Investigation of α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Using the Fluorescent Probe Thioflavin T
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Kinetics of α-Synuclein Fibrillation
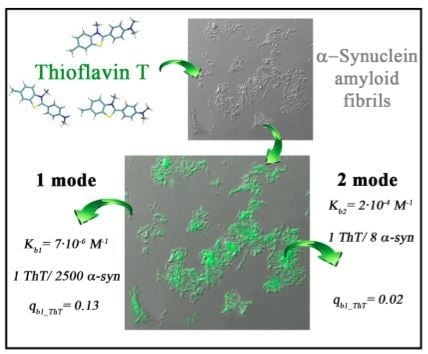
2.2. ThT-α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibril Binding Parameters
2.3. Photophysical Characteristics of ThT Bound to α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrilsα
2.4. The Possibility of the Existence of One More ThT-α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibril Binding Mode
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. α-Synuclein Expression and Purification
3.3. Investigation of the Kinetics of Amyloid Fibril Formation
3.4. Electron Microscopy
3.5. Confocal Microscopy
3.6. Equilibrium Microdialysis
3.7. Absorption Spectroscopy
3.8. Fluorescence Spectroscopy
3.9. Time-Resolved Fluorescence Measurements
3.10. CD Spectroscopy
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ueda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Identification of two distinct synucleins from human brain. FEBS Lett. 1994, 345, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lavedan, C. The synuclein family. Genome Res. 1998, 8, 871–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duda, J.E.; Shah, U.; Arnold, S.E.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. The expression of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synucleins in olfactory mucosa from patients with and without neurodegenerative diseases. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 160, 515–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakai, M.; Fujita, M.; Waragai, M.; Sugama, S.; Wei, J.; Akatsu, H.; Ohtaka-Maruyama, C.; Okado, H.; Hashimoto, M. Expression of alpha-synuclein, a presynaptic protein implicated in Parkinson’s disease, in erythropoietic lineage. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 358, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbour, R.; Kling, K.; Anderson, J.P.; Banducci, K.; Cole, T.; Diep, L.; Fox, M.; Goldstein, J.M.; Soriano, F.; Seubert, P.; et al. Red blood cells are the major source of alpha-synuclein in blood. Neuro-Degener. Dis. 2008, 5, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.X.; Campbell, B.C.; McLean, C.A.; Thyagarajan, D.; Gai, W.P.; Kapsa, R.M.; Beyreuther, K.; Masters, C.L.; Culvenor, J.G. Platelet alpha- and gamma-synucleins in Parkinson’s disease and normal control subjects. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2002, 4, 309–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michell, A.W.; Luheshi, L.M.; Barker, R.A. Skin and platelet alpha-synuclein as peripheral biomarkers of Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2005, 381, 294–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noori-Daloii, M.R.; Kheirollahi, M.; Mahbod, P.; Mohammadi, F.; Astaneh, A.N.; Zarindast, M.R.; Azimi, C.; Mohammadi, M.R. Alpha- and beta-synucleins mRNA expression in lymphocytes of schizophrenia patients. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2010, 14, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alim, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Arima, K.; Takeda, K.; Izumiyama, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kaji, H.; Shinoda, T.; Hisanaga, S.; Ueda, K. Tubulin seeds alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.; Qin, Z.J.; Hu, D.; Munishkina, L.A.; Fink, A.L. Alpha-synuclein can function as an antioxidant preventing oxidation of unsaturated lipid in vesicles. Biochemistry 2006, 45, 8135–8142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- George, J.M.; Jin, H.; Woods, W.S.; Clayton, D.F. Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 1995, 15, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, N.M.; Giasson, B.I. Snaring the function of alpha-synuclein. Cell 2005, 123, 359–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.J.; Jeitner, T.M.; Blass, J.P. The role of transglutaminases in neurodegenerative diseases: Overview. Neurochem. Int. 2002, 40, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breydo, L.; Wu, J.W.; Uversky, V.N. Alpha-synuclein misfolding and Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekman, D.; Light, S.; Bjorklund, A.K.; Elofsson, A. What properties characterize the hub proteins of the protein-protein interaction network of Saccharomyces cerevisiae? Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, P.H.; Zhen, W.; Poon, A.W.; Conway, K.A.