Overexpression of OsGID1 Enhances the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Isolation and Expression Patterns of OsGID1
2.2. Overexpression of OsGID1
2.3. Overexpressing OsGID1 Enhances the Resistance of Rice to BPH
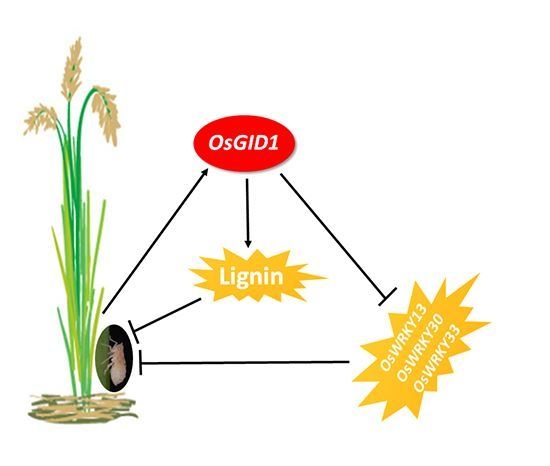
2.4. Overexpression of OsGID1 Suppressed the Expression of Three WRKY Transcription Factors
2.5. Overexpression of OsGID1 Alters Accumulation of BPH-induced H2O2, SA and Ethylene
2.6. Overexpression of OsGID1 Decreases the Population Density of Rice Planthoppers and Spiders in the Field
2.7. Overexpression of OsGID1 Reduces Rice Yield in the Field
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant and Insects
4.2. Structure of OsGID1 and Phylogenetic Analysis
4.3. Generating Transgenic Plants
4.4. RNA Extraction and Quantitative Real-time PCR
4.5. Plant Treatments
4.6. JA, JA-Ile, SA and Ethylene Measurements
4.7. Hydrogen Peroxide and Lignin Content Analysis
4.8. BPH Performance Assay
4.9. Field Experiment
4.10. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Furstenberg-Hagg, J.; Zagrobelny, M.; Bak, S. Plant defense against insect herbivores. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 10242–10297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howe, G.A.; Jander, G. Plant immunity to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 41–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Baldwin, I.T. New insights into plant responses to the attack from insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erb, M.; Meldau, S.; Howe, G.A. Role of phytohormones in insect-specific plant reactions. Trends Plant Sci. 2012, 17, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Pieterse, C.M.; Van der Does, D.; Zamioudis, C.; Leon-Reyes, A.; Van Wees, S.C. Hormonal modulation of plant immunity. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 28, 489–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuman, M.C.; Baldwin, I.T. The layers of plant responses to insect herbivores. Annu. Rev. Entomol. 2016, 61, 373–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyne, L.; Hofte, M.; De Vleesschauwer, D. Connecting growth and defense: the emerging roles of brassinosteroids and gibberellins in plant innate immunity. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 943–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaguchi, S. Gibberellin metabolism and its regulation. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2008, 59, 225–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daviere, J.M.; Achard, P. Gibberellin signaling in plants. Development 2013, 140, 1147–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Ashikari, M.; Nakajima, M.; Itoh, H.; Katoh, E.; Kobayashi, M.; Chow, T.Y.; Hsing, Y.I.; Kitano, H.; Yamaguchi, I.; et al. GIBBERELLIN INSENSITIVE DWARF1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin. Nature 2005, 437, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimada, A.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Nakatsu, T.; Nakajima, M.; Naoe, Y.; Ohmiya, H.; Kato, H.; Matsuoka, M. Structural basis for gibberellin recognition by its receptor GID1. Nature 2008, 456, 520–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverstone, A.L.; Ciampaglio, C.N.; Sun, T.P. The Arabidopsis RGA gene encodes a transcriptional regulator repressing the gibberellin signal transduction pathway. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 155–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, A.; Itoh, H.; Gomi, K.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Ishiyama, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Jeong, D.H.; An, G.; Kitano, H.; Ashikari, M.; et al. Accumulation of phosphorylated repressor for gibberellin signaling in an F-box mutant. Science 2003, 299, 1896–1898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.P. The molecular mechanism and evolution of the GA-GID1-DELLA signaling module in plants. Curr. Biol. 2011, 21, R338–R345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffiths, J.; Murase, K.; Rieu, I.; Zentella, R.; Zhang, Z.L.; Powers, S.J.; Gong, F.; Phillips, A.L.; Hedden, P.; Sun, T.P.; et al. Genetic characterization and functional analysis of the GID1 gibberellin receptors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 3399–3414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirano, K.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Matsuoka, M. GID1-mediated gibberellin signaling in plants. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 192–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Matsuoka, M. The perception of gibberellins: clues from receptor structure. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 503–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, M.; Shimada, A.; Takashi, Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Park, S.H.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Suzuki, H.; Katoh, E.; Iuchi, S.; Kobayashi, M.; et al. Identification and characterization of arabidopsis gibberellin receptors. Plant J. 2006, 46, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro, L.; Bari, R.; Achard, P.; Lison, P.; Nemri, A.; Harberd, N.P.; Jones, J.D. DELLAs control plant immune responses by modulating the balance of jasmonic acid and salicylic acid signaling. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 650–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vleesschauwer, D.; Seifi, H.S.; Filipe, O.; Haeck, A.; Huu, S.N.; Demeestere, K.; Hofte, M. The della protein slr1 integrates and amplifies salicylic acid—And jasmonic acid—Dependent innate immunity in rice. Plant Physiol. 2016, 170, 1831–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Matsuoka, M.; Kitano, H.; Asano, T.; Kaku, H.; Komatsu, S. gid1, a gibberellin-insensitive dwarf mutant, shows altered regulation of probenazole-inducible protein (PBZ1) in response to cold stress and pathogen attack. Plant Cell Environ. 2006, 29, 619–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Z.; Krosse, S.; Achard, P.; van Dam, N.M.; Bede, J.C. DELLA proteins modulate Arabidopsis defences induced in response to caterpillar herbivory. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 571–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Zhou, G.; Wang, Q.; Bian, W.; Erb, M.; Lou, Y. Prioritizing plant defence over growth through WRKY regulation facilitates infestation by non-target herbivores. eLife 2015, 4, e04805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, T.; Wang, W.; Cao, T.; Li, R.; Lou, Y. Silencing OsSLR1 enhances the resistance of rice to the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 2147–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.-G.; Zhang, G.-R.; Zhang, W.-Q.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, J. Biological control of rice insect pests in China. Biol. Control 2013, 67, 8–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Ju, H.; Zhou, G.; Zhu, C.; Erb, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, P.; Lou, Y. An EAR-motif-containing ERF transcription factor affects herbivore-induced signaling, defense and resistance in rice. Plant J. 2011, 68, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lu, J.; Li, J.C.; Ju, H.P.; Liu, X.L.; Erb, M.; Wang, X.; Lou, Y.G. Contrasting effects of ethylene biosynthesis on induced plant resistance against a chewing and a piercing-sucking herbivore in rice. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1670–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Qi, J.; Ren, N.; Cheng, J.; Erb, M.; Mao, B.; Lou, Y. Silencing OsHI-LOX makes rice more susceptible to chewing herbivores, but enhances resistance to a phloem feeder. Plant J. 2009, 60, 638–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Han, M.; Ryu, H.-S.; Kim, C.-Y.; Park, D.-S.; Ahn, Y.-K.; Jeon, J.-S. OsWRKY30 is a transcription activator that enhances rice resistance to the Xanthomonas oryzae pathovar oryzae. J. Plant Biol. 2013, 56, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koo, S.C.; Moon, B.C.; Kim, J.K.; Kim, C.Y.; Sung, S.J.; Kim, M.C.; Cho, M.J.; Cheong, Y.H. OsBWMK1 mediates SA-dependent defense responses by activating the transcription factor OsWRKY33. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 365–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, D.Y.; Xiao, J.; Ding, X.H.; Xiong, M.; Cai, M.; Cao, C.L.; Li, X.H.; Xu, C.G.; Wang, S.P. OsWRKY13 mediates rice disease resistance by regulating defense-related genes in salicylate- and jasmonate-dependent signaling. Mol. Plant Microbe Interact. 2007, 20, 492–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arimura, G.I.; Ozawa, R.; Maffei, M.E. Recent advances in plant early signaling in response to herbivory. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2011, 12, 3723–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, Y.G.; Baldwin, I.T. Silencing of a germin-like gene in Nicotiana attenuata improves performance of native herbivores. Plant Physiol. 