Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Oxidative Stress-Associated Liver Injury Induced by Chinese Herbal Medicine: An Experimental Evidence-Based Literature Review and Network Pharmacology Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in TCM-Induced Oxidative Hepatotoxicity
2.1. Redox Status in Physiology and Pathology
2.2. Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic System in Redox Homeostasis
2.3. Hepatotoxicity Caused by Specific Pro-Oxidant TCMs
2.4. Literature Search Methodology
2.5. Pure Compounds
2.6. Herbal Extracts
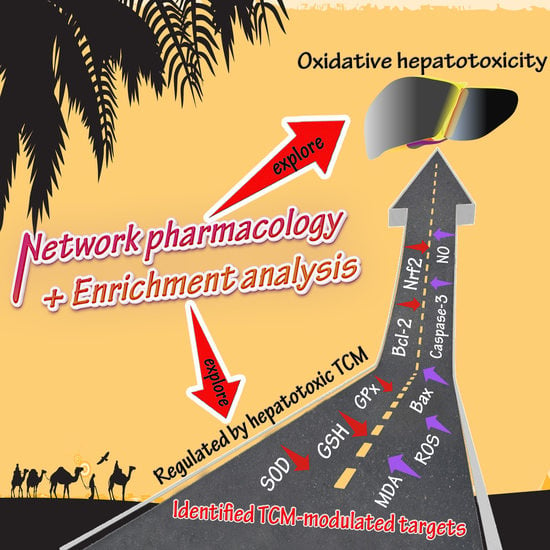
3. Network Pharmacology-Associated Study
3.1. Network Construction and Targets Discovery
3.2. Hepatotoxic Role of Identified TCM-Regulated Targets by Network Pharmacology
3.2.1. SOD, MDA, GSH, ROS, and GPx
3.2.2. Bax, Caspase-3, and Bcl-2
3.2.3. Nrf2 and NO
3.3. Bioinformatics Enrichment Analysis
3.4. RUCAM (Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method) in TCM-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Clinical Studies
3.4.1. RUCAM-Based Causality Assessment
3.4.2. Identified Hepatotoxic TCM in Case Reports Using RUCAM
3.5. Ethnopharmacology-Associated Challenges and Threats
4. Conclusions and Prospects
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ALD | alcoholic liver disease |
| ALP | alkaline phosphatase |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ALT | alanine transaminase |
| AST | aspartate aminotransferase |
| ATF6 | activating transcription factor 6 |
| ATP | adenosine triphosphate |
| CAT | catalase |
| CHOP | C/EBP homologous protein |
| CytC | cytochrome C |
| CYP2C19 | cytochrome P2C19 |
| CYP2E1 | cytochrome P2E1 |
| CYP3A | cytochrome P3A |
| CYP3A4 | cytochrome P3A4 |
| CYP450 | cytochrome P450 |
| DAVID | database for annotation, visualization and integrated discovery |
| DBil | direct bilirubin |
| eNOS | endothelial NO synthase |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| GPx | glutathione peroxidase |
| GRP78 | glucose regulated protein |
| GSH | glutathione |
| GST | glutathione S-transferase |
| HCC | hepatocellular carcinoma |
| HCV | hepatitis C virus |
| HILI | herb-induced liver injury |
| IBil | indirect bilirubin |
| IL-6 | interleukin 6 |
| IL-12 | interleukin-12 |
| IL-14 | interleukin-14 |
| IRE1 | inositol-requiring enzyme 1 |
| iNOS | inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinases |
| Keap1 | Kelch-like ECH-associated protein-1 |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| KOBAS | KEGG orthology-based annotation system |
| LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| LPC | lysophosphatidylcholine |
| LPS | lipopolysaccharide |
| MDA | malondialdehyde |
| NA(D)PH | nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase |
| NAFLD | non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NO | nitric oxide |
| NOS | nitric oxide synthase |
| NQO1 | NAD(P)H dehydrogenase, quinone 1 |
| Nrf1 | nuclear respiratory factor 1 |
| Nrf2 | nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 |
| MPT | mitochondrial permeability transition |
| MRP2 | multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 |
| MRP4 | multidrug resistance protein 4 |
| OATP2 | organic anion transporting polypeptide 2 |
| p38 MAPK | p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| p-JNK | phospho-c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| PERK | pancreatic ER kinase |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| PLA2 | phospholipase A2 |
| PPAR-α | peroxisome proliferator activated receptor α |
| PPAR-γ | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ |
| RNS | reactive nitrogen species |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| RUCAM | Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method |
| SOD | superoxide dismutases |
| TBil | total bilirubin |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor- β |
| TNF | tumor necrosis factor |
| UGT1A1 | uridine diphosphate glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 |
| 4-HNE | 4-hydroxynonenal |
References
- Mendes-Braz, M.; Martins, J.O. Diabetes Mellitus and Liver Surgery: The Effect of Diabetes on Oxidative Stress and Inflammation. Mediat. Inflamm. 2018, 2018, 2456579–2456590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taleb, A.; Ahmad, K.A.; Ihsan, A.U.; Qu, J.; Lin, N.; Hezam, K.; Koju, N.; Hui, L.; Qilong, D. Antioxidant effects and mechanism of silymarin in oxidative stress induced cardiovascular diseases. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 102, 689–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vida, C.; Martinez de Toda, I.; Garrido, A.; Carro, E.; Molina, J.A.; De la Fuente, M. Impairment of Several Immune Functions and Redox State in Blood Cells of Alzheimer’s Disease Patients. Relevant Role of Neutrophils in Oxidative Stress. Front. Immunol. 2017, 8, 1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, D.; Jing, S.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, G. Pterostilbene protects against acute renal ischemia reperfusion injury and inhibits oxidative stress, inducible nitric oxide synthase expression and inflammation in rats via the Toll-like receptor 4/nuclear factor-kappaB signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1029–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocak, C.; Kocak, F.E.; Akcilar, R.; Akcilar, A.; Savran, B.; Zeren, S.; Bayhan, Z.; Bayat, Z. Ukrain (NSC 631570) ameliorates intestinal ischemia-reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by reducing oxidative stress. Bosn. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2016, 16, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Xu, Y.; Guo, W.; Feng, Y. Supplementation of Micronutrient Selenium in Metabolic Diseases: Its Role as an Antioxidant. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 7478523–7478536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, L.; Khoury, J.; Kantorow, M. Parkin elimination of mitochondria is important for maintenance of lens epithelial cell ROS levels and survival upon oxidative stress exposure. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2017, 1863, 21–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Y.; Feng, Y. Neuroprotective effect of He-Ying-Qing-Re formula on retinal ganglion cell in diabetic retinopathy. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 214, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; You, J.; Li, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, Y. MicroRNA-542-3p suppresses tumor cell proliferation via targeting Smad2 inhuman osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 6895–6902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.G.; Sheng, X.P.; Huang, Y.P.; Wang, Y.T.; Jiang, C.H.; Zhang, J.; Yin, Z.Q. Triterpenic acids-enriched fraction from Cyclocarya paliurus attenuates non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via improving oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 104, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Li, S.; Hong, M.; Guo, W.; Man, K.; Cheng, C.S.; Chen, Z.; Feng, Y. Repression of WT1-Mediated LEF1 Transcription by Mangiferin Governs β-Catenin-Independent Wnt Signalling Inactivation in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 1819–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, C.; Gao, D.; Li, X.F.; Li, C.Y.; Li, R.S.; Zhao, Y.L.; Li, N.; Jia, G.L.; Pang, J.Y.; Cui, H.R.; et al. Inflammatory stress potentiates emodin-induced liver injury in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, M.; Ding, J.; Wang, M.; Zhang, J.; Zhu, X.; Guan, W. Kupffer-derived matrix metalloproteinase-9 contributes to liver fibrosis resolution. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2018, 14, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossini, E.; Bellofatto, K.; Farruggio, S.; Sigaudo, L.; Marotta, P.; Raina, G.; De Giuli, V.; Mary, D.; Pollesello, P.; Minisini, R.; et al. Levosimendan inhibits peroxidation in hepatocytes by modulating apoptosis/autophagy interplay. