Biocatalysis of Platycoside E and Platycodin D3 Using Fungal Extracellular β-Glucosidase Responsible for Rapid Platycodin D Production
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussions
2.1. Microbial Screening
2.2. Enzyme Induction
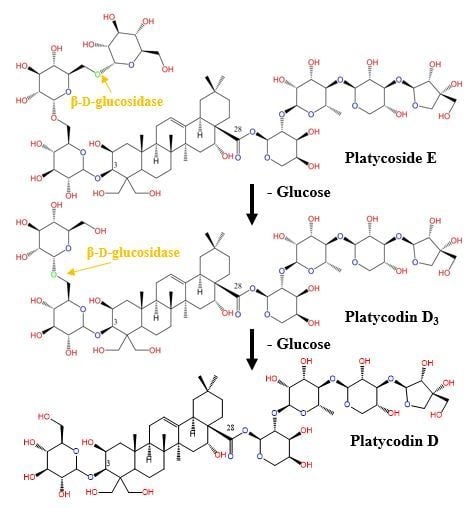
2.3. Biotransformation of Platycoside E and Platycodin D3 into Platycodin D
2.4. The Inhibitory Effects of Platycodin D on LPS-Induced IL-6 and Nitrite Production in RAW 264.7 (KCLB 40071) Mouse Macrophages
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Reagents
3.2. Preparation of Bacterial Crude Enzymes
3.3. Preparation of Fungal Crude Enzymes
3.4. Assay of β-d-Glucosidase Activity
3.5. Extraction of Crude Platycosides from Platycodi Radix
3.6. Biotransformation of Platycosides Using β-d-Glucosidase of A. usamii
3.7. Analysis of PE, PD3 and PD via HPLC-ELSD
3.8. Preparation of Platycodin D Using Preparative-HPLC
3.9. Chromatographic and Mass Spectrometric Conditions
3.10. Evaluation of Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Platycodin D
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PR | Platycodi radix |
| PE | Platycoside E |
| PD3 | Platycodin D3 |
| PD | Platycodin D |
| Glc | β-d-Glucopyranose |
| Api | β-d-Apiofuranose |
| Xyl | β-d-Xylopyranose |
| Rha | α-l-Rhamnopyranose |
| Ara | α-l-Arabinopyranose |
| pNP | para-Nitrophenol |
| BM | Basal medium |
| LPS | Lipopolysaccharide |
| NO | Nitrite |
| IL | Interleukin |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
References
- Nyakudya, E.; Jeong, J.H.; Lee, N.K.; Jeong, Y.S. Platycosides from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum and their Health Benefits. Prev. Nutr. Food Sci. 2014, 19, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, H.A.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, B.S.; Kim, E.J. Platycodon grandiflorus alleviates DNCB-induced atopy-like dermatitis in NC/Nga mice. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2012, 44, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, D.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, N.; Li, M.; Liu, Y. Platycodon grandiflorus—an ethnopharmacological, phytochemical and pharmacological review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 164, 147–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.K.; Zheng, Y.N.; Xu, B.J.; Okuda, H.; Kimura, Y. Saponins from platycodi radix ameliorate high fat diet-induced obesity in mice. J. Nutr. 2002, 132, 2241–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, I.J.; Ha, Y.W.; Kang, M.; Lee, J.; Park, D.; Kim, Y.S. Enzymatic transformation of platycosides and one-step separation of platycodin D by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. J. Sep. Sci. 2010, 33, 1916–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.Y.; Yan, Y.Z.; Arasu, M.V.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Park, S.U. Seasonal Variation of Saponin Contents in Platycodon grandiflorum. Biosci. Biotechnol. Res. Asia 2016, 13, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, J.; Zou, J.; Xie, T.; Kang, A.; Zhou, W.; Deng, H.; Mao, Y.; Di, L.; Wang, S. Pharmacokinetics, intestinal absorption and microbial metabolism of single platycodin D in comparison to Platycodi radix extract. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2015, 11, 750–755. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tada, A.; Kaneiwa, Y.; Shoji, J.; Shibata, S. Studies on the saponins of the root of Platycodon grandiflorum A. De Candolle. I. Isolation and the structure of platycodin-D. Chem. Pharm. Bull. (Tokyo) 1975, 23, 2965–2972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.Y.; Moon, K.D.; Seo, K.I.; Park, K.W.; Choi, M.S.; Do, G.M.; Jeong, Y.K.; Cho, Y.S.; Lee, M.K. Supplementation of SK1 from Platycodi radix ameliorates obesity and glucose intolerance in mice fed a high-fat diet. J. Med. Food 2009, 12, 629–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.J.; Kim, H.K.; Han, M.H.; Oh, Y.N.; Yoon, H.M.; Chung, Y.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Hwang, H.J.; Kim, B.W.; Choi, Y.H. Anti-inflammatory effects of saponins derived from the roots of Platycodon grandiflorus in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated BV2 microglial cells. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2013, 31, 1357–1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.L.; Harding, S.V.; Marinangeli, C.P.; Kim, Y.S.; Jones, P.J. Hypocholesterolemic and anti-obesity effects of saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum in hamsters fed atherogenic diets. