Repeats in S1 Proteins: Flexibility and Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
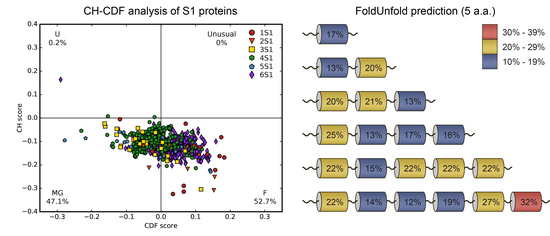
2.1. Analysis of Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder of the Bacterial S1 Proteins
2.2. Analysis of Intrinsic Flexibility and Disorder of the Bacterial S1 Proteins and Its Domains.
2.3. Flexibility of S1 Domain in the Bacterial Proteins
2.4. Analysis of the Ratio of Secondary Structures in the Bacterial S1 Proteins and Its Domains
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Construction of Ribosomal Proteins S1 Dataset
3.2. Number and Identification of Structural Domains in Protein Sequences
3.3. Prediction of Disordered Regions and Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder
3.3.1. FoldUnfold and IsUnstruct Programs
3.3.2. CH-CDF Analysis
3.4. Prediction of Secondary Structure
3.5. Analysis and Visualization
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| OB-fold | Oligonucleotide/oligosaccharide-binding fold |
| CH-plot | Charge–hydrophobicity plot |
| CDF | Cumulative distribution function |
| U | Unfolded |
| MG | Molten globule |
| F | Folded |
| SMART | Simple Modular Architecture Research Tool |
| ANK | Ankyrin |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
References
- Björklund, A.K.; Ekman, D.; Elofsson, A. Expansion of protein domain repeats. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, e114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jernigan, K.K.; Bordenstein, S.R. Tandem-repeat protein domains across the tree of life. PeerJ 2015, 3, e732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, M.A.; Petosa, C.; O’Donoghue, S.I.; Müller, C.W.; Bork, P. Comparison of ARM and HEAT protein repeats. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 309, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, M.A.; Perez-Iratxeta, C.; Ponting, C.P. Protein Repeats: Structures, Functions, and Evolution. J. Struct. Biol. 2001, 134, 117–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deryusheva, E.I.; Machulin, A.V.; Selivanova, O.M.; Galzitskaya, O. V Taxonomic distribution, repeats, and functions of the S1 domain-containing proteins as members of the OB-fold family. Proteins 2017, 85, 602–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machulin, A.; Deryusheva, E.; Selivanova, O.; Galzitskaya, O. Phylogenetic bacterial grouping by numbers of structural domains in the family of ribosomal proteins S1. Sci. Rep. under review.
- Arcus, V. OB-fold domains: A snapshot of the evolution of sequence, structure and function. Curr. Opin. Struct. Biol. 2002, 12, 794–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, J.; Agrawal, R.K.; Frank, J. Visualization of protein S1 within the 30S ribosomal subunit and its interaction with messenger RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 11991–11996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Salah, P.; Bisaglia, M.; Aliprandi, P.; Uzan, M.; Sizun, C.; Bontems, F. Probing the relationship between gram-negative and gram-positive S1 proteins by sequence analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 5578–5588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giraud, P.; Créchet, J.-B.; Uzan, M.; Bontems, F.; Sizun, C. Resonance assignment of the ribosome binding domain of E. coli ribosomal protein S1. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2015, 9, 107–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loveland, A.B.; Korostelev, A.A. Structural dynamics of protein S1 on the 70S ribosome visualized by ensemble cryo-EM. Methods 2018, 137, 55–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beckert, B.; Turk, M.; Czech, A.; Berninghausen, O.; Beckmann, R.; Ignatova, Z.; Plitzko, J.M.; Wilson, D.N. Structure of a hibernating 100S ribosome reveals an inactive conformation of the ribosomal protein S1. Nat. Microbiol. 