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13709–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, Y.; Delarue, P.; Scheraga, H.A.; Senet, P.; Maisuradze, G.G. From a Highly Disordered to a Metastable State: Uncovering Insights of alpha-Synuclein. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2018, 9, 1051–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhree, M.A.A.; Nolten, I.S.; Blum, C.; Claessens, M. Different Conformational Subensembles of the Intrinsically Disordered Protein alpha-Synuclein in Cells. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2018, 9, 1249–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreon, A.C.; Gambin, Y.; Lemke, E.A.; Deniz, A.A. Interplay of alpha-synuclein binding and conformational switching probed by single-molecule fluorescence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 5645–5650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Veldhuis, G.; Segers-Nolten, I.; Ferlemann, E.; Subramaniam, V. Single-molecule FRET reveals structural heterogeneity of SDS-bound alpha-synuclein. Chembiochem Eur. J. Chem. Biol. 2009, 10, 436–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuscher, B.; Kamp, F.; Mehnert, T.; Odoy, S.; Haass, C.; Kahle, P.J.; Beyer, K. Alpha-synuclein has a high affinity for packing defects in a bilayer membrane: A thermodynamics study. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 21966–21975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferkorn, C.M.; Jiang, Z.; Lee, J.C. Biophysics of alpha-synuclein membrane interactions. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Perovic, I.; Chittuluru, J.; Kaganovich, A.; Nguyen, L.T.; Liao, J.; Auclair, J.R.; Johnson, D.; Landeru, A.; Simorellis, A.K.; et al. A soluble alpha-synuclein construct forms a dynamic tetramer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 17797–17802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lassen, L.B.; Reimer, L.; Ferreira, N.; Betzer, C.; Jensen, P.H. Protein Partners of alpha-Synuclein in Health and Disease. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paleologou, K.E.; El-Agnaf, O.M. alpha-Synuclein aggregation and modulating factors. Sub-Cell. Biochem. 2012, 65, 109–164. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, S.J.; Wypych, J.; Steavenson, S.; Louis, J.C.; Citron, M.; Biere, A.L. alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis is nucleation-dependent. Implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 19509–19512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iljina, M.; Garcia, G.A.; Horrocks, M.H.; Tosatto, L.; Choi, M.L.; Ganzinger, K.A.; Abramov, A.Y.; Gandhi, S.; Wood, N.W.; Cremades, N.; et al. Kinetic model of the aggregation of alpha-synuclein provides insights into prion-like spreading. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E1206-15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dearborn, A.D.; Wall, J.S.; Cheng, N.; Heymann, J.B.; Kajava, A.V.; Varkey, J.; Langen, R.; Steven, A.C. alpha-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils with Two Entwined, Asymmetrically Associated Protofibrils. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 2310–2318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Griggs, A.; Rochet, J.C.; Stanciu, L.A. In vitro study of alpha-synuclein protofibrils by cryo-EM suggests a Cu(2+)-dependent aggregation pathway. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naiki, H.; Higuchi, K.; Hosokawa, M.; Takeda, T. Fluorometric determination of amyloid fibrils in vitro using the fluorescent dye, thioflavin T1. Anal. Biochem. 1989, 177, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LeVine, H., 3rd. Thioflavine T interaction with synthetic Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid peptides: Detection of amyloid aggregation in solution. Protein Sci. 1993, 2, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeVine, H., 3rd. Quantification of beta-sheet amyloid fibril structures with thioflavin T. Methods Enzymol. 1999, 309, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.; Biancalana, M.; Koide, S.; Shea, J.E. Binding Modes of Thioflavin-T to the Single-Layer beta-Sheet of the Peptide Self-Assembly Mimics. J. Mol. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancalana, M.; Makabe, K.; Koide, A.; Koide, S. Molecular mechanism of thioflavin-T binding to the surface of beta-rich peptide self-assemblies. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 385, 1052–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biancalana, M.; Koide, S. Molecular mechanism of Thioflavin-T binding to amyloid fibrils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2010, 1804, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morimoto, K.; Kawabata, K.; Kunii, S.; Hamano, K.; Saito, T.; Tonomura, B. Characterization of type I collagen fibril formation using thioflavin T fluorescent dye. J. Biochem. 2009, 145, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Velasco, A.; Fraser, G.; Beach, T.G.; Sue, L.; Osredkar, T.; Libri, V.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M.; Lockhart, A. In vitro high affinity alpha-synuclein binding sites for the amyloid imaging agent PIB are not matched by binding to Lewy bodies in postmortem human brain. J. Neurochem. 2008, 105, 1428–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenning, M.; Norrman, M.; Flink, J.M.; van de Weert, M.; Bukrinsky, J.T.; Schluckebier, G.; Frokjaer, S. Binding mode of Thioflavin T in insulin amyloid fibrils. J. Struct. Biol. 2007, 159, 483–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenning, M. Binding mode of Thioflavin T and other molecular probes in the context of amyloid fibrils-current status. J. Chem. Biol. 2009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, I.M.; Sulatskaya, A.I.; Uversky, V.N.; Turoverov, K.K. A new trend in the experimental methodology for the analysis of the thioflavin T binding to amyloid fibrils. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 45, 488–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fonin, A.V.; Sulatskaya, A.I.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K. Fluorescence of dyes in solutions with high absorbance. Inner filter effect correction. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Belousov, M.V.; Bondarev, S.A.; Zhouravleva, G.A.; Turoverov, K.K. Stoichiometry and Affinity of Thioflavin T Binding to Sup35p Amyloid Fibrils. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Povarova, O.I.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Uversky, V.N.; Turoverov, K.K. Binding stoichiometry and affinity of fluorescent dyes to proteins in different structural states. Methods Mol. Biol. 2012, 895, 441–460. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10737–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjaergaard, M.; Norholm, A.B.; Hendus-Altenburger, R.; Pedersen, S.F.; Poulsen, F.M.; Kragelund, B.B. Temperature-dependent structural changes in intrinsically disordered proteins: Formation of alpha-helices or loss of polyproline II? Prot. Sci. Publ. Prot. Soc. 2010, 19, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876–2890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ban, T.; Hamada, D.; Hasegawa, K.; Naiki, H.; Goto, Y. Direct observation of amyloid fibril growth monitored by thioflavin T fluorescence. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16462–16465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selivanova, O.M.; Glyakina, A.V.; Gorbunova, E.Y.; Mustaeva, L.G.; Suvorina, M.Y.; Grigorashvili, E.I.; Nikulin, A.D.; Dovidchenko, N.V.; Rekstina, V.V.; Kalebina, T.S.; et al. Structural model of amyloid fibrils for amyloidogenic peptide from Bgl2p-glucantransferase of S. cerevisiae cell wall and its modifying analog. New morphology of amyloid fibrils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zahn, R. Prion propagation and molecular chaperones. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1999, 32, 309–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Maskevich, A.A.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Uversky, V.N.; Turoverov, K.K. Fluorescence quantum yield of thioflavin T in rigid isotropic solution and incorporated into the amyloid fibrils. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oravcova, J.; Bohs, B.; Lindner, W. Drug-protein binding sites. New trends in analytical and experimental methodology. J. Chromatogr. B Biomed. Appl. 1996, 677, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krebs, M.R.; Bromley, E.H.; Donald, A.M. The binding of thioflavin-T to amyloid fibrils: Localisation and implications. J. Struct. Biol. 2005, 149, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maskevich, A.A.; Stsiapura, V.I.; Kuzmitsky, V.A.