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, H195–H200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Park, S.J.; Lim, J.H.; Yang, J.W.; Shin, J.C.; Lee, S.W.; Suh, J.W.; Hwang, S.B. Triterpenoid Saponins Isolated from Platycodon grandiflorum Inhibit Hepatitis C Virus Replication. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2013, 2013, 560417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, C.Y.; Lee, W.J.; Lee, E.B.; Choi, E.Y.; Ko, K.H. Platycodin D and D3 increase airway mucin release in vivo and in vitro in rats and hamsters. Planta Med. 2002, 68, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.H.; Oh, E.K.; Cho, H.D.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, M.K.; Seo, K.I. Crude saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum induce apoptotic cell death in RC-58T/h/SA#4 prostate cancer cells through the activation of caspase cascades and apoptosis-inducing factor. Oncol. Rep. 2013, 29, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Qin, H.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, R. Platycodin D, a triterpenoid saponin from Platycodon grandiflorum, induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in human hepatoma HepG2 cells by modulating the PI3K/Akt pathway. Tumour Biol. 2014, 35, 1267–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Q.; Pan, R.; Wang, L.; Peng, B.; Tang, J.; Liu, X. Platycodon grandiflorum induces apoptosis in SKOV3 human ovarian cancer cells through mitochondrial-dependent pathway. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2010, 38, 373–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.S.; Kim, A.K. Platycodin D induces apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. J. Med. Food 2010, 13, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chun, J.; Joo, E.J.; Kang, M.; Kim, Y.S. Platycodin D induces anoikis and caspase-mediated apoptosis via p38 MAPK in AGS human gastric cancer cells. J. Cell. Biochem. 2013, 114, 456–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.O.; Moon, D.O.; Choi, Y.H.; Shin, D.Y.; Kang, H.S.; Choi, B.T.; Lee, J.D.; Li, W.; Kim, G.Y. Platycodin D induces apoptosis and decreases telomerase activity in human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 2008, 261, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.; Zheng, H.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Optimization of β-glucuronidase activity from Lactobacillus delbrueckii Rh2 and and its use for biotransformation of baicalin and wogonoside. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2011, 54, 275–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Effects of ascorbic acid on α-l-arabinofuranosidase and α-l-arabinopyranosidase activities from Bifidobacterium longum RD47 and its application to whole cell bioconversion of ginsenoside. J. Korean Soc. Appl. Biol. Chem. 2015, 58, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Ji, G.E. Whole-cell biocatalysis for producing ginsenoside Rd from Rb1 using Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 26, 1206–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S. Finding and producing probiotic glycosylases for the biocatalysis of ginsenosides: A mini review. Molecules 2016, 21, 645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Ku, S.; Park, M.S.; Li, Z.; Ji, G.E. Acceleration of Aglycone Isoflavone and γ-Aminobutyric Acid Production from Doenjang Using Whole-Cell Biocatalysis Accompanied by Protease Treatment. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2017, 27, 1952–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegazy, M.E.F.; Mohamed, T.A.; ElShamy, A.I.; Abou-El-Hamd, H.M.; Mahalel, U.A.; Reda, E.H.; Shaheen, A.M.; Tawfik, W.A.; Shahat, A.A.; Shams, K.A. Microbial biotransformation as a tool for drug development based on natural products from mevalonic acid pathway: A review. J. Adv. Res. 2015, 6, 17–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; Zhao, L.C.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.N.; Liang, J.; Wang, H. Response surface methodology to optimize enzymatic preparation of Deapio-Platycodin D and Platycodin D from Radix Platycodi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 4089–4100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.K.; Nyakudya, E.; Jeong, Y.S. Bioconversion of Platycodon grandiflorum Saponins by the Platycodin D-Converting Microorganism, Yeast Cyberlindnera Fabianii. J. Food Biochem. 