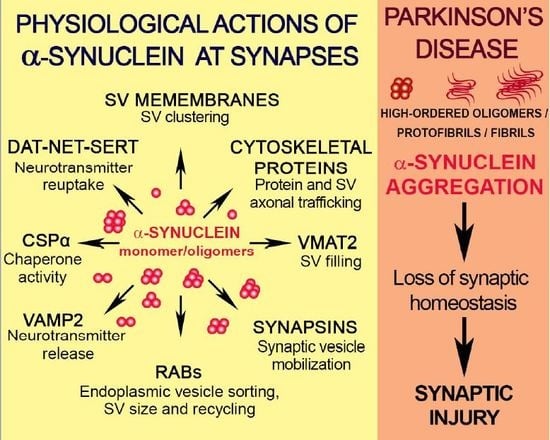
Living in Promiscuity: The Multiple Partners of Alpha-Synuclein at the Synapse in Physiology and Pathology
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Alpha-Synuclein Structure and Conformational Variety
3. Alpha-Synuclein Modulation of Protein Trafficking at the Synapse
4. Alpha-Synuclein: A Handyman in SV Machinery
5. Alpha-Synuclein Modulation of Neurotransmitter Reuptake and Receptors
6. Concluding Remarks
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yuan, J.; Zhao, Y. Evolutionary aspects of the synuclein super-family and sub-families based on large-scale phylogenetic and group-discrimination analysis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 441, 308–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maroteaux, L.; Campanelli, J.T.; Scheller, R.H. Synuclein: A neuron-specific protein localized to the nucleus and presynaptic nerve terminal. J. Neurosci. 1988, 8, 2804–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahle, P.J.; Neumann, M.; Ozmen, L.; Muller, V.; Jacobsen, H.; Schindzielorz, A.; Okochi, M.; Leimer, U.; van Der Putten, H.; Probst, A.; et al. Subcellular localization of wild-type and Parkinson’s disease-associated mutant alpha -synuclein in human and transgenic mouse brain. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 6365–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.L.; Hasadsri, L.; Woods, W.S.; George, J.M. Dynamic transport and localization of alpha-synuclein in primary hippocampal neurons. Mol. Neurodegener. 2010, 5, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Abeliovich, A.; Schmitz, Y.; Farinas, I.; Choi-Lundberg, D.; Ho, W.H.; Castillo, P.E.; Shinsky, N.; Verdugo, J.M.; Armanini, M.; Ryan, A.; et al. Mice lacking alpha-synuclein display functional deficits in the nigrostriatal dopamine system. Neuron 2000, 25, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemani, V.M.; Lu, W.; Berge, V.; Nakamura, K.; Onoa, B.; Lee, M.K.; Chaudhry, F.A.; Nicoll, R.A.; Edwards, R.H. Increased expression of alpha-synuclein reduces neurotransmitter release by inhibiting synaptic vesicle reclustering after endocytosis. Neuron 2010, 65, 66–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burre, J. The Synaptic Function of alpha-Synuclein. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2015, 5, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Withers, G.S.; George, J.M.; Banker, G.A.; Clayton, D.F. Delayed localization of synelfin (synuclein, NACP) to presynaptic terminals in cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Brain Res. Dev. Brain Res. 1997, 99, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Sudhof, T.C. Cell Biology and Pathophysiology of alpha-Synuclein. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2018, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.W.; Yang, R.; Guo, J.C.; Ren, H.M.; Zha, X.L.; Cheng, J.S.; Cai, D.F. Localization of alpha-synuclein to mitochondria within midbrain of mice. Neuroreport 2007, 18, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cole, N.B.; Dieuliis, D.; Leo, P.; Mitchell, D.C.; Nussbaum, R.L. Mitochondrial translocation of alpha-synuclein is promoted by intracellular acidification. Exp. Cell Res. 2008, 314, 2076–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, L.; Raghavendran, V.; Prabhu, B.M.; Avadhani, N.G.; Anandatheerthavarada, H.K. Mitochondrial import and accumulation of alpha-synuclein impair complex I in human dopaminergic neuronal cultures and Parkinson disease brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 9089–9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, K.; Nemani, V.M.; Wallender, E.K.; Kaehlcke, K.; Ott, M.; Edwards, R.H. Optical reporters for the conformation of alpha-synuclein reveal a specific interaction with mitochondria. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 12305–12317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Vives-Bauza, C.; Acin-Perez, R.; Yamamoto, A.; Tan, Y.; Li, Y.; Magrane, J.; Stavarache, M.A.; Shaffer, S.; Chang, S.; et al. PINK1 defect causes mitochondrial dysfunction, proteasomal deficit and alpha-synuclein aggregation in cell culture models of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2009, 4, e4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, A.; Navarria, L.; Falarti, E.; Zaltieri, M.; Bono, F.; Collo, G.; Spillantini, M.G.; Missale, C.; Spano, P. Redistribution of DAT/alpha-synuclein complexes visualized by "in situ" proximity ligation assay in transgenic mice modelling early Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e27959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colla, E.; Jensen, P.H.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Glabe, C.; Lee, M.K. Accumulation of toxic alpha-synuclein oligomer within endoplasmic reticulum occurs in alpha-synucleinopathy in vivo. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 3301–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.L.; Song, L.K.; Yuan, Y.H.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, J.L.; Zhu, P.; Chen, N.H. alpha-Synuclein is prone to interaction with the GC-box-like sequence in vitro. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2014, 34, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Area-Gomez, E.; Schon, E.A.; Przedborski, S. Novel subcellular localization for alpha-synuclein: Possible functional consequences. Front. Neuroanat. 2015, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guardia-Laguarta, C.; Area-Gomez, E.; Schon, E.A.; Przedborski, S. A new role for alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: Alteration of ER-mitochondrial communication. Mov. Disord. 2015, 30, 1026–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinho, R.; Paiva, I.; Jercic, K.G.; Fonseca-Ornelas, L.; Gerhardt, E.; Fahlbusch, C.; Garcia-Esparcia, P.; Kerimoglu, C.; Pavlou, M.A.; Villar-Pique, A.; et al. Nuclear localization and phosphorylation modulate pathological effects of Alpha-Synuclein. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, L.J.; Mallory, M.; Xia, Y.; Veinbergs, I.; Hashimoto, M.; Yoshimoto, M.; Thal, L.J.; Saitoh, T.; Masliah, E. Expression pattern of synucleins (non-Abeta component of Alzheimer’s disease amyloid precursor protein/alpha-synuclein) during murine brain development. J. Neurochem. 1998, 71, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayer, T.A.; Jakala, P.; Hartmann, T.; Havas, L.; McLean, C.; Culvenor, J.G.; Li, Q.X.; Masters, C.L.; Falkai, P.; Beyreuther, K. Alpha-synuclein accumulates in Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies but not in Alzheimer’s disease beta-amyloid plaque cores. Neurosci. Lett. 1999, 266, 213–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, J.E.; Schuck, T.M.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Differential expression and distribution of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synuclein in the developing human substantia nigra. Exp. Neurol. 2001, 168, 347–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.H.; Li, J.Y.; Dahlstrom, A.; Dotti, C.G. Axonal transport of synucleins is mediated by all rate components. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1999, 11, 3369–3376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gosavi, N.; Lee, H.J.; Lee, J.S.; Patel, S.; Lee, S.J. Golgi fragmentation occurs in the cells with prefibrillar alpha-synuclein aggregates and precedes the formation of fibrillar inclusion. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 48984–48992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alim, M.A.; Hossain, M.S.; Arima, K.; Takeda, K.; Izumiyama, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Kaji, H.; Shinoda, T.; Hisanaga, S.; Ueda, K. Tubulin seeds alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 2112–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, A.A.; Gitler, A.D.; Cashikar, A.; Haynes, C.M.; Hill, K.J.; Bhullar, B.; Liu, K.; Xu, K.; Strathearn, K.E.; Liu, F.; et al. Alpha-synuclein blocks ER-Golgi traffic and Rab1 rescues neuron loss in Parkinson’s models. Science 2006, 313, 324–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woods, W.S.; Boettcher, J.M.; Zhou, D.H.; Kloepper, K.D.; Hartman, K.L.; Ladror, D.T.; Qi, Z.; Rienstra, C.M.; George, J.M. Conformation-specific binding of alpha-synuclein to novel protein partners detected by phage display and NMR spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 34555–34567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thayanidhi, N.; Helm, J.R.; Nycz, D.C.; Bentley, M.; Liang, Y.; Hay, J.C. Alpha-synuclein delays endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-to-Golgi transport in mammalian cells by antagonizing ER/Golgi SNAREs. Mol. Biol. Cell 2010, 21, 1850–1863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, R.M.; Huang, Y.X.; Li, X.L.; Chen, C.; Shi, Q.; Wang, G.R.; Tian, C.; Wang, Z.Y.; Jing, Y.Y.; Gao, C.; et al. Molecular interaction of alpha-synuclein with tubulin influences on the polymerization of microtubule in vitro and structure of microtubule in cells. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2010, 37, 3183–3192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haggerty, T.; Credle, J.; Rodriguez, O.; Wills, J.; Oaks, A.W.; Masliah, E.; Sidhu, A. Hyperphosphorylated Tau in an alpha-synuclein-overexpressing transgenic model of Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2011, 33, 1598–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qureshi, H.Y.; Paudel, H.K. Parkinsonian neurotoxin 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) and alpha-synuclein mutations promote Tau protein phosphorylation at Ser262 and destabilize microtubule cytoskeleton in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 5055–5068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prots, I.; Grosch, J.; Brazdis, R.M.; Simmnacher, K.; Veber, V.; Havlicek, S.; Hannappel, C.; Krach, F.; Krumbiegel, M.; Schutz, O.; et al. alpha-Synuclein oligomers induce early axonal dysfunction in human iPSC-based models of synucleinopathies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 7813–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israeli, E.; Yakunin, E.; Zarbiv, Y.; Hacohen-Solovich, A.; Kisos, H.; Loeb, V.; Lichtenstein, M.; Ben-Gedalya, T.; Sabag, O.; Pikarsky, E.; et al. alpha-Synuclein expression selectively affects tumorigenesis in mice modeling Parkinson’s disease. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Xu, K. Alpha-synuclein contributes to malignant progression of human meningioma via the Akt/mTOR pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, M.; Suzuki, S.O.; Doh-ura, K.; Iwaki, T. alpha-Synuclein is expressed in a variety of brain tumors showing neuronal differentiation. Acta. Neuropathol. 2000, 99, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Kamitani, T. Parkinson’s disease-related protein, alpha-synuclein, in malignant melanoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deleersnijder, A.; Gerard, M.; Debyser, Z.; Baekelandt, V. The remarkable conformational plasticity of alpha-synuclein: Blessing or curse? Trends Mol. Med. 2013, 19, 368–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Intrinsically disordered proteins from A to Z. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2011, 43, 1090–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Fink, A.L. Evidence for a partially folded intermediate in alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 10737–10744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eliezer, D.; Kutluay, E.; Bussell, R., Jr.; Browne, G. Conformational properties of alpha-synuclein in its free and lipid-associated states. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 307, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norris, E.H.; Giasson, B.I.; Ischiropoulos, H.; Lee, V.M. Effects of oxidative and nitrative challenges on alpha-synuclein fibrillogenesis involve distinct mechanisms of protein modifications. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 27230–27240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoncini, C.W.; Fernandez, C.O.; Griesinger, C.; Jovin, T.M.; Zweckstetter, M. Familial mutants of alpha-synuclein with increased neurotoxicity have a destabilized conformation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 30649–30652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikiy, I.; Eliezer, D. Folding and misfolding of alpha-synuclein on membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1818, 1013–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ebrahimi-Fakhari, D.; Saidi, L.J.; Wahlster, L. Molecular chaperones and protein folding as therapeutic targets in Parkinson’s disease and other synucleinopathies. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2013, 1, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Scarlata, S.; Golebiewska, U. Linking alpha-synuclein properties with oxidation: A hypothesis on a mechanism underling cellular aggregation. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 2014, 46, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janowska, M.K.; Wu, K.P.; Baum, J. Unveiling transient protein-protein interactions that modulate inhibition of alpha-synuclein aggregation by beta-synuclein, a pre-synaptic protein that co-localizes with alpha-synuclein. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fusco, G.; Pape, T.; Stephens, A.D.; Mahou, P.; Costa, A.R.; Kaminski, C.F.; Kaminski Schierle, G.S.; Vendruscolo, M.; Veglia, G.; Dobson, C.M.; et al. Structural basis of synaptic vesicle assembly promoted by alpha-synuclein. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvagnion, C. The Role of Lipids Interacting with alpha-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, 433–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Z.; Krasnoslobodtsev, A.V.; Zhang, Y.; Ysselstein, D.; Rochet, J.C.; Blanchard, S.C.; Lyubchenko, Y.L. Effect of acidic pH on the stability of alpha-synuclein dimers. Biopolymers 2016, 105, 715–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgia, A.; Borgia, M.B.; Bugge, K.; Kissling, V.M.; Heidarsson, P.O.; Fernandes, C.B.; Sottini, A.; Soranno, A.; Buholzer, K.J.; Nettels, D.; et al. Extreme disorder in an ultrahigh-affinity protein complex. Nature 2018, 555, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borgia, A.; Kemplen, K.R.; Borgia, M.B.; Soranno, A.; Shammas, S.; Wunderlich, B.; Nettels, D.; Best, R.B.; Clarke, J.; Schuler, B. Transient misfolding dominates multidomain protein folding. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Goedert, M.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G. The Synucleinopathies: Twenty Years On. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, S51–S69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Cairns, N.J.; Lantos, P.L.; Goedert, M. Filamentous alpha-synuclein inclusions link multiple system atrophy with Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 251, 205–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Hasegawa, M.; Goedert, M. alpha-Synuclein in filamentous inclusions of Lewy bodies from Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 6469–6473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. The alpha-synucleinopathies: Parkinson’s disease, dementia with Lewy bodies, and multiple system atrophy. Ann. N Y Acad. Sci. 2000, 920, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Schmidt, M.L.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M. Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 1997, 388, 839–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, S.A.; Alcalay, R.N. Neuropathology of genetic synucleinopathies with parkinsonism: Review of the literature. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1504–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K. Neuropathological Staging of Brain Pathology in Sporadic Parkinson’s disease: Separating the Wheat from the Chaff. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2017, 7, S71–S85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rub, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angot, E.; Steiner, J.A.; Hansen, C.; Li, J.Y.; Brundin, P. Are synucleinopathies prion-like disorders? Lancet Neurol. 2010, 9, 1128–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olanow, C.W.; Brundin, P. Parkinson’s disease and alpha synuclein: Is Parkinson’s disease a prion-like disorder? Mov. Disord. 2013, 28, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brundin, P.; Ma, J.; Kordower, J.H. How strong is the evidence that Parkinson’s disease is a prion disorder? Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2016, 29, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grozdanov, V.; Danzer, K.M. Release and uptake of pathologic alpha-synuclein. Cell Tissue Res. 2018, 373, 175–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emmanouilidou, E.; Vekrellis, K. Exocytosis and Spreading of Normal and Aberrant alpha-Synuclein. Brain Pathol. 2016, 26, 398–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kordower, J.H.; Chu, Y.; Hauser, R.A.; Freeman, T.B.; Olanow, C.W. Lewy body-like pathology in long-term embryonic nigral transplants in Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 504–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordower, J.H.; Chu, Y.; Hauser, R.A.; Olanow, C.W.; Freeman, T.B. Transplanted dopaminergic neurons develop PD pathologic changes: A second case report. Mov. Disord. 2008, 23, 2303–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prusiner, S.B.; Woerman, A.L.; Mordes, D.A.; Watts, J.C.; Rampersaud, R.; Berry, D.B.; Patel, S.; Oehler, A.; Lowe, J.K.; Kravitz, S.N.; et al. Evidence for alpha-synuclein prions causing multiple system atrophy in humans with parkinsonism. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E5308–E5317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recasens, A.; Dehay, B. Alpha-synuclein spreading in Parkinson’s disease. Front Neuroanat. 2014, 8, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luk, K.C.; Kehm, V.M.; Zhang, B.; O’Brien, P.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Intracerebral inoculation of pathological alpha-synuclein initiates a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative alpha-synucleinopathy in mice. J. Exp. Med. 2012, 209, 975–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paumier, K.L.; Luk, K.C.; Manfredsson, F.P.; Kanaan, N.M.; Lipton, J.W.; Collier, T.J.; Steece-Collier, K.; Kemp, C.J.; Celano, S.; Schulz, E.; et al. Intrastriatal injection of pre-formed mouse alpha-synuclein fibrils into rats triggers alpha-synuclein pathology and bilateral nigrostriatal degeneration. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 82, 185–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, N.L.; Steiner, J.A.; Maroof, N.; Luk, K.C.; Madaj, Z.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M.; Brundin, P. Widespread transneuronal propagation of alpha-synucleinopathy triggered in olfactory bulb mimics prodromal Parkinson’s disease. J. Exp. Med. 2016, 213, 1759–1778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rey, N.L.; Wesson, D.W.; Brundin, P. The olfactory bulb as the entry site for prion-like propagation in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 109, 226–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Covell, D.J.; Medellin, C.; Stieber, A.; Robinson, J.L.; Zhang, B.; Pitkin, R.M.; Olufemi, M.F.; Luk, K.C.; et al. Cellular milieu imparts distinct pathological alpha-synuclein strains in alpha-synucleinopathies. Nature 2018, 557, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. The synaptic pathology of alpha-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 131–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellucci, A.; Mercuri, N.B.; Venneri, A.; Faustini, G.; Longhena, F.; Pizzi, M.; Missale, C.; Spano, P. Review: Parkinson’s disease: From synaptic loss to connectome dysfunction. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2016, 42, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calo, L.; Wegrzynowicz, M.; Santivanez-Perez, J.; Grazia Spillantini, M. Synaptic failure and alpha-synuclein. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faustini, G.; Longhena, F.; Varanita, T.; Bubacco, L.; Pizzi, M.; Missale, C.; Benfenati, F.; Bjorklund, A.; Spano, P.; Bellucci, A. Synapsin III deficiency hampers alpha-synuclein aggregation, striatal synaptic damage and nigral cell loss in an AAV-based mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2018, 136, 621–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Missale, C.; Pizzi, M.; Bellucci, A. Dopamine Transporter/alpha-Synuclein Complexes Are Altered in the Post Mortem Caudate Putamen of Parkinson’s Disease: An In Situ Proximity Ligation Assay Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Varanita, T.; Zaltieri, M.; Porrini, V.; Tessari, I.; Poliani, P.L.; Missale, C.; Borroni, B.; Padovani, A.; et al. Synapsin III is a key component of alpha-synuclein fibrils in Lewy bodies of PD brains. Brain Pathol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, A.A.; Ingrassia, A.; de Menezes, R.X.; van Kesteren, R.E.; Rozemuller, A.J.; Heutink, P.; van de Berg, W.D. Evidence for Immune Response, Axonal Dysfunction and Reduced Endocytosis in the Substantia Nigra in Early Stage Parkinson’s Disease. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0128651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereczki, E.; Branca, R.M.; Francis, P.T.; Pereira, J.B.; Baek, J.H.; Hortobagyi, T.; Winblad, B.; Ballard, C.; Lehtio, J.; Aarsland, D. Synaptic markers of cognitive decline in neurodegenerative diseases: A proteomic approach. Brain 2018, 141, 582–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bereczki, E.; Francis, P.T.; Howlett, D.; Pereira, J.B.; Hoglund, K.; Bogstedt, A.; Cedazo-Minguez, A.; Baek, J.H.; Hortobagyi, T.; Attems, J.; et al. Synaptic proteins predict cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body dementia. Alzheimers Dement. 2016, 12, 1149–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kramer, M.L.; Schulz-Schaeffer, W.J. Presynaptic alpha-synuclein aggregates, not Lewy bodies, cause neurodegeneration in dementia with Lewy bodies. J. Neurosci. 2007, 27, 1405–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Missale, C.; Pizzi, M.; Spano, P.; Bellucci, A. The Contribution of alpha-Synuclein Spreading to Parkinson’s Disease Synaptopathy. Neural. Plast. 2017, 2017, 5012129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uversky, V.N. A protein-chameleon: Conformational plasticity of alpha-synuclein, a disordered protein involved in neurodegenerative disorders. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2003, 21, 211–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; Kim, S.; Kang, M.; Ryu, Y.; Kim, T.D. Chaperone-like activities of alpha-synuclein: Alpha-synuclein assists enzyme activities of esterases. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 346, 1142–1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manda, K.M.; Yedlapudi, D.; Korukonda, S.; Bojja, S.; Kalivendi, S.V. The chaperone-like activity of alpha-synuclein attenuates aggregation of its alternatively spliced isoform, 112-synuclein in vitro: Plausible cross-talk between isoforms in protein aggregation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e98657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clayton, D.F.; George, J.M. The synucleins: A family of proteins involved in synaptic function, plasticity, neurodegeneration and disease. Trends Neurosci. 1998, 21, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.M. The synucleins. Genome Biol. 2002, 3, REVIEWS3002. [Google Scholar]
- Vamvaca, K.; Volles, M.J.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. The first N-terminal amino acids of alpha-synuclein are essential for alpha-helical structure formation in vitro and membrane binding in yeast. J. Mol. Biol. 2009, 389, 413–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Fink, A.L. Lipid binding inhibits alpha-synuclein fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 16873–16877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davidson, W.S.; Jonas, A.; Clayton, D.F.; George, J.M. Stabilization of alpha-synuclein secondary structure upon binding to synthetic membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 9443–9449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dikiy, I.; Eliezer, D. N-terminal acetylation stabilizes N-terminal helicity in lipid- and micelle-bound alpha-synuclein and increases its affinity for physiological membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 3652–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trexler, A.J.; Rhoades, E. N-Terminal acetylation is critical for forming alpha-helical oligomer of alpha-synuclein. Protein Sci. 2012, 21, 601–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sevcsik, E.; Trexler, A.J.; Dunn, J.M.; Rhoades, E. Allostery in a disordered protein: Oxidative modifications to alpha-synuclein act distally to regulate membrane binding. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 7152–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Souza, J.M.; Giasson, B.I.; Chen, Q.; Lee, V.M.; Ischiropoulos, H. Dityrosine cross-linking promotes formation of stable alpha -synuclein polymers. Implication of nitrative and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 18344–18349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burai, R.; Ait-Bouziad, N.; Chiki, A.; Lashuel, H.A. Elucidating the Role of Site-Specific Nitration of alpha-Synuclein in the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease via Protein Semisynthesis and Mutagenesis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5041–5052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ysselstein, D.; Joshi, M.; Mishra, V.; Griggs, A.M.; Asiago, J.M.; McCabe, G.P.; Stanciu, L.A.; Post, C.B.; Rochet, J.C. Effects of impaired membrane interactions on alpha-synuclein aggregation and neurotoxicity. Neurobiol. Dis. 2015, 79, 150–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigelny, I.F.; Sharikov, Y.; Kouznetsova, V.L.; Greenberg, J.P.; Wrasidlo, W.; Overk, C.; Gonzalez, T.; Trejo, M.; Spencer, B.; Kosberg, K.; et al. Molecular determinants of alpha-synuclein mutants’ oligomerization and membrane interactions. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2015, 6, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodner, C.R.; Maltsev, A.S.; Dobson, C.M.; Bax, A. Differential phospholipid binding of alpha-synuclein variants implicated in Parkinson′s disease revealed by solution NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 2010, 49, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaugler, M.N.; Genc, O.; Bobela, W.; Mohanna, S.; Ardah, M.T.; El-Agnaf, O.M.; Cantoni, M.; Bensadoun, J.C.; Schneggenburger, R.; Knott, G.W.; et al. Nigrostriatal overabundance of alpha-synuclein leads to decreased vesicle density and deficits in dopamine release that correlate with reduced motor activity. Acta Neuropathol. 2012, 123, 653–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jensen, P.H.; Nielsen, M.S.; Jakes, R.; Dotti, C.G.; Goedert, M. Binding of alpha-synuclein to brain vesicles is abolished by familial Parkinson’s disease mutation. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 26292–26294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Fukushima, H.; Masliah, E.; Xia, Y.; Iwai, A.; Yoshimoto, M.; Otero, D.A.; Kondo, J.; Ihara, Y.; Saitoh, T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding an unrecognized component of amyloid in Alzheimer disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 11282–11286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mor, D.E.; Ugras, S.E.; Daniels, M.J.; Ischiropoulos, H. Dynamic structural flexibility of alpha-synuclein. Neurobiol. Dis. 2016, 88, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giasson, B.I.; Murray, I.V.