Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease
Abstract
:1. Discovery of a Guardian Angel Adipocytokine
2. Tight Regulation of Adiponectin at Multiple Levels
2.1. The Role of Coactivators in Transcriptional Regulation of Adiponectin
2.2. Involvement of Multiple Co-Factors in Transcriptional Repression of Adiponectin
2.3. Control of Adiponectin Expression via Post-Translational Modifications
3. Physiological Functions of Adiponectin
3.1. A Central Role in the Reproductive System
3.2. Regulation of Insulin Sensitivity and Protection against Fatty Liver
3.3. Adiponectin in the Central Nervous System
4. Perturbations in Adiponectin Levels Manifest in Disease States
4.1. Association of Adiponectin with Inflammation
4.2. Adiponectin in Cardiovascular Diseases
5. Obese State and Adiponectin—An Inverse Relation
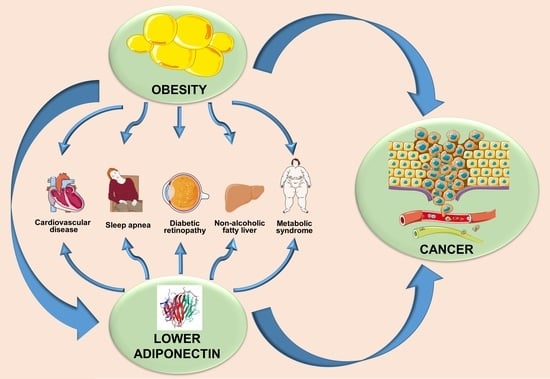
6. Adiponectin- and Obesity-Associated Disorders
6.1. Hypertension
6.2. Atherosclerosis
6.3. Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome
6.4. Diabetic Retinopathy
7. Obesity, Adiponectin, and Cancer: Interplay of Bigwigs
8. Adiponectin Orchestrates Multiple Biological Functions to Inhibit Cancer Progression
8.1. Inhibition of Angiogenesis
8.2. Inhibition of Growth and Proliferation
8.3. Inhibition of Invasion, Migration, and Metastasis
9. Molecular Mechanisms Mediating Adiponectin’s Effects in Cancer
10. Potential Therapeutic Modulation of Adiponectin
10.1. Pharmacological Agents
10.2. Weight Loss Interventions
11. Conclusions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Acrp30 | Adipocyte complement related protein of 30 kDa |
| apM1 | Adipose most abundant gene transcript1 |
| GBP28 | Gelatin-binding protein of 28 kDa |
| AdipoR1 | Adiponectin receptor 1 |
| AdipoR2 | Adiponectin receptor 2 |
| PPARγ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| TZD | Thiazolidinedione |
| PPRE | PPAR response element |
| HMW adiponectin | High molecular weight adiponectin |
| FoxO1 | Forkhead box protein O1 |
| Sirt1 | Sirtuin 1 |
| C/EBPα | CCAAT-enhancer-binding proteins |
| SERBP | Sterol regulatory element-binding proteins |
| SRE | SERBP response element |
| CREB | cAMP response element-binding protein |
| ATF3 | Activating transcription factor 3 |
| NFAT | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells |
| AP-2β | Activating enhancer binding protein-2β |
| IGFBP-3 | IGF-1-binding protein 3 |
| Id3 | Inhibitor of differentiation-3 |
| HIF1α | Hypoxia inducible factor alpha |
| TNFα | Tumor necrosis factor alpha |
| IFNγ | Interferon gamma |
| IL | Interleukin |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinases |
| ERK | Extracellular-signal-regulated kinase |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinases |
| ERp44 | ER chaperone protein 44 |
| Ero-1La | ERO1-like protein alpha |
| DsbA-L | Disulfide-bond A oxidoreductase-like protein |
| COX2 | Cyclooxygenase 2 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor |
| PGES | Prostaglandin E synthase |
| hCG | Human chorionic gonadotropin |
| AMPK | AMP activated protein kinase |
| PCOS | Polycystic ovary syndrome |
| SNP | Single nucleotide polymorphism |
| GLUT4 | Glucose transporter type 4 |
| CNS | Central nervous system |
| GH | Growth hormone |
| LH | Luteinizing hormone |
| eNOS | Endothelial NOS |
| NFκB | Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells |
| MMP | Matrix metalloproteinase |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| EP4 | Prostaglandin E2 receptor 4 |
| SphK | Sphingosine kinase |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion protein 1 |
| BMI | Body mass index |
| LDL | Low density lipoprotein |
| HDL | High density lipoprotein |
| apoA-I | Apolipoprotein A-I |
| NO | Nitric oxide |
| PI3K | Phosphoinositide 3-kinase |
| PDGF | Platelet-derived growth factor |
| HB-EGF | Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor |
| BFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| EGF | Epidermal growth factor |
| OSAS | Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome |
| T2DM | Type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| IARC | International agency for research on cancer |
| WCRF | World cancer research fund |
| SMD | Standard mean differences |
| RIA | Radioimmunoassay |
| ELISA | Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay |
| HGF | Hepatocyte growth factor |
| bFGF | Basic fibroblast growth factor |
| FGF-2 | Fibroblast growth factor-2 |
| HUVEC | Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells |
| mTOR | Mammalian target of rapamycin |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| Trx | Thioredoxin |
| CRC | Colorectal cancer |
| PTP1B | Protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung carcinoma |
| EMT | Epithelial to mesenchymal transition |
| PKA | Protein kinase A |
| IGF1 | Insulin like growth factor-1 |
| COPD | Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease |
| STAT3 | Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| GSK3β | Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta |
| DsbA-L | Disulfide-bond A oxidoreductase-like protein |
References
- Brochu-Gaudreau, K.; Rehfeldt, C.; Blouin, R.; Bordignon, V.; Murphy, B.D.; Palin, M.-F. Adiponectin action from head to toe. Endocrine 2010, 37, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.-X.; Zhao, X.-Y.; Lin, J.D. The brown fat secretome: Metabolic functions beyond thermogenesis. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2015, 26, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scherer, P.E.; Williams, S.; Fogliano, M.; Baldini, G.; Lodish, H.F. A novel serum protein similar to C1q, produced exclusively in adipocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 26746–26749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.; Liang, P.; Spiegelman, B.M. AdipoQ is a novel adipose-specific gene dysregulated in obesity. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 10697–10703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, K.; Okubo, K.; Shimomura, I.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Matsubara, K. cDNA cloning and expression of a novel adipose specific collagen-like factor, apM1 (AdiPose Most abundant Gene transcript 1). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1996, 221, 286–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y.; Tobe, T.; Choi-Miura, N.H.; Mazda, T.; Tomita, M. Isolation and characterization of GBP28, a novel gelatin-binding protein purified from human plasma. J. Biochem. 1996, 120, 803–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Du, X.; Brownlee, M.; Scherer, P.E. The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Waki, H.; Terauchi, Y.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Mori, Y.; Ide, T.; Murakami, K.; Tsuboyama-Kasaoka, N.; et al. The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat. Med. 2001, 7, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Combs, T.P.; Berg, A.H.; Obici, S.; Scherer, P.E.; Rossetti, L. Endogenous glucose production is inhibited by the adipose-derived protein Acrp30. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1875–1881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Kamon, J.; Minokoshi, Y.; Ito, Y.; Waki, H.; Uchida, S.; Yamashita, S.; Noda, M.; Kita, S.; Ueki, K.; et al. Adiponectin stimulates glucose utilization and fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nat. Med. 2002, 8, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.; Takahashi, N.; Hileman, S.M.; Patel, H.R.; Berg, A.H.; Pajvani, U.B.; Scherer, P.E.; Ahima, R.S. Adiponectin acts in the brain to decrease body weight. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, 524–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holland, W.L.; Miller, R.A.; Wang, Z.V.; Sun, K.; Barth, B.M.; Bui, H.H.; Davis, K.E.; Bikman, B.T.; Halberg, N.; Rutkowski, J.M.; et al. Receptor-mediated activation of ceramidase activity initiates the pleiotropic actions of adiponectin. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaurasia, B.; Summers, S.A. Ceramides—Lipotoxic Inducers of Metabolic Disorders. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 26, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, J.Y.; Holland, W.L.; Kusminski, C.M.; Sun, K.; Sharma, A.X.; Pearson, M.J.; Sifuentes, A.J.; McDonald, J.G.; Gordillo, R.; Scherer, P.E. Targeted Induction of Ceramide Degradation Leads to Improved Systemic Metabolism and Reduced Hepatic Steatosis. Cell Metab. 2015, 22, 266–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rutkowski, J.M.; Wang, Z.V.; Park, A.S.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, D.; Hu, M.C.; Moe, O.W.; Susztak, K.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin promotes functional recovery after podocyte ablation. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 24, 268–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dadson, K.; Turdi, S.; Hashemi, S.; Zhao, J.; Polidovitch, N.; Beca, S.; Backx, P.H.; McDermott, J.C.; Sweeney, G. Adiponectin is required for cardiac MEF2 activation during pressure overload induced hypertrophy. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2015, 86, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors. Endocr. Rev. 2005, 26, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hug, C.; Wang, J.; Ahmad, N.S.; Bogan, J.S.; Tsao, T.S.; Lodish, H.F. T-cadherin is a receptor for hexameric and high-molecular-weight forms of Acrp30/adiponectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 10308–10313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iwaki, M.; Matsuda, M.; Maeda, N.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Makishima, M.; Shimomura, I. Induction of Adiponectin, a Fat-Derived Antidiabetic and Antiatherogenic Factor, by Nuclear Receptors. Diabetes 2003, 52, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, J.G.; Javorschi, S.; Hevener, A.L.; Kruszynska, Y.T.; Norman, R.A.; Sinha, M.; Olefsky, J.M. The Effect of Thiazolidinediones on Plasma Adiponectin Levels in Normal, Obese, and Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Diabetes 2002, 51, 2968–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kanatani, Y.; Usui, I.; Ishizuka, K.; Bukhari, A.; Fujisaka, S.; Urakaze, M.; Haruta, T.; Kishimoto, T.; Naka, T.; Kobayashi, M. Effects of Pioglitazone on Suppressor of Cytokine Signaling 3 Expression. Potential Mech. Its Eff. Insul. Sensit. Adiponectin Expr. 2007, 56, 795–803. [Google Scholar]
- Nakae, J.; Kitamura, T.; Kitamura, Y.; Biggs, W.H.; Arden, K.C.; Accili, D. The Forkhead Transcription Factor Foxo1 Regulates Adipocyte Differentiation. Dev. Cell 2003, 4, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiao, L.; Shao, J. SIRT1 Regulates Adiponectin Gene Expression through Foxo1-C/Enhancer-binding Protein α Transcriptional Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39915–39924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-H.; Qiang, L.; Farmer, S.R. Phosphorylation of C/EBPβ at a Consensus Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase/Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3 Site Is Required for the Induction of Adiponectin Gene Expression during the Differentiation of Mouse Fibroblasts into Adipocytes. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2004, 24, 8671–8680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, B.; Jack, M.M.; Cushman, S.W.; Smith, U. Adiponectin gene activation by thiazolidinediones requires PPARγ2, but not C/EBPα—Evidence for differential regulation of the aP2 and adiponectin genes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 308, 933–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.B.; Moon, H.M.; Noh, M.J.; Lee, Y.S.; Jeong, H.W.; Yoo, E.J.; Kim, W.S.; Park, J.; Youn, B.-S.; Kim, J.W.; et al. Adipocyte Determination- and Differentiation-dependent Factor 1/Sterol Regulatory Element-binding Protein 1c Regulates Mouse Adiponectin Expression. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 22108–22117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, J.-W.; Klemm, D.J.; Vinson, C.; Lane, M.D. Role of CREB in Transcriptional Regulation of CCAAT/Enhancer-binding Protein β Gene during Adipogenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 4471–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.B.; Kong, M.; Kim, T.M.; Suh, Y.H.; Kim, W.-H.; Lim, J.H.; Song, J.H.; Jung, M.H. NFATc4 and ATF3 Negatively Regulate Adiponectin Gene Expression in 3T3-L1 Adipocytes. Diabetes 2006, 55, 1342–1352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ho, I.-C.; Kim, J.H.-J.; Rooney, J.W.; Spiegelman, B.M.; Glimcher, L.H. A potential role for the nuclear factor of activated T cells family of transcriptional regulatory proteins in adipogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 15537–15541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Liu, F. Transcriptional and post-translational regulation of adiponectin. Biochem. J. 2010, 425, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.-Y.; Kim, W.H.; Park, S.I. GO6976 prevents TNF-α-induced suppression of adiponectin expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: Putative involvement of protein kinase C. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 3473–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappalà, G.; Rechler, M.M. IGFBP-3, hypoxia and TNF-α inhibit adiponectin transcription. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 382, 785–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fasshauer, M.; Kralisch, S.; Klier, M.; Lossner, U.; Bluher, M.; Klein, J.; Paschke, R. Adiponectin gene expression and secretion is inhibited by interleukin-6 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 301, 1045–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusminski, C.M.; McTernan, P.G.; Schraw, T.; Kos, K.; O’Hare, J.P.; Ahima, R.; Kumar, S.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin complexes in human cerebrospinal fluid: Distinct complex distribution from serum. Diabetologia 2007, 50, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadowaki, T.; Yamauchi, T.; Kubota, N.; Hara, K.; Ueki, K.; Tobe, K. Adiponectin and adiponectin receptors in insulin resistance, diabetes, and the metabolic syndrome. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1784–1792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, S.A.; Kung, J.T. Mechanisms of adiponectin regulation and use as a pharmacological target. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2010, 10, 676–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, A.H.; Combs, T.P.; Scherer, P.E. ACRP30/adiponectin: An adipokine regulating glucose and lipid metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2002, 13, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, K.S.L.; Chan, L.; Chan, K.W.; Lam, J.B.B.; Lam, M.C.; Hoo, R.C.L.; Mak, W.W.N.; Cooper, G.J.S.; Xu, A. Post-translational Modifications of the Four Conserved Lysine Residues within the Collagenous Domain of Adiponectin Are Required for the Formation of Its High Molecular Weight Oligomeric Complex. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16391–16400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Richards, A.A.; Macdonald, G.A.; Charlton, H.K.; Prins, J.B.; Stephens, T.; Whitehead, J.P.; Jones, A. Adiponectin Multimerization Is Dependent on Conserved Lysines in the Collagenous Domain: Evidence for Regulation of Multimerization by Alterations in Posttranslational Modifications. Mol. Endocrinol. 2006, 20, 1673–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Z.V.; Schraw, T.D.; Kim, J.-Y.; Khan, T.; Rajala, M.W.; Follenzi, A.; Scherer, P.E. Secretion of the Adipocyte-Specific Secretory Protein Adiponectin Critically Depends on Thiol-Mediated Protein Retention. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 3716–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Qiang, L.; Wang, H.; Farmer, S.R. Adiponectin Secretion Is Regulated by SIRT1 and the Endoplasmic Reticulum Oxidoreductase Ero1-Lα. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 27, 4698–4707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.A.; Kung, J.; Ciaraldi, T.P.; Choe, C.; Christiansen, L.; Mudaliar, S.; Henry, R.R. Selective regulation of cellular and secreted multimeric adiponectin by antidiabetic therapies in humans. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E767–E773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, M.; Zhou, L.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.L.; Wetzel, M.D.; Xiang, R.; Zhang, J.; Xin, X.; Dong, L.Q.; Liu, F. A disulfide-bond A oxidoreductase-like protein (DsbA-L) regulates adiponectin multimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18302–18307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mitchell, M.; Armstrong, D.T.; Robker, R.L.; Norman, R.J. Adipokines: Implications for female fertility and obesity. Reproduction 2005, 130, 583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chabrolle, C.; Tosca, L.; Dupont, J.L. Regulation of adiponectin and its receptors in rat ovary by human chorionic gonadotrophin treatment and potential involvement of adiponectin in granulosa cell steroidogenesis. Reproduction 2007, 133, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leff, T. AMP-activated protein kinase regulates gene expression by direct phosphorylation of nuclear proteins. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2003, 31, 224–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, J.; Chabrolle, C.; Ramé, C.; Tosca, L.; Coyral-Castel, S. Role of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors, adenosine monophosphate-activated kinase, and adiponectin in the ovary. Ppar Res. 2008, 2008, 176275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archanco, M.; Gómez-Ambrosi, J.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Frühbeck, G.; Burrell, M.A. Expression of Leptin and Adiponectin in the Rat Oviduct. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 2007, 55, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Morimoto, C.; Koga, K.; Harada, M.; Yoshino, O.; Hirata, T.; Hirota, Y.; Taketani, Y.; Takemura, Y.; Osuga, Y.; Yano, T.; et al. Expression of Adiponectin Receptors and Its Possible Implication in the Human Endometrium. Endocrinology 2006, 147, 3203–3210. [Google Scholar]
- Breitfeld, J.; Stumvoll, M.; Kovacs, P. Genetics of adiponectin. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2157–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokushige, K.; Hashimoto, E.; Noto, H.; Yatsuji, S.; Taniai, M.; Torii, N.; Shiratori, K. Influence of adiponectin gene polymorphisms in Japanese patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 976–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, M.J.; Lee, G.Y.; Chung, J.-J.; Ahn, Y.H.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, J.B. Adiponectin Increases Fatty Acid Oxidation in Skeletal Muscle Cells by Sequential Activation of AMP-Activated Protein Kinase, p38 Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase, and Peroxisome Proliferator–Activated Receptor α. Diabetes 2006, 55, 2562–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomas, E.; Tsao, T.-S.; Saha, A.K.; Murrey, H.E.; Zhang, C.c.; Itani, S.I.; Lodish, H.F.; Ruderman, N.B. Enhanced muscle fat oxidation and glucose transport by ACRP30 globular domain: Acetyl–CoA carboxylase inhibition and AMP-activated protein kinase activation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 16309–16313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceddia, R.B.; Somwar, R.; Maida, A.; Fang, X.; Bikopoulos, G.; Sweeney, G. Globular adiponectin increases GLUT4 translocation and glucose uptake but reduces glycogen synthesis in rat skeletal muscle cells. Diabetologia 2005, 48, 132–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Palanivel, R.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Y.; Xu, A.; Wang, Y.; Sweeney, G. Hyperglycemia- and hyperinsulinemia-induced alteration of adiponectin receptor expression and adiponectin effects in L6 myoblasts. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 2005, 35, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tsuchida, A.; Yamauchi, T.; Ito, Y.; Hada, Y.; Maki, T.; Takekawa, S.; Kamon, J.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, R.; Hara, K.; et al. Insulin/Foxo1 Pathway Regulates Expression Levels of Adiponectin Receptors and Adiponectin Sensitivity. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 30817–30822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kharroubi, I.; Rasschaert, J.; Eizirik, D.L.; Cnop, M. Expression of adiponectin receptors in pancreatic β cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 312, 1118–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, W.; Li, X.; Liu, C.; Yang, J.; Ye, L.; Tang, J.; Gu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Hong, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Globular adiponectin augments insulin secretion from pancreatic Islet β cells at high glucose concentrations. Endocrine 2006, 30, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, M.; Ohara-Imaizumi, M.; Kubota, N.; Hashimoto, S.; Eto, K.; Kanno, T.; Kubota, T.; Wakui, M.; Nagai, R.; Noda, M.; et al. Adiponectin induces insulin secretion in vitro and in vivo at a low glucose concentration. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zyromski, N.J.; Mathur, A.; Pitt, H.A.; Wade, T.E.; Wang, S.; Swartz-Basile, D.A.; Prather, A.D.; Lillemoe, K.D. Cannabinoid Receptor-1 Blockade Attenuates Acute pancreatitis in Obesity by An adiponectin Mediated Mechanism. J. Gastrointest. Surg. 2009, 13, 831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemer, J.; Pinky, P.D.; Govindarajulu, M.; Hong, H.; Judd, R.; Amin, R.H.; Moore, T.; Dhanasekaran, M.; Reed, M.N.; Suppiramaniam, V. Role of Adiponectin in Central Nervous System Disorders. Neural Plast. 2018, 2018, 4593530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Fuentes, A.J.; Rodriguez-Pacheco, F.; Castaño, J.P.; Pinilla, L.; Tena-Sempere, M.; Malagon, M.a.M.; Dieguez, C.; Tovar, S. Regulation of Pituitary Cell Function by Adiponectin. Endocrinology 2007, 148, 401–410. [Google Scholar]
- Nishimura, M.; Izumiya, Y.; Higuchi, A.; Shibata, R.; Qiu, J.; Kudo, C.; Shin, H.K.; Moskowitz, M.A.; Ouchi, N. Adiponectin Prevents Cerebral Ischemic Injury Through Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase–Dependent Mechanisms. Circulation 2008, 117, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neumeier, M.; Weigert, J.; Schäffler, A.; Wehrwein, G.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Schölmerich, J.; Wrede, C.; Buechler, C. Different effects of adiponectin isoforms in human monocytic cells. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2006, 79, 803–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wulster-Radcliffe, M.C.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Wang, J.; Christian, J.A.; Spurlock, M.E. Adiponectin differentially regulates cytokines in porcine macrophages. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 316, 924–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.M.; Wolf, D.; Rumpold, H.; Enrich, B.; Tilg, H. Adiponectin induces the anti-inflammatory cytokines IL-10 and IL-1RA in human leukocytes. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 323, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šenolt, L.; Pavelka, K.; Housa, D.; Haluzík, M. Increased adiponectin is negatively linked to the local inflammatory process in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cytokine 2006, 35, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebina, K.; Fukuhara, A.; Ando, W.; Hirao, M.; Koga, T.; Oshima, K.; Matsuda, M.; Maeda, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ochi, T.; et al. Serum adiponectin concentrations correlate with severity of rheumatoid arthritis evaluated by extent of joint destruction. Clin. Rheumatol. 2009, 28, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehling, A.; Schäffler, A.; Herfarth, H.; Tarner, I.H.; Anders, S.; Distler, O.; Paul, G.; Distler, J.; Gay, S.; Schölmerich, J.; et al. The Potential of Adiponectin in Driving Arthritis. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 4468–4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, T.; Tokunaga, K.; Shimomura, I.; Nishida, M.; Yoshida, S.; Kotani, K.; Islam, A.H.M.W.; Keno, Y.; Kobatake, T.; Nagai, Y.; et al. Contribution of visceral fat accumulation to the development of coronary artery disease in non-obese men. Atherosclerosis 1994, 107, 239–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, H.; Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Walsh, K.; Kumada, M.; Abe, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y. Selective Suppression of Endothelial Cell Apoptosis by the High Molecular Weight Form of Adiponectin. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, e27–e31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsuka, F.; Sugiyama, S.; Kojima, S.; Maruyoshi, H.; Funahashi, T.; Matsui, K.; Sakamoto, T.; Yoshimura, M.; Kimura, K.; Umemura, S.; et al. Plasma Adiponectin Levels Are Associated with Coronary Lesion Complexity in Men with Coronary Artery Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2006, 48, 1155–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibata, R.; Sato, K.; Pimentel, D.R.; Takemura, Y.; Kihara, S.; Ohashi, K.; Funahashi, T.; Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Adiponectin protects against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through AMPK- and COX-2–dependent mechanisms. Nat. Med. 2005, 11, 1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, Y.; Ohashi, K.; Shibata, R.; Pimentel, D.R.; Kihara, S.; Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Cyclooxygenase-2 induction by adiponectin is regulated by a sphingosine kinase-1 dependent mechanism in cardiac myocytes. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 1147–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Okamoto, Y.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Novel Modulator for Endothelial Adhesion Molecules. Circulation 1999, 100, 2473–2476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cnop, M.; Havel, P.J.; Utzschneider, K.M.; Carr, D.B.; Sinha, M.K.; Boyko, E.J.; Retzlaff, B.M.; Knopp, R.H.; Brunzell, J.D.; Kahn, S.E. Relationship of adiponectin to body fat distribution, insulin sensitivity and plasma lipoproteins: Evidence for independent roles of age and sex. Diabetologia 2003, 46, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasmussen, M.S.; Lihn, A.S.; Pedersen, S.B.; Bruun, J.M.; Rasmussen, M.; Richelsen, B. Adiponectin Receptors in Human Adipose Tissue: Effects of Obesity, Weight Loss, and Fat Depots. Obesity 2006, 14, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spranger, J.; Kroke, A.; Möhlig, M.; Bergmann, M.M.; Ristow, M.; Boeing, H.; Pfeiffer, A.F.H. Adiponectin and protection against type 2 diabetes mellitus. Lancet 2003, 361, 226–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, K.; Horikoshi, M.; Yamauchi, T.; Yago, H.; Miyazaki, O.; Ebinuma, H.; Imai, Y.; Nagai, R.; Kadowaki, T. Measurement of the High–Molecular Weight Form of Adiponectin in Plasma Is Useful for the Prediction of Insulin Resistance and Metabolic Syndrome. Diabetes Care 2006, 29, 1357–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruchat, S.-M.; Loos, R.J.F.; Rankinen, T.; Vohl, M.-C.; Weisnagel, S.J.; Després, J.-P.; Bouchard, C.; Pérusse, L. Associations between glucose tolerance, insulin sensitivity and insulin secretion phenotypes and polymorphisms in adiponectin and adiponectin receptor genes in the Quebec Family Study. Diabet. Med. 2008, 25, 400–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.V.; Scherer, P.E. Adiponectin, Cardiovascular Function, and Hypertension. Hypertension 2008, 51, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kurukulasuriya, L.R.; Stas, S.; Lastra, G.; Manrique, C.; Sowers, J.R. Hypertension in Obesity. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2008, 37, 647–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantartzis, K.; Rittig, K.; Balletshofer, B.; Machann, J.; Schick, F.; Porubska, K.; Fritsche, A.; Häring, H.-U.; Stefan, N. The Relationships of Plasma Adiponectin with a Favorable Lipid Profile, Decreased Inflammation, and Less Ectopic Fat Accumulation Depend on Adiposity. Clin. Chem. 2006, 52, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okada, T.; Saito, E.; Kuromori, Y.; Miyashita, M.; Iwata, F.; Hara, M.; Harada, K. Relationship between serum adiponectin level and lipid composition in each lipoprotein fraction in adolescent children. Atherosclerosis 2006, 188, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vergès, B.; Petit, J.M.; Duvillard, L.; Dautin, G.; Florentin, E.; Galland, F.; Gambert, P. Adiponectin Is an Important Determinant of ApoA-I Catabolism. Arteriosclerosis. Thrombosis. Vasc. Biol. 2006, 26, 1364–1369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Seino, Y.; Hirose, H.; Saito, I.; Itoh, H. High-molecular-weight adiponectin is a predictor of progression to metabolic syndrome: A population-based 6-year follow-up study in Japanese men. Metabolism 2009, 58, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lara-Castro, C.; Luo, N.; Wallace, P.; Klein, R.L.; Garvey, W.T. Adiponectin Multimeric Complexes and the Metabolic Syndrome Trait Cluster. Diabetes 2006, 55, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, H.; Nuhoglu, C.; Ursavas, I.S.; Isildak, S.; Basaran, E.O.; Kilic, M.Y. Obesity and asymptomatic hypertension among children aged 6–13 years living in Bursa, Turkey. Fam. Pr. 2013, 30, 629–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Cho, N.H.; Yun, C.H.; Lee, S.K.; Yoon, D.W.; Cho, H.J.; Ahn, J.H.; Seo, J.A.; Kim, S.G.; Choi, K.M.; et al. Association of obstructive sleep apnea and glucose metabolism in subjects with or without obesity. Diabetes Care 2013, 36, 3909–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Walsh, K. Obesity, adiponectin and vascular inflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003, 14, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwashima, Y.; Katsuya, T.; Ishikawa, K.; Ouchi, N.; Ohishi, M.; Sugimoto, K.; Fu, Y.; Motone, M.; Yamamoto, K.; Matsuo, A.; et al. Hypoadiponectinemia is an independent risk factor for hypertension. Hypertension 2004, 43, 1318–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- di Chiara, T.; Licata, A.; Argano, C.; Duro, G.; Corrao, S.; Scaglione, R. Plasma adiponectin: A contributing factor for cardiac changes in visceral obesity-associated hypertension. Blood Press 2014, 23, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Nishida, M.; Matsuyama, A.; Okamoto, Y.; Ishigami, M.; Kuriyama, H.; Kishida, K.; Nishizawa, H.; et al. Adipocyte-derived plasma protein, adiponectin, suppresses lipid accumulation and class A scavenger receptor expression in human monocyte-derived macrophages. Circulation 2001, 103, 1057–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avogaro, A.; de Kreutzenberg, S.V. Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in obesity. Clin. Chim. Acta 2005, 360, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimamoto, Y.; Mizukoshi, M.; Kuroi, A.; Imanishi, T.; Takeshita, T.; Terada, M.; Akasaka, T. Is visceral fat really a coronary risk factor? A multi-detector computed tomography study. Int. Heart J. 2013, 54, 273–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.H.; Hong, E.S.; Lim, S. Clinical implications of adipocytokines and newly emerging metabolic factors with relation to insulin resistance and cardiovascular health. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rega-Kaun, G.; Kaun, C.; Wojta, J. More than a simple storage organ: Adipose tissue as a source of adipokines involved in cardiovascular disease. Thromb. Haemost. 2013, 110, 641–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Melean, C.M.; Somers, V.K.; Rodriguez-Escudero, J.P.; Singh, P.; Sochor, O.; Llano, E.M.; Lopez-Jimenez, F. Mechanisms of adverse cardiometabolic consequences of obesity. Curr. Atheroscler Rep. 2013, 15, 364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarreal-Molina, M.T.; Antuna-Puente, B. Adiponectin: Anti-inflammatory and cardioprotective effects. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2143–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I. Roles of adiponectin and oxidative stress in obesity-associated metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2014, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuda, M.; Shimomura, I.; Sata, M.; Arita, Y.; Nishida, M.; Maeda, N.; Kumada, M.; Okamoto, Y.; Nagaretani, H.; Nishizawa, H.; et al. Role of adiponectin in preventing vascular stenosis. The missing link of adipo-vascular axis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 37487–37491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, N.; Walsh, K. Cardiovascular and metabolic regulation by the adiponectin/C1q/tumor necrosis factor-related protein family of proteins. Circulation 2012, 125, 3066–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, J.L.; Narang, I. Sleeping too close together: Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea in childhood and adolescence. Paediatr. Respir Rev. 2014, 15, 211–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargens, T.A.; Guill, S.G.; Kaleth, A.S.; Nickols-Richardson, S.M.; Miller, L.E.; Zedalis, D.; Gregg, J.M.; Gwazdauskas, F.; Herbert, W.G. Insulin resistance and adipose-derived hormones in young men with untreated obstructive sleep apnea. Sleep Breath 2013, 17, 403–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Kishida, K.; Kihara, S.; Yoshida, R.; Funahashi, T.; Shimomura, I. Nocturnal falls of adiponectin levels in sleep apnea with abdominal obesity and impact of hypoxia-induced dysregulated adiponectin production in obese murine mesenteric adipose tissue. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magalang, U.J.; Cruff, J.P.; Rajappan, R.; Hunter, M.G.; Patel, T.; Marsh, C.B.; Raman, S.V.; Parinandi, N.L. Intermittent hypoxia suppresses adiponectin secretion by adipocytes. Exp. Clin. Endocrinol. Diabetes 2009, 117, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, B.E. Overview of epidemiologic studies of diabetic retinopathy. Ophthalmic Epidemiol. 2007, 14, 179–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, M.I.; Sonmez, A.; Acikel, C.; Celik, T.; Bingol, N.; Pinar, M.; Bayraktar, Z.; Ozata, M. Adiponectin may play a part in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2004, 151, 135–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vainio, H.; Bianchini, F. (Eds.) IARC Handbook of Cancer Prevention; IARC Press: Lyon, France, 2002; Volume 6. [Google Scholar]