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Povarova, O.I.; Uversky, V.N.; Turoverov, K.K. Spectral properties of thioflavin T in solvents with different dielectric properties and in a fibril-incorporated form. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 1392–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Lavysh, A.V.; Maskevich, A.A.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K. Thioflavin T fluoresces as excimer in highly concentrated aqueous solutions and as monomer being incorporated in amyloid fibrils. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsova, I.M.; Sulatskaya, A.I.; Maskevich, A.A.; Uversky, V.N.; Turoverov, K.K. High Fluorescence Anisotropy of Thioflavin T in Aqueous Solution Resulting from Its Molecular Rotor Nature. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Rodina, N.P.; Polyakov, D.S.; Kuznatsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K. Investigation of amyloid fibrils on the basis of full-length and truncated forms of beta-2-microglobulin with the use of equilibrium microdialysis. In Proceedings of the 7th European Conference on Biology and Medical Sciences, Rome, Italy, 27–29 July 2015; pp. 11–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sulatskaya, A.I.; Rodina, N.P.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K. Different conditions of fibrillogenesis cause polymorphysm of lysozyme amyloid fibrils. J. Mol. Struct. 2017, 1140, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabenauer, M.; Bernstein, S.L.; Lee, J.C.; Wyttenbach, T.; Dupuis, N.F.; Gray, H.B.; Winkler, J.R.; Bowers, M.T. Spermine binding to Parkinson’s protein alpha-synuclein and its disease-related A30P and A53T mutants. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 11147–11154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladimirov, Y.A.; Litvin, F.F. Photobiology and spectroscopic methods. In Handbook of General Biophisics; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 1964; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- O’Connor, D.V.P.D. Time-Correlated Single Photon Counting; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1984; pp. 37–54. [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt, D.W. An algorithm for least-squares estimation of non linear parameters. J. Soc. Ind. Appl. Math. 1963, 11, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Conditions | λabs_max, nm | Mode | εi,max × 10−4, M−1cm−1 | Kbi × 10−5, M−1 | ni | qi |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α-synuclein fibrils (by absorption spectroscopy) | 438 ± 4 | 1 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.13 ± 0.20 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| α-synuclein fibrils (by absorption and fluorescence spectroscopy) | 438 ± 4 | 1 | 1.8 ± 0.3 | 0.3 ± 0.3 | 0.13 ± 0.20 | 0.02 ± 0.01 |
| 2 | 7.0 ± 2.0 | 70 ± 10 | (4 ± 10) × 10−4 | 0.13 ± 0.04 | ||
| Insulin fibrils [41] | 450 | 1 | 2.3 | 0.4 | 0.14 | 0.27 |
| 2 | 7.9 | 78 | 0.02 | 0.72 | ||
| Lysozyme fibrils [41] | 449 | 1 | 6.2 | 0.6 | 0.25 | 0.0001 |
| 2 | 5.3 | 72 | 0.11 | 0.44 | ||
| Aβ42 fibrils [41] | 440 | 1 | 1.4 | 0.2 | 0.26 | 0.03 |
| 2 | 8.7 | 70 | 0.004 | 0.18 | ||
| Free in aqueous solution [51] | 412 | - | 3.2 | - | - | 0.0001 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sulatskaya, A.I.; Rodina, N.P.; Sulatsky, M.I.; Povarova, O.I.; Antifeeva, I.A.; Kuznetsova, I.M.; Turoverov, K.K. Investigation of α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Using the Fluorescent Probe Thioflavin T. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092486
Sulatskaya AI, Rodina NP, Sulatsky MI, Povarova OI, Antifeeva IA, Kuznetsova IM, Turoverov KK. Investigation of α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Using the Fluorescent Probe Thioflavin T. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092486
Chicago/Turabian StyleSulatskaya, Anna I., Natalia P. Rodina, Maksim I. Sulatsky, Olga I. Povarova, Iuliia A. Antifeeva, Irina M. Kuznetsova, and Konstantin K. Turoverov. 2018. "Investigation of α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Using the Fluorescent Probe Thioflavin T" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092486
APA StyleSulatskaya, A. I., Rodina, N. P., Sulatsky, M. I., Povarova, O. I., Antifeeva, I. A., Kuznetsova, I. M., & Turoverov, K. K. (2018). Investigation of α-Synuclein Amyloid Fibrils Using the Fluorescent Probe Thioflavin T. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2486. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092486