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0124742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez, C.; Checa, S.K.; Soncini, F.C. CpxR/CpxA-controls scsABCD transcription to counteract copper and oxidative stress in Salmonella Typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortezaee, K.; Khanlarkhani, N. Melatonin application in targeting oxidative-induced liver injuries: A review. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 4015–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhang, H.; Shen, F.; Liu, X.; Fu, J. Hydrogen-rich water attenuates oxidative stress in rats with traumatic brain injury via Nrf2 pathway. J. Surg. Res. 2018, 228, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovalcikova, A.; Gyuraszova, M.; Vavrincova-Yaghi, D.; Vavrinec, P.; Tothova, L.; Boor, P.; Sebekova, K.; Celec, P. Oxidative stress in the brain caused by acute kidney injury. Metab. Brain Dis. 2018, 33, 961–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, C.G.; Procianoy, R.S.; Neto, E.C.; Silveira, R.C. Preterm Neonates with Respiratory Distress Syndrome: Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury and Oxidative Stress. J. Immunol. Res. 2018, 2018, 6963754–6963758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkel, T. Signal transduction by reactive oxygen species. J. Cell Biol. 2011, 194, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Souayed, N.; Chennoufi, M.; Boughattas, F.; Haouas, Z.; Maaroufi, K.; Miled, A.; Ben-Attia, M.; Aouam, K.; Reinberg, A.; Boughattas, N.A. Circadian variation in murine hepatotoxicity to the antituberculosis agent <<Isoniazide>>. Chronobiol. Int. 2015, 32, 1201–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; He, T.; Farrar, S.; Ji, L.; Liu, T.; Ma, X. Antioxidants Maintain Cellular Redox Homeostasis by Elimination of Reactive Oxygen Species. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 44, 532–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farzaei, M.H.; Zobeiri, M.; Parvizi, F.; El-Senduny, F.F.; Marmouzi, I.; Coy-Barrera, E.; Naseri, R.; Nabavi, S.M.; Rahimi, R.; Abdollahi, M. Curcumin in Liver Diseases: A Systematic Review of the Cellular Mechanisms of Oxidative Stress and Clinical Perspective. Nutrients 2018, 10, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefaki, M.; Papaevgeniou, N.; Chondrogianni, N. Redox regulation of proteasome function. Redox. Biol. 2017, 13, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rivero Osimani, V.L.; Valdez, S.R.; Guinazu, N.; Magnarelli, G. Alteration of syncytiotrophoblast mitochondria function and endothelial nitric oxide synthase expression in the placenta of rural residents. Reprod. Toxicol. 2016, 61, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.C. Antioxidants in the treatment of chronic liver diseases: Why is the efficacy evidence so weak in humans? Hepatology 2008, 48, 1359–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nowicki, C.J.; Kashian, D.R. Comparison of lipid peroxidation and catalase response in invasive dreissenid mussels exposed to single and multiple stressors. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 1643–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marchlewicz, M.; Szypulska-Koziarska, D.; Grzegrzolka, A.; Kruk, J.; Duchnik, E.; Wiszniewska, B. [Protection against oxidative stress in male reproductive system]. Pomeranian J. Life Sci. 2016, 62, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Neale, P.A.; Achard, M.E.S.; Escher, B.I.; Leusch, F.D.L. Exploring the oxidative stress response mechanism triggered by environmental water samples. Environ. Sci. Process Impacts 2017, 19, 1126–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Han, T.; Xue, L.M.; Han, P.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Huang, B.K.; Zhang, H.; Ming, Q.L.; Peng, W.; Qin, L.P. Hepatotoxicity of kaurene glycosides from Xanthium strumarium L. fruits in mice. Pharmazie 2011, 66, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.V.; Shrivastava, A.; Jyotshna; Chaturvedi, U.; Singh, S.C.; Shanker, K.; Saxena, J.K.; Bhatia, G.; Pal, A. A mechanism-based pharmacological evaluation of efficacy of Flacourtia indica in management of dyslipidemia and oxidative stress in hyperlipidemic rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2016, 27, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nauser, T.; Gebicki, J.M. Physiological Concentrations of Ascorbate Cannot Prevent the Potentially Damaging Reactions of Protein Radicals in Humans. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 1702–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabrese, V.; Cornelius, C.; Rizzarelli, E.; Owen, J.B.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; Butterfield, D.A. Nitric oxide in cell survival: A janus molecule. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 2717–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dizdaroglu, M.; Jaruga, P. Mechanisms of free radical-induced damage to DNA. Free Radic. Res. 2012, 46, 382–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajka-Kuzniak, V.; Szaefer, H.; Ignatowicz, E.; Adamska, T.; Markowski, J.; Baer-Dubowska, W. Influence of Cloudy Apple Juice on N-Nitrosodiethylamine-Induced Liver Injury and Phases I and Ii Biotransformation Enzymes in Rat Liver. Acta Pol. Pharm. 2015, 72, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lim, E.J.; Chin, R.; Nachbur, U.; Silke, J.; Jia, Z.; Angus, P.W.; Torresi, J. Hepatitis C-induced hepatocyte apoptosis following liver transplantation is enhanced by immunosuppressive agents. J. Viral Hepat. 2016, 23, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belka, M.; Baczek, T. The Metabolism of Anticancer Drugs by the Liver: Current Approaches to the Drug Development Process. Curr. Drug Metab. 2015, 16, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuen, M.F.; Tam, S.; Fung, J.; Wong, D.K.; Wong, B.C.; Lai, C.L. Traditional Chinese medicine causing hepatotoxicity in patients with chronic hepatitis B infection: A 1-year prospective study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2006, 24, 1179–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motoyama, H.; Enomoto, M.; Yasuda, T.; Fujii, H.; Kobayashi, S.; Iwai, S.; Morikawa, H.; Takeda, T.; Tamori, A.; Sakaguchi, H.; et al. [Drug-induced liver injury caused by an herbal medicine, bofu-tsu-sho-san]. Nihon Shokakibyo Gakkai Zasshi 2008, 105, 1234–1239. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.H.; Wang, J.D.; Chen, P.C. Risk of liver injury associated with Chinese herbal products containing radix bupleuri in 639,779 patients with hepatitis B virus infection. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e16064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.M.; Ko, H.L.; Lee, J.R.; Park, C.A.; Byun, S.H.; Ku, S.K.; Cho, I.J.; Kim, S.C. Epimedium koreanum Ameliorates Oxidative Stress-Mediated Liver Injury by Activating Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 469–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Z.J.; Lao, L.; Wong, C.W.; Feng, Y. The Role of Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 26087–26124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, F.; Liang, Y.; Xu, L.; Ji, L.; Yao, N.; Liu, R.; Shi, L.; Liang, T. Exploration in the cascade working mechanisms of liver injury induced by total saponins extracted from Rhizoma Dioscorea bulbifera. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2016, 83, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, X.M.; Miao, L.L.; Cai, Y.; Gong, L.K.; Ren, J. ROS generated by CYP450, especially CYP2E1, mediate mitochondrial dysfunction induced by tetrandrine in rat hepatocytes. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1229–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- He, F.Q.; Qiu, B.Y.; Li, T.K.; Xie, Q.; Cui, D.J.; Huang, X.L.; Gan, H.T. Tetrandrine suppresses amyloid-β-induced inflammatory cytokines by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway in murine BV2 microglial cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2011, 11, 1220–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, Y.; Feng, D.C.; Xiao, B.G.; Xu, L.Y. Tetrandrine suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced microglial activation by inhibiting NF-kappaB pathway. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2008, 29, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, P.; Xu, Y.; Wei, R.; Li, H.; Tang, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, S.S.; Zhang, C. Efficacy of tetrandrine on lowering intraocular pressure in animal model with ocular hypertension. J. Glaucoma 2011, 20, 183–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, W.Y.; Li, D.; Cai, D.E.; Huang, X.Y.; Zheng, B.Y.; Huang, Y.H.; Chen, Z.X.; Wang, X.Z. Hepatitis B virus X protein sensitizes HL-7702 cells to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis through modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 37, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ji, L.; Xiong, A.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z. Involvement of intracellular glutathione in regulating isoline-induced cytotoxicity in human normal liver L-02 cells. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2013, 29, 567–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.Y.; Ji, L.L.; Wang, Z.T. Pyrrolizidine alkaloid isoline-induced oxidative injury in various mouse tissues. Exp. Toxicol. Pathol. 2010, 62, 251–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.Y.; Kang, H.; Ji, L.L.; Yang, Y.Q.; Liu, T.Y.; Cao, Z.W.; Morahan, G.; Wang, Z.T. Proteomic characterization of the possible molecular targets of pyrrolizidine alkaloid isoline-induced hepatotoxicity. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 34, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Guo, X.; Huang, W.; Peng, Y.; Zheng, J. Comparative Study of Hepatotoxicity of Pyrrolizidine Alkaloids Retrorsine and Monocrotaline. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2017, 30, 532–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.H.; Tai, W.C.; Khan, I.; Lu, C.; Lu, Y.; Wong, W.Y.; Chan, W.Y.; Wendy Hsiao, W.L.; Lin, G. Toxicoproteomic assessment of liver responses to acute pyrrolizidine alkaloid intoxication in rats. J. Environ. Sci. Health C Environ. Carcinog. Ecotoxicol. Rev. 2018, 36, 65–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tu, M.; Li, L.; Lei, H.; Ma, Z.; Chen, Z.; Sun, S.; Xu, S.; Zhou, H.; Zeng, S.; Jiang, H. Involvement of organic cation transporter 1 and CYP3A4 in retrorsine-induced toxicity. Toxicology 2014, 322, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.; Duan, G.; He, J.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Meng, Y. Geniposide attenuates epilepsy symptoms in a mouse model through the PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β signaling pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 15, 1136–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, H.; Li, Y.; Qian, H.; Qi, X.; Wu, G.; Zhang, H.; Xu, M.; Rao, Z.; Li, J.L.; Wang, L.; et al. Effects of Geniposide from Gardenia Fruit Pomace on Skeletal-Muscle Fibrosis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 5802–5811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Shou, K.; Gong, C.; Yang, H.; Yang, Y.; Bao, T. Anti-Inflammatory Effect of Geniposide on Osteoarthritis by Suppressing the Activation of p38 MAPK Signaling Pathway. Biomed. Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 8384576–8384587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zhang, T.; Tao, J.S.; Zhang, L.Y.; Shi, J.R.; Ji, G. Potential hepatotoxicity of geniposide, the major iridoid glycoside in dried ripe fruits of Gardenia jasminoides (Zhi-zi). Nat. Prod. Res. 2013, 27, 929–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Z.A.; Sun, M.N.; Hu, Z.S. Saikosaponin a Ameliorates LPS-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Mice. Inflammation 2018, 41, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, T.H.; Park, S.; You, M.H.; Lim, J.H.; Min, S.H.; Kim, B.M. A potential therapeutic effect of saikosaponin C as a novel dual-target anti-Alzheimer agent. J. Neurochem. 2016, 136, 1232–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.J.; Zhao, R.Z.; Xiang, F.J. Vinegar amount in the process affected the components of vinegar-baked Radix Bupleuri and its hepatoprotective effect. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Li, X.; Lu, J.; Huang, Y.; Lv, L.; Luan, Y.; Liu, R.; Sun, R. Saikosaponins induced hepatotoxicity in mice via lipid metabolism dysregulation and oxidative stress: A proteomic study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Zhang, L. BRCA1 expression serves a role in vincristine resistance in colon cancer cells. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 345–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zeng, F.; Ju, R.J.; Liu, L.; Xie, H.J.; Mu, L.M.; Lu, W.L. Efficacy in Treating Lung Metastasis of Invasive Breast Cancer with Functional Vincristine Plus Dasatinib Liposomes. Pharmacology 2018, 101, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Setty, B.A.; Stanek, J.R.; Mascarenhas, L.; Miller, A.; Bagatell, R.; Okcu, F.; Nicholls, L.; Lysecki, D.; Gupta, A.A. VIncristine, irinotecan, and temozolomide in children and adolescents with relapsed rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2018, 65, e26728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shati, A.A.; Elsaid, F.G. Hepatotoxic effect of subacute vincristine administration activates necrosis and intrinsic apoptosis in rats: Protective roles of broccoli and Indian mustard. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Wu, Y.; Wang, M.; Chen, W.; Jiang, J. Meta-analysis of the clinical value of oxymatrine on sustained virological response in chronic hepatitis B. Ann. Hepatol. 2016, 15, 482–491. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Shi, H.J.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.G.; Xia, L.; Song, H.B.; Bo, K.P.; Ma, W. Efficacy of oxymatrine for treatment and relapse suppression of severe plaque psoriasis: Results from a single-blinded randomized controlled clinical trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 176, 1446–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, Y.G.; Jing, S.; Li, L.; Gao, J.Q.; Shen, Z.Y.; Liu, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wu, M.L.; Wang, Y.; Xu, C.Q.; et al. Antiarrhythmic effects and ionic mechanisms of oxymatrine from Sophora flavescens. Phytother. Res. 2010, 24, 1844–1849. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Pan, D.; Wang, Y.; Yang, N.; Xiang, L.; Cai, X.; Feng, Y. Hepatoprotection and hepatotoxicity of Heshouwu, a Chinese medicinal herb: Context of the paradoxical effect. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2017, 108, 407–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, M.; Gagnier, J.J.; Little, C.V.; Parsons, T.J.; Blumle, A.; Chrubasik, S. Evidence of effectiveness of herbal medicinal products in the treatment of arthritis. Part 2: Rheumatoid arthritis. Phytother. Res. 2009, 23, 1647–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.J.; Jiang, Z.Z.; Zhang, L.Y. Triptolide: Progress on research in pharmacodynamics and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 155, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, G.; Zhuang, X.; Xiao, W.; Kong, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, H. Role of CYP3A in regulating hepatic clearance and hepatotoxicity of triptolide in rat liver microsomes and sandwich-cultured hepatocytes. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 71, 90–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, T.; Huang, X.; Su, Y.; Ji, J.; Su, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, L. Glycyrrhizin accelerates the metabolism of triptolide through induction of CYP3A in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ya, G.; Rui, H. Inhibitory Effects of Triptolide on Human Liver Cytochrome P450 Enzymes and P-Glycoprotein. Eur. J. Drug Metab. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 42, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Z.; Chen, L.; Fang, P.; Cai, H.; Tang, H.; Peng, Y.; Deng, Y.; Cao, L.; Li, H.; Zhang, B.; et al. Mechanisms of Triptolide-Induced Hepatotoxicity and Protective Effect of Combined Use of Isoliquiritigenin: Possible Roles of Nrf2 and Hepatic Transporters. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.X.; Du, F.Y.; Liu, H.X.; Ji, J.B.; Xing, J. Investigation of the active components in Tripterygium wilfordii leading to its acute hepatotoxicty and nephrotoxicity. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2015, 162, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, Z.; Li, X.; Wu, Q.; Hu, S.; Yang, X. The research on the anti-inflammatory activity and hepatotoxicity of triptolide-loaded solid lipid nanoparticle. Pharmacol. Res. 2005, 51, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.X.; Li, M.H.; Tao, L.; Ruan, L.Y.; Hong, W.; Chen, C.; Zhao, W.L.; Xu, H.; Chen, J.F.; Wang, J.S. Anti-Cancer Effects of Emodin on HepG2 Cells as Revealed by (1)H NMR Based Metabolic Profiling. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 1943–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.Y.; Jin, M.L.; Kang, N.J.; Park, G.; Choi, Y.W. Anti-inflammatory effects of novel polygonum multiflorum compound via inhibiting NF-kappaB/MAPK and upregulating the Nrf2 pathways in LPS-stimulated microglia. Neurosci. Lett. 2017, 651, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, E.Y.; Bayarsengee, U.; Wang, C.C.; Chiang, Y.H.; Cheng, C.W. The natural compound 2,3,5,4′-tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d glucoside protects against adriamycin-induced nephropathy through activating the Nrf2-Keap1 antioxidant pathway. Environ. Toxicol. 2018, 33, 72–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.L.; Ma, J.; Zheng, L.; Li, H.J.; Li, P. Determination of emodin in L-02 cells and cell culture media with liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry: Application to a cellular toxicokinetic study. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2012, 71, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.H.; Kang, K.Y.; Kim, J.J.; Lee, S.J.; Son, Y.J.; Paik, S.H.; Yee, S.T. Effects of Hot Water Extracts from Polygonum multiflorum on Ovariectomy Induced Osteopenia in Mice. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2016, 2016, 8970585–8970594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, S.; Xu, J.W. Biological Activities of 2,3,5,4′-Tetrahydroxystilbene-2-O-β-d-Glucoside in Antiaging and Antiaging-Related Disease Treatments. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2016, 2016, 4973239–4973253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Jiang, Z.; Zhou, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, L. [Study on hepatotoxicity of aqueous extracts of Polygonum multiforum in rats after 28-day oral administration-analysis on correlation of cholestasis]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2012, 37, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Xie, J.; Mao, X.J.; Wang, M.J.; Li, N.; Wang, J.; Zhaori, G.T.; Zhao, R.H. Hepatoxicity of major constituents and extractions of Radix Polygoni Multiflori and Radix Polygoni Multiflori Praeparata. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2011, 137, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Lin, L.; Lin, H.; Qu, C.; Yan, L.; Ni, J. Interpretation the Hepatotoxicity Based on Pharmacokinetics Investigated Through Oral Administrated Different Extraction Parts of Polygonum multiflorum on Rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, Y.K.; Li, C.Y.; Li, R.Y.; He, L.Z.; Cui, H.R.; Yin, P.; Zhang, C.E.; Li, P.Y.; Sang, X.X.; Wang, Y.; et al. Cis-stilbene glucoside in Polygonum multiflorum induces immunological idiosyncratic hepatotoxicity in LPS-treated rats by suppressing PPAR-gamma. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2017, 38, 1340–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Chen, X.; Huang, Q.; Fang, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, G. Toxicity of raw and processed roots of Polygonum multiflorum. Fitoterapia 2012, 83, 469–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fan, X.; Zhu, J.Y.; Sun, Y.; Luo, L.; Yan, J.; Yang, X.; Yu, J.; Tang, W.Q.; Ma, W.; Liang, H.P. Evodiamine Inhibits Zymosan-Induced Inflammation In Vitro and In Vivo: Inactivation of NF-kappaB by Inhibiting IkappaBalpha Phosphorylation. Inflammation 2017, 40, 1012–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schramm, A.; Hamburger, M. Gram-scale purification of dehydroevodiamine from Evodia rutaecarpa fruits, and a procedure for selective removal of quaternary indoloquinazoline alkaloids from Evodia extracts. Fitoterapia 2014, 94, 127–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, C.C.; Wu, M.S.; Shen, S.C.; Ko, C.H.; Chen, C.H.; Yang, L.L.; Chen, Y.C. Activation of JNK contributes to evodiamine-induced apoptosis and G2/M arrest in human colorectal carcinoma cells: A structure-activity study of evodiamine. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e99729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, X.; He, X.; Zhu, N.; Liu, J.; Wu, Y.; Li, Y.; et al. Rutaecarpine suppresses atherosclerosis in ApoE-/- mice through upregulating ABCA1 and SR-BI within RCT. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1634–1647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Sun, R. [Study on efficacy accompanied by side effects of water extraction components of Evodiae Fructus based on syndrome model]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015, 40, 2753–2759. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cai, Q.; Wei, J.; Zhao, W.; Shi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wei, R.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, Q. Toxicity of Evodiae fructus on rat liver mitochondria: The role of oxidative stress and mitochondrial permeability transition. Molecules 2014, 19, 21168–21182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Li, X.; Sun, R. [“Dose-time-toxicity” relationship study on hepatotoxicity caused by multiple dose water extraction components of Evodiae Fructus to mice]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2012, 37, 2223–2227. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uyangaa, E.; Choi, J.Y.; Ryu, H.W.; Oh, S.R.; Eo, S.K. Anti-herpes Activity of Vinegar-processed Daphne genkwa Flos via Enhancement of Natural Killer Cell Activity. Immune Netw. 2015, 15, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Chou, G.; Hseu, Y.; Yang, H.; Kwan, H.; Yu, Z. Isolation of anticancer constituents from flos genkwa (Daphne genkwa Sieb.et Zucc.) through bioassay-guided procedures. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yun, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; You, J.R.; Kwon, E.; Jang, J.J.; Park, I.A.; Kim, H.C.; Kim, H.H.; Che, J.H.; et al. Evaluation of subchronic (13 week) toxicity and genotoxicity potential of vinegar-processed Genkwa Flos. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2015, 72, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Investigation of potential toxic components based on the identification of Genkwa Flos chemical constituents and their metabolites by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a Q Exactive high-resolution benchtop quadrupole Orbitrap mass spectrometer. J. Sep. Sci. 2018, 41, 3328–3338. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Liang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Zhu, X.; Feng, W.; Liang, J.; Ito, Y. Studies on a Simple and Efficient Method for Large-Scale Preparation of Genkwanin from Daphne Genkwa Sieb. Et Zucc. Using Normal-Phase Flash Chromatography. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2014, 37, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.G.; Guo, J.; Zhu, K.Y.; Tao, W.; Chen, Y.; Liu, P.; Hua, Y.; Tang, Y.; Duan, J.A. How impaired efficacy happened between Gancao and Yuanhua: Compounds, targets and pathways. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Duan, J.A.; Guo, J.; Shang, E.; Tang, Y.; Qian, Y.; Tao, W.; Liu, P. Yuanhuapine-induced intestinal and hepatotoxicity were correlated with disturbance of amino acids, lipids, carbohydrate metabolism and gut microflora function: A rat urine metabonomic study. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1026, 183–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Li, C.P. [Anti-mite activities of 25 kinds of traditional Chinese medicines for Demodex folliculorum]. Zhong Yao Cai 2006, 29, 1013–1015. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shi, J.; Zhou, J.; Ma, H.; Guo, H.; Ni, Z.; Duan, J.; Tao, W.; Qian, D. An in vitro metabolomics approach to identify hepatotoxicity biomarkers in human L02 liver cells treated with pekinenal, a natural compound. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2016, 408, 1413–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.; Miao, P.P.; Guo, C.E.; Chen, H.Y.; Ma, P.K.; Li, H.P.; Zhu, H.Y.; Gao, X.; Zhang, Y.J. [In vitro effects of Genkwa Flos chloroform extract on activity of human liver microsomes UGTs and UGT1A1]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2016, 41, 3296–3302. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sreejith, G.; Latha, P.G.; Shine, V.J.; Anuja, G.I.; Suja, S.R.; Sini, S.; Shyama, S.; Pradeep, S.; Shikha, P.; Rajasekharan, S. Anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory and anti-lipidperoxidant effects of Cassia occidentalis Linn. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2010, 48, 494–498. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, G.; Tiwari, S.; Ansari, K.M.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Khanna, V.K.; Chaudhari, B.P.; Vashistha, V.M.; Raisuddin, S.; Das, M. Association between children death and consumption of Cassia occidentalis seeds: Clinical and experimental investigations. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira-Filho, J.P.; Cagnini, D.Q.; Badial, P.R.; Pessoa, M.A.; Del Piero, F.; Borges, A.S. Hepatoencephalopathy syndrome due to Cassia occidentalis (Leguminosae, Caesalpinioideae) seed ingestion in horses. Equine Vet. J. 2013, 45, 240–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chhapola, V.; Kanwal, S.K.; Sharma, A.G.; Kumar, V. Hepatomyoencephalopathy Secondary to Cassia occidentalis Poisoning: Report of Three Cases from North India. Indian J. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 22, 454–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, H.P.; Batish, D.R.; Kaur, S.; Arora, K.; Kohli, R.K. alpha-Pinene inhibits growth and induces oxidative stress in roots. Ann. Bot. 2006, 98, 1261–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Yadav, A.; Yadav, A.; Ansari, K.M.; Chaturvedi, R.K.; Vashistha, V.M.; Raisuddin, S.; Das, M. Hepatic transcriptional analysis in rats treated with Cassia occidentalis seed: Involvement of oxidative stress and impairment in xenobiotic metabolism as a putative mechanism of toxicity. Toxicol. Lett. 2014, 229, 273–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntchapda, F.; Barama, J.; Kemeta Azambou, D.R.; Etet, P.F.; Dimo, T. Diuretic and antioxidant activities of the aqueous extract of leaves of Cassia occidentalis (Linn.) in rats. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2015, 8, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- James, K.D.; Kennett, M.J.; Lambert, J.D. Potential role of the mitochondria as a target for the hepatotoxic effects of (-)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate in mice. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 111, 302–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, L.L.; Shen, Z.L.; Li, Y.L.; Bao, Y.Q.; Lu, H. Oxymatrine Causes Hepatotoxicity by Promoting the Phosphorylation of JNK and Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Mediated by ROS in LO2 Cells. Mol. Cells 2018, 41, 401–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Wang, M.; Wang, M.; Tian, Y.; Sun, X.; Sun, G.; Sun, X. Bavachinin Induces Oxidative Damage in HepaRG Cells through p38/JNK MAPK Pathways. Toxins 2018, 10, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, Q.; Sun, L.; Lv, M.; Yu, P.; Chen, X. Investigation of the mechanisms of Genkwa Flos hepatotoxicity by a cell metabolomics strategy combined with serum pharmacology in HL-7702 liver cells. Xenobiotica 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Yu, L.; Chen, W.; Lu, X.; Fan, X. Circulating exosomal microRNAs reveal the mechanism of Fructus Meliae Toosendan-induced liver injury in mice. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 2832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Yao, L.; Guo, K.; Wang, X.; Wang, Q.; Li, W. Hepatocellular toxicity of oxalicumone A via oxidative stress injury and mitochondrial dysfunction in healthy human liver cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 743–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, W.; Cui, X.; Liu, J.; Wei, Y. Arsenic Induces Thioredoxin 1 and Apoptosis in Human Liver HHL-5 Cells. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2018, 181, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, S.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Yang, P.; Dang, X.; Wei, H.; Hu, N.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Y. Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum Involved in the Regulation of Bile Acids Metabolism in Hepatic Injury. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 41, 869–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xue, Y.; Chen, Q.; Sun, J. Hydroxyapatite nanoparticle-induced mitochondrial energy metabolism impairment in liver cells: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2017, 37, 1004–1016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, X.; Deng, X.; Shi, J.; Zhang, M.; Sun, G.; Tang, S.; Huang, Q.; Sun, X. The chronic hepatotoxicity assessment of the herbal formula Zishen Yutai pill. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, X.H.; Yuan, Y.Y.; Liu, M. The assessment of the chronic hepatotoxicity induced by Polygoni Multiflori Radix in rats: A pilot study by using untargeted metabolomics method. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 203, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyagbemi, A.A.; Omobowale, T.O.; Asenuga, E.R.; Afolabi, J.M.; Adejumobi, O.A.; Adedapo, A.A.; Yakubu, M.A. Effect of arsenic acid withdrawal on hepatotoxicity and disruption of erythrocyte antioxidant defense system. Toxicol. Rep. 2017, 4, 521–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, A.Y.; Jang, Y.; Hong, S.H.; Chang, S.H.; Park, S.; Kim, S.; Kang, K.S.; Kim, J.E.; Cho, M.H. Ephedrine-induced mitophagy via oxidative stress in human hepatic stellate cells. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2017, 42, 461–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prakash, C.; Kumar, V. Chronic Arsenic Exposure-Induced Oxidative Stress is Mediated by Decreased Mitochondrial Biogenesis in Rat Liver. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 2016, 173, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Q.; Li, W.K.; Zhou, Z.P.; Li, Y.Y.; Xiong, T.W.; Du, Y.Z.; Wei, L.X.; Liu, J. The Tiβn medicine Zuotai differs from HgCl2 and MeHg in producing liver injury in mice. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2016, 78, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, H.; Zhang, L.; Gu, L.L.; Hou, B.Y.; Du, G.H. Oxymatrine Induces Liver Injury through JNK Signalling Pathway Mediated by TNF-alpha In Vivo. Basic Clin. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 119, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.Y.; Sun, R. [Study on efficacy and accompanying toxic and side effects of volatile oil of Evodia Fructus based on stomach cold syndrome model]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015, 40, 3838–3844. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Ji, C.; Lu, X.; Tong, W.; Fan, X.; Gao, Y. Integrated expression profiles of mRNA and microRNA in the liver of Fructus Meliae Toosendan water extract injured mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.N.; Ho, H.K.; Tan, L.L.; Tan, M.M.; Zhang, Q.; Low, M.Y.; Chan, C.L.; Koh, H.L. Hepatotoxic potential of asarones: In vitro evaluation of hepatotoxicity and quantitative determination in herbal products. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Z.T.; Qi, X.M.; Sheng, J.J.; Ma, L.L.; Ni, X.; Ren, J.; Huang, C.G.; Pan, G.Y. Timosaponin A3 induces hepatotoxicity in rats through inducing oxidative stress and down-regulating bile acid transporters. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 1188–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, M.D.; Cao, P.P.; Zhang, C.F.; Huang, F.; Xu, X.H.; Liu, B.L.; Zhang, M. Astin B, a cyclic pentapeptide from Aster tataricus, induces apoptosis and autophagy in human hepatic L-02 cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2014, 223, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, R.M.; Wang, J.J.; Chen, J.Y.; Sun, L.J.; Chen, Y. Effects of arecoline on hepatic cytochrome P450 activity and oxidative stress. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 609–614. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, Y.; Niu, C.; Wang, J.; Ji, L.; Wang, Z. Diosbulbin B-induced liver injury in mice and its mechanism. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 729–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Jin, R.M.; Chen, C.X. [Comparative study on hepatic toxicity of gardeniae fructus and Huanglian Jiedu decoction]. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2013, 38, 2365–2369. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Emoto, Y.; Yoshizawa, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Yuki, M.; Yuri, T.; Yoshikawa, Y.; Sayama, K.; Tsubura, A. Green Tea Extract-induced Acute Hepatotoxicity in Rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2014, 27, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amin, K.A.; Hashem, K.S.; Al-Muzafar, H.M.; Taha, E.M. Oxidative hepatotoxicity effects of monocrotaline and its amelioration by lipoic acid, S-adenosyl methionine and vitamin E. J. Complement. Integr. Med. 2014, 11, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Li, S.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Cheung, F.; Feng, Y. A Biomedical Investigation of the Hepatoprotective Effect of Radix salviae miltiorrhizae and Network Pharmacology-Based Prediction of the Active Compounds and Molecular Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, S.; Tan, H.Y.; Wang, N.; Mu, S.; Hao, X.; Feng, Y. A Network Pharmacology-Based Study on the Hepatoprotective Effect of Fructus Schisandrae. Molecules 2017, 22, 1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stojanovic, M.; Todorovic, D.; Scepanovic, L.; Mitrovic, D.; Borozan, S.; Dragutinovic, V.; Labudovic-Borovic, M.; Krstic, D.; Colovic, M.; Djuric, D. Subchronic methionine load induces oxidative stress and provokes biochemical and histological changes in the rat liver tissue. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boelsterli, U.A.; Hsiao, C.J. The heterozygous Sod2(+/−) mouse: Modeling the mitochondrial role in drug toxicity. Drug Discov. Today 2008, 13, 982–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osman, H.G.; Gabr, O.M.; Lotfy, S.; Gabr, S. Serum levels of bcl-2 and cellular oxidative stress in patients with viral hepatitis. Indian J. Med. Microbiol. 2007, 25, 323–329. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zhou, F.; Jiang, H.; Wang, Z.; Hua, C.; Zhang, Y. Chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) polysaccharides attenuate high-fat diet induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease via AMPK activation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 118, 886–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichoz-Lach, H.; Michalak, A. Oxidative stress as a crucial factor in liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 8082–8091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabado, J.; Casanovas, A.; Tarabal, O.; Hereu, M.; Piedrafita, L.; Caldero, J.; Esquerda, J.E. Accumulation of misfolded SOD1 in dorsal root ganglion degenerating proprioceptive sensory neurons of transgenic mice with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 852163–852176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsikas, D. Assessment of lipid peroxidation by measuring malondialdehyde (MDA) and relatives in biological samples: Analytical and biological challenges. Anal. Biochem. 2017, 524, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandari, S.; Agarwal, M.P.; Dwivedi, S.; Banerjee, B.D. Monitoring oxidative stress across worsening Child Pugh class of cirrhosis. Indian J. Med. Sci. 2008, 62, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stewart, R.K.; Dangi, A.; Huang, C.; Murase, N.; Kimura, S.; Stolz, D.B.; Wilson, G.C.; Lentsch, A.B.; Gandhi, C.R. A novel mouse model of depletion of stellate cells clarifies their role in ischemia/reperfusion- and endotoxin-induced acute liver injury. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, J.; Wu, D.D.; Zhang, J.X.; Wang, J.; Ma, J.J.; Hu, X.; Dong, W.G. Mitochondrial pathway mediated by reactive oxygen species involvement in alpha-hederin-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertero, E.; Maack, C. Calcium Signaling and Reactive Oxygen Species in Mitochondria. Circ. Res. 2018, 122, 1460–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadenas, S. Mitochondrial uncoupling, ROS generation and cardioprotection. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2018, 1859, 940–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, S.; Sun, J.L.; Yao, H.; Ma, L. Effect of uric acid on mitochondrial function and oxidative stress in hepatocytes. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 15028644–15028655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.L.; Norhaizan, M.E.; Chan, L.C. ROS-Mediated Mitochondrial Pathway is Required for Manilkara Zapota (L.) P. Royen Leaf Methanol Extract Inducing Apoptosis in the Modulation of Caspase Activation and EGFR/NF-kappaB Activities of HeLa Human Cervical Cancer Cells. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 6578648–6578667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakeyama, H.; Akiyama, T.; Takahashi, K.; Amano, H.; Kadono, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Oshima, Y.; Itabe, H.; Nakayama, K.I.; Nakayama, K.; et al. Negative feedback loop in the Bim-caspase-3 axis regulating apoptosis and activity of osteoclasts. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1631–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, C.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, J.; Zheng, G. Antiproliferative effect of urolithin A, the ellagic acid-derived colonic metabolite, on hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2.2.15 cells by targeting Lin28a/let-7a axis. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, e7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, W.; Ma, X.; Yang, H.; Hua, W.; Chen, B.; Cai, G. Hepatitis B X-interacting protein promotes cisplatin resistance and regulates CD147 via Sp1 in ovarian cancer. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 497–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Xiao, J.; Zhang, R.; Huang, F.; Liu, L.; Deng, Y.; Ma, Y.; Wei, Z.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Lychee (Litchi chinensis Sonn.) Pulp Phenolic Extract Confers a Protective Activity against Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice by Alleviating Mitochondrial Dysfunction. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 5000–5009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishina, T.; Deguchi, Y.; Miura, R.; Yamazaki, S.; Shinkai, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Okumura, K.; Kumagai, Y.; Nakano, H. Critical Contribution of Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-related Factor 2 (NRF2) to Electrophile-induced Interleukin-11 Production. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.S.; Harrison, D.J.; Kisielewski, D.; Cassidy, D.M.; McNeilly, A.D.; Gallagher, J.R.; Walsh, S.V.; Honda, T.; McCrimmon, R.J.; Dinkova-Kostova, A.T.; et al. Experimental Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis and Liver Fibrosis Are Ameliorated by Pharmacologic Activation of Nrf2 (NF-E2 p45-Related Factor 2). Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 5, 367–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akino, N.; Wada-Hiraike, O.; Terao, H.; Honjoh, H.; Isono, W.; Fu, H.; Hirano, M.; Miyamoto, Y.; Tanikawa, M.; Harada, M.; et al. Activation of Nrf2 might reduce oxidative stress in human granulosa cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 470, 96–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qaisiya, M.; Coda Zabetta, C.D.; Bellarosa, C.; Tiribelli, C. Bilirubin mediated oxidative stress involves antioxidant response activation via Nrf2 pathway. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 512–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramezani, A.; Nahad, M.P.; Faghihloo, E. The role of Nrf2 transcription factor in viral infection. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 6366–6382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Chen, Q.; Tao, J. Astaxanthin Promotes Nrf2/ARE Signaling to Inhibit HG-Induced Renal Fibrosis in GMCs. Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 117. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Tian, B.; Lu, Z.N.; Guo, X.L. Regulation and role of nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in multidrug resistance of hepatocellular carcinoma. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 280, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Y.; Li, J.X.; Wang, Y.L.; Mao, T.Y.; Chen, C.; Xie, T.H.; Han, Y.F.; Tan, X.; Han, H.X. Yinchen Linggui Zhugan Decoction Ameliorates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Rats by Regulating the Nrf2/ARE Signaling Pathway. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 6178358–6178369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, Y.; Xia, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhu, Y. The potential of chrysophanol in protecting against high fat-induced cardiac injury through Nrf2-regulated anti-inflammation, anti-oxidant and anti-fibrosis in Nrf2 knockout mice. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2017, 93, 1175–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Premont, R.T.; Rockey, D.C. Endothelial nitric-oxide synthase (eNOS) is activated through G-protein-coupled receptor kinase-interacting protein 1 (GIT1) tyrosine phosphorylation and Src protein. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 18163–18174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stoessel, A.; Paliege, A.; Theilig, F.; Addabbo, F.; Ratliff, B.; Waschke, J.; Patschan, D.; Goligorsky, M.S.; Bachmann, S. Indolent course of tubulointerstitial disease in a mouse model of subpressor, low-dose nitric oxide synthase inhibition. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2008, 295, F717–F725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Okuyama, T.; Nakatake, R.; Kaibori, M.; Okumura, T.; Kon, M.; Nishizawa, M. A sense oligonucleotide to inducible nitric oxide synthase mRNA increases the survival rate of rats in septic shock. Nitric Oxide 2018, 72, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gazdic, M.; Simovic Markovic, B.; Vucicevic, L.; Nikolic, T.; Djonov, V.; Arsenijevic, N.; Trajkovic, V.; Lukic, M.L.; Volarevic, V. Mesenchymal stem cells protect from acute liver injury by attenuating hepatotoxicity of liver natural killer T cells in an inducible nitric oxide synthase- and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-dependent manner. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2018, 12, e1173–e1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freitas de Lima, F.; Lescano, C.H.; Arrigo, J.D.S.; Cardoso, C.A.L.; Coutinho, J.P.; Moslaves, I.S.B.; Ximenes, T.; Kadri, M.C.T.; Weber, S.S.; Perdomo, R.T.; et al. Anti-inflammatory, antiproliferative and cytoprotective potential of the Attalea phalerata Mart. ex Spreng. pulp oil. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleniewska, P.; Goraca, A. Influence of endothelin 1 receptor blockers and a nitric oxide synthase inhibitor on reactive oxygen species formation in rat lungs. Physiol. Res. 2016, 65, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Depinay, N.; Franetich, J.F.; Gruner, A.C.; Mauduit, M.; Chavatte, J.M.; Luty, A.J.; van Gemert, G.J.; Sauerwein, R.W.; Siksik, J.M.; Hannoun, L.; et al. Inhibitory effect of TNF-alpha on malaria pre-erythrocytic stage development: Influence of host hepatocyte/parasite combinations. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.W.; Priyamvada, S.; Khan, S.A.; Khan, S.; Gangopadhyay, A.; Yusufi, A.N. Fish/flaxseed oil protect against nitric oxide-induced hepatotoxicity and cell death in the rat liver. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 302–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rigi, A.; Heidarian, E.; Amini, S.A. Protective and anti-inflammatory effects of hydroalcoholic leaf extract of Origanum vulgare on oxidative stress, TNF-alpha gene expression and liver histological changes in paraquat-induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 9, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang Da, W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; He, X.; Wang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Hai, Y.; Gao, R. Chinese Herbal Medicine Hepatotoxicity: The Evaluation and Recognization Based on Large-scale Evidence Ddatabase. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Eickhoff, A. Herbal hepatotoxicity in traditional and modern medicine: actual key issues and new encouraging steps. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danan, G.; Teschke, R. RUCAM in Drug and Herb Induced Liver Injury: The Update. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Danan, G.; Teschke, R. Drug-Induced Liver Injury: Why is the Roussel Uclaf Causality Assessment Method (RUCAM) Still Used 25 Years After Its Launch? Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 735–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.C.; Mao, Y.M.; Chen, C.W.; Chen, J.J.; Chen, J.; Cong, W.M.; Ding, Y.; Duan, Z.P.; Fu, Q.C.; Guo, X.Y.; et al. CSH guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of drug-induced liver injury. Hepatol. Int. 2017, 11, 221–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenzel, C.; Teschke, R. Herbal Hepatotoxicity: Clinical Characteristics and Listing Compilation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melchart, D.; Hager, S.; Albrecht, S.; Dai, J.; Weidenhammer, W.; Teschke, R. Herbal Traditional Chinese Medicine and suspected liver injury: A prospective study. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1141–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Glass, X.; Schulze, J. Herbal hepatotoxicity by Greater Celandine (Chelidonium majus): Causality assessment of 22 spontaneous reports. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2011, 61, 282–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Frenzel, C.; Glass, X.; Schulze, J.; Eickhoff, A. Greater Celandine hepatotoxicity: A clinical review. Ann. Hepatol. 2012, 11, 838–848. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Glass, X.; Schulze, J.; Eickhoff, A. Suspected Greater Celandine hepatotoxicity: Liver-specific causality evaluation of published case reports from Europe. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 24, 270–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teschke, R.; Schwarzenboeck, A.; Hennermann, K.H. Kava hepatotoxicity: Clinical survey and critical analysis of 26 suspected cases. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 20, 1182–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, K.; Yu, Y.; He, C.; Wang, M.; Wang, S.; Li, X. RUCAM scale-based diagnosis, clinical features and prognosis of 140 cases of drug-induced liver injury. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi 2014, 22, 938–941. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.; Ye, Y.; Yang, X.; Jiao, Y. Systematic Review on Chinese Herbal Medicine Induced Liver Injury. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 3560812–3560827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Natural Compound | Sources of Chinese Medicine | Study Type | Cell or Animal | Biochemical Markers of Hepatotoxicity | Type of Injury | Reporting Date | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vincristine | Catharanthus roseus | In vivo | Wistar rat | ALT, AST, IL-12. IL-4, p53, cleaved caspase-3, Bax↑; Bcl-2↓ | Hepatitis | 2018 | [66] |