2006, 140, 1126–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.L.; Yang, Y.N.; He, Z.H. Roles of plant hormones and their interplay in rice immunity. Mol. Plant 2013, 6, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huangfu, J.; Li, J.; Li, R.; Ye, M.; Kuai, P.; Zhang, T.; Lou, Y. The transcription factor OsWRKY45 negatively modulates the resistance of rice to the brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, X.; Lou, Y.; Cheng, J. Role of ethylene signaling in the production of rice volatiles induced by the rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2006, 51, 2457–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhou, G.; Xiang, C.; Du, M.; Cheng, J.; Liu, S.; Lou, Y. β-glucosidase treatment and infestation by the rice brown planthopper Nilaparvata lugens elicit similar signaling pathways in rice plants. Chin. Sci. Bull. 2008, 53, 53–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.C. Comparison of Defense responses in Rice Induced by Feeding and Oviposition of the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens and Their Underlying Mechanisms. Ph.D. Thesis, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Du, H.; Chang, Y.; Huang, F.; Xiong, L. GID1 modulates stomatal response and submergence tolerance involving abscisic acid and gibberellic acid signaling in rice. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2015, 57, 954–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Huot, B.; Yao, J.; Montgomery, B.L.; He, S.Y. Growth-defense tradeoffs in plants: A balancing act to optimize fitness. Mol. Plant 2014, 7, 1267–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, D.L.; Yao, J.; Mei, C.S.; Tong, X.H.; Zeng, L.J.; Li, Q.; Xiao, L.T.; Sun, T.P.; Li, J.; Deng, X.W.; et al. Plant hormone jasmonate prioritizes defense over growth by interfering with gibberellin signaling cascade. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1192–E1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Daviere, J.M.; Achard, P. A pivotal role of DELLAs in regulating multiple hormone signals. Mol. Plant 2016, 9, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, X.L.; Lee, L.Y.C.; Xia, K.F.; Yen, Y.Y.; Yu, H. DELLAs modulate jasmonate signaling via competitive binding to JAZs. Dev. Cell 2010, 19, 884–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achard, P.; Renou, J.P.; Berthome, R.; Harberd, N.P.; Genschik, P. Plant DELLAs restrain growth and promote survival of adversity by reducing the levels of reactive oxygen species. Curr. Biol. 2008, 18, 656–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuno, A.; Hirano, K.; Asano, K.; Takase, W.; Masuda, R.; Morinaka, Y.; Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Kitano, H.; Matsuoka, M. New approach to increasing rice lodging resistance and biomass yield through the use of high gibberellin producing varieties. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago, R.; Barros-Rios, J.; Malvar, R.A. Impact of cell wall composition on maize resistance to pests and diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 6960–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hu, L.F.; Ye, M.; Li, R.; Zhang, T.F.; Zhou, G.X.; Wang, Q.; Lu, J.; Lou, Y.G. The rice transcription factor WRKY53 suppresses herbivore-induced defenses by acting as a negative feedback modulator of mitogen-activated protein kinase activity. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2907–2921. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, G.J.; Meng, X.Z.; Wang, R.G.; Mao, G.H.; Han, L.; Liu, Y.D.; Zhang, S.Q. Dual-level regulation of ACC synthase activity by MPK3/MPK6 cascade and its downstream WRKY transcription factor during ethylene induction in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, S.; Forno, D.A.; Cock, J.H. Laboratory Manual for Physiological Studies of Rice, 3rd ed.; International Rice Research Institute: Los Baños, Philippines, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Q.; Yin, X.R.; Zeng, J.K.; Ge, H.; Song, M.; Xu, C.J.; Li, X.; Ferguson, B.I.; Chen, K.S. Activator- and repressor-type MYB transcription factors are involved in chilling injury induced flesh lignification in loquat via their interactionswith the phenylpropanoid pathway. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 4349–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, L.; Cao, T.; Zhang, J.; Lou, Y. Overexpression of OsGID1 Enhances the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092744
Chen L, Cao T, Zhang J, Lou Y. Overexpression of OsGID1 Enhances the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092744
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Lin, Tiantian Cao, Jin Zhang, and Yonggen Lou. 2018. "Overexpression of OsGID1 Enhances the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092744
APA StyleChen, L., Cao, T., Zhang, J., & Lou, Y. (2018). Overexpression of OsGID1 Enhances the Resistance of Rice to the Brown Planthopper Nilaparvata lugens. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2744. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092744