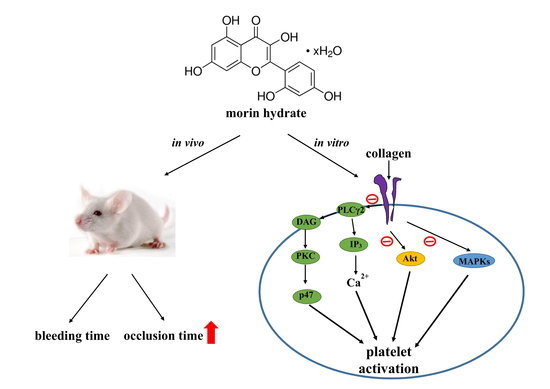
Novel Therapeutic Agent against Platelet Activation In Vitro and Arterial Thrombosis In Vivo by Morin Hydrate
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of Morin Hydrate on Aggregation of Washed Human Platelets Stimulated by Various Agonists
2.2. Regulatory Role of Morin Hydrate in ATP Release, Relative [Ca2+]i Mobilization, and Surface P-Selectin Expression in Washed Human Platelets
2.3. Effects of Morin Hydrate on Cytotoxicity, the PLCγ2–PKC Cascade, and Akt Activation
2.4. Effect of Morin Hydrate on p38 MAPK, ERK2, and JNK1 Activation
2.5. Evaluation of OH·-Scavenging Activity of Morin Hydrate through Electron Spin Resonance (ESR) Spectrometry
2.6. Effects of Morin Hydrate on Platelet Thrombi in Mesenteric Microvessels and Bleeding Time In Vivo
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals and Reagents
4.2. Platelet Aggregation
4.3. Measurement of Relative [Ca2+]i Mobilization
4.4. Flow Cytometric Analysis of Surface P-selectin Expression
4.5. Detection of Lactate Dehydrogenase
4.6. Immunoblotting of Protein Phosphorylation
4.7. Measurement of OH· Formation in the Platelet Suspensions or Fenton Reaction Solution Through Electron Spin Resonance Spectrometry
4.8. Measurement of Sodium Fluorescein-Induced Thrombus Formation in Mouse Mesenteric Microvessels
4.9. Measurement of Bleeding Time in Mouse Tail Vein
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, J.; O’Prey, J.; Harrison, P.R. Enhanced sensitivity of human oral tumours to the flavonol, morin, during cancer progression: Involvement of the Akt and stress kinase pathways. Carcinogenesis 2003, 24, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, B.B.; Shishodia, S. Molecular targets of dietary agents for prevention and therapy of cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2006, 7, 1397–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lotito, S.B.; Frei, B. Consumption of flavonoid-rich foods and increased plasma antioxidant capacity in humans: Cause, consequence, or epiphenomenon? Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2006, 41, 1727–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanasaki, Y.; Ogawa, S.; Fukui, S. The correlation between active oxygens scavenging and antioxidative effects of flavonoids. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1994, 16, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempuraj, D.; Madhappan, B.; Christodoulou, S.; Boucher, W.; Cao, J.; Papadopoulou, N.; Cetrulo, C.L.; Theoharides, T.C. Flavonols inhibit proinflammatory mediator release, intracellular calcium ion levels and protein kinase C theta phosphorylation in human mast cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, N.; Tong, B.; Zhang, X.; Dou, Y.; Wu, X.; Xia, Y.; Dai, Y.; Wei, Z.F. Antiarthritis effect of morin is associated with inhibition of synovial angiogenesis. Drug Dev. Res. 2015, 76, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawabata, T.; Tanaka, T.; Honjo, S.; Kakumoto, M.; Hara, A.; Makita, H.; Tatematsu, N.; Ushida, T.; Tsuda, H.; Mori, H. Chemopreventive effect of dietary flavonoid morin on chemically induced rat tongue carcinogenesis. Int. J. Cancer 1999, 83, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Peluso, M.R. Flavonoids attenuate cardiovascular disease, inhibit phosphodiesterase, and modulate lipid homeostasis in adipose tissue and liver. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood) 2006, 231, 1287–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, J.R.; Lee, C.R.; Lin, C.H.; Hsiao, G.; Ko, W.C.; Chen, Y.C. Mechanisms involved in the antiplatelet activity of Staphylococcus aureus lipoteichoic acid in human platelets. Thromb. Haemost. 2000, 83, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tzeng, S.H.; Ko, W.C.; Ko, F.N.; Teng, C.M. Inhibition of platelet aggregation by some flavonoids. Thromb. Res. 1991, 64, 91–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.; Cramer, E.M. Platelet α-granules. Blood Rev. 1993, 7, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singer, W.D.; Brown, H.A.; Sternweis, P.C. Regulation of eukaryotic phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C and phospholipase D. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1997, 6, 475–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woulfe, D.S. Akt signaling in platelet and thrombosis. Expert Rev. Hematol. 2010, 3, 81–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugaud, F.; Nadal-Wollbold, F.; Levy-Toledano, S.; Rosa, J.P.; Bryckaert, M. Regulation of c-jun-NH2 terminal kinase and extracellular-signal regulated kinase in human platelets. Blood 1999, 94, 3800–3805. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Niedergang, F.; Alcover, A.; Knight, C.G.; Farndale, R.W.; Barnes, M.J.; Francischetti, I.M.; Bon, C.; Leduc, M. Convulxin binding to platelet receptor GPVI: Competition with collagen related peptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2000, 273, 246–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.H.; Chung, C.H.; Kuo, H.L.; Hsu, C.C.; Huang, T.F. The highly specific platelet glycoprotein (GP) VI agonist trowaglerix impaired collagen-induced platelet aggregation ex vivo through matrix metalloproteinase-dependent GPVI shedding. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 669–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.H.; Wu, W.B.; Huang, T.F. Aggretin, a snake venom-derived endothelial integrin alpha 2 beta 1 agonist, induces angiogenesis via expression of vascular endothelial growth factor. Blood 2004, 103, 2105–2113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nieswandt, B.; Watson, S.P. Platelet-collagen interaction: Is GPVI the central receptor? Blood 2003, 102, 449–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jiang, H.