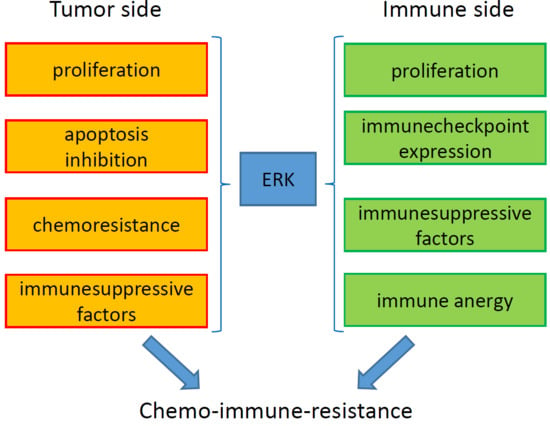
ERK is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. ERKs Favor an Aggressive Phenotype in Tumors in Response to Pleiotropic Intrinsic and Extrinsic Stimuli
3. ERKs Favor the Adaptation to Environmental Stresses
4. ERKs Mediate the Resistance to Chemotherapy
4.1. ERKs Enhance Survival and Prevent Apoptosis in Response to Chemotherapy
4.2. ERKs Mediate Chemoresistance Cooperating with Tumor Microenvironment Factors
4.3. ERKs Increase Expression and Activity of ABC Transporters
5. ERKs are Pleiotropic Modulators of Tumor Immune-Resistance and Immune-Escape
5.1. ERK Activity in Cancer Cell Modulates the Tumor Immune-Environment
5.2. ERK Activity in Tumor/Infiltrating Immune Cells
6. ERK-Driven Circuitries Determining Chemoresistance and Immune-Resistance
7. Conclusions and Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ERK | extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| JNK | c-Jun amino-terminal kinase |
| MAPK | mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| TKR | tyrosine kinase receptors |
| RAS | rat sarcoma 2 viral oncogene homolog |
| RAF | rapidly accelerated fibrosarcoma |
| MEK | MAPK/ERK kinase |
| CD120 | cluster of differentiation 120 |
| Syk | spleen tyrosine kinase |
| SRC-1 | steroid receptor coactivator-1 |
| Pax6 | paired box protein 6 |
| NFAT | nuclear factor of activated T-cells |
| Elk-1 | ETS domain-containing protein-1 |
| MEF2 | myocyte enhancer factor-2 |
| AP1 | activator protein-1 (c-jun and c-fos) |
| c-myc | avian myelocytomatosis virus oncogene cellular homolog |
| STAT | signal transducer and activator of transcription-3 |
| RSK | ribosomal S6 kinase |
| MSK | mitogen-and stress-activated kinase |
| DNMT3B | DNA (cytosine -5-)-methyltransferase 3β |
| CDK | cyclin-dependent kinases |
| eIF2B | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2β |
| GSK3β | glycogen synthase kinase 3-β |
| CREBP | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| SRF | serum response factor |
| NF-kB | nuclear factor-kB |
| HMG14 | high mobility group-14 |
| TCGA | Tissue Cancer Genome Atlas |
| UTR | untranslated region |
| EGFR | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| Her2 | receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 |
| PDGFR | platelet-derived growth factor receptor |
| IGF1-R | insulin-like growth factor 1 |
| VEGFR | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| Flt3 | fms-like tyrosine kinase 3 |
| Lgr | leucine-rich repeat-containing G-protein coupled receptor |
| WNT | wingless/integrated |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| FAK | focal adhesion kinase |
| RAP1 | Ras proximate 1 |
| GRB2 | growth factor receptor-bound protein 2 |
| EMT | epithelial-mesenchymal transition |
| MyD88 | myeloid differentiation factor 88 |
| IRAK | IL-1 receptor–associated kinase |
| IL | interleukin |
| ACP | actin capping protein |
| PI3K | phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| AKT | protein kinase B |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| Bax | Bcl-2-like protein 4 |
| PARP | poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| AMPK | AMP-activated protein kinase |
| mTOR | mammalian target of rapamycin |
| p70S6K | ribosomal protein S6 kinase |
| Smad | small mother against decapentaplegic |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| KIF15 | kinesin family member 15 |
| GAP | GTPase activating protein |
| NF1 | Neurofibtomin 1 |
| RASA1 | RAS P21 Protein Activator |
| DUSP | Dual Specificity Phosphatase |
| KSR1 | kinase suppressor of Ras-1 |
| ER | endoplasmic reticulum |
| DJ-1 | deglycase protein DJ-1 |
| SOD1 | superoxide dismutase 1 |
| COX2 | cyclooxygenase 2 |
| CBLB | casitas B-lineage lymphoma proto-oncogene-b |
| MKK | effectors mitogen activated kinase kinase |
| eIF4E | eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E |
| BMP4 | bone-morphogenetic protein 4 |
| tmTNF-α | transmembrane tumor necrosis factor-α |
| RIP3 | receptor-interacting protein 3 |
| CDC37 | cells division cycle 37 homolog |
| HSP90 | heat shock protein 90 |
| FOXO1 | O-class forkhead factor |
| IQGAP | Ras GTPase-activating-like protein |
| FGFR4 | fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 |
| HK2 | hexokinase 2 |
| Drp1 | dynamin-related protein 1 |
| Ell3 | RNA polymerase II elongation factor |
| NID1 | nidogen 1 |
| CTGF | connective tissue growth factor |
| CXCR | C-X-C chemokine receptor |
| hERG1 | human ether-‘a-go-go related gene 1 |
| JAK2 | Janus kinase 2 |
| LPP | lipoma-preferred partner |
| IGFBP2 | insulin-like growth factor binding protein-2 |
| TGF-β | transforming growth factor-β |
| IL-6R | interleukin 6 receptor |
| GP130 | glycoprotein 130 |
| Bad | Bcl-2-associated death promoter |
| HMGB1 | high mobility group box 1 protein |
| DAMP | danger-associate molecule pattern |
| RAGE | receptor for advanced glycation end product |
| ABC | ATP binding cassette |
| Pgp | P-glycoprotein |
| MRP | multidrug resistance related protein |
| BCRP | breast cancer resistance protein |
| HIF-1α | hypoxia-inducible factor-1α |
| GPR55 | G protein-coupled receptor 55 |
| G-CSF | granulocytic-colony stimulating factor |
| Sorcin | soluble resistance-related calcium binding protein |
| ABCB5 | ATP binding cassette subfamily B member 5 |
| TKI | tyrosine kinase inhibitor |
| DC | dendritc cells |
| TAM | tumor-associated macrophage |
| TIL | T-infiltrating lymphocyte |
| NK | natural killer |
| MHC | major hystocompability complex |
| ICP | immune checkpoint |
| Treg | T-regulatory cell |
| MDSC | myeloid-derived suppressor cell |
| PD-1L | programmed death-1 ligand |
| IDO | indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase |
| CXCL | chemokine ligand |
| LAG-3 | lymphocyte-activation gene 3 |
| EML4 | echinoderm microtubule associated protein-like 4 |
| ALK | anaplastic lymphoma kinase |
| NKG2D | NK group 2 member D |
| CTLA-4 | cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte antigen 4 |
| TIM3 | T-cell immunoglobulin mucin 3 |
| TCR | T-cell receptor |
| DGK-α | diacylglycerol kinase-α |
| HBsAg | hepatitis B surface antigen |
| AIMP1 | aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multifunctional protein 1 |
| PKC | protein kinase C |
| Th17 | T-helper 17 |
| FPPS | farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase |
| CSF-1R | colony stimulating factor-1 receptor |
References
- Roux, P.P.; Blenis, J. ERK and p38 MAPK-activated protein kinases: A family of protein kinases with diverse biological functions. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2004, 68, 32–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscà, R.; Pouysségur, J.; Lenormand, P. ERK1 and ERK2 Map Kinases: Specific Roles or Functional Redundancy? Front. Cell. Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, e53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, S.; Seger, S. The extracellular signal-regulated kinase: Multiple substrates regulate diverse cellular functions. Growth Factors. 2006, 24, 21–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. ERK1/2 MAP kinases: Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol. Res. 2012, 66, 105–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Megiorni, F.; Camero, S.; Ceccarelli, S.; McDowell, H.P.; Mannarino, O.; Marampon, F.; Pizer, B.; Shukla, R.; Pizzuti, A.; Marchese, C.; et al. DNMT3B in vitro knocking-down is able to reverse embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma cell phenotype through inhibition of proliferation and induction of myogenic differentiation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 79342–79356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Narbonne, P.; Maddox, P.S.; Labbé, J.-C. DAF-18/PTEN signals through AAK-1/AMPK to inhibit MPK-1/MAPK in feedback control of germline stem cell proliferation. PLoS Genet. 