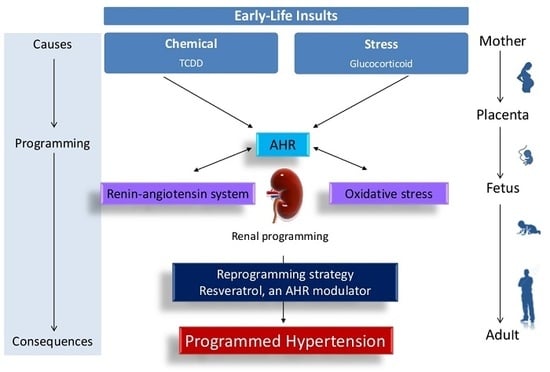
Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor?
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Morphometric Values and Blood Pressures
2.2. Plasma Levels of l-Cysteine, l-Arginine, ADMA, and SDMA
2.3. Immunohistochemistry Staining of 8-OHdG
2.4. Renal mRNA Expression of Genes in AHR Pathway and RAS
2.5. Protein Levels of AHR, AT1R, and AT2R
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animal Models
4.2. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
4.3. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.4. Western Blotting
4.5. Immunohistochemistry Staining
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ACE | Angiotensin-converting enzyme |
| ADMA | Asymmetric dimethylarginine |
| AHR | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| AT1R | Angiotensin II type 1 receptor |
| AT2R | Angiotensin II type 2 receptor |
| DEX | Dexamethasone |
| DOHaD | Developmental origins of health and disease |
| EDC | Endocrine disrupting chemical |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| RAS | Renin–angiotensin system |
| SDMA | Symmetric dimethylarginine |
| TCDD | 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin |
| 8-OHdG | 8-Hydroxydeoxyguanosine |
References
- Hanson, M. The birth and future health of DOHaD. J. Dev. Orig. Health Dis. 2015, 6, 434–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirkley, A.G.; Sargis, R.M. Environmental endocrine disruption of energy metabolism and cardiovascular risk. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2014, 14, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.H.; Lim, J.E.; Park, H.; Jee, S.H. Body burden of persistent organic pollutants on hypertension: A meta-analysis. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2016, 23, 14284–14293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragon, A.C.; Goens, M.B.; Carbett, E.; Walker, M.K. Perinatal 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin exposure sensitizes offspring to angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 2008, 8, 145–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seckl, J.R. Glucocorticoid programming of the fetus; adult phenotypes and molecular mechanisms. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2001, 185, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheen, J.M.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, C.C.; Huang, L.T.; Chang, H.Y.; Tain, Y.L. Prenatal dexamethasone-induced programmed hypertension and renal programming. Life Sci. 2015, 132, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Chen, C.C.; Sheen, J.M.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Kuo, H.C.; Huang, L.T. Melatonin attenuates prenatal dexamethasone-induced blood pressure increase in a rat model. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2014, 8, 216–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhanabalan, S.; Mathur, P.P.; Latha, P. TCDD and corticosterone on testicular steroidogenesis and antioxidant system of epididymal sperm in rats. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2015, 1, 811–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonneveld, E.; Jonas, A.; Meijer, O.C.; Brouwer, A.; van der Burg, B. Glucocorticoid-enhanced expression of dioxin target genes through regulation of the rat aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Toxicol. Sci. 2007, 99, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N. The role of endogenous aryl hydrocarbon receptor signaling in cardiovascular physiology. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. Res. 2011, 2, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kett, M.M.; Denton, K.M. Renal programming: Cause for concern? Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2011, 300, R791–R803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paixão, A.D.; Alexander, B.T. How the kidney is impacted by the perinatal maternal environment to develop hypertension. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 89, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Developmental origins of chronic kidney disease: Should we focus on early life? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawal, A.O. Air particulate matter induced oxidative stress and inflammation in cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis: The role of Nrf2 and AhR-mediated pathways. Toxicol. Lett. 2017, 270, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, N.; Agbor, L.N.; Scott, J.A.; Zalobowski, T.; Elased, K.M.; Trujillo, A.; Duke, M.S.; Wolf, V.; Walsh, M.T.; Born, J.L.; et al. An activated renin-angiotensin system maintains normal blood pressure in aryl hydrocarbon receptor heterozygous mice but not in null mice. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2010, 80, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Joles, J.A. Reprogramming: A preventive strategy in hypertension focusing on the kidney. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berman, A.Y.; Motechin, R.A.; Wiesenfeld, M.Y.; Holz, M.K. The therapeutic potential of resveratrol: A review of clinical trials. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2017, 1, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Sheen, J.M.; Lin, I.C.; Yu, H.R.; Huang, L.T.; Hsu, C.N. Resveratrol prevents the combined maternal plus postweaning high-fat-diets-induced hypertension in male offspring. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2017, 48, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papoutsis, A.J.; Selmin, O.I.; Borg, J.L.; Romagnolo, D.F. Gestational exposure to the AhR agonist 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin induces BRCA-1 promoter hypermethylation and reduces BRCA-1 expression in mammary tissue of rat offspring: Preventive effects of resveratrol. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 261–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Targeting on asymmetric dimethylarginine related nitric oxide-reactive oxygen species imbalance to reprogram the development of hypertension. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bode-Boger, S.M.; Scalera, F.; Ignarro, L.J. The l-arginine paradox: Importance of the l-arginine/asymmetrical dimethylarginine ratio. Pharmacol. Ther. 2007, 114, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Hsu, C.N. Toxic dimethylarginines: Asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA). Toxins 2017, 9, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- İlhan, S.; Ateşşahin, D.; Ateşşahin, A.; Mutlu, E.; Onat, E.; Şahna, E. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-induced hypertension: The beneficial effects of melatonin. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2015, 1, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Chan, S.H.H.; Chan, J.Y.H. Biochemical basis for pharmacological intervention as a reprogramming strategy against hypertension and kidney disease of developmental origin. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2018, 153, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefont-Rousselot, D. Resveratrol and Cardiovascular Diseases. Nutrients 2016, 8, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, N.P.; Singh, U.S.; Nagarkatti, M.; Nagarkatti, P.S. Resveratrol (3,5,4′-trihydroxystilbene) protects pregnant mother and fetus from the immunotoxic effects of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulero-Navarro, S.; Fernandez-Salguero, P.M. New trends in aryl hydrocarbon receptor biology. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thandapilly, S.J.; Louis, X.L.; Behbahani, J.; Movahed, A.; Yu, L.; Fandrich, R.; Zhang, S.; Kardami, E.; Anderson, H.D.; Netticadan, T. Reduced hemodynamic load aids low-dose resveratrol in reversing cardiovascular defects in hypertensive rats. Hypertens. Res. 2013, 6, 866–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiskirchen, S.; Weiskirchen, R. Resveratrol: How Much Wine Do You Have to Drink to Stay Healthy? Adv. Nutr. 2016, 7, 706–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Reckelhoff, J.F. Gender differences in the regulation of blood pressure. Hypertension 2001, 7, 1199–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqi, A.S.; Dalsenter, P.R.; Marker, H.J.; Chahoud, I. Reproductive toxicity and tissue concentrations of low doses of 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin in male offspring rats exposed throughout pregnancy and lactation. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 150, 383–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franczak, A.; Nynca, A.; Valdez, K.E.; Mizinga, K.M.; Petroff, B.K. Effects of acute and chronic exposure to the aryl hydrocarbon receptor agonist 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin on the transition to reproductive senescence in female Sprague-Dawley rats. Biol. Reprod. 2006, 74, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soylemez, S.; Sepici, A.; Akar, F. Resveratrol supplementation gender independently improves endothelial reactivity and suppresses superoxide production in healthy rats. Cardiovasc. Drugs Ther. 2009, 23, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tain, Y.L.; Lin, Y.J.; Sheen, J.M.; Yu, H.R.; Tiao, M.M.; Chen, C.C.; Tsai, C.C.; Huang, L.T.; Hsu, C.N. High Fat Diets Sex-Specifically Affect the Renal Transcriptome and Program Obesity, Kidney Injury, and Hypertension in the Offspring. Nutrients 2017, 9, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Control | DEX | TCDD | DEX + TCDD | DEX + TCDD + R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 7 | n = 8 | n = 8 | n = 8 | n = 8 | |
| Mortality | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Body weight (BW) (g) | 532 ± 62 | 526 ± 60 | 523 ± 29 | 470 ± 30 | 512 ± 87 |
| Left kidney weight (g) | 2.08 ± 0.18 | 1.91 ± 0.29 | 1.8 ± 0.16 | 1.75 ± 0.15 a | 1.73 ± 0.18 a |
| Left kidney weight/100 g BW | 0.39 ± 0.04 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 0.38 ± 0.05 | 0.34 ± 0.04 |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 143 ± 3 | 151 ± 3 a | 158 ± 4 a | 164 ± 6 a,b | 143 ± 9 b,c,d |
| Diastolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 66 ± 6 | 63 ± 5 | 70 ± 3 | 76 ± 5 b | 69 ± 11 |
| Mean arterial pressure (mmHg) | 92 ± 5 | 92 ± 3 | 100 ± 3 a,b | 106 ± 4 a,b,c | 94 ± 9 |
| Control | DEX | TCDD | DEX + TCDD | DEX + TCDD + R | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n = 7 | n = 8 | n = 8 | n = 8 | n = 8 | |
| l-Citrulline (μM) | 32.9 ± 4.8 | 32.5 ± 5.3 | 28.9 ± 6.0 | 30.8 ± 2.3 | 16 ± 9.2 |
| l-Arginine (μM) | 129.3 ± 30.6 | 150.5 ± 47.9 | 120.7 ± 27.7 | 130.1 ± 24.3 | 146.8 ± 35.5 |
| ADMA (μM) | 0.24 ± 0.09 | 0.73 ± 0.09 a | 0.6 ± 0.33 | 1.04 ± 0.59 a | 0.44 ± 0.89 b |
| SDMA (μM) | 0.08 ± 0.04 | 0.23 ± 0.52 a | 0.14 ± 0.55 | 0.58 ± 0.54 a | 0.26 ± 0.55 |
| l-arginine-to-ADMA ratio (μM/μM) | 587 ± 221 | 203 ± 53 | 246 ± 108 | 203 ± 181 | 336 ± 84 |
| Gene | Forward (5′–3′) | Reverse (5′–3′) |
|---|---|---|
| Ahr | gtcctcagcaggaacgaaag | ccagggaagtccaactgtgt |
| Ahrr | cagcaacatggcttctttca | tgaagcactgcattccagac |
| Cyp1a1 | gcactctggacaaacacctg | atatccaccttctcgcctgg |
| Ren | aacattaccagggcaactttcact | acccccttcatggtgatctg |
| Atp6ap2 | gaggcagtgaccctcaacat | ccctcctcacacaacaaggt |
| Agt | gcccaggtcgcgatgat | tgtacaagatgctgagtgaggcaa |
| Ace | caccggcaaggtctgctt | cttggcatagtttcgtgaggaa |
| Agtr1a | gctgggcaacgagtttgtct | cagtccttcagctggatcttca |
| Agtr1b | caatctggctgtggctgactt | tgcacatcacaggtccaaaga |
| Rn18s | gccgcggtaattccagctcca | cccgcccgctcccaagatc |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsu, C.-N.; Lin, Y.-J.; Lu, P.-C.; Tain, Y.-L. Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082459
Hsu C-N, Lin Y-J, Lu P-C, Tain Y-L. Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(8):2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082459
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsu, Chien-Ning, Yu-Ju Lin, Pei-Chen Lu, and You-Lin Tain. 2018. "Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 8: 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082459
APA StyleHsu, C. -N., Lin, Y. -J., Lu, P. -C., & Tain, Y. -L. (2018). Maternal Resveratrol Therapy Protects Male Rat Offspring against Programmed Hypertension Induced by TCDD and Dexamethasone Exposures: Is It Relevant to Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(8), 2459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19082459