- Iskander, K.; Farhour, R.; Ficek, M.; Ray, A. Obesity-related complications: Few biochemical phenomena with reference to tumorigenesis. Malays. J. Pathol. 2013, 35, 1–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kwan, M.L.; John, E.M.; Caan, B.J.; Lee, V.S.; Bernstein, L.; Cheng, I.; Gomez, S.L.; Henderson, B.E.; Keegan, T.H.; Kurian, A.W.; et al. Obesity and mortality after breast cancer by race/ethnicity: The California Breast Cancer Survivorship Consortium. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 95–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyoshi, Y.; Funahashi, T.; Kihara, S.; Taguchi, T.; Tamaki, Y.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Noguchi, S. Association of Serum Adiponectin Levels with Breast Cancer Risk. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 5699–5704. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Wang, Y. Adiponectin and breast cancer. Med. Oncol. 2011, 28, 1288–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surmacz, E. Leptin and adiponectin: Emerging therapeutic targets in breast cancer. J. Mammary Gland Biol. Neoplasia 2013, 18, 321–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohbuchi, Y.; Suzuki, Y.; Hatakeyama, I.; Nakao, Y.; Fujito, A.; Iwasaka, T.; Isaka, K. A lower serum level of middle-molecular-weight adiponectin is a risk factor for endometrial cancer. Int. J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 19, 667–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerenidi, T.; Lada, M.; Tsaroucha, A.; Georgoulias, P.; Mystridou, P.; Gourgoulianis, K.I. Clinical significance of serum adipokines levels in lung cancer. Med. Oncol. 2013, 30, 507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosova, F.; Coskun, T.; Kaya, Y.; Kara, E.; Ari, Z. Adipocytokine levels of colon cancer patients before and after treatment. Bratisl. Lek. Listy 2013, 114, 394–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liao, L.M.; Schwartz, K.; Pollak, M.; Graubard, B.I.; Li, Z.; Ruterbusch, J.; Rothman, N.; Davis, F.; Wacholder, S.; Colt, J.; et al. Serum leptin and adiponectin levels and risk of renal cell carcinoma. Obesity 2013, 21, 1478–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, T.; Ye, P.; Peng, X.; Wu, L.L.; Yu, G.Y. Circulating adiponectin levels in various malignancies: An updated meta-analysis of 107 studies. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 48671–48691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, X. Effect of adiponectin on apoptosis: Proapoptosis or antiapoptosis? BioFactors 2010, 36, 179–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Gu, M.; Wang, Q.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Z. Role of adiponectin in prostate cancer: A preliminary study. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue Natl. J. Androl. 2017, 23, 975–981. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, Q.; Zheng, J.; Yao, X.; Peng, B. Adiponectin inhibits VEGF-A in prostate cancer cells. Tumor Biol. 2015, 36, 4287–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, A.; Nepal, S.; Kim, M.J.; Chang, J.H.; Kim, S.-H.; Jeong, G.-S.; Jeong, C.-H.; Park, G.H.; Jung, S.; Lim, J.; et al. Critical Role of AMPK/FoxO3A Axis in Globular Adiponectin-Induced Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. J. Cell. Physiol. 2016, 231, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, S.-Q.; Zhang, C.-G.; Yuan, J.-F.; Yang, H.-M.; Zhao, S.-D.; Zhang, H. Adiponectin induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma through differential modulation of thioredoxin proteins. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2015, 93, 221–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otani, K.; Ishihara, S.; Yamaguchi, H.; Murono, K.; Yasuda, K.; Nishikawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Kiyomatsu, T.; Hata, K.; Kawai, K.; et al. Adiponectin and colorectal cancer. Surg. Today 2017, 47, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujisawa, T.; Endo, H.; Tomimoto, A.; Sugiyama, M.; Takahashi, H.; Saito, S.; Inamori, M.; Nakajima, N.; Watanabe, M.; Kubota, N.; et al. Adiponectin suppresses colorectal carcinogenesis under the high-fat diet condition. Gut 2008, 57, 1531–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Moon, H.-S.; Liu, X.; Nagel, J.M.; Chamberland, J.P.; Diakopoulos, K.N.; Brinkoetter, M.T.; Hatziapostolou, M.; Wu, Y.; Robson, S.C.; Iliopoulos, D.; et al. Salutary effects of adiponectin on colon cancer: In vivo and in vitro studies in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 561–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bråkenhielm, E.; Veitonmäki, N.; Cao, R.; Kihara, S.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Zhivotovsky, B.; Funahashi, T.; Cao, Y. Adiponectin-induced antiangiogenesis and antitumor activity involve caspase-mediated endothelial cell apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 2476–2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Lam, J.B.; Lam, K.S.L.; Liu, J.; Lam, M.C.; Hoo, R.L.C.; Wu, D.; Cooper, G.J.S.; Xu, A. Adiponectin Modulates the Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3β/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway and Attenuates Mammary Tumorigenesis of MDA-MB-231 Cells in Nude Mice. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 11462–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.H.; Lee, Y.Y.; Yu, B.Y.; Yang, B.-S.; Cho, K.-H.; Yoon, D.K.; Roh, Y.K. Adiponectin induces growth arrest and apoptosis of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cell. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2005, 28, 1263–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mutoh, M.; Teraoka, N.; Takasu, S.; Takahashi, M.; Onuma, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Kubota, N.; Iseki, T.; Kadowaki, T.; Sugimura, T.; et al. Loss of Adiponectin Promotes Intestinal Carcinogenesis in Min and Wild-type Mice. Gastroenterology 2011, 140, 2000–2008.e2002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, A.; Chumanevich, A.; Fletcher, E.; Larsen, B.; Lattwein, K.; Kaur, K.; Fayad, R. Adiponectin deficiency: Role in chronic inflammation induced colon cancer. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1822, 527–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Saxena, A.; Baliga, M.S.; Ponemone, V.; Kaur, K.; Larsen, B.; Fletcher, E.; Greene, J.; Fayad, R. Mucus and adiponectin deficiency: Role in chronic inflammation-induced colon cancer. Int. J. Colorectal Dis. 2013, 28, 1267–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, A.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, K.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, H.K.; Jang, S.-H.; Kim, S.-E.; Lee, G.Y.; Lee, J.-W.; Jung, S.-A.; et al. Adiponectin represses colon cancer cell proliferation via AdipoR1- and -R2-mediated AMPK activation. Mol. Endocrinol. 2010, 24, 1441–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Liu, J.; You, L.; Li, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y. Association between adiponectin polymorphisms and the risk of colorectal cancer. Genet. Test. Mol. Biomark. 2015, 19, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliaferro-Smith, L.; Nagalingam, A.; Knight, B.B.; Oberlick, E.; Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D. Integral role of PTP1B in adiponectin-mediated inhibition of oncogenic actions of leptin in breast carcinogenesis. Neoplasia 2013, 15, 23–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Du, G.; Wan, X. Acrp30 inhibits leptin-induced metastasis by downregulating the JAK/STAT3 pathway via AMPK activation in aggressive SPEC-2 endometrial cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2012, 27, 1488–1496. [Google Scholar]