2017, 13, e1006738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steelman, L.S.; Chappell, W.H.; Abrams, S.L.; Kempf, R.C.; Long, J.; Laidler, P.; Mijatovic, S.; Maksimovic-Ivanic, D.; Stivala, F.; Mazzarino, M.C.; et al. Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging (Albany NY) 2011, 3, 192–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, Y.; Fu, X.; Ran, Q.; Yang, K.; Wen, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, F. Globularifolin exerts anticancer effects on glioma U87 cells through inhibition of Akt/mTOR and MEK/ERK signaling pathways in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Biochimie 2017, 142, 144–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, S.S.; Máximo, V.; Coelho, R.; Batista, R.; Soares, P.; Guerreiro, S.G.; Sobrinho-Simões, M.; Monteiro, M.P.; Pignatelli, D. Telomerase and N-Cadherin Differential Importance in Adrenocortical Cancers and Adenomas. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2064–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Su, X.; Fang, J.; Xin, X.; Zhao, X.; Gaur, U.; Wen, Q.; Xu, J.; Little, P.J.; Zheng, W. Tanshinone IIA Attenuates Insulin Like Growth Factor 1-Induced Cell Proliferation in PC12 Cells through the PI3K/Akt and MEK/ERK Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjum, R.; Blenis, J. The RSK family of kinases: Emerging roles in cellular signalling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 747–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomson, S.A.; Clayton, L.; Hazzalin, C.A.; Rose, S.; Barratt, M.J.; Mahadevan, L.C. The nucleosomal response associated with immediate early gene induction is mediated via alternative MAP kinase cascades: MSK1 as a potential histone H3/HMG-14 kinase. EMBO J. 1999, 18, 4779–4793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deak, M.; Clifton, A.D.; Lucocq, L.M.; Alessi, D.R. Mitogen- and stress-activated protein kinase-1 (MSK1) is directly activated by MAPK and SAPK2/p38, and may mediate activation of CREB. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 4426–4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetz, C. The unfolded protein response: Controlling cell fate decisions under ER stress and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2012, 13, 89–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chevet, E.; Hetz, C.; Samali, A. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-activated cell reprogramming in oncogenesis. Cancer Discov. 2015, 5, 586–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Z.; Cui, M.; Tian, J. Chemoresistance and targeting of growth factors/cytokines signalling pathways: Towards the development of effectivetherapeutic strategy for endometrial cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2018, 8, 1317–1331. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Jiang, X.; Yang, Z. NRAGE confers poor prognosis and promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance in gastric cancer. Gene 2018, 668, 114–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tian, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Z.; Ji, Z. Down-regulating IL-6/GP130 targets improved the anti-tumor effects of 5-fluorouracil in colon cancer. Apoptosis 2018, 23, 356–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Si, W.; Shen, J.; Du, C.; Lou, W.; Bao, C.; Zheng, H.; Pan, J.; Zhong, G.; Xu, L.; et al. miR-27b-3p inhibits proliferation and potentially reverses multi-chemoresistance by targeting CBLB/GRB2 in breast cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zha, J.; Lei, M. Inhibiting ERK/Mnk/eIF4E broadly sensitizes ovarian cancer response to chemotherapy. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2018, 20, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, J.; Zeng, S.; Zhang, Y.; Deng, G.; Qu, Y.; Guo, C.; Yin, L.; Han, Y.; Cai, C.; Li, Y.; et al. BMP4 promotes oxaliplatin resistance by an induction of epithelial-mesenchymal transition via MEK1/ERK/ELK1 signaling in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 411, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhai, L.; Ma, S.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, L.; Li, N.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, T.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, H.; et al. Down-regulation of RIP3 potentiates cisplatin chemoresistance by triggering HSP90-ERK pathway mediated DNA repair in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2018, 418, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.W.; Jin, X.; Zhao, Y.; Pan, Y.; Yang, J.; Karnes, R.J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, H. AKT-phosphorylated FOXO1 suppresses ERK activation and chemoresistance by disrupting IQGAP1-MAPK interaction. EMBO J. 2017, 36, 995–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.J.; Wu, D.W.; Wang, Y.C.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. PAK1 confers chemoresistance and poor outcome in non-small cell lung cancer via β-catenin-mediated stemness. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Wang, S.; Zhao, W.; Duan, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, H.; Tian, Y.; Wang, D.; Zhao, J.; An, T.; et al. Mechanistic Exploration of Cancer Stem Cell Marker Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channel α2δ1 Subunit-mediated Chemotherapy Resistance in Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 2148–2158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, G.; Deng, S.; Guo, W.; Yu, L.; Yang, J.; Zhou, S.; Gao, T. Notch pathway inhibition using DAPT, a γ-secretase inhibitor (GSI), enhances the antitumor effect of cisplatin in resistant osteosarcoma. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 3–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borriello, L.; Nakata, R.; Sheard, M.A.; Fernandez, G.E.; Sposto, R.; Malvar, J.; Blavier, L.; Shimada, H.; Asgharzadeh, S.; Seeger, R.C.; et al. Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Share Characteristics and Protumorigenic Activity with Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 5142–5157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Han, S.; Li, Z.; Master, L.M.; Master, Z.W.; Wu, A. Exogenous IGFBP-2 promotes proliferation, invasion, and chemoresistance to temozolomide in glioma cells via the integrin β1-ERK pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2014, 111, 1400–1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Wang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wu, H.; Xia, T.; Xiao, J.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, Y.; et al. ERK/Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission is involved in the MSC-induced drug resistance of T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia cells. Cell Death Dis. 2016, 7, e2459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zdanov, S.; Mandapathil, M.; Abu Eid, R.; Adamson-Fadeyi, S.; Wilson, W.; Qian, J.; Carnie, A.; Tarasova, N.; Mkrtichyan, M.; Berzofsky, J.A.; Whiteside, T.L.; et al. Mutant KRAS Conversion of Conventional T Cells into Regulatory T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 354–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopecka, J.; Porto, S.; Lusa, S.; Gazzano, E.; Salzano, G.; Pinzòn-Daza, M.L.; Giordano, A.; Desiderio, V.; Ghigo, D.; De Rosa, G.; et al. Zoledronic acid-encapsulating self-assembling nanoparticles and doxorubicin: A combinatorial approach to overcome simultaneously chemoresistance and immunoresistance in breast tumors. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20753–20772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Zhao, Y.; Fang, J.; Cui, R.; Xiao, Y.; Xu, Q. SHP2 negatively regulates HLA-ABC and PD-L1 expression via STAT1 phosphorylation in prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 53518–53530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, V.; Lim, T.S.; Lee, J.; Steinberg, J.; Szmyd, R.; Tham, M.; Yaligar, J.; Kaldis, P.; Abastado, J.P.; Chew, V. TLR3 agonist and Sorafenib combinatorial therapy promotes immune activation and controls hepatocellular carcinoma progression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27252–27266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Lin, Z.; Peng, P.; Wang, J.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Huang, J.; Liu, L.; Sheng, J.; et al. KRAS mutation-induced upregulation of PD-L1 mediates immune escape in human lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2017, 66, 1175–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Salaroglio, I.C.; Campia, I.; Kopecka, J.; Gazzano, E.; Orecchia, S.; Ghigo, D.; Riganti, C. Zoledronic acid overcomes chemoresistance and immunosuppression of malignant mesothelioma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 1128–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.N.; Zhang, J.Y.; Xu, H.M. The roles of serum CXCL16 in circulating Tregs and gastrointestinal stromal tumor cells. Onco Targets Ther. 2016, 9, 3939–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, B.; Shi, X.; Zhang, J.; Qin, J.; Zhang, N.; Ren, H.; Qian, M.; Siwko, S.; Carmon, K.; Liu, Q.; et al. Inhibition of Rspo-Lgr4 Facilitates Checkpoint Blockade Therapy by Switching Macrophage Polarization. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4929–4942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiu, X.Y.; Hu, D.X.; Chen, W.Q.; Chen, R.Q.; Qian, S.R.; Li, C.Y.; Li, Y.J.; Xiong, X.X.; Liu, D.; Pan, F.; et al. PD-L1 confers glioblastoma multiforme malignancy via Ras binding and Ras/Erk/EMT activation. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1754–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, G.A.; Der, C.J.; Rossman, K.L. RAS isoforms and mutations in cancer at a glance. J. Cell. Sci. 2016, 129, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jetschke, K.; Viehweger, H.; Freesmeyer, M.; Warnke, J.P.; Mawrin, C. Primary pineal malignant melanoma with B-RafV600E mutation: A case report and brief review of the literature. Acta Neurochir. (Wien) 2015, 157, 1267–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikshit, A.; Jin, Y.J.; Degan, S.; Hwang, J.; Foster, M.W.; Li, C.Y.; Zhang, J.Y. UBE2N Promotes Melanoma Growth via MEK/FRA1/SOX10 Signaling. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 6462–6472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Caunt, C.J.; Sale, M.J.; Smith, P.D.; Cook, S.J. MEK1 and MEK 2inhibitors and cancertherapy: The long and winding road. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2015, 15, 577–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estep, A.L.; Palmer, C.; McCormick, F.; Rauen, K.A. Mutationanalysisof BRAF, MEK1 and MEK2 in 15 ovarian cancer cel llines: Implications for therapy. PLoS ONE 2007, 2, e1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, J.P.; VanBrocklin, M.W.; Lastwika, K.J.; McKinney, A.J.; Brandner, S.; Holmen, S.L. Activated MEK cooperates with Ink4a/Arf loss or Akt activation to induce gliomas in vivo. Oncogene 2011, 30, 1341–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bugaj, L.J.; Sabnis, A.J.; Mitchell, A.; Garbarino, J.E.; Toettcher, J.E.; Bivona, T.G.; Lim, W.A. Cancer mutations and targeted drugs can disrupt dynamic signal encoding by the Ras-Erk pathway. Science 2018, 361, eaao3048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, G.C.; Chockalingam, S.; Melegh, Z.; Greenhough, A.; Malik, S.; Szemes, M.; Park, J.H.; Kaidi, A.; Zhou, L.; Catchpoole, D.; et al. LGR5 regulates pro-survival MEK/ERK and proliferative Wnt/β-catenin signalling in neuroblastoma. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 40053–40067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seguin, L.; Desgrosellier, J.S.; Weis, S.M.; Cheresh, D.A. Integrins and cancer: Regulators of cancer stemness, metastasis, and drug resistance. Trends Cell Biol. 2015, 25, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Weinberg, R.A. Integrin beta1-focal adhesion kinase signaling directs the proliferation of metastatic cancer cells disseminated in the lungs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 10290–10295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T.; Brooks, M.W.; Inan, M.F.; Reinhardt, F.; Weinberg, R.A. The outgrowth of micrometastases is enabled by the formation of filopodium-like protrusions. Cancer Discov. 2012, 2, 706–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, W.; Chen, C.; Dong, M.; Wang, G.; Zhou, J.; Song, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ding, S. Calreticulin promotes EGF-induced EMT in pancreatic cancer cells via Integrin/EGFR-ERK/MAPK signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Delcorde, J.; Tang, T.; Downey, G.P.; McCulloch, C.A. Regulation of IL-1 signaling through control of focal adhesion assembly. FASEB J. 2018, 32, 3119–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, X.; Barbour, M.; Hou, K.; Gao, C.; Cao, S.; Zheng, J.; Zhao, Y.; Mu, R.; Jiang, H.R. Interleukin-33 predicts poor prognosis and promotes ovarian cancer cell growth and metastasis through regulating ERK and JNK signaling pathways. Mol Oncol. 2016, 10, 113–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, S.; Chen, X.; Lin, H.J.; Lin, J. Inhibition of interleukin 8/C-X-C chemokine receptor 1,/2 signaling reduces malignant features in human pancreatic cancer cells. Int. J. Oncol. 2018, 53, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, L.; Li, F.; Shao, M.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, X.; Luan, H.; Qi, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liang, L.; et al. IL-8 is up-regulated in cervical cancer tissues and is associated with the proliferation and migration of HeLa cervical cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2018, 15, 1350–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franzè, E.; Dinallo, V.; Rizzo, A.; Di Giovangiulio, M.; Bevivino, G.; Stolfi, C.; Caprioli, F.; Colantoni, A.; Ortenzi, A.; Grazia, A.D.; et al. Interleukin-34 sustains pro-tumorigenic signals in colon cancer tissue. Oncotarget 2017, 9, 3432–3445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, J.; Wang, G.Y.; Arima, K.; Guan, S.P.; Waters, M.R.; Cavenee, W.K.; Pan, E.; Aliwarga, E.; Chong, S.T.; Kok, C.Y.L.; et al. Interleukin-13 receptor alpha 2 cooperates with EGFRvIII signaling to promote glioblastoma multiforme. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, e1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.L.; Chen, X.; Wu, T.; Zhang, X.W.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Ji, Z.Z. Knockdown of TMPRSS3 inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation, invasion and EMT via regulation of the ERK1/2 and PI3K/Akt pathways. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2018, 107, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; He, C.Y.; Hu, L.; Shi, H.P.; Li, J.F.; Gu, Q.L.; Su, L.P.; Liu, B.Y.; Li, C.; Zhu, Z. Long noncoding RNA UCA1 promotes tumour metastasis by inducing GRK2 degradation in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett. 2017, 408, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Tang, S.; Guo, X.; Yang, C.; Jia, K. CT45A1 siRNA silencing suppresses the proliferation, metastasis and invasion of lung cancer cells by downregulating the ERK/CREB signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 16, 6708–6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ma, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, L. SPARCL1 suppresses the proliferation and migration of human ovarian cancer cells via the MEK/ERK signaling. Exp. Ther. Med. 2018, 16, 3195–3201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, P.; Su, C.; Luo, X.; Zeng, H.; Zhao, L.; Wei, L.; Zhang, X.; Varghese, Z.; Moorhead, J.F.; Chen, Y.; et al. Dietary oleic acid-induced CD36 promotes cervical cancer cell growth and metastasis via up-regulation Src/ERK pathway. Cancer Lett. 2018, 438, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, X.; Cao, H.; Zhan, L.; Yin, C.; Wang, G.; Liang, P.; Li, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, B.; Huang, Q.; et al. Mitochondrial fission promotes cell migration by Ca(2+)/CaMKII/ERK/FAK pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2018, 38, 1263–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.; Tang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Xing, Z.; Guo, Z.; Wang, W.; Xu, Z.; Liu, Z. Nitidine chloride induces apoptosis and inhibits tumor cell proliferation via suppressing ERK signaling pathway in renal cancer. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 66, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Ren, L.; Liu, C.; Xia, T.; Zha, X.; Wang, S. Phenformin Induces Cell Cycle Change, Apoptosis, and Mesenchymal-Epithelial Transition and Regulates the AMPK/mTOR/p70s6k and MAPK/ERK Pathways in Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, N.; Guo, Z.; Zhao, G.; Jia, G.; Luo, B.; Shen, X.; Bai, Y. Inhibition of microRNA-21-3p suppresses proliferation as well as invasion and induces apoptosis by targeting RNA-binding protein with multiple splicing through Smad4/extra cellular signal-regulated protein kinase signalling pathway in human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2018, 45, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liu, L.; Sun, S.; Zhang, L.; Ye, B.; et al. MICAL1 facilitates breast cancer cell proliferation via ROS-sensitive ERK/cyclin D pathway. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2018, 22, 3108–3118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierro, C.; Zhang, X.; Kankeu, C.; Trebak, M.; Bootman, M.D.; Roderick, H.L. Oncogenic KRAS suppresses store-operated Ca(2+) entry and I(CRAC) through ERK pathway-dependent remodelling of STIM expression in colorectal cancer cell lines. Cell Calcium. 2018, 72, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Xie, C.; Jiang, J. KIF15 promotes pancreatic cancer proliferation via the MEK-ERK signalling pathway. Br. J. Cancer 2017, 117, 245–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennig, A.; Markwart, R.; Esparza-Franco, M.A.; Ladds, G.; Rubio, I. Ras activation revisited: Role of GEF and GAP systems. Biol. Chem. 2015, 396, 831–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eroglu, Z.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Hu-Lieskovan, S.; Kim, D.W.; Algazi, A.; Johnson, D.B.; Liniker, E.; Ben, K.; Munhoz, R.; Rapisuwon, S.; et al. High response rate to PD-1 blockade in desmoplastic melanomas. Nature 2018, 553, 347–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haworth, K.B.; Arnold, M.A.; Pierson, C.R.; Choi, K.; Yeager, N.D.; Ratner, N.; Roberts, R.D.; Finlay, J.L.; Cripe, T.P. Immune profiling of NF1-associated tumors reveals histologic subtype distinctions and heterogeneity: Implications for immunotherapy. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 82037–82048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T.; Desmeules, P.; Smith, R.S.; Drilon, A.; Somwar, R.; Ladanyi, M. RASA1 and NF1 are Preferentially Co-Mutated and Define A Distinct Genetic Subset of Smoking-Associated Non-Small Cell Lung Carcinomas Sensitive to MEK Inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 1436–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kidger, A.M.; Keyse, S.M. The regulation of oncogenic Ras/ERK signalling by dual-specificity mitogen activated protein kinase phosphatases (MKPs). Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 50, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rushworth, L.K.; Kidger, A.M.; Delavaine, L.; Stewart, G.; van Schelven, S.; Davidson, J.; Bryant, C.J.; Caddye, E.; East, P.; Caunt, C.J.; et al. Dual-specificity phosphatase 5 regulates nuclear ERK activityand suppresses skin cancer by inhibiting mutant Harvey-Ras(HRasQ61L)-driven SerpinB2 expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 18267–18272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, T.; Sunamura, M.; Motoi, F.; Matsuno, S.; Horii, A. Potential tumorsuppressive pathway involving DUSP6/MKP-3 in pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Pathol. 2003, 162, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okudela, K.; Yazawa, T.; Woo, T.; Sakaeda, M.; Ishii, J.; Mitsui, H.; Shimoyamada, H.; Sato, H.; Tajiri, M.; Ogawa, N.; et al. Down-regulation of DUSP6 expression in lung cancer: Its mechanism and potential role in carcinogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 867–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shojaee, S.; Caeser, R.; Buchner, M.; Park, E.; Swaminathan, S.; Hurtz, C.; Geng, H.; Chan, L.N.; Klemm, L.; Hofmann, W.K.; et al. Erk Negative Feedback Control Enables Pre-B Cell Transformation and Represents a Therapeutic Target in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell. 2015, 28, 114–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stevens, P.D.; Wen, Y.A.; Xiong, X.; Zaytseva, Y.Y.; Li, A.T.; Wang, C.; Stevens, A.T.; Farmer, T.N.; Gan, T.; Weiss, H.L.; et al. Erbin Suppresses KSR1-Mediated RAS/RAF Signaling and Tumorigenesis in Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4839–4852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, F.; Yang, X.; Geng, M.; Huang, M. Targeting ERK, an Achilles’ Heel of the MAPK pathway, in cancer therapy. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 552–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Rezov, V.; Joensuu, E.; Vartiainen, V.; Rönty, M.; Yin, M.; Myllärniemi, M.; Koli, K. Pirfenidone decreases mesothelioma cell proliferation and migration via inhibition of ERK and AKT and regulates mesothelioma tumor microenvironment in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, e10070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauer, S.J.; Tarpley, M.; Shah, I.; Save, A.V.; Lyerly, H.K.; Patierno, S.R.; Williams, K.P.; Devi, G.R. Bisphenol A activates EGFR and ERK promoting proliferation, tumor spheroid formation and resistance to EGFR pathway inhibition in estrogen receptor-negative inflammatory breast cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 252–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Wang, Y.; Duan, F.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Luo, L.; Liu, L.; Leung, E.L.H.; Yao, X. Krukovine Suppresses KRAS-Mutated Lung Cancer Cell Growth and Proliferation by Inhibiting the RAF-ERK Pathway and Inactivating AKT Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, e958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, M.; Zhao, L.M.; Yang, X.X.; Shan, Y.N.; Cui, W.X.; Chen, L.; Shan, B.E. p-Hydroxylcinnamaldehyde induces the differentiation of oesophageal carcinoma cells via the cAMP-RhoA-MAPK signalling pathway. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, e31315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herz, C.; Tran, H.T.T.; Schlotz, N.; Michels, K.; Lamy, E. Low-dose levels of bisphenol A inhibit telomerase via ER/GPR30-ERK signalling, impair DNA integrity and reduce cell proliferation in primary PBMC. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, e16631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Ferry, C.H.; Blazanin, N.; Bility, M.T.; Khozoie, C.; Kang, B.H.; Glick, A.B.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Peters, J.M. PPARβ/δ promotes HRAS-induced senescence and tumor suppression by potentiating p-ERK and repressing p-AKT signaling. Oncogene 2014, 33, 5348–5359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, J.; Wang, Z.; Ma, L.; Peng, B.; Mao, K.; Li, C.; Su, M.; Zhou, C.; Peng, G. Baicalein and baicalin inhibit colon cancer using two distinct fashions of apoptosis and senescence. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 20089–20102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kochetkova, E.Y.; Blinova, G.I.; Bystrova, O.A.; Martynova, M.G.; Pospelov, V.A.; Pospelova, T.V. Targeted elimination of senescent Ras-transformed cells by suppression of MEK/ERK pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 2017, 9, 2352–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, R.; Piao, M.J.; Oh, M.C.; Park, J.E.; Shilnikova, K.; Moon, Y.J.; Kim, D.H.; Jung, U.; Kim, I.G.; Hyun, J.W. Protective Effect of an Isoflavone, Tectorigenin, Against Oxidative Stress-induced Cell Death via Catalase Activation. J. Cancer Prev. 2016, 21, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oh, S.E.; Mouradian, M.M. Cytoprotective mechanisms of DJ-1 against oxidative stress through modulating ERK1/2 and ASK1 signal transduction. Redox Biol. 2018, 14, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Lou, S.; Ying, M.; Yang, B. DJ-1 as a human oncogene and potential therapeutic target. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handly, L.N.; Pilko, A.; Wollman, R. Paracrine communication maximizes cellular response fidelity in wound signaling. Elife 2015, 4, e09652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsythe, N.; Refaat, A.; Javadi, A.; Khawaja, H.; Weir, J.A.; Emam, H.; Allen, W.L.; Burkamp, F.; Popovici, V.; Jithesh, P.V.; et al. The Unfolded Protein Response: A Novel Therapeutic Target for Poor Prognostic BRAF Mutant Colorectal Cancer. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2018, 17, 1280–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, H.; Craig, M.J.; Ying, C.; Varsos, Z.S.; Czarnieski, P.; Alva, A.S.; Hernandez, J.; Fuller, D.; Daignault, S.; Healy, P.N.; Pienta, K.J. IL-4 induces proliferation in prostate cancer PC3 cells under nutrient-depletion stress through the activation of the JNK-pathway and survivin up-regulation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2012, 113, 1569–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casado, P.; Bilanges, B.; Rajeeve, V.; Vanhaesebroeck, B.; Cutillas, P.R. Environmental stress affects the activity of metabolic and growth factor signaling networks and induces autophagy markers in MCF7 breast cancer cells. Mol. Cell. Proteomics 2014, 13, 836–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Xu, A.; Zhou, H.; Wu, L.; Randers-Pehrson, G.; Santella, R.M.; Yu, Z.; Hei, T.K. Mechanism of genotoxicity induced by targeted cytoplasmic irradiation. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Hu, W.; Liu, T.; Rana, U.; Aguilera-Barrantes, I.; Kong, A.; Kumar, S.N.; Wang, B.; Gao, P.; Wang, X.; et al. Nogo-B receptor increases the resistance of estrogen receptor positive breast cancer to paclitaxel. Cancer Lett. 2018, 419, 233–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhou, W.; Tang, K.; Chen, X.; Feng, Z.; Chen, J. Silencing Aurora A leads to re-sensitization of breast cancer cells to Taxol through downregulation of SRC-mediated ERK and mTOR pathways. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 2011–2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.Y.; Kuo, K.K.; Kuo, T.L.; Lee, K.T.; Cheng, K.H. The activation of MEK/ERK signaling pathway by bone morphogenetic protein 4 to increase hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation and migration. Mol. Cancer Res. 2012, 10, 415–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.X.; Ju, H.Q.; Wang, F.; Chen, L.Z.; Wu, Q.N.; Sheng, H.; Mo, H.Y.; Pan, Z.Z.; Xie, D.; Kang, T.B.; et al. Inhibition of the NF-kB pathway by nafamostat mesilate suppresses colorectal cancer growth and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 2016, 380, 87–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Lin, G.; Yan, Y.; Li, X.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yin, B.; Wu, Y.; Li, Z.; Yang, X.P. Transmembrane TNF-alpha promotes chemoresistance in breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2018, 37, 3456–3470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Chen, S.; Yang, W.; Cheng, X.; Ye, Y.; Mao, J.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Ji, J. FGFR4 Links Glucose Metabolism and Chemotherapy Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 47, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Zhang, M.; Cong, Q.; Zhang, M.X.; Zhang, M.Y.; Lu, Y.Y.; Xu, C.J. Hexokinase 2 confers resistance to cisplatin in ovarian cancer cells by enhancing cisplatin-induced autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 95, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.Y.; Chiang, S.F.; Chen, W.T.; Ke, T.W.; Chen, T.W.; You, Y.S.; Lin, C.Y.; Chao, K.S.C.; Huang, C.Y. HMGB1 promotes ERK-mediated mitochondrial Drp1 phosphorylation for chemoresistance through RAGE in colorectal cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Chu, H.; Yang, X.; Meng, Y.; Shi, P.; Gou, S. Metformin Increases Sensitivity of Pancreatic Cancer Cells to Gemcitabine by Reducing CD133+ Cell Populations and Suppressing ERK/P70S6K Signaling. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 14404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tung, S.L.; Huang, W.C.; Hsu, F.C.; Yang, Z.P.; Jang, T.H.; Chang, J.W.; Chuang, C.M.; Lai, C.R.; Wang, L.H. miRNA-34c-5p inhibits amphiregulin-induced ovarian cancer stemness and drug resistance via downregulation of the AREG-EGFR-ERK pathway. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, H.J.; Kim, G.; Park, K.S. Ell3 stimulates proliferation, drug resistance, and cancer stem cell properties of breast cancer cells via a MEK/ERK-dependent signaling pathway. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 437, 557–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senthebane, D.A.; Jonker, T.; Rowe, A.; Thomford, N.E.; Munro, D.; Dandara, C.; Wonkam, A.; Govender, D.; Calder, B.; Soares, N.C.; et al. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Chemoresistance: 3D Extracellular Matrices as Accomplices. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, X.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, H.; Wen, T.; Zhang, K.; Huo, X.; et al. NID1, a new regulator of EMT required for metastasis and chemoresistance of ovarian cancer cells. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 33110–33121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lesniak, D.; Xu, Y.; Deschenes, J.; Lai, R.; Thoms, J.; Murray, D.; Gosh, S.; Mackey, J.R.; Sabri, S.; Abdulkarim, B. Beta1-integrin circumvents the antiproliferative effects of trastuzumab in human epidermal growth factor receptor-2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 8620–8628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gendron, S.; Couture, J.; Aoudjit, F. Integrin α2β1 inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis in T lymphocytes by protein phosphatase 2A-dependent activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 48633–48643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naci, D.; El Azreq, M.A.; Chetoui, N.; Lauden, L.; Sigaux, F.; Charron, D.; Al-Daccak, R.; Aoudjit, F. α2β1 integrin promotes chemoresistance against doxorubicin in cancer cells through extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK). J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 17065–17076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, H.C.; Huang, C.Y.; Su, H.L.; Tang, C.H. CCN2 enhances resistance to cisplatin-mediating cell apoptosis in human osteosarcoma. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e90159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pillozzi, S.; Masselli, M.; De Lorenzo, E.; Accordi, B.; Cilia, E.; Crociani, O.; Amedei, A.; Veltroni, M.; D’Amico, M.; Basso, G.; et al. Chemotherapy resistance in acute lymphoblastic leukemia requires hERG1 channels and is overcome by hERG1 blockers. Blood 2011, 117, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, C.S.; Yeung, T.L.; Yip, K.P.; Wong, K.K.; Ho, S.Y.; Mangala, L.S.; Sood, A.K.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Sheng, J.; Wong, S.T.; et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate endothelial adhesion protein LPP to promote ovarian cancer chemoresistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, M.R.; Choi, H.M.; Kang, H.N.; Lee, Y.; Joo, H.S.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, H.R.; Hong, M.H.; Yoon, S.O.; Cho, B.C. ERK-dependent IL-6 autocrine signaling mediates adaptive resistance to pan-PI3K inhibitor BKM120 in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncogene 2018, 37, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, H.; Yang, Z.; Xu, N.; Liu, B.; Fu, Z.; Lian, C.; Guo, H. Connective tissue growth factor promotes temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma through TGF-β1-dependent activation of Smad/ERK signaling. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottesman, M.M.; Fojo, T.; Bates, S.E. Multidrug resistance in cancer: role of ATP-dependent transporters. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riganti, C.; Castella, B.; Kopecka, J.; Campia, I.; Coscia, M.; Pescarmona, G.; Bosia, A.; Ghigo, D.; Massaia, M. Zoledronic acid restores doxorubicin chemosensitivity and immunogenic cell death in multidrug-resistant human cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e60975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rigoni, M.; Riganti, C.; Vitale, C.; Griggio, V.; Campia, I.; Robino, M.; Foglietta, M.; Castella, B.; Sciancalepore, P.; Buondonno, I.; et al. Simvastatin and downstream inhibitors circumvent constitutive and stromal cell-induced resistance to doxorubicin in IGHV unmutated CLL cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 29833–29846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kopecka, J.; Porto, S.; Lusa, S.; Gazzano, E.; Salzano, G.; Giordano, A.; Desiderio, V.; Ghigo, D.; Caraglia, M.; De Rosa, G.; et al. Self-assembling nanoparticles encapsulating zoledronic acid revert multidrug resistance in cancer cells. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 31461–31478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- He, X.; Wang, J.; Wei, W.; Shi, M.; Xin, B.; Zhang, T.; Shen, X. Hypoxia regulates ABCG2 activity through the activivation of ERK1/2/HIF-1α and contributes to chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2016, 17, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Wan, C.; Luo, Q.; Huang, Z.; Luo, Q. Genistein-inhibited cancer stem cell-like properties and reduced chemoresistance of gastric cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 3432–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Zhou, X.; Qu, H.; Ma, Y.; Yue, Z.; Shang, W.; Wang, P.; Xie, S.; Li, Y.; Sun, Y. TRIB2 knockdown as a regulator of chemotherapy resistance and proliferation via the ERK/STAT3 signaling pathway in human chronic myelogenous leukemia K562/ADM cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1910–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hussain, I.; Waheed, S.; Ahmad, K.A.; Pirog, J.E.; Syed, V. Scutellaria baicalensis targets the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α and enhances cisplatin efficacy in ovarian cancer. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 119, 7515–7524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, L.; Liu, H.G.; Dong, S.Y.; Yang, F.; Wang, Q.X.; Guo, G.L.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhang, X.H. Upregulation of CD44v6 contributes to acquired chemoresistance via the modulation of autophagy in colon cancer SW480 cells. Tumour Biol. 2016, 37, 8811–8824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.S.; Bernier, M.; Wainer, I.W. Selective GPR55 antagonism reduces chemoresistance in cancer cells. Pharmacol Res. 2016, 111, 757–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El Azreq, M.A.; Naci, D.; Aoudjit, F. Collagen/β1 integrin signaling up-regulates the ABCC1/MRP-1 transporter in an ERK/MAPK-dependent manner. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2012, 23, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.Y.; Yu, L.; Liu, B.L.; He, X.J.; Zhang, B.Y. Downregulation of P-gp, Ras and p-ERK1/2 contributes to the arsenic trioxide-induced reduction in drug resistance towards doxorubicin in gastric cancer cell lines. Mol. Med. Rep. 2015, 12, 7335–7343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinette, V.; Placet, M.; Arguin, G.; Gendron, F.P. Multidrug Resistance-Associated Protein 2 Expression Is Up-regulated by Adenosine 5′-Triphosphate in Colorectal Cancer Cells and Enhances Their Survival to Chemotherapeutic Drugs. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0136080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, C.; Meng, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huo, X.; Sun, P.; Sun, H.; Ma, X.; Peng, J.; Liu, K. Targeting P-glycoprotein and SORCIN: Dihydromyricetin strengthens anti-proliferative efficiency of adriamycin via MAPK/ERK and Ca(2+)–mediated apoptosis pathways in MCF-7/ADR and K562/ADR. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 3066–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.; Shen, J.; Du, C.; Chen, D.; Gu, X.; Li, C.; Yao, M.; Pan, J.; Cheng, J.; Jiang, D.; et al. A miR-20a/MAPK1/c-Myc regulatory feedback loop regulates breast carcinogenesis and chemoresistance. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 406–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pu, Y.; Yi, Q.; Zhao, F.; Wang, H.; Cai, W.; Cai, S. MiR-20a-5p represses multi-drug resistance in osteosarcoma by targeting the KIF26B gene. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 5, 16–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, L.; Li, X.; Zhou, F.; Jin, Z.; Chen, D.; Wang, P.; Zhang, S.; Zhuge, Y.; Shang, Y.; Zou, X. Downregulation of leucine-rich repeats and immunoglobulin-like domains 1 by microRNA-20a modulates gastric cancer multidrug resistance. Cancer Sci. 2018, 109, 1044–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, L.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, L.; He, M.; Bai, X.; Yu, L.; Wei, M. MiR-302a/b/c/d cooperatively sensitizes breast cancer cells to adriamycin via suppressing P-glycoprotein(P-gp) by targeting MAP/ERK kinase kinase 1 (MEKK1). J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 35, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J. Cancer stem cells and chemoresistance: The smartest survives the raid. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 160, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stacy, A.E.; Jansson, P.J.; Richardson, D.R. Molecular pharmacology of ABCG2 and its role in chemoresistance. Mol. Pharmacol. 2013, 84, 655–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riganti, C.; Salaroglio, I.C.; Caldera, V.; Campia, I.; Kopecka, J.; Mellai, M.; Annovazzi, L.; Bosia, A.; Ghigo, D.; Schiffer, D. Temozolomide down-regulates P-glycoprotein expression in glioblastoma stem cells by interfering with the Wnt3a/glycogen synthase-3 kinase/β-catenin pathway. Neuro Oncol. 2013, 15, 1502–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, B.J.; Saab, K.R.; Ma, J.; Schatton, T.; Pütz, P.; Zhan, Q.; Murphy, G.F.; Gasser, M.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Frank, N.Y.; et al. ABCB5 maintains melanoma-initiating cells through a proinflammatory cytokine signaling circuit. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 4196–4207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerezo, D.; Ruiz-Alcaraz, A.J.; Lencina-Guardiola, M.; Cánovas, M.; García-Peñarrubia, P.; Martínez-López, I.; Martín-Orozco, E. Attenuated JNK signaling in multidrug-resistant leukemic cells. Dual role of MAPK in cell survival. Cell Signal. 2017, 30, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; To, K.K.W.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Luo, M.; Wang, F.; Yan, S.; Fu, L. Dacomitinib potentiates the efficacy of conventional chemotherapeutic agents via inhibiting the drug efflux function of ABCG2 in vitro and in vivo. J.Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 37, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, Z.; Guo, X.; To, K.K.W.; Chen, Z.; Fang, X.; Luo, M.; Ma, C.; Xu, J.; Yan, S.; Fu, L. Olmutinib (HM61713) reversed multidrug resistance by inhibiting the activity of ATP-binding cassette subfamily G member 2 in vitro and in vivo. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2018, 8, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeratichamroen, S.; Lirdprapamongkol, K.; Svasti, J. Mechanism of ECM-induced dormancy and chemoresistance in A549 human lung carcinoma cells. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 39, 1765–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kumari, R.; Chouhan, S.; Singh, S.; Chhipa, R.R.; Ajay, A.K.; Bhat, M.K. Constitutively activated ERK sensitizes cancer cells to doxorubicin: Involvement of p53-EGFR-ERK pathway. J. Biosci. 2017, 42, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluzzi, L.; Buqué, A.; Keep, O.; Zitvogel, L.; Kroemer, G. Immunogenic cell death in cancer and infectious disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2017, 17, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, K.; Iyoda, T.; Okada, M.; Yamasaki, S.; Fujii, S.I. Immune suppression and reversal of the suppressive tumor microenvironment. Int. Immunol. 2018, 30, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsu, T.I.; Wang, Y.C.; Hung, C.Y.; Yu, C.H.; Su, W.C.; Chang, W.C.; Hung, J.J. Positive feedback regulation between IL10 and EGFR promotes lung cancer formation. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20840–20854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruscetti, M.; Leibold, J.; Bott, M.J.; Fennell, M.; Kulick, A.; Salgado, N.R.; Chen, C.C.; Ho, Y.J.; Sanchez-Rivera, F.J.; Feucht, J.; et al. NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity contributes to tumor control by a cytostatic drug combination. Science 2018, 362, 1416–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ye, Y.L.; Li, M.X.; Ye, S.B.; Huang, W.R.; Cai, T.T.; He, J.; Peng, J.Y.; Duan, T.H.; Cui, J.; et al. CXCL2/MIF-CXCR2 signaling promotes the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and is correlated with prognosis in bladder cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, X.; Shi, W.; Xu, Y.; Xu, C.; Zhao, T.; Geng, B.; Yang, J.; Pan, J.; Hu, S.; Zhang, C.; et al. Tumor-derived lactate induces M2 macrophage polarization via the activation of the ERK/STAT3 signaling pathway in breast cancer. Cell Cycle 2018, 17, 428–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeda, K.; Nakayama, M.; Hayakawa, Y.; Kojima, Y.; Ikeda, H.; Imai, N.; Ogasawara, K.; Okumura, K.; Thomas, D.M.; Smyth, M.J. IFN-γ is required for cytotoxic T cell-dependent cancer genome immunoediting. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ji, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, G.; Zhang, J.; Jin, R.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Liang, X.; Huang, D.; et al. Sorafenib-resistant hepatocellular carcinoma stratified by phosphorylated ERK activates PD-1 immune checkpoint. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 41274–41284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hemon, P.; Jean-Louis, F.; Ramgolam, K.; Brignone, C.; Viguier, M.; Bachelez, H.; Triebel, F.; Charron, D.; Aoudjit, F.; Al-Daccak, R.; et al. MHC class II engagement by its ligand LAG-3 (CD223) contributes to melanoma resistance to apoptosis. J. Immunol. 2011, 186, 5173–5183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.; Matsumoto, S.; Fujita, Y.; Kuroda, A.; Menju, T.; Sonobe, M.; Kondo, N.; Torii, I.; Nakano, T.; Lara, P.N.; et al. Trametinib plus 4-Methylumbelliferone Exhibits Antitumor Effects by ERK Blockade and CD44 Downregulation and Affects PD-1 and PD-L1 in Malignant Pleural Mesothelioma. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017, 12, 477–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, P.L.; Wu, T.C.; Wu, D.W.; Wang, L.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, H. An increase in BAG-1 by PD-L1 confers resistance to tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small cell lung cancer via persistent activation of ERK signalling. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 85, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loi, S.; Dushyanthen, S.; Beavis, P.A.; Salgado, R.; Denkert, C.; Savas, P.; Combs, S.; Rimm, D.L.; Giltnane, J.M.; Estrada, M.V.; et al. RAS/MAPK Activation Is Associated with Reduced Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer: Therapeutic Cooperation Between MEK and PD-1/PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 1499–1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Mezzadra, R.; Schumacher, T.N. Regulation and Function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 2018, 48, 434–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, N.; Fang, W.; Zhan, J.; Hong, S.; Tang, Y.; Kang, S.; Zhang, Y.; He, X.; Zhou, T.; Qin, T.; et al. Upregulation of PD-L1 by EGFR Activation Mediates the Immune Escape in EGFR-Driven NSCLC: Implication for Optional Immune Targeted Therapy for NSCLC Patients with EGFR Mutation. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2015, 10, 910–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- .Zerdes, I.; Matikas, A.; Bergh, J.; Rassidakis, G.Z.; Foukakis, T. Genetic, transcriptional and post-translational regulation of the programmed death protein ligand 1 in cancer: Biology and clinical correlations. Oncogene 2018, 37, 4639–4661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.; Zhou, J.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Wargo, J.; Hodi, F.S. The activation of MAPK in melanoma cells resistant to BRAF inhibition promotes PD-L1 expression that is reversible by MEK and PI3K inhibition. Clin. Cancer Res. 2013, 19, 598–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumimoto, H.; Takano, A.; Teramoto, K.; Daigo, Y. RAS-mitogenactivated protein kinase signal is required for enhanced PD-L1 expression in human lung cancers. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Concha-Benavente, F.; Srivastava, R.M.; Trivedi, S.; Lei, Y.; Chandran, U.; Seethala, R.R.; Freeman, G.J.; Ferris, R.L. Identification of the cellintrinsic and -extrinsic pathways downstream of EGFR and IFNg that induce PD-L1 expression in head and neck cancer. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Zeng, Y.; Du, W.; Zhu, J.; Shen, D.; Liu, Z.; Huang, J.A. The EGFR pathway is involved in the regulation of PD-L1 expression via the IL-6/JAK/STAT3 signaling pathway in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 49, 1360–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Coelho, M.A.; de Carné Trécesson, S.; Rana, S.; Zecchin, D.; Moore, C.; Molina-Arcas, M.; East, P.; Spencer-Dene, B.; Nye, E.; Barnouin, K.; et al. Oncogenic RAS Signaling Promotes Tumor Immunoresistance by Stabilizing PD-L1 mRNA. Immunity 2017, 47, 1083–1099.