| Epigallocatechin-3-gallate | Green tea | In vivo | C57BL/6 mouse | SOD, GPx, respiratory complex-I -III, sirtuin 3, FOXO3, Nrf2↓ | Hepatitis and hemorrhage | 2018 | [114] |
| Oxymatrine | Sophora flavescens | In vitro | L-02 cells | Pro-caspase-3 -4 -8 -9, GRP78, CHOP, p-JNK, IREI, ATF6, PERK, Bax, MDA, ROS↑; SOD, Bcl-2↓ | Cell apoptosis | 2018 | [115] |
| Bavachinin | Fructus psoraleae | In vitro | HepaRG cells | JNK, p-p38, ROS, MAPK, MDA↑; SOD, GSH, CAT↓ | Cell necrosis | 2018 | [116] |
| Genkwa Flos extract | Genkwa flos | In vitro & in vivo | HL-7702 cells; SD rat | ALT, AST, MDA↑; CAT, GSH, SOD, NO, NOS↓ | Metabolism Dysregulation | 2018 | [117] |
| Fructus Meliae Toosendan extract | Fructus meliae toosendan | In vivo | BALB/c mouse | ALT, AST, MDA, p53, p21, Cyclin E, Bax, CytC, caspase-3 -9, CDK2, ROS↑; Bcl-2, Nrf2, miR-370-3p↓ | Cell apoptosis | 2018 | [118] |
| Oxalicumone A | Penicillium oxalicum | In vitro | L-02 cells | ALT, AST, ROS, Caspase 3, MDA, NO, Fas, Bax, LDH, CytC↑; Bcl-2, GSH, SOD↓ | Cell apoptosis | 2018 | [119] |
| Arsenic extract | Arsenic | In vitro | HHL-5 cell | Thioredoxin 1 (Trx1), TrxR1, ROS↑; Bax, CytC, Bcl-2↓ | Cell apoptosis | 2018 | [120] |
| Pinelliae Rhizoma Praeparatum | Pinelliae rhizoma | In vivo | ICR mouse | ALT, AST, ALP, bile acid, Mrp3, MDA↑; SOD, GSH, GPx, Bsep, Mrp2, Nrf2↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2018 | [121] |
| Hydroxyapatitenanoparticles extract | Hydroxyapatite nanoparticles | In vitro & In vivo | BRL cells; SD rat | TNF-α, NO, MDA, ROS↑; respiratory complex-I, -II, -III, GSH, SOD↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2018 | [122] |
| Zishen Yutai pill extract | Zishen yutai pill | In vivo | SD rat | AST, ALP, ALT, MDA, LDH, PDGF, Cholestasis, Bile acid↑; SOD, GPx↓ | Cell necrosis | 2017 | [123] |
| Polygoni Multiflori Radix extract | Polygonum multiflorum thunb | In vivo | SD rat | ALT, AST, ALP, LDH, bilirubin, creatinine↑SOD↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2017 | [70] [124] |
| Arsenic acid | Arsenic | In vivo | Wistar rat | MDA, NO↑; SOD, GSH, GST, GPx↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2017 | [125] |
| Saikosaponins | Radix bupleuri | In vitro & In vivo | HepG2 cells; Kunming mouse | CYP2E1, AST, ALT, LDH, ROS, iNOS↑; GSH↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2017 | [62] |
| Ephedrine | Ephedra sinica | In vitro | LX-2 cells | Parkin, SOD2, ROS, Cox IV, p62, LC3 I, LC3 II↑ | Excessive Mitophagy | 2017 | [126] |
| Arsenic extract | Arsenic | In vivo | Wister rat | Bax, caspase-3↑, CytC, SOD, complexes I, COX-I-IV, NRF-1-2, PGC-1α, Tfam↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2016 | [127] |
| Dioscorea Bulbifera saponins | Dioscorea bulbifera | In vitro & In vivo | L-02 cells; Wister rat | ALT, AST, cytochromes P450, cholestasis↑; SOD, GPx, GST, GR, GCL↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2016 | [43] |
| Zuotai extract | Zuotai | In vivo | Kunming mouse | ALT, AST, HgS, MeHg, metallothionein-1, heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), Egr1, Gst-mu, mKC, MIP-2, NAD(P)H, Nqo1, Gclc↑ | Cell inflammation | 2016 | [128] |
| Oxymatrine | Sophora flavescens | In vivo | ICR mouse | ALT, AST, ALP, TNF-α, caspase-9, -8, -3, TRADD, p-SAPK, p-JNK↑ | Cell apoptosis | 2016 | [129] |
| Evodia Fructus volatile oil | Evodia fructus | In vivo | Kunming mouse | ALT, AST, PGE2, MDA, NO, NOS↑; SOD, GSH, GPx↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2015 | [130] |
| Fructus Meliae Toosendan extract | Fructus meliae toosendan | In vivo | BALB/c mouse | ALT, AST, ALP, bilirubin, cholesterol↑; Nrf2↓ | Cell necrosis | 2015 | [131] |
| Triptolide | Tripterygium wilfordii | In vivo | Kunmingmouse | ALT, AST, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), CREA↑; GSH↓ | Acute hepatic necrosis | 2015 | [77] |
| Asarones | Asarum | In vitro | THLE-2 cells | Caspase-3 -7, MDA↑; GSH, GSSG↓ | Cell apoptosis | 2015 | [132] |
| Timosaponin A3 | Anemarrhena asphodeloides | In vivo | SD rat | Bile acid, ROS, HO-1↑; Ntcp, Bsep, Mrp2, Cyp7a1, F-actin↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2014 | [133] |
| Astin B | Aster tataricus | In vitro | L-02 cells | ROS, JNK, CytC, Bax, caspases-9, -3, LC3-II↑; GSH, Bcl-2, p62↓ | Cell apoptosis and inflammation | 2014 | [134] |
| Cassia Occidentalis extract | Cassia occidentalis | In vivo | Wister rat | TGF-β, JNK, Bax, MDA↑; Akt, CREB1, CYP1A1, CYP2B1, CAT, SOD1, IL-6, SOD, GR↓ | Metabolism dysregulation and apoptosis | 2014 | [112] |
| Arecoline Hydrobromide | Areca catechu | In vivo | Wister rat | ALT, AST, MDA, CYP2B, CYP2E1↑; SOD, CAT, GPx, GSH↓ | Liver cirrhosis and HCC | 2014 | [135] |
| Diosbulbin B | Dioscorea bulbifera | In vivo | ICR mouse | ALT, AST, ALP, MDA↑; GPx, GST, SOD, CAT↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2014 | [136] |
| Evodiae Fructus extract | Evodiae fructus | In vivo | SD rat | MDA, CytC, AST, ALT, NO, NOS↑; SOD, GSH, GPx↓ | Cell necrosis | 2014 | [94] [95] |
| Gardeniae Fructus extract | Gardeniae fructus | In vivo | SD rat | ALT, AST, ALP, bile acid, MDA, TNF-α, Bax↑; SOD, GPx, Bcl-2↓ | Cell inflammation, necrosis and apoptosis | 2014 | [137] |
| Green tea extract | Green tea | In vivo | SD rat | ALT, AST, ALP, TBil, bilirubin, caspase-3, MDA, TG, GST-P↑ | Metabolism dysregulation and apoptosis | 2014 | [138] |
| Monocrotaline | Rattlebush | In vivo | SD rat | GSH, GR, GPx, GST↓ | Metabolism dysregulation | 2014 | [139] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Wang, N.; Xu, Y.; Tan, H.-Y.; Li, S.; Feng, Y. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Oxidative Stress-Associated Liver Injury Induced by Chinese Herbal Medicine: An Experimental Evidence-Based Literature Review and Network Pharmacology Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092745
Zhang C, Wang N, Xu Y, Tan H-Y, Li S, Feng Y. Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Oxidative Stress-Associated Liver Injury Induced by Chinese Herbal Medicine: An Experimental Evidence-Based Literature Review and Network Pharmacology Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092745
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cheng, Ning Wang, Yu Xu, Hor-Yue Tan, Sha Li, and Yibin Feng. 2018. "Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Oxidative Stress-Associated Liver Injury Induced by Chinese Herbal Medicine: An Experimental Evidence-Based Literature Review and Network Pharmacology Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092745
APA StyleZhang, C., Wang, N., Xu, Y., Tan, H. -Y., Li, S., & Feng, Y. (2018). Molecular Mechanisms Involved in Oxidative Stress-Associated Liver Injury Induced by Chinese Herbal Medicine: An Experimental Evidence-Based Literature Review and Network Pharmacology Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2745. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092745