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Z.; Smrcka, A.V.; Wu, D. Roles of PLC-beta2 and -beta3 and PI3Kgamma in chemoattractant-mediated signal transduction. Science 2000, 287, 1046–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.J. PKD at the crossroads of DAG and PKC signaling. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2006, 27, 317–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ragab, A.; Séverin, S.; Gratacap, M.P.; Aguado, E.; Malissen, M.; Jandrot-Perrus, M.; Malissen, B.; Ragab-Thomas, J.; Payrastre, B. Roles of the C-terminal tyrosine residues of LAT in GP VI-induced platelet activation: Insights into the mechanism of PLC gamma 2 activation. Blood 2007, 110, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsig, L.; Wong, R.; Feramisco, J.; Nadeau, D.R.; Varki, N.M.; Varki, A. Heparin and cancer revisited: Mechanistic connections involving platelets, P-selectin, carcinoma mucins, and tumor metastasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3352–3357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kaibuchi, K.; Sano, K.; Hoshijima, M.; Takai, Y.; Nishizuka, Y. Phosphatidylinositol turnover in platelet activation; calcium mobilization and protein phosphorylation. Cell Calcium 1982, 3, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.; Karin, M. Mammalian MAP kinase signaling cascades. Nature 2001, 410, 37–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, F.; Kauskot, A.; Rosa, J.P.; Bryckaert, M. Mitogen-activated protein kinases in hemostasis and thrombosis. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2008, 6, 2007–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Adam, F.; Kauskot, A.; Nurden, P.; Sulpice, E.; Hoylaerts, M.F.; Davis, R.J.; Rosa, J.P.; Bryckaert, M. Platelet JNK1 is involved in secretion and thrombus formation. Blood 2010, 115, 4083–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Canobbio, I.; Reineri, S.; Sinigaglia, F.; Balduini, C.; Torti, M. A role for p38 MAP kinase in platelet activation by von Willebrand factor. Thromb. Haemost. 2004, 91, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; De, S.; Damron, D.S.; Chen, W.S.; Hay, N.; Byzova, T.V. Impaired platelet responses to thrombin and collagen in AKT-1-deficient mice. Blood 2004, 104, 1703–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jayakumar, T.; Chen, W.F.; Lu, W.J.; Chou, D.S.; Hsiao, G.; Hsu, C.Y.; Sheu, J.R.; Hsieh, C.Y. A novel antithrombotic effect of sulforaphane via activation of platelet adenylate cyclase: Ex vivo and in vivo studies. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2013, 24, 1086–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wachowicz, B.; Olas, B.; Zbikowska, H.M.; Buczyński, A. Generation of reactive oxygen species in blood platelets. Platelets 2002, 13, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Kang, K.A.; Piao, M.J.; Maeng, Y.H.; Lee, K.H.; Chang, W.Y.; You, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Kang, S.S.; Hyun, J.W. Cellular protection of morin against the oxidative stress induced by hydrogen peroxide. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2009, 177, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Wu, N.; Miao, J.; Huang, Z.; Li, X.; Jia, P.; Guo, Y.; Jia, D. Protective effect of morin on myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 42, 1379–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, D.S.; Hsiao, G.; Shen, M.Y.; Tsai, Y.J.; Chen, T.F.; Sheu, J.R. ESR spin trapping of a carbon-centered free radical from agonist-stimulated human platelets. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2005, 39, 237–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, G.; Lin, K.H.; Chang, Y.; Chen, T.L.; Tzu, N.H.; Chou, D.S.; Sheu, J.R. Protective mechanisms of inosine in platelet activation and cerebral ischemic damage. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 1998–2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsia, C.-W.; Wu, M.-P.; Velusamy, M.; Hsia, C.-H.; Chou, D.-S.; Tsai, C.-L.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Jayakumar, T.; Chung, C.-L.; Sheu, J.-R. Novel Therapeutic Agent against Platelet Activation In Vitro and Arterial Thrombosis In Vivo by Morin Hydrate. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082386
Hsia C-W, Wu M-P, Velusamy M, Hsia C-H, Chou D-S, Tsai C-L, Hsu C-Y, Jayakumar T, Chung C-L, Sheu J-R. Novel Therapeutic Agent against Platelet Activation In Vitro and Arterial Thrombosis In Vivo by Morin Hydrate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082386
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsia, Chih-Wei, Ming-Ping Wu, Marappan Velusamy, Chih-Hsuan Hsia, Duen-Suey Chou, Cheng-Lin Tsai, Chia-Yuan Hsu, Thanasekaran Jayakumar, Chi-Li Chung, and Joen-Rong Sheu. 2018. "Novel Therapeutic Agent against Platelet Activation In Vitro and Arterial Thrombosis In Vivo by Morin Hydrate" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082386
APA StyleHsia, C. -W., Wu, M. -P., Velusamy, M., Hsia, C. -H., Chou, D. -S., Tsai, C. -L., Hsu, C. -Y., Jayakumar, T., Chung, C. -L., & Sheu, J. -R. (2018). Novel Therapeutic Agent against Platelet Activation In Vitro and Arterial Thrombosis In Vivo by Morin Hydrate. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2386. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082386