2018, 3, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bycroft, M.; Hubbard, T.J.; Proctor, M.; Freund, S.M.; Murzin, A.G. The solution structure of the S1 RNA binding domain: a member of an ancient nucleic acid-binding fold. Cell 1997, 88, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert, M.; Edge, R.E.; Lario, P.; Cook, M.A.; Strynadka, N.C.J.; Mackie, G.A.; McIntosh, L.P. Structural characterization of the RNase E S1 domain and identification of its oligonucleotide-binding and dimerization interfaces. J. Mol. Biol. 2004, 341, 37–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beuth, B.; Pennell, S.; Arnvig, K.B.; Martin, S.R.; Taylor, I.A. Structure of a Mycobacterium tuberculosis NusA-RNA complex. EMBO J. 2005, 24, 3576–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battiste, J.L.; Pestova, T.V.; Hellen, C.U.; Wagner, G. The eIF1A solution structure reveals a large RNA-binding surface important for scanning function. Mol. Cell 2000, 5, 109–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giri, L.; Subramanian, A.R. Hydrodynamic properties of protein S1 from Escherichia coli ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1977, 81, 199–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Laughrea, M.; Moore, P.B. Physical properties of ribosomal protein S1 and its interaction with the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1977, 112, 399–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labischinski, H.; Subramanian, A.R. Protein S1 from Escherichia coli ribosomes: an improved isolation procedure and shape determination by small-angle X-ray scattering. Eur. J. Biochem. 1979, 95, 359–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillers, I.Y.; Moore, P.B. Position of protein S1 in the 30 S ribosomal subunit of Escherichia coli. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 153, 761–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorda, J.; Xue, B.; Uversky, V.N.; Kajava, A. V Protein tandem repeats - the more perfect, the less structured. FEBS J. 2010, 277, 2673–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.; Oldfield, C.; Meng, J.; Hsu, W.L.; Xue, B.; Uversky, V.N.; Romero, P.; Dunker, A.K. Subclassifying disordered proteins by the CH-CDF plot method. Pac. Symp. Biocomput. 2012, 128–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, H.; Jiang, W.; Inouye, M.; Heinemann, U. Crystal structure of CspA, the major cold shock protein of Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1994, 91, 5119–5123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heikinheimo, P.; Tuominen, V.; Ahonen, A.K.; Teplyakov, A.; Cooperman, B.S.; Baykov, A.A.; Lahti, R.; Goldman, A. Toward a quantum-mechanical description of metal-assisted phosphoryl transfer in pyrophosphatase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3121–3126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Delarbre, L.; Stevenson, C.E.; White, D.J.; Mitchenall, L.A.; Pau, R.N.; Lawson, D.M. Two crystal structures of the cytoplasmic molybdate-binding protein ModG suggest a novel cooperative binding mechanism and provide insights into ligand-binding specificity. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 308, 1063–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galzitskaya, O.V.; Garbuzynskiy, S.O.; Lobanov, M.Y. Prediction of amyloidogenic and disordered regions in protein chains. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2006, 2, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galzitskaya, O.V.; Garbuzynskiy, S.O.; Lobanov, M.Y. FoldUnfold: Web server for the prediction of disordered regions in protein chain. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 2948–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobanov, M.Y.; Galzitskaya, O.V. The Ising model for prediction of disordered residues from protein sequence alone. Phys. Biol. 2011, 8, 035004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deryusheva, E.; Machulin, A.; Nemashkalova, E.; Glyakina, A.; Galzitskaya, O. Search for functional flexible regions in the G-protein family: new reading of the FoldUnfold program. Protein Pept. Lett. 2018, 25, 589–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunker, A.K.; Lawson, J.D.; Brown, C.J.; Williams, R.M.; Romero, P.; Oh, J.S.; Oldfield, C.J.; Campen, A.M.; Ratliff, C.M.; Hipps, K.W.; et al. Intrinsically disordered proteins. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2001, 19, 26–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tompa, P.; Fersht, A. Structure and Function of Intrinsically Disordered Proteins; Chapman and Hall/CRC: New York, NY, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hierlmeier, T.; Merl, J.; Sauert, M.; Perez-Fernandez, J.; Schultz, P.; Bruckmann, A.; Hamperl, S.; Ohmayer, U.; Rachel, R.; Jacob, A.; et al. Rrp5p, Noc1p and Noc2p form a protein module which is part of early large ribosomal subunit precursors in S. cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 1191–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayas, R.M.; Maita, H.; Staley, J.P. Exon ligation is proofread by the DExD/H-box ATPase Prp22p. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2006, 13, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, M.S.; Gippert, G.P.; Soman, K.V.; Case, D.A.; Wright, P.E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science 1989, 245, 635–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, M.R.; Wojtowicz, W.M.; Andre, I.; Qian, B.; Wu, W.; Baker, D.; Eisenberg, D.; Zipursky, S.L. A double S shape provides the structural basis for the extraordinary binding specificity of Dscam isoforms. Cell 2008, 134, 1007–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkins, P.A.; Ho, Y.S.; Smith, W.W.; Janson, C.A.; D’Alessio, K.J.; McQueney, M.S.; Cummings, M.D.; Romanic, A.M. Structure of the C-terminally truncated human ProMMP9, a gelatin-binding matrix metalloproteinase. Acta Crystallogr. D Biol. Crystallogr. 2002, 58, 1182–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Amblar, M.; Barbas, A.; Gomez-Puertas, P.; Arraiano, C.M. The role of the S1 domain in exoribonucleolytic activity: substrate specificity and multimerization. Rna 2007, 13, 317–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boni, I.V.; Artamonova, V.S.; Dreyfus, M. The last RNA-binding repeat of the Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S1 is specifically involved in autogenous control. J. Bacteriol. 2000, 182, 5872–5879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lobanov, M.Y.; Sokolovskiy, I.V.; Galzitskaya, O.V. IsUnstruct: prediction of the residue status to be ordered or disordered in the protein chain by a method based on the Ising model. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2013, 31, 1034–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyte, J.; Doolittle, R.F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J. Mol. Biol. 1982, 157, 105–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xue, B.; Oldfield, C.J.; Dunker, A.K.; Uversky, V.N. CDF it all: Consensus prediction of intrinsically disordered proteins based on various cumulative distribution functions. FEBS Lett. 2009, 583, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pace, C.N.; Vajdos, F.; Fee, L.; Grimsley, G.; Gray, T. How to measure and predict the molar absorption coefficient of a protein. Protein Sci. 1995, 4, 2411–2423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drozdetskiy, A.; Cole, C.; Procter, J.; Barton, G.J. JPred4: a protein secondary structure prediction server. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, W389–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Number of Structural S1 Domains | FoldUnfold (11 aa) | FoldUnfold (5 aa) | IsUnstruct | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| % Disorder for Each Domain | Full Length Proteins | % Disorder for Each Domain | Full Length Proteins | % Disorder for Each Domain | Full Length Proteins | ||||