2016, 40, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basholli-Salihu, M.; Schuster, R.; Mulla, D.; Praznik, W.; Viernstein, H.; Mueller, M. Bioconversion of piceid to resveratrol by selected probiotic cell extracts. Bioproc. Biosyst. Eng. 2016, 39, 1879–1885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Corcoran, B.; Stanton, C.; Fitzgerald, G.; Ross, R. Survival of probiotic lactobacilli in acidic environments is enhanced in the presence of metabolizable sugars. Appl. Environ. Microb. 2005, 71, 3060–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, S.; You, H.J.; Ji, G.E. Enhancement of anti-tumorigenic polysaccharide production, adhesion, and branch formation of Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 by phytic acid. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2009, 18, 749–754. [Google Scholar]
- Adnan, M.; Zheng, W.; Islam, W.; Arif, M.; Abubakar, Y.S.; Wang, Z.; Lu, G. Carbon catabolite repression in filamentous fungi. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fusco, F.A.; Fiorentino, G.; Pedone, E.; Contursi, P.; Bartolucci, S.; Limauro, D. Biochemical characterization of a novel thermostable β-glucosidase from Dictyoglomus turgidum. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 113, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.J.; Ahn, H.J.; Ji, G.E. Transformation of rutin to antiproliferative quercetin-3-glucoside by Aspergillus niger. J. Agric. Food chem. 2010, 58, 10886–10892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wie, H.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Hwang, I.K.; Ji, G.E. Enzymatic modification of saponins from Platycodon grandiflorum with Aspergillus niger. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2007, 55, 8908–8913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, H.; Kim, D.H.; Ji, G.E. Transformation of ginsenosides Rb2 and Rc from Panax ginseng by food microorganisms. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 2102–2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammirato, C.; Miltner, A.; Kaestner, M. Effects of wood char and activated carbon on the hydrolysis of cellobiose by β-glucosidase from Aspergillus niger. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2011, 43, 1936–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, A.; Fu-H, N.; Batool, K.; Bibi, A. Microbial β-Glucosidase: Sources, Production and Applications. J. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 5, 31–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, S.K.; Raha, S.K.; Dey, S.K.; Chakrabarty, S. Induction and catabolite repression of β-glucosidase synthesis in Myceliophthora thermophila D-14 (= ATCC 48104). Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 1988, 54, 2152–2153. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Xu, J.; Kou, Y.; Lv, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, W.; Chen, G.; Liu, W. Differential involvement of β-glucosidases from Hypocrea jecorina in rapid induction of cellulase genes by cellulose and cellobiose. Eukaryot. Cell 2012, 11, 1371–1381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znameroski, E.A.; Coradetti, S.T.; Roche, C.M.; Tsai, J.C.; Iavarone, A.T.; Cate, J.H.; Glass, N.L. Induction of lignocellulose-degrading enzymes in Neurospora crassa by cellodextrins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 6012–6017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gottschalk, G. Bacterial Metabolism; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Charalampopoulos, D.; Pandiella, S.; Webb, C. Evaluation of the effect of malt, wheat and barley extracts on the viability of potentially probiotic lactic acid bacteria under acidic conditions. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2003, 82, 133–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamayo-Ramos, J.A.; Flipphi, M.; Pardo, E.; Manzanares, P.; Orejas, M. l-Rhamnose induction of Aspergillus nidulans α-l-rhamnosidase genes is glucose repressed via a CreA-independent mechanism acting at the level of inducer uptake. Microb. Cell Fact. 2012, 11, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Y.K.; Yao, H.J.; Cho, Y.T. Effective induction, purification and characterization of Trichoderma koningii G-39 β-xylosidase with high transferase activity. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2000, 31, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saloheimo, M.; Nakari-SetäLä, T.; Tenkanen, M.; Penttilä, M. cDNA cloning of a Trichoderma reesei cellulase and demonstration of endoglucanase activity by expression in yeast. Eur. J. Biochem. 