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. A hydrophobic stretch of 12 amino acid residues in the middle of alpha-synuclein is essential for filament assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 2380–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Theillet, F.X.; Binolfi, A.; Bekei, B.; Martorana, A.; Rose, H.M.; Stuiver, M.; Verzini, S.; Lorenz, D.; van Rossum, M.; Goldfarb, D.; et al. Structural disorder of monomeric alpha-synuclein persists in mammalian cells. Nature 2016, 530, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulmer, T.S.; Bax, A. Comparison of structure and dynamics of micelle-bound human alpha-synuclein and Parkinson disease variants. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 43179–43187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, J.M.; Jin, H.; Woods, W.S.; Clayton, D.F. Characterization of a novel protein regulated during the critical period for song learning in the zebra finch. Neuron 1995, 15, 361–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dedmon, M.M.; Christodoulou, J.; Wilson, M.R.; Dobson, C.M. Heat shock protein 70 inhibits alpha-synuclein fibril formation via preferential binding to prefibrillar species. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 14733–14740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giasson, B.I.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M.; Duda, J.E.; Leight, S.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. A panel of epitope-specific antibodies detects protein domains distributed throughout human alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2000, 59, 528–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, H.; Hasegawa, M.; Dohmae, N.; Kawashima, A.; Masliah, E.; Goldberg, M.S.; Shen, J.; Takio, K.; Iwatsubo, T. alpha-Synuclein is phosphorylated in synucleinopathy lesions. Nat. Cell Biol. 2002, 4, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paleologou, K.E.; Schmid, A.W.; Rospigliosi, C.C.; Kim, H.Y.; Lamberto, G.R.; Fredenburg, R.A.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr.; Fernandez, C.O.; Eliezer, D.; Zweckstetter, M.; et al. Phosphorylation at Ser-129 but not the phosphomimics S129E/D inhibits the fibrillation of alpha-synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 16895–16905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, W.; West, N.; Colla, E.; Pletnikova, O.; Troncoso, J.C.; Marsh, L.; Dawson, T.M.; Jakala, P.; Hartmann, T.; Price, D.L.; et al. Aggregation promoting C-terminal truncation of alpha-synuclein is a normal cellular process and is enhanced by the familial Parkinson’s disease-linked mutations. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 2162–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowther, R.A.; Jakes, R.; Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Synthetic filaments assembled from C-terminally truncated alpha-synuclein. FEBS Lett. 1998, 436, 309–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Sudhof, T.C. alpha-Synuclein assembles into higher-order multimers upon membrane binding to promote SNARE complex formation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, E4274–E4283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, P.H.; Zhen, W.; Poon, A.W.; Conway, K.A.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. NACP, a protein implicated in Alzheimer’s disease and learning, is natively unfolded. Biochemistry 1996, 35, 13709–13715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurry, T.; Ullman, O.; Fisher, C.K.; Perovic, I.; Pochapsky, T.; Stultz, C.M. The dynamic structure of alpha-synuclein multimers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 3865–3872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartels, T.; Choi, J.G.; Selkoe, D.J. alpha-Synuclein occurs physiologically as a helically folded tetramer that resists aggregation. Nature 2011, 477, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Jiang, S.; Cui, Y.; Yue, Z.; Su, C.; Sun, J.; Sheng, S.; Tian, J. The n-terminal 5-MER peptide analogue P165 of amyloid precursor protein exerts protective effects on SH-SY5Y cells and rat hippocampus neuronal synapses. Neuroscience 2011, 173, 169–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fauvet, B.; Mbefo, M.K.; Fares, M.B.; Desobry, C.; Michael, S.; Ardah, M.T.; Tsika, E.; Coune, P.; Prudent, M.; Lion, N.; et al. alpha-Synuclein in central nervous system and from erythrocytes, mammalian cells, and Escherichia coli exists predominantly as disordered monomer. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 15345–15364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Gathagan, R.J.; Lee, V.M. Distinct alpha-Synuclein strains and implications for heterogeneity among alpha-Synucleinopathies. Neurobiol. Dis. 2018, 109, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. Light at the End of the Amyloid TunnelPublished as part of the Biochemistry series “Biochemistry to Bedside”. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 5921–5922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peelaerts, W.; Baekelandt, V. alpha-synuclein folds: The cards are on the table. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 359–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salveson, P.J.; Spencer, R.K.; Nowick, J.S. X-ray Crystallographic Structure of Oligomers Formed by a Toxic beta-Hairpin Derived from alpha-Synuclein: Trimers and Higher-Order Oligomers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 4458–4467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Hilaly, Y.K.; Biasetti, L.; Blakeman, B.J.; Pollack, S.J.; Zibaee, S.; Abdul-Sada, A.; Thorpe, J.R.; Xue, W.F.; Serpell, L.C. The involvement of dityrosine crosslinking in alpha-synuclein assembly and deposition in Lewy Bodies in Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, N.; Mor, D.E.; Lightfoot, R.; Malkus, K.; Giasson, B.; Ischiropoulos, H. Evidence of native alpha-synuclein conformers in the human brain. J. Biol. Chem. 2014, 289, 7929–7934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pivato, M.; De Franceschi, G.; Tosatto, L.; Frare, E.; Kumar, D.; Aioanei, D.; Brucale, M.; Tessari, I.; Bisaglia, M.; Samori, B.; et al. Covalent alpha-synuclein dimers: Chemico-physical and aggregation properties. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e50027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dettmer, U.; Newman, A.J.; Luth, E.S.; Bartels, T.; Selkoe, D. In vivo cross-linking reveals principally oligomeric forms of alpha-synuclein and beta-synuclein in neurons and non-neural cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 6371–6385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luth, E.S.; Bartels, T.; Dettmer, U.; Kim, N.C.; Selkoe, D.J. Purification of alpha-synuclein from human brain reveals an instability of endogenous multimers as the protein approaches purity. Biochemistry 2015, 54, 279–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.K.; Han, J.H.; Jang, J.Y.; Yun, S.E.; Kim, G.Y.; Kang, S.; Rhim, H. A novel link between the conformations, exposure of specific epitopes, and subcellular localization of alpha-synuclein. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2015, 1850, 2497–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Das, U.; Scott, D.A.; Tang, Y.; McLean, P.J.; Roy, S. alpha-synuclein multimers cluster synaptic vesicles and attenuate recycling. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 2319–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galvagnion, C.; Buell, A.K.; Meisl, G.; Michaels, T.C.; Vendruscolo, M.; Knowles, T.P.; Dobson, C.M. Lipid vesicles trigger alpha-synuclein aggregation by stimulating primary nucleation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buell, A.K.; Galvagnion, C.; Gaspar, R.; Sparr, E.; Vendruscolo, M.; Knowles, T.P.; Linse, S.; Dobson, C.M. Solution conditions determine the relative importance of nucleation and growth processes in alpha-synuclein aggregation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 7671–7676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breydo, L.; Wu, J.W.; Uversky, V.N. Alpha-synuclein misfolding and Parkinson’s disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 261–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldwin, A.J.; Knowles, T.P.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Fitzpatrick, A.W.; Devlin, G.L.; Shammas, S.L.; Waudby, C.A.; Mossuto, M.F.; Meehan, S.; Gras, S.L.; et al. Metastability of native proteins and the phenomenon of amyloid formation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14160–14163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartl, F.U.; Bracher, A.; Hayer-Hartl, M. Molecular chaperones in protein folding and proteostasis. Nature 2011, 475, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, T.P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Dobson, C.M. The amyloid state and its association with protein misfolding diseases. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 15, 384–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cremades, N.; Cohen, S.I.; Deas, E.; Abramov, A.Y.; Chen, A.Y.; Orte, A.; Sandal, M.; Clarke, R.W.; Dunne, P.; Aprile, F.A.; et al. Direct observation of the interconversion of normal and toxic forms of alpha-synuclein. Cell 2012, 149, 1048–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bousset, L.; Pieri, L.; Ruiz-Arlandis, G.; Gath, J.; Jensen, P.H.; Habenstein, B.; Madiona, K.; Olieric, V.; Bockmann, A.; Meier, B.H.; et al. Structural and functional characterization of two alpha-synuclein strains. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woerman, A.L.; Stohr, J.; Aoyagi, A.; Rampersaud, R.; Krejciova, Z.; Watts, J.C.; Ohyama, T.; Patel, S.; Widjaja, K.; Oehler, A.; et al. Propagation of prions causing synucleinopathies in cultured cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E4949–E4958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fazili, N.A.; Naeem, A. Exploring the Transition of Human alpha-Synuclein from Native to the Fibrillar State: Insights into the Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s Disease. J. Fluoresc. 2016, 26, 1659–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Ferreira, R.; Taylor, N.M.; Mona, D.; Ringler, P.; Lauer, M.E.; Riek, R.; Britschgi, M.; Stahlberg, H. Cryo-EM structure of alpha-synuclein fibrils. Elife 2018, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flynn, J.D.; McGlinchey, R.P.; Walker, R.L., 3rd; Lee, J.C. Structural features of alpha-synuclein amyloid fibrils revealed by Raman spectroscopy. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 767–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Ge, P.; Murray, K.A.; Sheth, P.; Zhang, M.; Nair, G.; Sawaya, M.R.; Shin, W.S.; Boyer, D.R.; Ye, S.; et al. Cryo-EM of full-length alpha-synuclein reveals fibril polymorphs with a common structural kernel. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 3609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, E.A.; Graves, C.L.; Mishizen-Eberz, A.J.; Lupoli, M.A.; Lynch, D.R.; Englander, S.W.; Axelsen, P.H.; Giasson, B.I. The E46K mutation in alpha-synuclein increases amyloid fibril formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 7800–7807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conway, K.A.; Lee, S.J.; Rochet, J.C.; Ding, T.T.; Williamson, R.E.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Acceleration of oligomerization, not fibrillization, is a shared property of both alpha-synuclein mutations linked to early-onset Parkinson’s disease: Implications for pathogenesis and therapy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 571–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narhi, L.; Wood, S.J.; Steavenson, S.; Jiang, Y.; Wu, G.M.; Anafi, D.; Kaufman, S.A.; Martin, F.; Sitney, K.; Denis, P.; et al. Both familial Parkinson’s disease mutations accelerate alpha-synuclein aggregation. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 9843–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharya, S.; Saha, S.; Ahmad, B.; Lapidus, L.J. Effects of Mutations on the Reconfiguration Rate of alpha-Synuclein. J. Phys. Chem. B 2015, 119, 15443–15450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaro, D.F.; Rodrigues, E.F.; Langohr, R.; Shahpasandzadeh, H.; Ribeiro, T.; Guerreiro, P.; Gerhardt, E.; Krohnert, K.; Klucken, J.; Pereira, M.D.; et al. Systematic comparison of the effects of alpha-synuclein mutations on its oligomerization and aggregation. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, J.; Erana, H.; Lopez-Martinez, E.; Claes, N.; Martin, V.F.; Solis, D.M.; Bals, S.; Cortajarena, A.L.; Castilla, J.; Liz-Marzan, L.M. Detection of amyloid fibrils in Parkinson’s disease using plasmonic chirality. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, 3225–3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, M.D.; Comellas, G.; Nieuwkoop, A.J.; Covell, D.J.; Berthold, D.A.; Kloepper, K.D.; Courtney, J.M.; Kim, J.K.; Barclay, A.M.; Kendall, A.; et al. Solid-state NMR structure of a pathogenic fibril of full-length human alpha-synuclein. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2016, 23, 409–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciolino, N.; Burz, D.S.; Shekhtman, A. In-Cell NMR Spectroscopy of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins. Proteomics 2018, e1800055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, J.A.; Rodrigues, M.; De, S.; Flagmeier, P.; Gandhi, S.; Dobson, C.M.; Klenerman, D.; Lee, S.F. Optical Structural Analysis of Individual alpha-Synuclein Oligomers. Angew Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 4886–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Morfini, G.A.; Langhamer, L.B.; He, Y.; Brady, S.T.; Kordower, J.H. Alterations in axonal transport motor proteins in sporadic and experimental Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2012, 135, 2058–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chung, C.Y.; Koprich, J.B.; Siddiqi, H.; Isacson, O. Dynamic changes in presynaptic and axonal transport proteins combined with striatal neuroinflammation precede dopaminergic neuronal loss in a rat model of AAV alpha-synucleinopathy. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prots, I.; Veber, V.; Brey, S.; Campioni, S.; Buder, K.; Riek, R.; Bohm, K.J.; Winner, B. alpha-Synuclein oligomers impair neuronal microtubule-kinesin interplay. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21742–21754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yuan, Y.H.; Sun, J.D.; Li, J.; Li, Z.P.; Chen, N.H. Nigrostriatal dynein changes in A53T alpha-synuclein transgenic mice. F1000Res 2014, 3, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toba, S.; Jin, M.; Yamada, M.; Kumamoto, K.; Matsumoto, S.; Yasunaga, T.; Fukunaga, Y.; Miyazawa, A.; Fujita, S.; Itoh, K.; et al. Alpha-synuclein facilitates to form short unconventional microtubules that have a unique function in the axonal transport. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cartelli, D.; Aliverti, A.; Barbiroli, A.; Santambrogio, C.; Ragg, E.M.; Casagrande, F.V.; Cantele, F.; Beltramone, S.; Marangon, J.; De Gregorio, C.; et al. alpha-Synuclein is a Novel Microtubule Dynamase. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 33289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartelli, D.; Cappelletti, G. Microtubule Destabilization Paves the Way to Parkinson’s Disease. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 6762–6774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carnwath, T.; Mohammed, R.; Tsiang, D. The direct and indirect effects of alpha-synuclein on microtubule stability in the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2018, 14, 1685–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, P.H.; Hager, H.; Nielsen, M.S.; Hojrup, P.; Gliemann, J.; Jakes, R. alpha-synuclein binds to Tau and stimulates the protein kinase A-catalyzed tau phosphorylation of serine residues 262 and 356. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 25481–25489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giasson, B.I.; Forman, M.S.; Higuchi, M.; Golbe, L.I.; Graves, C.L.; Kotzbauer, P.T.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Initiation and synergistic fibrillization of tau and alpha-synuclein. Science 2003, 300, 636–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duka, T.; Duka, V.; Joyce, J.N.; Sidhu, A. Alpha-Synuclein contributes to GSK-3beta-catalyzed Tau phosphorylation in Parkinson’s disease models. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 2820–2830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waxman, E.A.; Giasson, B.I. Characterization of kinases involved in the phosphorylation of aggregated alpha-synuclein. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 89, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotzbauer, P.T.; Giasson, B.I.; Kravitz, A.V.; Golbe, L.I.; Mark, M.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau in familial Parkinson’s disease caused by the A53T alpha-synuclein mutation. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolopoulou, K.; Grammenoudi, S.; Samiotaki, M.; Skoulakis, E.M.C. Differential effects of 14-3-3 dimers on Tau phosphorylation, stability and toxicity in vivo. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2018, 27, 2244–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tugaeva, K.V.; Tsvetkov, P.O.; Sluchanko, N.N. Bacterial co-expression of human Tau protein with protein kinase A and 14-3-3 for studies of 14-3-3/phospho-Tau interaction. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.; Schumacher, B.; Landrieu, I.; Bartel, M.; Smet-Nocca, C.; Jang, A.; Choi, H.S.; Jeon, N.L.; Chang, K.A.; Kim, H.S.; et al. Involvement of 14-3-3 in tubulin instability and impaired axon development is mediated by Tau. FASEB J. 2015, 29, 4133–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadik, G.; Tanaka, T.; Kato, K.; Yanagi, K.; Kudo, T.; Takeda, M. Differential interaction and aggregation of 3-repeat and 4-repeat tau isoforms with 14-3-3zeta protein. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 383, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluchanko, N.N.; Seit-Nebi, A.S.; Gusev, N.B. Phosphorylation of more than one site is required for tight interaction of human tau protein with 14-3-3zeta. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 2739–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obsil, T.; Ghirlando, R.; Klein, D.C.; Ganguly, S.; Dyda, F. Crystal structure of the 14-3-3zeta:serotonin N-acetyltransferase complex. a role for scaffolding in enzyme regulation. Cell 2001, 105, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, D.; Riess, O.; Bornemann, A. Specification of 14-3-3 proteins in Lewy bodies. Ann. Neurol. 2003, 54, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plotegher, N.; Kumar, D.; Tessari, I.; Brucale, M.; Munari, F.; Tosatto, L.; Belluzzi, E.; Greggio, E.; Bisaglia, M.; Capaldi, S.; et al. The chaperone-like protein 14-3-3eta interacts with human alpha-synuclein aggregation intermediates rerouting the amyloidogenic pathway and reducing alpha-synuclein cellular toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 5615–5629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrerova, N.; Petrucelli, L.; Farrer, M.; Mehta, N.; Choi, P.; Hardy, J.; Wolozin, B. alpha-Synuclein shares physical and functional homology with 14-3-3 proteins. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 5782–5791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamoto, Y.; Akiguchi, I.; Nakamura, S.; Honjyo, Y.; Shibasaki, H.; Budka, H. 14-3-3 proteins in Lewy bodies in Parkinson disease and diffuse Lewy body disease brains. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2002, 61, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yacoubian, T.A.; Slone, S.R.; Harrington, A.J.; Hamamichi, S.; Schieltz, J.M.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Standaert, D.G. Differential neuroprotective effects of 14-3-3 proteins in models of Parkinson’s disease. Cell Death Dis. 2010, 1, e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Kao, S.Y.; Lee, F.J.; Song, W.; Jin, L.W.; Yankner, B.A. Dopamine-dependent neurotoxicity of alpha-synuclein: A mechanism for selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson disease. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Fineberg, N.S.; Gray, M.; Yacoubian, T.A. alpha-Synuclein overexpression represses 14-3-3theta transcription. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2013, 51, 1000–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, M.A.; Ellis, C.E.; Markey, S.P.; Nussbaum, R.L. Proteomics analysis identifies phosphorylation-dependent alpha-synuclein protein interactions. Mol. Cell Proteomics. 2008, 7, 2123–2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Underwood, R.; Kamath, A.; Britain, C.; McFerrin, M.B.; McLean, P.J.; Volpicelli-Daley, L.A.; Whitaker, R.H.; Placzek, W.J.; Becker, K.; et al. 14-3-3 Proteins Reduce Cell-to-Cell Transfer and Propagation of Pathogenic alpha-Synuclein. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 8211–8232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Esposito, A.; Dohm, C.P.; Kermer, P.; Bahr, M.; Wouters, F.S. alpha-Synuclein and its disease-related mutants interact differentially with the microtubule protein tau and associate with the actin cytoskeleton. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 26, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sousa, V.L.; Bellani, S.; Giannandrea, M.; Yousuf, M.; Valtorta, F.; Meldolesi, J.; Chieregatti, E. {alpha}-synuclein and its A30P mutant affect actin cytoskeletal structure and dynamics. Mol. Biol. Cell 2009, 20, 3725–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xun, Z.; Sowell, R.A.; Kaufman, T.C.; Clemmer, D.E. Protein expression in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Proteome Res. 2007, 6, 348–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichibangase, T.; Saimaru, H.; Takamura, N.; Kuwahara, T.; Koyama, A.; Iwatsubo, T.; Imai, K. Proteomics of Caenorhabditis elegans over-expressing human alpha-synuclein analyzed by fluorogenic derivatization-liquid chromatography/tandem mass spectrometry: Identification of actin and several ribosomal proteins as negative markers at early Parkinson’s disease stages. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2008, 22, 232–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ordonez, D.G.; Lee, M.K.; Feany, M.B. alpha-synuclein Induces Mitochondrial Dysfunction through Spectrin and the Actin Cytoskeleton. Neuron 2018, 97, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenster, S.D.; Chung, W.J.; Zhai, R.; Cases-Langhoff, C.; Voss, B.; Garner, A.M.; Kaempf, U.; Kindler, S.; Gundelfinger, E.D.; Garner, C.C. Piccolo, a presynaptic zinc finger protein structurally related to bassoon. Neuron 2000, 25, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao-Rikitsu, E.; Mochida, S.; Inoue, E.; Deguchi-Tawarada, M.; Inoue, M.; Ohtsuka, T.; Takai, Y. Physical and functional interaction of the active zone proteins, CAST, RIM1, and Bassoon, in neurotransmitter release. J. Cell Biol. 2004, 164, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fejtova, A.; Davydova, D.; Bischof, F.; Lazarevic, V.; Altrock, W.D.; Romorini, S.; Schone, C.; Zuschratter, W.; Kreutz, M.R.; Garner, C.C.; et al. Dynein light chain regulates axonal trafficking and synaptic levels of Bassoon. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 341–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mukherjee, K.; Yang, X.; Gerber, S.H.; Kwon, H.B.; Ho, A.; Castillo, P.E.; Liu, X.; Sudhof, T.C. Piccolo and bassoon maintain synaptic vesicle clustering without directly participating in vesicle exocytosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 6504–6509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vargas, K.J.; Schrod, N.; Davis, T.; Fernandez-Busnadiego, R.; Taguchi, Y.V.; Laugks, U.; Lucic, V.; Chandra, S.S. Synucleins Have Multiple Effects on Presynaptic Architecture. Cell Rep. 2017, 18, 161–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.A.; Tabarean, I.; Tang, Y.; Cartier, A.; Masliah, E.; Roy, S. A pathologic cascade leading to synaptic dysfunction in alpha-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 8083–8095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masaracchia, C.; Hnida, M.; Gerhardt, E.; Lopes da Fonseca, T.; Villar-Pique, A.; Branco, T.; Stahlberg, M.A.; Dean, C.; Fernandez, C.O.; Milosevic, I.; et al. Membrane binding, internalization, and sorting of alpha-synuclein in the cell. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2018, 6, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chutna, O.; Goncalves, S.; Villar-Pique, A.; Guerreiro, P.; Marijanovic, Z.; Mendes, T.; Ramalho, J.; Emmanouilidou, E.; Ventura, S.; Klucken, J.; et al. The small GTPase Rab11 co-localizes with alpha-synuclein in intracellular inclusions and modulates its aggregation, secretion and toxicity. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 6732–6745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bridi, J.C.; Hirth, F. Mechanisms of alpha-Synuclein Induced Synaptopathy in Parkinson’s Disease. Front Neurosci. 2018, 12, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, D.; Roy, S. alpha-Synuclein inhibits intersynaptic vesicle mobility and maintains recycling-pool homeostasis. J. Neurosci. 2012, 32, 10129–10135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lautenschlager, J.; Stephens, A.D.; Fusco, G.; Strohl, F.; Curry, N.; Zacharopoulou, M.; Michel, C.H.; Laine, R.; Nespovitaya, N.; Fantham, M.; et al. C-terminal calcium binding of alpha-synuclein modulates synaptic vesicle interaction. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabin, D.E.; Shimazu, K.; Murphy, D.; Cole, N.B.; Gottschalk, W.; McIlwain, K.L.; Orrison, B.; Chen, A.; Ellis, C.E.; Paylor, R.; et al. Synaptic vesicle depletion correlates with attenuated synaptic responses to prolonged repetitive stimulation in mice lacking alpha-synuclein. J. Neurosci. 2002, 22, 8797–8807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.; Kim, S.; Varkey, J.; Lou, X.; Song, J.K.; Diao, J.; Langen, R.; Shin, Y.K. Nonaggregated alpha-synuclein influences SNARE-dependent vesicle docking via membrane binding. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 3889–3896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.K.; Choi, M.G.; Kim, J.Y.; Yang, Y.; Lai, Y.; Kweon, D.H.; Lee, N.K.; Shin, Y.K. Large alpha-synuclein oligomers inhibit neuronal SNARE-mediated vesicle docking. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 4087–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cesca, F.; Baldelli, P.; Valtorta, F.; Benfenati, F. The synapsins: Key actors of synapse function and plasticity. Prog. Neurobiol. 2010, 91, 313–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rockenstein, E.; Nuber, S.; Overk, C.R.; Ubhi, K.; Mante, M.; Patrick, C.; Adame, A.; Trejo-Morales, M.; Gerez, J.; Picotti, P.; et al. Accumulation of oligomer-prone alpha-synuclein exacerbates synaptic and neuronal degeneration in vivo. Brain 2014, 137, 1496–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larson, M.E.; Greimel, S.J.; Amar, F.; LaCroix, M.; Boyle, G.; Sherman, M.A.; Schley, H.; Miel, C.; Schneider, J.A.; Kayed, R.; et al. Selective lowering of synapsins induced by oligomeric alpha-synuclein exacerbates memory deficits. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4648–E4657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betzer, C.; Movius, A.J.; Shi, M.; Gai, W.P.; Zhang, J.; Jensen, P.H. Identification of synaptosomal proteins binding to monomeric and oligomeric alpha-synuclein. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0116473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kile, B.M.; Guillot, T.S.; Venton, B.J.; Wetsel, W.C.; Augustine, G.J.; Wightman, R.M. Synapsins differentially control dopamine and serotonin release. J. Neurosci. 2010, 30, 9762–9770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogen, I.L.; Boulland, J.L.; Mariussen, E.; Wright, M.S.; Fonnum, F.; Kao, H.T.; Walaas, S.I. Absence of synapsin I and II is accompanied by decreases in vesicular transport of specific neurotransmitters. J. Neurochem. 2006, 96, 1458–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zaltieri, M.; Grigoletto, J.; Longhena, F.; Navarria, L.; Favero, G.; Castrezzati, S.; Colivicchi, M.A.; Della Corte, L.; Rezzani, R.; Pizzi, M.; et al. alpha-synuclein and synapsin III cooperatively regulate synaptic function in dopamine neurons. J. Cell Sci. 2015, 128, 2231–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouroupi, G.; Taoufik, E.; Vlachos, I.S.; Tsioras, K.; Antoniou, N.; Papastefanaki, F.; Chroni-Tzartou, D.; Wrasidlo, W.; Bohl, D.; Stellas, D.; et al. Defective synaptic connectivity and axonal neuropathology in a human iPSC-based model of familial Parkinson’s disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E3679–E3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monzio Compagnoni G, K.G.; Samarani, M.; Aureli, M.; Faustini, G.; Bellucci, A.; Ronchi, D.; Bordoni, A.; Garbellini, M.; Salani, S.; Fortunato, F.; et al. Mitochondrial Dysregulation and Impaired Autophagy in iPSC-Derived Dopaminergic Neurons of Multiple System Atrophy. Stem. Cell Rep. 2018, 11, 1185–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, A.R.; Stout, K.A.; Ozawa, M.; Lohr, K.M.; Hoffman, C.A.; Bernstein, A.I.; Li, Y.; Wang, M.; Sgobio, C.; Sastry, N.; et al. Synaptic vesicle glycoprotein 2C (SV2C) modulates dopamine release and is disrupted in Parkinson disease. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E2253–E2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorenberg, E.L.; Chandra, S.S. The Role of Co-chaperones in Synaptic Proteostasis and Neurodegenerative Disease. Front Neurosci. 2017, 11, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burre, J.; Sharma, M.; Tsetsenis, T.; Buchman, V.; Etherton, M.R.; Sudhof, T.C. Alpha-synuclein promotes SNARE-complex assembly in vivo and in vitro. Science 2010, 329, 1663–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lou, X.; Kim, J.; Hawk, B.J.; Shin, Y.K. alpha-Synuclein may cross-bridge v-SNARE and acidic phospholipids to facilitate SNARE-dependent vesicle docking. Biochem. J. 2017, 474, 2039–2049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diao, J.; Burre, J.; Vivona, S.; Cipriano, D.J.; Sharma, M.; Kyoung, M.; Sudhof, T.C.; Brunger, A.T. Native alpha-synuclein induces clustering of synaptic-vesicle mimics via binding to phospholipids and synaptobrevin-2/VAMP2. Elife 2013, 2, e00592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, M.L.; Gandhi, S. Crucial role of protein oligomerization in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 3631–3644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Reitbock, P.; Anichtchik, O.; Bellucci, A.; Iovino, M.; Ballini, C.; Fineberg, E.; Ghetti, B.; Della Corte, L.; Spano, P.; Tofaris, G.K.; et al. SNARE protein redistribution and synaptic failure in a transgenic mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2010, 133, 2032–2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Logan, T.; Bendor, J.; Toupin, C.; Thorn, K.; Edwards, R.H. alpha-Synuclein promotes dilation of the exocytotic fusion pore. Nat. Neurosci. 2017, 20, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.T.; Soll, L.G.; Tessari, I.; Bubacco, L.; Morgan, J.R. alpha-Synuclein Dimers Impair Vesicle Fission during Clathrin-Mediated Synaptic Vesicle Recycling. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Taoufiq, Z.; Thorn-Seshold, O.; Trauner, D.; Hasegawa, M.; Takahashi, T. Wild-Type Monomeric alpha-Synuclein Can Impair Vesicle Endocytosis and Synaptic Fidelity via Tubulin Polymerization at the Calyx of Held. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 6043–6052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vargas, K.J.; Makani, S.; Davis, T.; Westphal, C.H.; Castillo, P.E.; Chandra, S.S. Synucleins regulate the kinetics of synaptic vesicle endocytosis. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 9364–9376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoncini, C.W.; Rasia, R.M.; Lamberto, G.R.; Binolfi, A.; Zweckstetter, M.; Griesinger, C.; Fernandez, C.O. Structural characterization of the intrinsically unfolded protein beta-synuclein, a natural negative regulator of alpha-synuclein aggregation. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hashimoto, M.; Rockenstein, E.; Mante, M.; Mallory, M.; Masliah, E. beta-Synuclein inhibits alpha-synuclein aggregation: A possible role as an anti-parkinsonian factor. Neuron 2001, 32, 213–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.Y.; Lansbury, P.T., Jr. Beta-synuclein inhibits formation of alpha-synuclein protofibrils: A possible therapeutic strategy against Parkinson’s disease. Biochemistry 2003, 42, 3696–3700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N.; Li, J.; Souillac, P.; Millett, I.S.; Doniach, S.; Jakes, R.; Goedert, M.; Fink, A.L. Biophysical properties of the synucleins and their propensities to fibrillate: Inhibition of alpha-synuclein assembly by beta- and gamma-synucleins. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 11970–11978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, Y.H.; Eliezer, D. Secondary structure and dynamics of micelle bound beta- and gamma-synuclein. Protein Sci. 2006, 15, 1162–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.W.; Buell, A.K.; Michaels, T.C.; Meisl, G.; Carozza, J.; Flagmeier, P.; Vendruscolo, M.; Knowles, T.P.; Dobson, C.M.; Galvagnion, C. beta-Synuclein suppresses both the initiation and amplification steps of alpha-synuclein aggregation via competitive binding to surfaces. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Singh, P.; Roy, S.; Bhat, R. Comparative Analysis of the Conformation, Aggregation, Interaction, and Fibril Morphologies of Human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-Synuclein Proteins. Biochemistry 2018, 57, 3830–3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.T.; Chen, A.Q.; Kong, Q.; Zhu, H.; Ma, C.M.; Qin, C. Inhibition of vesicular monoamine transporter-2 activity in alpha-synuclein stably transfected SH-SY5Y cells. Cell Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 28, 35–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotharius, J.; Brundin, P. Impaired dopamine storage resulting from alpha-synuclein mutations may contribute to the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2395–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, J.A.; Stokholm, K.; Zareba-Paslawska, J.; Jakobsen, S.; Vang, K.; Gjedde, A.; Landau, A.M.; Romero-Ramos, M. Early synaptic dysfunction induced by alpha-synuclein in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, S.; Fukae, J.; Mori, H.; Mizuno, Y.; Hattori, N. Positive immunoreactivity for vesicular monoamine transporter 2 in Lewy bodies and Lewy neurites in substantia nigra. Neurosci. Lett. 2006, 396, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, E.E.; Horgan, C.P.; Goud, B.; McCaffrey, M.W. The Rab family of proteins: 25 years on. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2012, 40, 1337–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shi, M.M.; Shi, C.H.; Xu, Y.M. Rab GTPases: The Key Players in the Molecular Pathway of Parkinson’s Disease. Front Cell Neurosci. 2017, 11, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalfo, E.; Gomez-Isla, T.; Rosa, J.L.; Nieto Bodelon, M.; Cuadrado Tejedor, M.; Barrachina, M.; Ambrosio, S.; Ferrer, I. Abnormal alpha-synuclein interactions with Rab proteins in alpha-synuclein A30P transgenic mice. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 63, 302–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, F.; Yang, W.; Florio, J.B.; Rockenstein, E.; Spencer, B.; Orain, X.M.; Dong, S.X.; Li, H.; Chen, X.; Sung, K.; et al. Synuclein impairs trafficking and signaling of BDNF in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gitler, A.D.; Bevis, B.J.; Shorter, J.; Strathearn, K.E.; Hamamichi, S.; Su, L.J.; Caldwell, K.A.; Caldwell, G.A.; Rochet, J.C.; McCaffery, J.M.; et al. The Parkinson’s disease protein alpha-synuclein disrupts cellular Rab homeostasis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 145–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goncalves, S.A.; Macedo, D.; Raquel, H.; Simoes, P.D.; Giorgini, F.; Ramalho, J.S.; Barral, D.C.; Ferreira Moita, L.; Outeiro, T.F. shRNA-Based Screen Identifies Endocytic Recycling Pathway Components That Act as Genetic Modifiers of Alpha-Synuclein Aggregation, Secretion and Toxicity. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dinter, E.; Saridaki, T.; Nippold, M.; Plum, S.; Diederichs, L.; Komnig, D.; Fensky, L.; May, C.; Marcus, K.; Voigt, A.; et al. Rab7 induces clearance of alpha-synuclein aggregates. J. Neurochem. 