- Man, K.; Ng, K.T.P.; Xu, A.; Cheng, Q.; Lo, C.M.; Xiao, J.W.; Sun, B.S.; Lim, Z.X.H.; Cheung, J.S.; Wu, E.X.; et al. Suppression of Liver Tumor Growth and Metastasis by Adiponectin in Nude Mice through Inhibition of Tumor Angiogenesis and Downregulation of Rho Kinase/IFN-Inducible Protein 10/Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 Signaling. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 967–977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, E.; Guo, H.; Shen, M.; Yu, H.; Gu, D.; Mao, W.; Wang, X. Adiponectin inhibits migration and invasion by reversing epithelial-mesenchymal transition in non-small cell lung carcinoma. Oncol. Rep. 2018, 40, 1330–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taliaferro-Smith, L.; Nagalingam, A.; Zhong, D.; Zhou, W.; Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D. LKB1 is required for adiponectin-mediated modulation of AMPK-S6K axis and inhibition of migration and invasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 2009, 28, 2621–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.K.; Sharma, D. Metastasis suppression by adiponectin: LKB1 rises up to the challenge. Cell Adh Migr 2010, 4, 358–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.J.; Nagaraju, G.P.; Nagalingam, A.; Muniraj, N.; Kuppusamy, P.; Walker, A.; Woo, J.; Gyorffy, B.; Gabrielson, E.; Saxena, N.K.; et al. ADIPOQ/adiponectin induces cytotoxic autophagy in breast cancer cells through STK11/LKB1-mediated activation of the AMPK-ULK1 axis. Autophagy 2017, 13, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniele, A.; de Rosa, A.; Nigro, E.; Scudiero, O.; Capasso, M.; Masullo, M.; de Laurentiis, G.; Oriani, G.; Sofia, M.; Bianco, A. Adiponectin oligomerization state and adiponectin receptors airway expression in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2012, 44, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, L.; Gasser, J.; Zhao, J.; Yang, B.; Li, F.; Zhao, A.Z. Human adiponectin inhibits cell growth and induces apoptosis in human endometrial carcinoma cells, HEC-1-A and RL95 2. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2007, 14, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieudonne, M.N.; Bussiere, M.; Santos, E.D.; Leneveu, M.C.; Giudicelli, Y.; Pecquery, R. Adiponectin mediates antiproliferative and apoptotic responses in human MCF7 breast cancer cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 345, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.J. Signal transduction by the JNK group of MAP kinases. Cell 2000, 103, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirosumi, J.; Tuncman, G.; Chang, L.; Gorgun, C.Z.; Uysal, K.T.; Maeda, K.; Karin, M.; Hotamisligil, G.S. A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 2002, 420, 333–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, N.K.; Fu, P.P.; Nagalingam, A.; Wang, J.; Handy, J.; Cohen, C.; Tighiouart, M.; Sharma, D.; Anania, F.A. Adiponectin modulates C-jun N-terminal kinase and mammalian target of rapamycin and inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 1762–1773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, D.; Wang, J.; Fu, P.P.; Sharma, S.; Nagalingam, A.; Mells, J.; Handy, J.; Page, A.J.; Cohen, C.; Anania, F.A.; et al. Adiponectin antagonizes the oncogenic actions of leptin in hepatocellular carcinogenesis. Hepatology 2010, 52, 1713–1722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vara, J.A.F.; Casado, E.; de Castro, J.; Cejas, P.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; Gonzalez-Baron, M. PI3K/Akt signalling pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2004, 30, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, M.; Takahashi, H.; Hosono, K.; Endo, H.; Kato, S.; Yoneda, K.; Nozaki, Y.; Fujita, K.; Yoneda, M.; Wada, K.; et al. Adiponectin inhibits colorectal cancer cell growth through the AMPK/mTOR pathway. Int. J. Oncol. 2009, 34, 339–344. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Lam, J.B.; Chow, K.H.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.; Moon, R.T.; Wang, Y. Adiponectin stimulates Wnt inhibitory factor-1 expression through epigenetic regulations involving the transcription factor specificity protein 1. Carcinogenesis 2008, 29, 2195–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ouchi, N.; Kihara, S.; Arita, Y.; Okamoto, Y.; Maeda, K.; Kuriyama, H.; Hotta, K.; Nishida, M.; Takahashi, M.; Muraguchi, M.; et al. Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-kappaB signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation 2000, 102, 1296–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, A.; Knight, C.; Xu, L.Y.; Cooper, G.J.S. Hydroxylation and Glycosylation of the Four Conserved Lysine Residues in the Collagenous Domain of Adiponectin: POTENTIAL ROLE IN THE MODULATION OF ITS INSULIN-SENSITIZING ACTIVITY. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 19521–19529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halberg, N.; Schraw, T.D.; Wang, Z.V.; Kim, J.-Y.; Yi, J.; Hamilton, M.P.; Luby-Phelps, K.; Scherer, P.E. Systemic Fate of the Adipocyte-Derived Factor Adiponectin. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1961–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Das, K.; Lin, Y.; Widen, E.; Zhang, Y.; Scherer, P.E. Chromosomal Localization, Expression Pattern, and Promoter Analysis of the Mouse Gene Encoding Adipocyte-Specific Secretory Protein Acrp30. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 280, 1120–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, A.; Yamasaki, H.; Kuwahara, H.; Moriuchi, A.; Fukushima, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Fukushima, T.; Takahashi, R.; Abiru, N.; Uotani, S.; et al. Identification of the promoter region required for human adiponectin gene transcription: Association with CCAAT/enhancer binding protein-β and tumor necrosis factor-α. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 331, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kai, T.; Arima, S.; Taniyama, Y.; Nakabou, M.; Kanamasa, K. Comparison of the Effect of Lipophilic and Hydrophilic Statins on Serum Adiponectin Levels in Patients with Mild Hypertension and Dyslipidemia: Kinki Adiponectin Interventional (KAI) Study. Clin. Exp. Hypertens. 2008, 30, 530–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Tong, G.; Xu, W.; Pan, J.; Ryan, K.; Yang, R.; Shuldiner, A.R.; Gong, D.-W.; Zhu, D. Anti-inflammatory effects of simvastatin on adipokines in type 2 diabetic patients with carotid atherosclerosis. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 2009, 6, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsutamoto, T.; Yamaji, M.; Kawahara, C.; Nishiyama, K.; Fujii, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Horie, M. Effect of simvastatin vs. rosuvastatin on adiponectin and haemoglobin A1c levels in patients with non-ischaemic chronic heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2009, 11, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, H.-Y.; Xiao, Y.-W.; Jiang, G.-H.; Wang, Z.-Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, M. Effect of Atorvastatin Versus Rosuvastatin on Levels of Serum Lipids, Inflammatory Markers and Adiponectin in Patients with Hypercholesterolemia. Pharm. Res. 2009, 26, 958–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.K.; Quon, M.J.; Han, S.H.; Ahn, J.Y.; Jin, D.K.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, D.S.; Shin, E.K. Vascular and Metabolic Effects of Combined Therapy with Ramipril and Simvastatin in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. Hypertension 2005, 45, 1088–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagamia, S.; Pandian, A.; Cheema, F.; Natarajan, R.; Khan, Q.A.; Patel, A.D.; Merchant, N.; Sola, S.; Khan, B.V. The Role of Quinapril in the Presence of a Weight Loss Regimen: Endothelial Function and Markers of Obesity in Patients with the Metabolic Syndrome. Prev. Cardiol. 2007, 10, 204–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, K.K.; Quon, M.J.; Han, S.H.; Chung, W.-J.; Ahn, J.Y.; Seo, Y.-H.; Kang, M.H.; Ahn, T.H.; Choi, I.S.; Shin, E.K. Additive Beneficial Effects of Losartan Combined with Simvastatin in the Treatment of Hypercholesterolemic, Hypertensive Patients. Circulation 2004, 110, 3687–3692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negro, R.; Formoso, G.; Hassan, H. The effects of irbesartan and telmisartan on metabolic parameters and blood pressure in obese, insulin resistant, hypertensive patients. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2006, 29, 957–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuhashi, M.; Ura, N.; Higashiura, K.; Murakami, H.; Tanaka, M.; Moniwa, N.; Yoshida, D.; Shimamoto, K. Blockade of the Renin-Angiotensin System Increases Adiponectin Concentrations in Patients with Essential Hypertension. Hypertension 2003, 42, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-S.; Jeng, C.-Y.; Wu, T.-J.; Tanaka, S.; Funahashi, T.; Matsuzawa, Y.; Wang, J.-P.; Chen, C.-L.; Tai, T.-Y.; Chuang, L.-M. Synthetic Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor-γ Agonist, Rosiglitazone, Increases Plasma Levels of Adiponectin in Type 2 Diabetic Patients. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 376–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonelli, J.; Li, W.; Kishore, P.; Pajvani, U.B.; Kwon, E.; Weaver, C.; Scherer, P.E.; Hawkins, M. Mechanisms of Early Insulin-Sensitizing Effects of Thiazolidinediones in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Araki, T.; Emoto, M.; Konishi, T.; Ikuno, Y.; Lee, E.; Teramura, M.; Motoyama, K.; Yokoyama, H.; Mori, K.; Koyama, H.; et al. Glimepiride increases high-density lipoprotein cholesterol via increasing adiponectin levels in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 2009, 58, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Xie, C.; Lu, S.; Nichols, R.G.; Tian, Y.; Li, L.; Patel, D.; Ma, Y.; Brocker, C.N.; Yan, T.; et al. Intermittent Fasting Promotes White Adipose Browning and Decreases Obesity by Shaping the Gut Microbiota. Cell Metab. 2017, 26, 672–685.e674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirico, F.; Bianco, A.; D’Alicandro, G.; Castaldo, C.; Montagnani, S.; Spera, R.; di Meglio, F.; Nurzynska, D. Effects of Physical Exercise on Adiponectin, Leptin, and Inflammatory Markers in Childhood Obesity: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Child. Obes. (Print) 2018, 14, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Becic, T.; Studenik, C.; Hoffmann, G. Exercise Increases Adiponectin and Reduces Leptin Levels in Prediabetic and Diabetic Individuals: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Med. Sci. 2018, 6, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Diseases | Findings |
|---|---|
| Hypertension | Obese patients suffering from hypertension display lower adiponectin. |
| Atherosclerosis | Higher incidences of cardiovascular events are associated with lower hypoadiponectinemia. |
| Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome | OSAS (Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome) patients revealed lower expression level of adiponectin compared to control patients. |
| Diabetic retinopathy | T2DM patients with diabetic retinopathy have lower levels of adiponectin compared to T2DM patients without diabetic retinopathy. |
| Cancer | Multiple evidences suggest low adiponectin levels are associated with the threat of developing several types of cancers. |
| Metabolic syndrome | Metabolic syndrome represents a group of complications like obesity, hypertension, dyslipidemia, hyperglycemia, and insulin resistance. Enhancement of metabolic syndrome components is associated with a decrease in adiponectin concentration in plasma [88]. |
| Dyslipidemia | Disorder of lipid metabolism leading to high levels of LDL, serum triglycerides, and decreased levels of HDL. Inverse association exists between adiponectin level with LDL and serum triglycerides with a positive association with HDL levels [89]. |
| Hepatic disease non-alcoholic fat | Inverse association exists between adiponectin level in liver with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease as well as non-alcoholic steatohepatitis [90]. |
| Cancer Type | Ethnicity | Sample | Cases/Control | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast cancer | Caucasian | Serum sample | 74/76 | RIA | [120] |
| Liver cancer | Asian | Serum sample | 59/334 | ELISA | [121] |
| Liver cancer | Asian | Serum sample | 97/97 | ELISA | [122] |
| Colorectal cancer | Asian | Plasma sample | 165/102 | ELISA | [123] |
| Colorectal cancer | Caucasian | Serum sample | 1206/1206 | ELISA | [124] |
| Multiple myeloma | Caucasian | Plasma sample | 174/348 | ELISA | [125] |
| Endometrial cancer | Caucasian | Serum sample | 62/124 | ELISA | [126] |
| Breast cancer | Asian | Serum sample | 66/66 | Other method | [127] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Parida, S.; Siddharth, S.; Sharma, D. Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102519
Parida S, Siddharth S, Sharma D. Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2019; 20(10):2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102519
Chicago/Turabian StyleParida, Sheetal, Sumit Siddharth, and Dipali Sharma. 2019. "Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 20, no. 10: 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102519
APA StyleParida, S., Siddharth, S., & Sharma, D. (2019). Adiponectin, Obesity, and Cancer: Clash of the Bigwigs in Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 20(10), 2519. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20102519