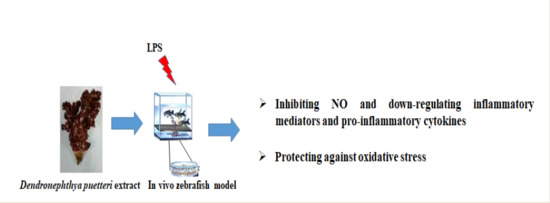
Soft Coral Dendronephthya puetteri Extract Ameliorates Inflammations by Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effect of DPE on Survival Rate, Heart Beat Rate, and Morphological Changes in Zebrafish Embryo
2.2. Effect of DPE on Cell Death in Zebrafish Embryos
2.3. In Vivo Effect of DPE on LPS-Induced ROS Generation
2.4. In Vivo Protective Effect of DPE on LPS-Induced Cell Death
2.5. In Vivo Effect of DPE on LPS-Induced NO Production
2.6. In Vivo Effect of DPE on LPS-Induced Expression of Inflammatory Mediators and Pro-inflammatory Cytokines
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Preparation of the Soft Coral Dendronephthya puetteri Extract (DPE)
4.2. Origin and Maintenance of Parental Zebrafish
4.3. Measurement of Embryo Toxicity
4.4. Evaluation of Cell Death and Generation of Intracellular Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and Nitric Oxide (NO) in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish Embryo
4.5. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Analysis
4.6. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Palladino, M.A.; Bahjat, F.R.; Theodorakis, E.A.; Moldawer, L.L. Anti-TNF-alpha therapies: The next generation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2003, 2, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines as mediators in the pathogenesis of septic shock. Chest 1997, 112, 321S–329S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serhan, C.N.; Savill, J. Resolution of inflammation: the beginning programs the end. Nat. Immunol. 2005, 6, 1191–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oikarinen, A.; Haapasaari, K.M.; Sutinen, M.; Tasanen, K. The molecular basis of glucocorticoid-induced skin atrophy: Topical glucocorticoid apparently decreases both collagen synthesis and the corresponding collagen mRNA level in human skin in vivo. Br. J. Dermatol. 1998, 139, 1106–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lakshmi, V.; Kumar, R. Metabolites from Sinularia species. Nat. Prod. Res. 2009, 23, 801–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blunt, J.W.; Copp, B.R.; Keyzers, R.A.; Munroa, M.H.G.; Prinsep, M.R. Marine natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2012, 29, 144–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhayat, E.S.; Ibrahim, S.R.M.; Fouad, M.A.; Mohamed, G.A. Dendronephthols A-C, new sesquiterpenoids from the Red Sea soft coral Dendronephthya sp. Tetrahedron 2014, 70, 3822–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, C.H.; Wen, Z.H.; Chen, I.M.; Su, J.H.; Huang, H.C.; Chiang, M.Y.; Sheu, J.H. Anti-inflammatory steroids from the octocoral Dendronephthya griffin. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 3554–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Deng, Z.; Guan, H.; van Ofwegen, L.; Proksch, P.; Lin, W. Steroids from the soft coral Dendronephthya sp. Steroids 2005, 70, 13–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomono, Y.; Hirota, H.; Imahara, Y.; Fusetani, N.J. Four new steroids from two octocorals. J. Nat. Prod. 1999, 62, 1538–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Oh, J.Y.; Shanura Fernando, I.P.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Kim, E.A.; Lee, W.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Soft corals collected from Jeju Island; a potential source of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals. J. Chitin Chitosan 2016, 21, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanura Fernando, I.P.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, S.Y.; Lee, S.H.; Lee, W.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Identification of sterols from the soft coral Dendronephthya gigantea and their anti-inflammatory potential. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 55, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shanura Fernando, I.P.; Asanka Sanjeewa, K.K.; Kim, H.S.; Wang, L.; Lee, W.W.; Jeon, Y.J. Apoptotic and antiproliferative properties of 3β-hydroxy-Δ5-steroidal congeners from a partially purified column fraction of Dendronephthya gigantean against HL-60 and MCF-7 cancer cells. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2018, 38, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eisen, J.S. Zebrafish make a big splash. Cell 1996, 87, 969–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fishman, M.C. Zebrafish genetics: The enigma of arrival. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10554–10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, S.; Champagne, D.L.; Spaink, H.P.; Richardson, M.K. Zebrafish embryos and larvae: A new generation of disease models and drug screens. Birth Defects Res. C Embryo Today 2011, 93, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, J.H.; Guo, S.Y.; Zhu, F.; Zhu, J.J.; Chen, Y.X.; Huang, C.J.; Gao, J.M.; Dong, Q.X.; Xuan, Y.X.; Li, C.Q. A zebrafish phenotypic assay for assessing drug-induced hepatotoxicity. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2013, 67, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- den Hertog, J. Chemical genetics: Drug screens in zebrafish. Biosci. Rep. 2005, 25, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Y.F.; Chiou, M.C.; Tsai, J.N.; Wen, C.C.; Wang, Y.H.; Cheng, C.C.; Chen, Y.H. Resveratrol treatment attenuates the wound-induced inflammation in zebrafish larvae through the suppression of myeloperoxidase expression. J. Food Drug Anal. 2011, 19, 167–173. [Google Scholar]