2016, 138, 758–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, H.; Kawamura, S.; Ozaki, K. An essential role of Rab5 in uniformity of synaptic vesicle size. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 3583–3590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, E.J.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, Y.H.; Michael, S.; Masliah, E.; Min, D.S.; Lee, S.J. Phospholipase D1 regulates autophagic flux and clearance of alpha-synuclein aggregates. Cell Death Differ. 2014, 21, 1132–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristupa, Z.B.; McConkey, F.; Liu, F.; Man, H.Y.; Lee, F.J.; Wang, Y.T.; Niznik, H.B. Protein kinase-mediated bidirectional trafficking and functional regulation of the human dopamine transporter. Synapse 1998, 30, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melikian, H.E.; Buckley, K.M. Membrane trafficking regulates the activity of the human dopamine transporter. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 7699–7710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorkina, T.; Hoover, B.R.; Zahniser, N.R.; Sorkin, A. Constitutive and protein kinase C-induced internalization of the dopamine transporter is mediated by a clathrin-dependent mechanism. Traffic 2005, 6, 157–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holton, K.L.; Loder, M.K.; Melikian, H.E. Nonclassical, distinct endocytic signals dictate constitutive and PKC-regulated neurotransmitter transporter internalization. Nat. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rao, A.; Simmons, D.; Sorkin, A. Differential subcellular distribution of endosomal compartments and the dopamine transporter in dopaminergic neurons. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2011, 46, 148–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gabriel, L.R.; Wu, S.; Kearney, P.; Bellve, K.D.; Standley, C.; Fogarty, K.E.; Melikian, H.E. Dopamine transporter endocytic trafficking in striatal dopaminergic neurons: Differential dependence on dynamin and the actin cytoskeleton. J. Neurosci. 2013, 33, 17836–17846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chadchankar, H.; Ihalainen, J.; Tanila, H.; Yavich, L. Decreased reuptake of dopamine in the dorsal striatum in the absence of alpha-synuclein. Brain Res. 2011, 1382, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellucci, A.; Collo, G.; Sarnico, I.; Battistin, L.; Missale, C.; Spano, P. Alpha-synuclein aggregation and cell death triggered by energy deprivation and dopamine overload are counteracted by D2/D3 receptor activation. J. Neurochem. 2008, 106, 560–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, B.; Saha, K.; Rana, T.; Becker, J.P.; Sambo, D.; Davari, P.; Goodwin, J.S.; Khoshbouei, H. Dopamine Transporter Activity Is Modulated by alpha-Synuclein. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 29542–29554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swant, J.; Goodwin, J.S.; North, A.; Ali, A.A.; Gamble-George, J.; Chirwa, S.; Khoshbouei, H. alpha-Synuclein stimulates a dopamine transporter-dependent chloride current and modulates the activity of the transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 43933–43943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, F.J.; Liu, F.; Pristupa, Z.B.; Niznik, H.B. Direct binding and functional coupling of alpha-synuclein to the dopamine transporters accelerate dopamine-induced apoptosis. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wersinger, C.; Prou, D.; Vernier, P.; Sidhu, A. Modulation of dopamine transporter function by alpha-synuclein is altered by impairment of cell adhesion and by induction of oxidative stress. FASEB J. 2003, 17, 2151–2153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisos, H.; Ben-Gedalya, T.; Sharon, R. The clathrin-dependent localization of dopamine transporter to surface membranes is affected by alpha-synuclein. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2014, 52, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perfeito, R.; Lazaro, D.F.; Outeiro, T.F.; Rego, A.C. Linking alpha-synuclein phosphorylation to reactive oxygen species formation and mitochondrial dysfunction in SH-SY5Y cells. Mol. Cell Neurosci. 2014, 62, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buddhala, C.; Loftin, S.K.; Kuley, B.M.; Cairns, N.J.; Campbell, M.C.; Perlmutter, J.S.; Kotzbauer, P.T. Dopaminergic, serotonergic, and noradrenergic deficits in Parkinson disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2015, 2, 949–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Del Tredici, K.; Braak, H. Dysfunction of the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system and related circuitry in Parkinson’s disease-related dementia. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2013, 84, 774–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wersinger, C.; Jeannotte, A.; Sidhu, A. Attenuation of the norepinephrine transporter activity and trafficking via interactions with alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 3141–3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wersinger, C.; Rusnak, M.; Sidhu, A. Modulation of the trafficking of the human serotonin transporter by human alpha-synuclein. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 55–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannotte, A.M.; McCarthy, J.G.; Redei, E.E.; Sidhu, A. Desipramine modulation of alpha-, gamma-synuclein, and the norepinephrine transporter in an animal model of depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 2009, 34, 987–998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeannotte, A.M.; Sidhu, A. Regulation of the norepinephrine transporter by alpha-synuclein-mediated interactions with microtubules. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2007, 26, 1509–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deusser, J.; Schmidt, S.; Ettle, B.; Plotz, S.; Huber, S.; Muller, C.P.; Masliah, E.; Winkler, J.; Kohl, Z. Serotonergic dysfunction in the A53T alpha-synuclein mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruden, M.A.; Davydova, T.V.; Narkevich, V.B.; Fomina, V.G.; Wang, C.; Kudrin, V.S.; Morozova-Roche, L.A.; Sewell, R.D. Noradrenergic and serotonergic neurochemistry arising from intranasal inoculation with alpha-synuclein aggregates which incite parkinsonian-like symptoms. Behav. Brain Res. 2015, 279, 191–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falsone, S.F. The yin and yang of amyloid aggregation. Future Sci. OA 2015, 1, FSO40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Kim, B.N.; Cho, S.C. The dopamine transporter gene and the impulsivity phenotype in attention deficit hyperactivity disorder: A case-control association study in a Korean sample. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2006, 40, 730–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bono, F.; Savoia, P.; Guglielmi, A.; Gennarelli, M.; Piovani, G.; Sigala, S.; Leo, D.; Espinoza, S.; Gainetdinov, R.R.; Devoto, P.; et al. Role of Dopamine D2/D3 Receptors in Development, Plasticity, and Neuroprotection in Human iPSC-Derived Midbrain Dopaminergic Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1054–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urrea, L.; Segura-Feliu, M.; Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Hervera, A.; Pedraz, L.; Garcia-Aznar, J.M.; Vila, M.; Samitier, J.; Torrents, E.; Ferrer, I.; et al. Involvement of Cellular Prion Protein in alpha-Synuclein Transport in Neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 1847–1860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrivastava, A.N.; Redeker, V.; Fritz, N.; Pieri, L.; Almeida, L.G.; Spolidoro, M.; Liebmann, T.; Bousset, L.; Renner, M.; Lena, C.; et al. alpha-synuclein assemblies sequester neuronal alpha3-Na+/K+-ATPase and impair Na+ gradient. EMBO J. 2015, 34, 2408–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, X.; Ou, M.T.; Karuppagounder, S.S.; Kam, T.I.; Yin, X.; Xiong, Y.; Ge, P.; Umanah, G.E.; Brahmachari, S.; Shin, J.H.; et al. Pathological alpha-synuclein transmission initiated by binding lymphocyte-activation gene 3. Science 2016, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Longhena, F.; Faustini, G.; Spillantini, M.G.; Bellucci, A. Living in Promiscuity: The Multiple Partners of Alpha-Synuclein at the Synapse in Physiology and Pathology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010141
Longhena F, Faustini G, Spillantini MG, Bellucci A. Living in Promiscuity: The Multiple Partners of Alpha-Synuclein at the Synapse in Physiology and Pathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(1):141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010141
Chicago/Turabian StyleLonghena, Francesca, Gaia Faustini, Maria Grazia Spillantini, and Arianna Bellucci. 2019. "Living in Promiscuity: The Multiple Partners of Alpha-Synuclein at the Synapse in Physiology and Pathology" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 1: 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010141
APA StyleLonghena, F., Faustini, G., Spillantini, M. G., & Bellucci, A. (2019). Living in Promiscuity: The Multiple Partners of Alpha-Synuclein at the Synapse in Physiology and Pathology. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(1), 141. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20010141