1997, 249, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suto, M.; Tomita, F. Induction and catabolite repression mechanisms of cellulase in fungi. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 92, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.R.; Youn, S.Y.; Ji, G.E.; Park, M.S. Production of α-and β-galactosidases from Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum RD47. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 24, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, Y.W.; Na, Y.C.; Seo, J.J.; Kim, S.-N.; Linhardt, R.J.; Kim, Y.S. Qualitative and quantitative determination of ten major saponins in Platycodi Radix by high performance liquid chromatography with evaporative light scattering detection and mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2006, 1135, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, J.W.; Noh, E.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Sim, J.S.; Ha, Y.W.; Shin, E.M.; Lee, E.B.; Cheong, C.S.; Kim, Y.S. Anti-inflammatory activity of prosapogenin methyl ester of platycodin D via nuclear factor-kappaB pathway inhibition. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2008, 31, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, K.S.; Noh, E.J.; Zhao, H.L.; Jung, S.H.; Kang, S.S.; Kim, Y.S. Inhibition of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase II by Platycodon grandiflorum saponins via suppression of nuclear factor-kappaB activation in RAW 264.7 cells. Life Sci. 2005, 76, 2315–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Y.; Zhou, L.; Wang, C. Effects of platycodin D on IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 40, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Y.; Xin, Z.; Liu, B.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Li, F. Platycodin D Inhibits Inflammatory Response in LPS-Stimulated Primary Rat Microglia Cells through Activating LXRα-ABCA1 Signaling Pathway. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.T.; Yang, G.W.; Qi, C.H.; Zhou, L.; Hu, J.G.; Wang, M.S. Anti-Inflammatory activity of platycodin D on alcohol-induced fatty liver rats via TLR4-MYD88-NF-κB singal path. Afr. J. Tradit. Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 13, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, H.J.; Ahn, H.J.; Kim, J.Y.; Wu, Q.Q.; Ji, G.E. High expression of β-glucosidase in Bifidobacterium bifidum BGN4 and application in conversion of isoflavone glucosides during fermentation of soy milk. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2015, 25, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, C.H.; Visser, J.; Schreier, P. β-glucosidases from five black Aspergillus species: Study of their physico-chemical and biocatalytic properties. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2000, 48, 4929–4936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, S.W.; Park, S.J.; Shin, J.C.; Yang, J.W.; Lim, J.H. Pharmaceutical Composition for Preventing or Treating Hepatitis C, Comprising the Roots Extract of Platycodon Grandiflorum or Platycodon Grandiflorum Saponin Components. U.S. Patemt US 2011/0274656 A1, 10 November 2011. [Google Scholar]






© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, H.J.; You, H.J.; Park, M.S.; Johnston, T.V.; Ku, S.; Ji, G.E. Biocatalysis of Platycoside E and Platycodin D3 Using Fungal Extracellular β-Glucosidase Responsible for Rapid Platycodin D Production. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092671
Ahn HJ, You HJ, Park MS, Johnston TV, Ku S, Ji GE. Biocatalysis of Platycoside E and Platycodin D3 Using Fungal Extracellular β-Glucosidase Responsible for Rapid Platycodin D Production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092671
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Hyung Jin, Hyun Ju You, Myung Su Park, Tony V. Johnston, Seockmo Ku, and Geun Eog Ji. 2018. "Biocatalysis of Platycoside E and Platycodin D3 Using Fungal Extracellular β-Glucosidase Responsible for Rapid Platycodin D Production" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092671
APA StyleAhn, H. J., You, H. J., Park, M. S., Johnston, T. V., Ku, S., & Ji, G. E. (2018). Biocatalysis of Platycoside E and Platycodin D3 Using Fungal Extracellular β-Glucosidase Responsible for Rapid Platycodin D Production. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2671. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092671