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, M.J.; Xu, L.J.; Yang, L.; Tsai, Y.; Keng, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.O.; Chen, Y. Radiation alters PD-L1/NKG2D ligand levels in lung cancer cells and leads to immune escape from NK cell cytotoxicity via IL-6-MEK/Erk signaling pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 80506–80520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, L.; Xie, X.H.; Zhu, Z.H. Calotropin regulates the apoptosis of non-small cell cancer by regulating the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte associated antigen 4-mediated TGF-β/ERK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7683–7691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, L.K.; Mireau, L.R.; Ostergaard, H.L. A role for phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase in TCR-stimulated ERK activation leading to paxillin phosphorylation and CTL degranulation. J. Immunol. 2005, 175, 8138–8145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gravelle, P.; Do, C.; Franchet, C.; Mueller, S.; Oberic, L.; Ysebaert, L.; Larocca, L.M.; Hohaus, S.; Calmels, M.N.; Frenois, F.X.; et al. Impaired functional responses in follicular lymphoma CD8(+)TIM-3(+) T lymphocytes following TCR engagement. Oncoimmunology 2016, 5, e1224044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.J.; Lee, M.J.; Shin, D.C.; Kim, J.S.; Chwae, Y.J.; Kwon, M.H.; Kim, K.; Park, S. Activation of mitogen activated protein kinase-Erk kinase (MEK) increases T cell immunoglobulin mucin domain-3 (TIM-3) transcription in human T lymphocytes and a human mast cell line. Mol. Immunol. 2011, 48, 1778–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prinz, P.U.; Mendler, A.N.; Masouris, I.; Durner, L.; Oberneder, R.; Noessner, E. High DGK-α and disabled MAPK pathways cause dysfunction of human tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells that is reversible by pharmacologic intervention. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 5990–6000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, X.; Zhang, D.; Ren, G.; Shi, B.; Wang, C.; Kosinska, A.D.; Wang, S.; Zhou, X.; et al. Polarization of Monocytic Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells by Hepatitis B Surface Antigen Is Mediated via ERK/IL-6/STAT3 Signaling Feedback and Restrains the Activation of T Cells in Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 4873–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, H.J.; Lim, H.X.; Song, J.H.; Lee, A.; Kim, E.; Cho, D.; Cohen, E.P.; Kim, T.S. Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-interacting multifunctional protein 1 suppresses tumor growth in breast cancer-bearing mice by negatively regulating myeloid-derived suppressor cell functions. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2016, 65, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gato-Cañas, M.; Martinez de Morentin, X.; Blanco-Luquin, I.; Fernandez-Irigoyen, J.; Zudaire, I.; Liechtenstein, T.; Arasanz, H.; Lozano, T.; Casares, N.; Chaikuad, A.; et al. A core of kinase-regulated interactomes defines the neoplastic MDSC lineage. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 27160–27175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, A.S.; Wu, X.; Zhuang, G.; Ngu, H.; Kasman, I.; Zhang, J.; Vernes, J.M.; Jiang, Z.; Meng, Y.G.; Peale, F.V.; et al. An interleukin-17-mediated paracrine network promotes tumor resistance to anti-angiogenic therapy. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 1114–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Yao, S.; Dann, S.M.; Qin, H.; Elson, C.O.; Cong, Y. ERK differentially regulates Th17- and Treg-cell development and contributes to the pathogenesis of colitis. Eur. J. Immunol. 2013, 43, 1716–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kopecka, J.; Campia, I.; Brusa, D.; Doublier, S.; Matera, L.; Ghigo, D.; Bosia, A.; Riganti, C. Nitric oxide and P-glycoprotein modulate the phagocytosis of colon cancer cells. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2011, 15, 1492–1504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, D.; Wakimoto, H.; Peters, C.W.; Antoszczyk, S.J.; Rabkin, S.D.; Martuza, R.L. Combinatorial Effects of VEGFR Kinase Inhibitor Axitinib and Oncolytic Virotherapy in Mouse and Human Glioblastoma Stem-Like Cell Models. Clin. Cancer Res. 2018, 24, 3409–3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurimoto, R.; Iwasawa, S.; Ebata, T.; Ishiwata, T.; Sekine, I.; Tada, Y.; Tatsumi, K.; Koide, S.; Iwama, A.; Takiguchi, Y. Drug resistance originating from a TGF-β/FGF-2-driven epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and its reversion in human lung adenocarcinoma cell lines harboring an EGFR mutation. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 1825–1836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, K.; Azuma, K.; Kawahara, A.; Hattori, S.; Iwama, E.; Tanizaki, J.; Harada, T.; Matsumoto, K.; Takayama, K.; Takamori, S.; et al. Induction of PD-L1 Expression by the EML4-ALK Oncoprotein and Downstream Signaling Pathways in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 4014–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shen, M.; Xu, L.J.; Yang, X.; Tsai, Y.; Keng, P.C.; Chen, Y.; Lee, S.O. Enhancing NK cell-mediated cytotoxicity to cisplatin-resistant lung cancer cells via MEK/Erk signaling inhibition. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Yuan, W.; Wang, H.; Chen, K.; Li, D.; Li, D. PD-1/PD-L1 interaction up-regulates MDR1/P-gp expression in breast cancer cells via PI3K/AKT and MAPK/ERK pathways. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 99901–99912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Black, M.; Barsoum, I.B.; Truesdell, P.; Cotechini, T.; Macdonald-Goodfellow, S.K.; Petroff, M.; Siemens, D.R.; Koti, M.; Craig, A.W.; Graham, C.H. Activation of the PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint confers tumor cell chemoresistance associated with increased metastasis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 10557–10567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ock, C.Y.; Kim, S.; Keam, B.; Kim, S.; Ahn, Y.O.; Chung, E.J.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, T.M.; Kwon, S.K.; Jeon, Y.K.; et al. Changes in programmed death-ligand 1 expression during cisplatin treatment in patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 97920–97927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, M.; Liu, P.; Wang, K.; Glorieux, C.; Hu, Y.; Wen, S.; Jiang, W.; Huang, P. Chemotherapy induces tumor immune evasion by upregulation of programmed cell death ligand 1 expression in bone marrow stromal cells. Mol. Oncol. 2017, 11, 358–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Laprevotte, E.; Cochaud, S.; du Manoir, S.; Lapierre, M.; Dejou, C.; Philippe, M.; Giustiniani, J.; Frewer, K.A.; Sanders, A.J.; Jiang, W.G.; et al. The IL-17B-IL-17 receptor B pathway promotes resistance to paclitaxel in breast tumors through activation of the ERK1/2 pathway. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 113360–113372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olson, O.C.; Kim, H.; Quail, D.F.; Foley, E.A.; Joyce, J.A. Tumor-Associated Macrophages Suppress the Cytotoxic Activity of Antimitotic Agents. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 101–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Salaroglio, I.C.; Mungo, E.; Gazzano, E.; Kopecka, J.; Riganti, C. ERK is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102505
Salaroglio IC, Mungo E, Gazzano E, Kopecka J, Riganti C. ERK is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102505
Chicago/Turabian StyleSalaroglio, Iris C., Eleonora Mungo, Elena Gazzano, Joanna Kopecka, and Chiara Riganti. 2019. "ERK is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102505
APA StyleSalaroglio, I. C., Mungo, E., Gazzano, E., Kopecka, J., & Riganti, C. (2019). ERK is a Pivotal Player of Chemo-Immune-Resistance in Cancer. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102505