Endothelial AMP-Activated Kinase α1 Phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and Decreases Endothelial NO Formation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Consequences of Global AMPKα Deletion on Vascular Responsiveness
2.2. Consequence of Endothelial-Specific AMPKα Deletion on Vascular Responsiveness
2.3. Vascular Responses to AMPK Activators
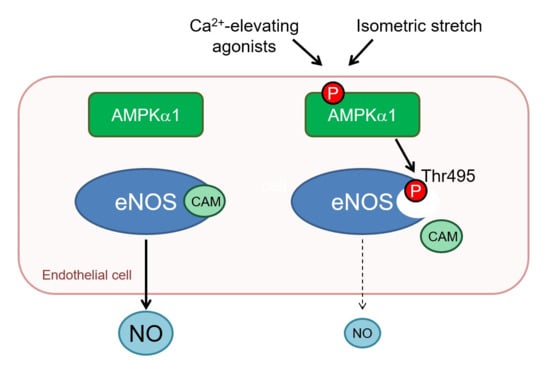
2.4. AMPKα1 and eNOS Phosphorylation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Animals
4.3. Vascular Reactivity Measurements
4.4. Cell Culture
4.5. Adenoviral Transduction of Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells
4.6. In Vitro Kinase Assay
4.7. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Knock-Down of AMPKα1
4.8. Immunoblotting
4.9. Statistical Analyses
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| eNOS | endothelial nitric-oxide synthase |
| AICAR | 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide |
| VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| PPAR | peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor |
| SNP | sodium nitroprusside |
| ACh | acetylcholine |
| PE | phenylephrine |
| L-NAME | Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester |
| CRISPR | clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats |
| Cas9 | CRISPR-associated protein 9 |
References
- Musi, N.; Fujii, N.; Hirshman, M.F.; Ekberg, I.; Froberg, S.; Ljungqvist, O.; Thorell, A.; Goodyear, L.J. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is activated in muscle of subjects with type 2 diabetes during exercise. Diabetes 2001, 50, 921–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laderoute, K.R.; Amin, K.; Calaoagan, J.M.; Knapp, M.; Le, T.; Orduna, J.; Foretz, M.; Viollet, B. 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) is induced by low-oxygen and glucose deprivation conditions found in solid-tumor microenvironments. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 5336–5347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herzig, S.; Shaw, R.J. AMPK: Guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 121–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisslthaler, B.; Fleming, I. Activation and signaling by the AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells. Circ. Res. 2009, 105, 114–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bess, E.; Fisslthaler, B.; Fromel, T.; Fleming, I. Nitric oxide-induced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase α2 subunit attenuates IκB kinase activity and inflammatory responses in endothelial cells. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacicedo, J.M.; Yagihashi, N.; Keaney, J.F.; Ruderman, N.B.; Ido, Y. AMPK inhibits fatty acid-induced increases in NF-κB transactivation in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 324, 1204–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, D.; Mogi, M.; Walsh, K. AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling in endothelial cells is essential for angiogenesis in response to hypoxic stress. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31000–31006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.W.; Deng, Y.P.; Han, X.; Ren, G.F.; Cai, J.; Jiang, G.J. Metformin improves the angiogenic functions of endothelial progenitor cells via activating AMPK/eNOS pathway in diabetic mice. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2016, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reihill, J.A.; Ewart, M.A.; Hardie, D.G.; Salt, I.P. AMP-activated protein kinase mediates VEGF-stimulated endothelial NO production. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 354, 1084–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.K.; Lam, K.S.; Wang, Y.; Huang, Y.; Carling, D.; Wu, D.; Wong, C.; Xu, A. Adiponectin-induced endothelial nitric oxide synthase activation and nitric oxide production are mediated by APPL1 in endothelial cells. Diabetes 2007, 56, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyle, J.G.; Logan, P.J.; Ewart, M.A.; Reihill, J.A.; Ritchie, S.A.; Connell, J.M.; Cleland, S.J.; Salt, I.P. Rosiglitazone stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in human aortic endothelial cells via AMP-activated protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 11210–11217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossoni, L.; Wareing, M.; Wenceslau, C.; Al-Abri, M.; Cobb, C.; Austin, C. Acute simvastatin increases endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation via AMP-activated protein kinase and reduces contractility of isolated rat mesenteric resistance arteries. Clin. Sci. (Lond.) 2011, 121, 449–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Morrow, V.A.; Foufelle, F.; Connell, J.M.; Petrie, J.R.; Gould, G.W.; Salt, I.P. Direct activation of AMP-activated protein kinase stimulates nitric-oxide synthesis in human aortic endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 31629–31639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.J.; Xie, Z.; Viollet, B.; Zou, M.H. Activation of the AMP-activated kinase by antidiabetes drug metformin stimulates nitric oxide synthesis in vivo by promoting the association of heat shock protein 90 and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Diabetes 2006, 55, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, M.H.; Kirkpatrick, S.S.; Davis, B.J.; Nelson, J.S.; Wiles, W.G.; Schlattner, U.; Neumann, D.; Brownlee, M.; Freeman, M.B.; Goldman, M.H. Activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase by the anti-diabetic drug metformin in vivo. Role of mitochondrial reactive nitrogen species. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 43940–43951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hien, T.T.; Oh, W.K.; Quyen, B.T.; Dao, T.T.; Yoon, J.H.; Yun, S.Y.; Kang, K.W. Potent vasodilation effect of amurensin G is mediated through the phosphorylation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2012, 84, 1437–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Dai, Y.; Yan, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, J.; Liu, J.; Cha, L.; Mu, J. Resveratrol lowers blood pressure in spontaneously hypertensive rats via calcium-dependent endothelial NO production. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2016, 38, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, I.; Fisslthaler, B.; Dixit, M.; Busse, R. Role of PECAM-1 in the shear-stress-induced activation of Akt and the endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) in endothelial cells. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 4103–4111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dixit, M.; Bess, E.; Fisslthaler, B.; Hartel, F.V.; Noll, T.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Shear stress-induced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase regulates FoxO1a and angiopoietin-2 in endothelial cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2008, 77, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisslthaler, B.; Fleming, I.; Keseru, B.; Walsh, K.; Busse, R. Fluid shear stress and NO decrease the activity of the hydroxy-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in endothelial cells via the AMP-activated protein kinase and FoxO1. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, e12–e21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thors, B.; Halldorsson, H.; Jonsdottir, G.; Thorgeirsson, G. Mechanism of thrombin mediated eNOS phosphorylation in endothelial cells is dependent on ATP levels after stimulation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2008, 1783, 1893–1902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bradley, E.A.; Eringa, E.C.; Stehouwer, C.D.; Korstjens, I.; van Nieuw Amerongen, G.P.; Musters, R.; Sipkema, P.; Clark, M.G.; Rattigan, S. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by 5-aminoimidazole-4-carboxamide-1-beta-d-ribofuranoside in the muscle microcirculation increases nitric oxide synthesis and microvascular perfusion. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2010, 30, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, H.; Schubert, K.M.; Blodow, S.; Kreutz, C.P.; Erdogmus, S.; Wiedenmann, M.; Qiu, J.; Fey, T.; Ruth, P.; Lubomirov, L.T.; et al. AMPK Dilates Resistance Arteries via Activation of SERCA and BKCa Channels in Smooth Muscle. Hypertension 2015, 66, 108–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schubert, K.M.; Qiu, J.; Blodow, S.; Wiedenmann, M.; Lubomirov, L.T.; Pfitzer, G.; Pohl, U.; Schneider, H. The AMP-Related Kinase (AMPK) Induces Ca2+-Independent Dilation of Resistance Arteries by Interfering With Actin Filament Formation. Circ. Res. 2017, 121, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, B.; Rahman, A.; Arner, A. AMP-activated kinase relaxes agonist induced contractions in the mouse aorta via effects on PKC signaling and inhibits NO-induced relaxation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 695, 88–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schuhmacher, S.; Foretz, M.; Knorr, M.; Jansen, T.; Hortmann, M.; Wenzel, P.; Oelze, M.; Kleschyov, A.L.; Daiber, A.; Keaney, J.F.; et al. α1 AMP-activated protein kinase preserves endothelial function during chronic angiotensin II treatment by limiting Nox2 upregulation. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goirand, F.; Solar, M.; Athea, Y.; Viollet, B.; Mateo, P.; Fortin, D.; Leclerc, J.; Hoerter, J.; Ventura-Clapier, R.; Garnier, A. Activation of AMP kinase alpha1 subunit induces aortic vasorelaxation in mice. J. Physiol. 2007, 581, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Enkhjargal, B.; Godo, S.; Sawada, A.; Suvd, N.; Saito, H.; Noda, K.; Satoh, K.; Shimokawa, H. Endothelial AMP-activated protein kinase regulates blood pressure and coronary flow responses through hyperpolarization mechanism in mice. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 1505–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Xu, J.; Song, P.; Viollet, B.; Zou, M.H. In vivo activation of AMP-activated protein kinase attenuates diabetes-enhanced degradation of GTP cyclohydrolase I. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1893–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahmann, N.; Woods, A.; Carling, D.; Heller, R. Thrombin activates AMP-activated protein kinase in endothelial cells via a pathway involving Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase beta. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2006, 26, 5933–5945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stahmann, N.; Woods, A.; Spengler, K.; Heslegrave, A.; Bauer, R.; Krause, S.; Viollet, B.; Carling, D.; Heller, R. Activation of AMP-activated protein kinase by vascular endothelial growth factor mediates endothelial angiogenesis independently of nitric-oxide synthase. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 10638–10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, I.; Bauersachs, J.; Fisslthaler, B.; Busse, R. Calcium-independent activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase in response to tyrosine phosphatase inhibitors and fluid shear stress. Circ. Res. 1998, 82, 686–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, J.C.; El, K.D.; Chereau, C.; Lanone, S.; Huang, X.L.; De Buys Roessingh, A.S.; Mercier, J.C.; Dall’Ava-Santucci, J.; Dinh-Xuan, A.T. Involvement of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II in endothelial NO production and endothelium-dependent relaxation. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2003, 284, H2311–H2319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, M.; Xu, S.; Maitland-Toolan, K.A.; Zuccollo, A.; Hou, X.; Jiang, B.; Wierzbicki, M.; Verbeuren, T.J.; Cohen, R.A. Polyphenols stimulate AMP-activated protein kinase, lower lipids, and inhibit accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetic LDL receptor-deficient mice. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2180–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimmeler, S.; Fleming, I.; Fisslthaler, B.; Hermann, C.; Busse, R.; Zeiher, A.M. Activation of nitric oxide synthase in endothelial cells by Akt-dependent phosphorylation. Nature 1999, 399, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fulton, D.; Mcgiff, J.C.; Quilley, J. Pharmacological evaluation of an epoxide as the putative hyperpolarizing factor mediating the nitric oxide-independent vasodilator effect of bradykinin in the rat heart. J. Pharm. Exp. Ther. 1999, 287, 497–503. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.P.; Mitchelhill, K.I.; Michell, B.J.; Stapleton, D.; Rodriguez-Crespo, I.; Witters, L.A. AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of endothelial no synthase. FEBS Lett. 1999, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michell, B.J.; Chen, Z.p.; Tiganis, T.; Stapleton, D.; Katsis, F.; Power, D.A.; Sim, A.T.; Kemp, B.E. Coordinated control of endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation by protein kinase C and the cAMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 17625–17628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, I.; Fisslthaler, B.; Dimmeler, S.; Kemp, B.E.; Busse, R. Phosphorylation of Thr(495) regulates Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent endothelial nitric oxide synthase activity. Circ. Res. 2001, 88, E68–E75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaskin, F.S.; Kamada, K.; Yusof, M.; Korthuis, R.J. 5′-AMP-activated protein kinase activation prevents postischemic leukocyte-endothelial cell adhesive interactions. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, H326–H332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Smith, C.A.; Chen, G.; Sharma, B.; Miner, A.S.; Barbee, R.W.; Ratz, P.H. The AMP-dependent protein kinase (AMPK) activator A-769662 causes arterial relaxation by reducing cytosolic free calcium independently of an increase in AMPK phosphorylation. Front. Pharmacol. 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.E.; Ross, F.A.; Kleinert, M.; Sylow, L.; Knudsen, J.R.; Gowans, G.J.; Hardie, D.G.; Richter, E.A. PT-1 selectively activates AMPKγ1 complexes in mouse skeletal muscle, but activates all three +¦ subunit complexes in cultured human cells by inhibiting the respiratory chain. Biochem. J. 2015, 467, 461–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bultot, L.; Jensen, T.E.; Lai, Y.C.; Madsen, A.L.B.; Collodet, C.; Kviklyte, S.; Deak, M.; Yavari, A.; Foretz, M.; Ghaffari, S.; et al. Benzimidazole derivative small-molecule 991 enhances AMPK activity and glucose uptake induced by AICAR or contraction in skeletal muscle. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2016, 311, E706–E719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Liang, B.; Viollet, B.; Zou, M.H. Inhibition of the AMP-activated protein kinase-alpha2 accentuates agonist-induced vascular smooth muscle contraction and high blood pressure in mice. Hypertension 2011, 57, 1010–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, G.Q.; Li, Y.B.; Du, B.; Meng, Y. Resveratrol via activation of AMPK lowers blood pressure in DOCA-salt hypertensive mice. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2015, 37, 616–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröller-Schön, S.; Jansen, T.; Hauptmann, F.; Schüler, A.; Heeren, T.; Hausding, M.; Oelze, M.; Viollet, B.; Keaney, J.F.; Wenzel, P.; et al. α1AMP-activated protein kinase mediates vascular protective effects of exercise. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2012, 32, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, M.; Liang, B.; Xu, J.; Xie, Z.; Liu, C.; Viollet, B.; Yan, D.; Zou, M.H. AMPKalpha2 deletion causes aberrant expression and activation of NAD(P)H oxidase and consequent endothelial dysfunction in vivo: Role of 26S proteasomes. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1117–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mount, P.F.; Kemp, B.E.; Power, D.A. Regulation of endothelial and myocardial NO synthesis by multi-site eNOS phosphorylation. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2007, 42, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michell, B.J.; Griffiths, J.E.; Mitchelhill, K.I.; Rodriguez-Crespo, I.; Tiganis, T.; Bozinovski, S.; de Montellano, P.R.O.; Kemp, B.E.; Pearson, R.B. The Akt kinase signals directly to endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Curr. Biol. 1999, 9, 845–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallis, B.; Corthals, G.L.; Goodlett, D.R.; Ueba, H.; Kim, F.; Presnell, S.R.; Figeys, D.; Harrison, D.G.; Berk, B.C.; Aebersold, R.; et al. Identification of flow-dependent endothelial nitric-oxide synthase phosphorylation sites by mass spectrometry and regulation of phosphorylation and nitric oxide production by the phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase inhibitor LY294002. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30101–30108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohashi, J.; Sawada, A.; Nakajima, S.; Noda, K.; Takaki, A.; Shimokawa, H. Mechanisms for enhanced endothelium-derived hyperpolarizing factor-mediated responses in microvessels in mice. Circ. J. 2012, 76, 1768–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoyagi, M.; Arvai, A.S.; Tainer, J.A.; Getzoff, E.D. Structural basis for endothelial nitric oxide synthase binding to calmodulin. EMBO J. 2003, 22, 766–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chen, Z.; Peng, I.C.; Sun, W.; Su, M.I.; Hsu, P.H.; Fu, Y.; Zhu, Y.; DeFea, K.; Pan, S.; Tsai, M.D.; et al. AMP-activated protein kinase functionally phosphorylates endothelial nitric oxide synthase Ser633. Circ. Res. 2009, 104, 496–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, E.; Anter, E.; Zou, M.H.; Keaney, J.F., Jr. Estradiol-mediated endothelial nitric oxide synthase association with heat shock protein 90 requires adenosine monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. Circulation 2005, 111, 3473–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zippel, N.; Malik, R.A.; Fromel, T.; Popp, R.; Bess, E.; Strilic, B.; Wettschureck, N.; Fleming, I.; Fisslthaler, B. Transforming growth factor-beta-activated kinase 1 regulates angiogenesis via AMP-activated protein kinase-α1 and redox balance in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2013, 33, 2792–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Busse, R.; Lamontagne, D. Endothelium-derived bradykinin is responsible for the increase in calcium produced by angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors in human endothelial cells. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch. Pharmacol. 1991, 344, 126–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michaelis, U.R.; Falck, J.R.; Schmidt, R.; Busse, R.; Fleming, I. Cytochrome P4502C9-derived epoxyeicosatrienoic acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in endothelial cells. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2005, 25, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| pEC50 Values | Solvent | L-NAME | −E | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | −7.04 ± 0.13 | −7.43 ± 0.10 | −7.21 ± 0.05 | |||
| AMPKΔEC | −6.77 ± 0.05 | * | −7.31 ± 0.09 | §§ | −7.13 ± 0.05 | §§ |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zippel, N.; Loot, A.E.; Stingl, H.; Randriamboavonjy, V.; Fleming, I.; Fisslthaler, B. Endothelial AMP-Activated Kinase α1 Phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and Decreases Endothelial NO Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092753
Zippel N, Loot AE, Stingl H, Randriamboavonjy V, Fleming I, Fisslthaler B. Endothelial AMP-Activated Kinase α1 Phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and Decreases Endothelial NO Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2018; 19(9):2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092753
Chicago/Turabian StyleZippel, Nina, Annemarieke E. Loot, Heike Stingl, Voahanginirina Randriamboavonjy, Ingrid Fleming, and Beate Fisslthaler. 2018. "Endothelial AMP-Activated Kinase α1 Phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and Decreases Endothelial NO Formation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 19, no. 9: 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092753
APA StyleZippel, N., Loot, A. E., Stingl, H., Randriamboavonjy, V., Fleming, I., & Fisslthaler, B. (2018). Endothelial AMP-Activated Kinase α1 Phosphorylates eNOS on Thr495 and Decreases Endothelial NO Formation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 19(9), 2753. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19092753