- Park, K.H.; Cho, K.H. A zebrafish model for the rapid evaluation of pro-oxidative and inflammatory death by lipopolysaccharide, oxidized low-density lipoproteins, and glycated high-density lipoproteins. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2011, 31, 904–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, C.I.; Jee, Y.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, M.; Kim, J.S.; Jeon, Y.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava in zebrafish model. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenical, W. Marine soft corals of the genus Pseudopterogorgia: A resource for novel anti-inflammatory diterpenoids. J. Nat. Prod. 1987, 50, 1001–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, J.; Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.; Yang, X.; Long, L.; Liu, Y. Chemical and biological studies of soft corals of the Nephtheidae family. Chem. Biodivers. 2011, 8, 1011–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radhika, P.; Rao, P.R.; Archana, J.; Rao, N.K. Anti-inflammatory activity of a new sphingosine derivative and cembrenoid diterpene (lobohedleolide) isolated from marine soft corals of Sinularia crassa Tixier-Durivault and Lobophytum species of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2005, 28, 1311–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De, L.E.; Zaccaria, G.M.; Hadhoud, M.; Rizzo, G.; Ponzini, R.; Morbiducci, U.; Santoro, M.M. ZebraBeat: A flexible platform for the analysis of the cardiac rate in zebrafish embryos. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 649–652. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Gooneratne, R.; Huang, X.; Lai, R.; Wei, J.; Wang, W. A rapid in vivo zebrafish model to elucidate oxidative stress-mediated PCB126-induced apoptosis and developmental toxicity. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2015, 84, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T.N.; Holbrook, J. Oxidants, oxidative stress and the biology of aging. Nature 2000, 408, 239–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Cheon, B.S.; Kim, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, H.P. Effects of naturally occurring flavonoids on nitric oxide production in the macrophage cell line RAW 264.7 and their structure-activity relationships. Biochem. Pharmacol. 1999, 58, 759–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.H.; Ko, C.I.; Ahn, G.; You, S.G.; Kim, J.S.; Heu, M.S.; Kim, J.; Jee, Y.; Jeon, Y.J. Molecular characteristics and anti-inflammatory activity of the fucoidan extracted from Ecklonia cava. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 89, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Proinflammatory cytokines. Chest 2000, 118, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Nardin, E. The role of inflammatory and immunological mediators in periodontitis and cardiovascular disease. Ann. Periodontol. 2001, 6, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, T. Interleukin 6 and its receptor: Ten years later. Int. Rev. Immunol. 1998, 16, 249–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, J.S.; Karackattu, S.L.; Fleegal, M.A.; Sumners, C. Cytokine-stimulated inducible nitric oxide synthase expression in astroglia: Role of Erk mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-κB. Glia 2003, 41, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.C.; Cha, S.H.; Wijesinghe, W.A.J.P.; Kang, S.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, E.A.; Song, C.B.; Jeon, Y.J. Protective effect of marine algae phlorotannins against AAPH-induced oxidative stress in zebrafish embryo. Food Chem. 2013, 138, 950–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, E.-A.; Ding, Y.; Yang, H.-W.; Heo, S.-J.; Lee, S.-H. Soft Coral Dendronephthya puetteri Extract Ameliorates Inflammations by Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092695
Kim E-A, Ding Y, Yang H-W, Heo S-J, Lee S-H. Soft Coral Dendronephthya puetteri Extract Ameliorates Inflammations by Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092695
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Eun-A, Yuling Ding, Hye-Won Yang, Soo-Jin Heo, and Seung-Hong Lee. 2018. "Soft Coral Dendronephthya puetteri Extract Ameliorates Inflammations by Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092695
APA StyleKim, E. -A., Ding, Y., Yang, H. -W., Heo, S. -J., & Lee, S. -H. (2018). Soft Coral Dendronephthya puetteri Extract Ameliorates Inflammations by Suppressing Inflammatory Mediators and Oxidative Stress in LPS-Stimulated Zebrafish. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2695. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092695