| 1S1 | 20 ± 3 | 25 ± 10 | 17 ± 11 | 22 ± 13 | 17 ± 11 | 24 ± 17 | |||
| 2S1 | 1 | 16 ± 1 | 20 ± 11 | 1 | 13 ± 6 | 20 ± 5 | 1 | 18 ± 5 | 19 ± 10 |
| 2 | 24 ± 10 | 2 | 20 ± 10 | 2 | 28 ± 11 | ||||
| 3S1 | 1 | 17 ± 1 | 15 ± 9 | 1 | 20 ± 6 | 26 ± 7 | 1 | 36 ± 13 | 26 ± 9 |
| 2 | 21 ± 7 | 2 | 21 ± 7 | 2 | 36 ± 16 | ||||
| 3 | 0 | 3 | 13 ± 6 | 3 | 20 ± 4 | ||||
| 4S1 | 1 | 21 ± 5 | 18 ± 5 | 1 | 25 ± 7 | 30 ± 4 | 1 | 24 ± 9 | 22 ± 5 |
| 2 | 18 ± 1 | 2 | 13 ± 5 | 2 | 24 ± 5 | ||||
| 3 | 21 ± 6 | 3 | 17 ± 8 | 3 | 28 ± 10 | ||||
| 4 | 18 ± 3 | 4 | 16 ± 7 | 4 | 23 ± 7 | ||||
| 5S1 | 1 | 21 ± 3 | 17 ± 13 | 1 | 22 ± 12 | 30 ± 11 | 1 | 28 ± 16 | 21 ± 15 |
| 2 | 21 ± 5 | 2 | 15 ± 8 | 2 | 23 ± 13 | ||||
| 3 | 20 ± 3 | 3 | 22 ± 12 | 3 | 28 ± 13 | ||||
| 4 | 24 ± 1 | 4 | 22 ± 8 | 4 | 35 ± 16 | ||||
| 5 | 18 ± 2 | 5 | 22 ± 5 | 5 | 28 ± 10 | ||||
| 6S1 | 1 | 24 ± 9 | 13 ± 4 | 1 | 22 ± 8 | 27 ± 3 | 1 | 27 ± 12 | 16 ± 4 |
| 2 | 18 ± 3 | 2 | 14 ± 8 | 2 | 22 ± 7 | ||||
| 3 | 18 ± 4 | 3 | 12 ± 6 | 3 | 21 ± 3 | ||||
| 4 | 19 ± 3 | 4 | 19 ± 6 | 4 | 24 ± 4 | ||||
| 5 | 20 ± 5 | 5 | 27 ± 7 | 5 | 25 ± 5 | ||||
| 6 | 22 ± 7 | 6 | 32 ± 9 | 6 | 45 ± 19 | ||||
| Protein Name | Source Organism | UniProt Code | Percent of Flexibility/Disorder | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FoldUnfold (11 aa) | FoldUnfold (5 aa) | IsUnstruct | |||
| S1 domain PNPase | E. coli | P05055 | 0 | 17 | 17 |
| Protein YhgF | E. coli | P46837 | 0 | 0 | 11 |
| Antitermination protein NusA | E. coli | P0AFF6 | 0 | 36 | 26 |
| Ribonuclease R | E. coli | P21499 | 13 | 6 | 27 |
| Ribonuclease E | E. coli | P21513 | 0 | 20 | 26 |
| Tex-like protein N-terminal domain protein | Kingella denitrificans | F0F1S0 | 0 | 0 | 13 |
| Number of Structural S1 Domains | JPred | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| % aa in the Regions Connecting Secondary Structures (Separate Domains) | % aa in the Regions Connecting Secondary Structures (Full Length Proteins) | % aa of the Linkers between Structural Domains (Full Length Proteins) | ||
| 1S1 | 41 ± 6 | 49 ± 7 | 45 ± 13 | |
| 2S1 | 1 | 50 ± 6 | 47 ± 3 | 33 ± 13 |
| 2 | 41 ± 4 | |||
| 3S1 | 1 | 48 ± 3 | 46 ± 4 | 38 ± 7 |
| 2 | 44 ± 10 | |||
| 3 | 43 ± 3 | |||
| 4S1 | 1 | 47 ± 2 | 51 ± 2 | 38 ± 7 |
| 2 | 47 ± 6 | |||
| 3 | 51 ± 4 | |||
| 4 | 44 ± 2 | |||
| 5S1 | 1 | 49 ± 3 | 53 ± 4 | 33 ± 8 |
| 2 | 51 ± 4 | |||
| 3 | 51 ± 5 | |||
| 4 | 48 ± 3 | |||
| 5 | 48 ± 6 | |||
| 6S1 | 1 | 47 ± 2 | 52 ± 2 | 27 ± 3 |
| 2 | 52 ± 5 | |||
| 3 | 49 ± 3 | |||
| 4 | 50 ± 4 | |||
| 5 | 51 ± 4 | |||
| 6 | 47 ± 3 | |||
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Machulin, A.; Deryusheva, E.; Lobanov, M.; Galzitskaya, O. Repeats in S1 Proteins: Flexibility and Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102377
Machulin A, Deryusheva E, Lobanov M, Galzitskaya O. Repeats in S1 Proteins: Flexibility and Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102377
Chicago/Turabian StyleMachulin, Andrey, Evgenia Deryusheva, Mikhail Lobanov, and Oxana Galzitskaya. 2019. "Repeats in S1 Proteins: Flexibility and Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102377
APA StyleMachulin, A., Deryusheva, E., Lobanov, M., & Galzitskaya, O. (2019). Repeats in S1 Proteins: Flexibility and Tendency for Intrinsic Disorder. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2377. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102377