.; Yim, M.-J.; Lee, J.M.; Han, M.H.; Kim, S.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, G.-Y.; Park, E.K.; et al. Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082308
Park C, Jeong J-W, Lee D-S, Yim M-J, Lee JM, Han MH, Kim S, Kim H-S, Kim G-Y, Park EK, et al. Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082308
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Cheol, Jin-Woo Jeong, Dae-Sung Lee, Mi-Jin Yim, Jeong Min Lee, Min Ho Han, Suhkmann Kim, Heui-Soo Kim, Gi-Young Kim, Eui Kyun Park, and et al. 2018. "Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082308
APA StylePark, C., Jeong, J. -W., Lee, D. -S., Yim, M. -J., Lee, J. M., Han, M. H., Kim, S., Kim, H. -S., Kim, G. -Y., Park, E. K., Jeon, Y. -J., Cha, H. -J., & Choi, Y. H. (2018). Sargassum serratifolium Extract Attenuates Interleukin-1β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Inflammatory Response in Chondrocytes by Suppressing the Activation of NF-κB, p38 MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2308. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082308